ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS презентация
Содержание
- 2. Fungi Very large and diverse group of microorganisms Broken down into
- 3. FUNGAL INFECTIONS Yeast infections Candida species Cryptococcus neoformats Moulds (filamentous fungi)
- 4. Infection disease caused by fungi called mycoses Major Types of Mycoses
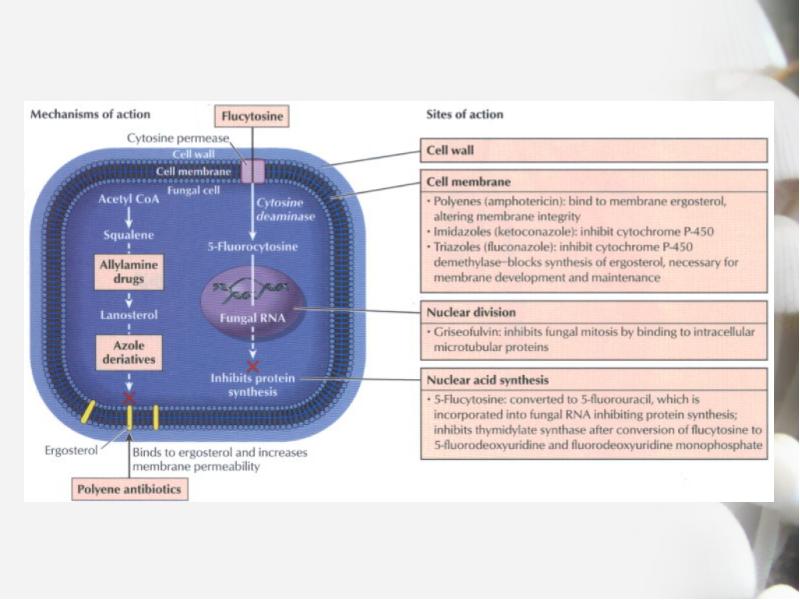
- 5. Antifungal agents Drugs used to treat fungal infection Systemic: amphotericin B,
- 6. Antifungal agents Polyene antibiotics Nystatin Amphotericin B Imidazoles and triazoles*
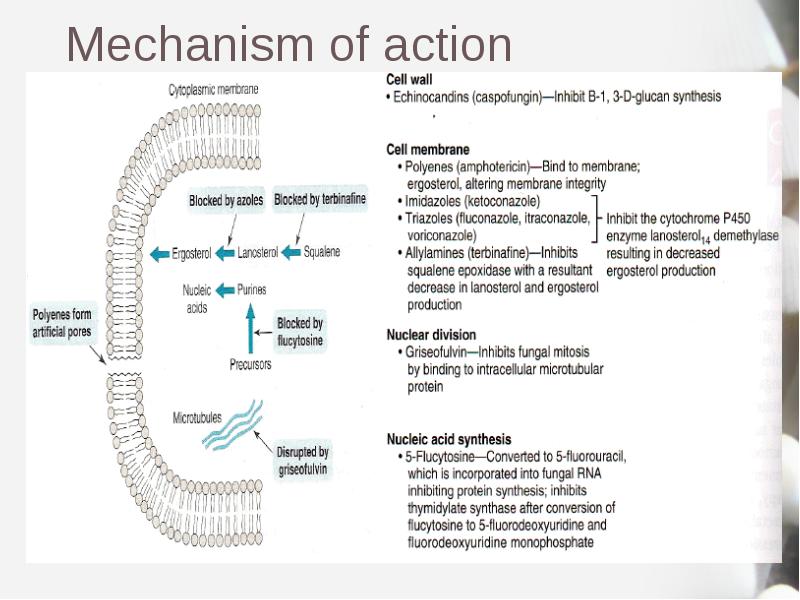
- 7. Mechanism of action
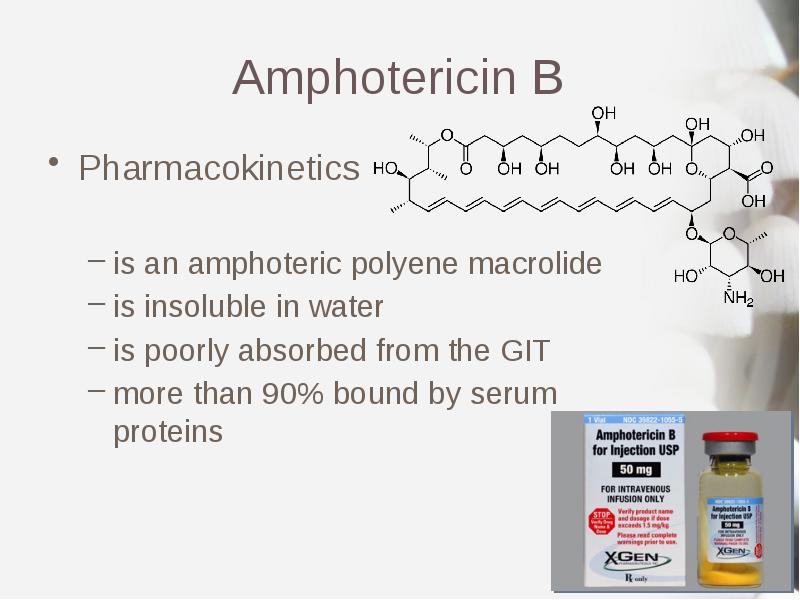
- 8. Amphotericin B Pharmacokinetics is an amphoteric polyene macrolide is insoluble
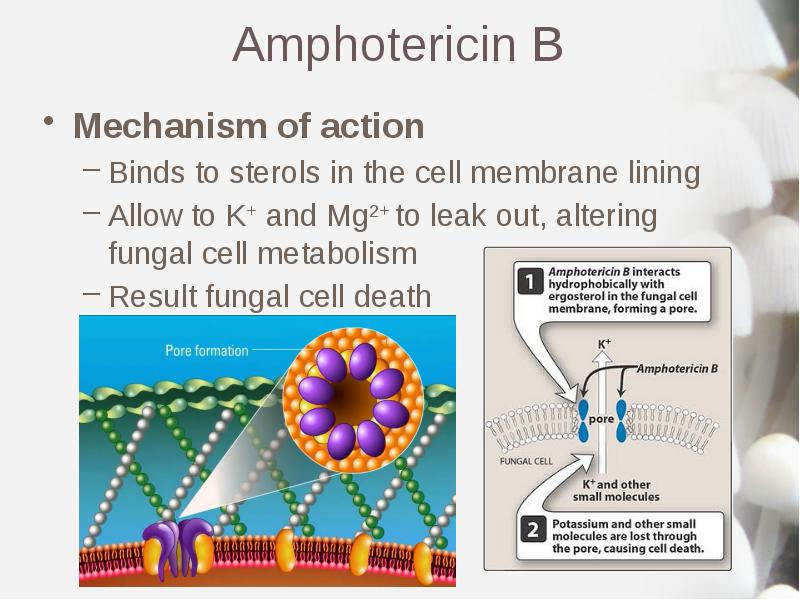
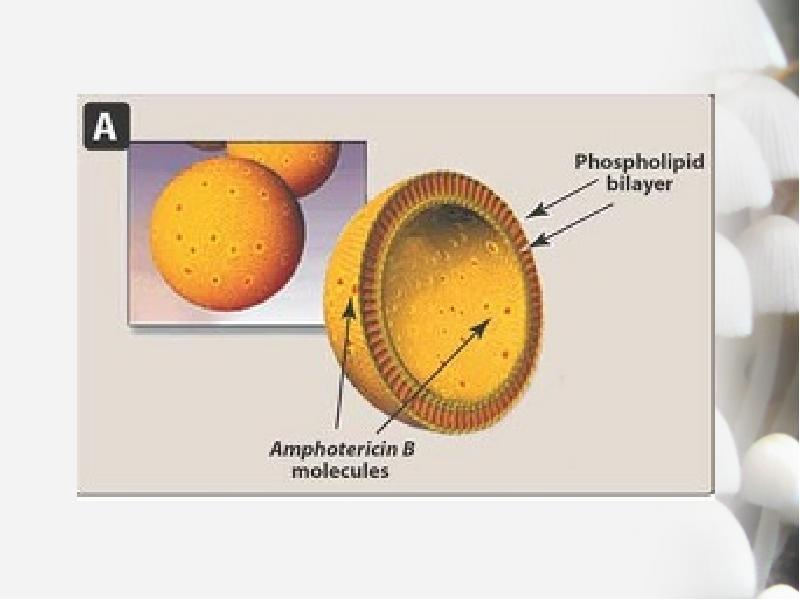
- 9. Amphotericin B Mechanism of action Binds to sterols in the cell
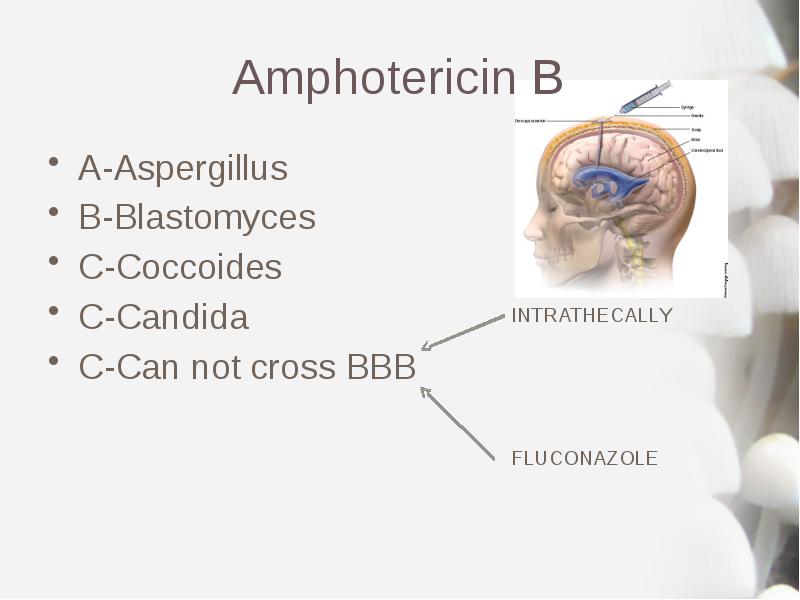
- 10. Amphotericin B A-Aspergillus B-Blastomyces C-Coccoides C-Candida C-Can not cross BBB
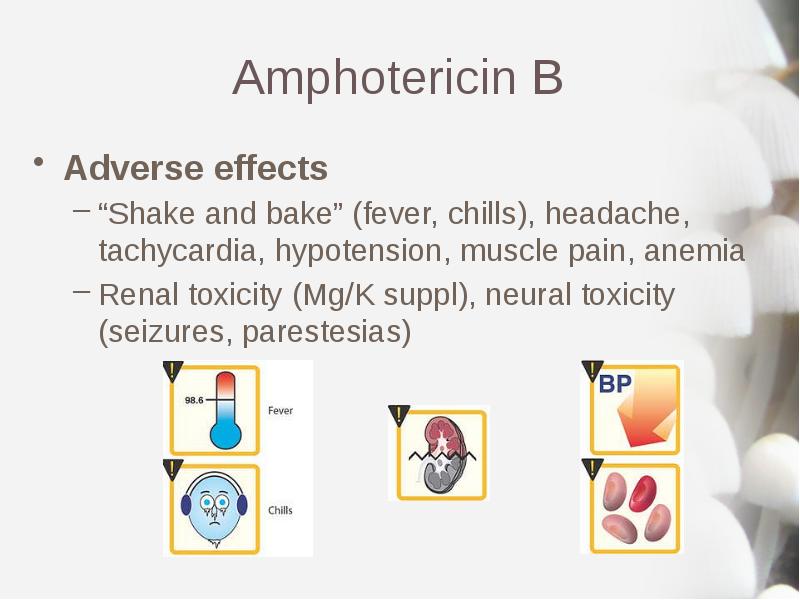
- 11. Amphotericin B Adverse effects “Shake and bake” (fever, chills), headache, tachycardia,
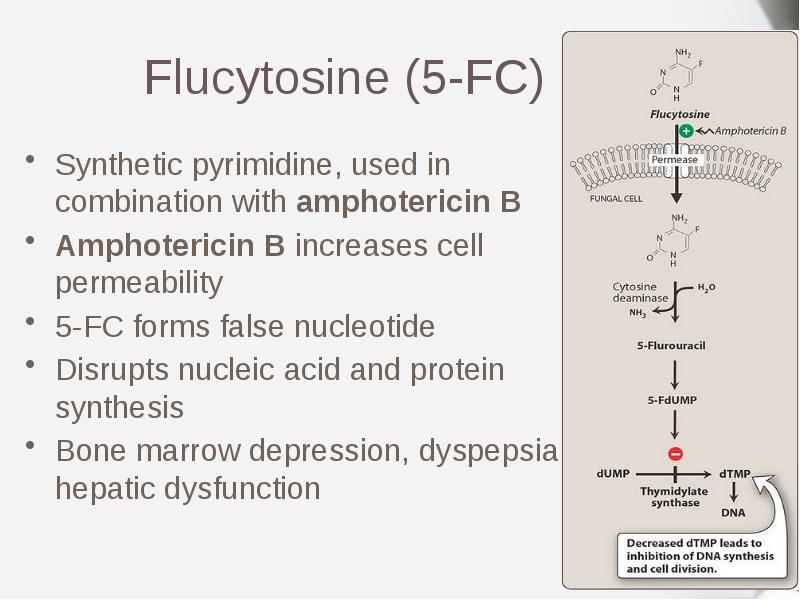
- 13. Flucytosine (5-FC) Synthetic pyrimidine, used in combination with amphotericin B Amphotericin
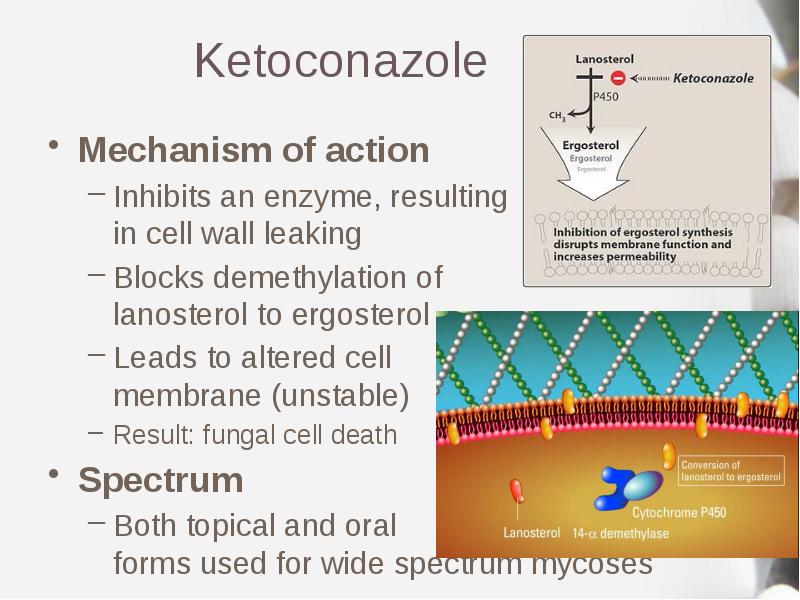
- 14. Ketoconazole Mechanism of action Inhibits an enzyme, resulting in cell wall
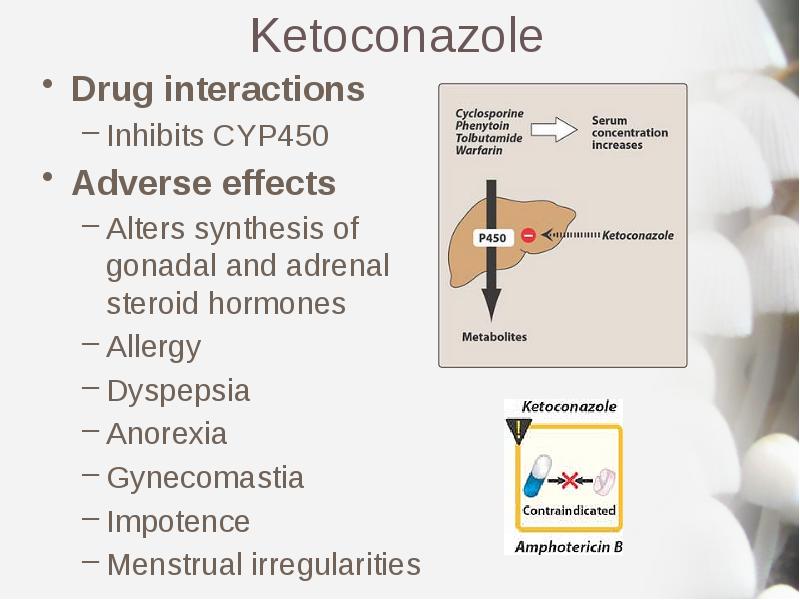
- 15. Ketoconazole Drug interactions Inhibits CYP450 Adverse effects Alters synthesis of
- 16. Caspofungin Belongs to Echinocandis Inhibits β(1,3)-D-glucan synthesis destroying cell wall, resulting
- 17. Terbinafine Oral form is essential for the treatment of onychomycoses Cream
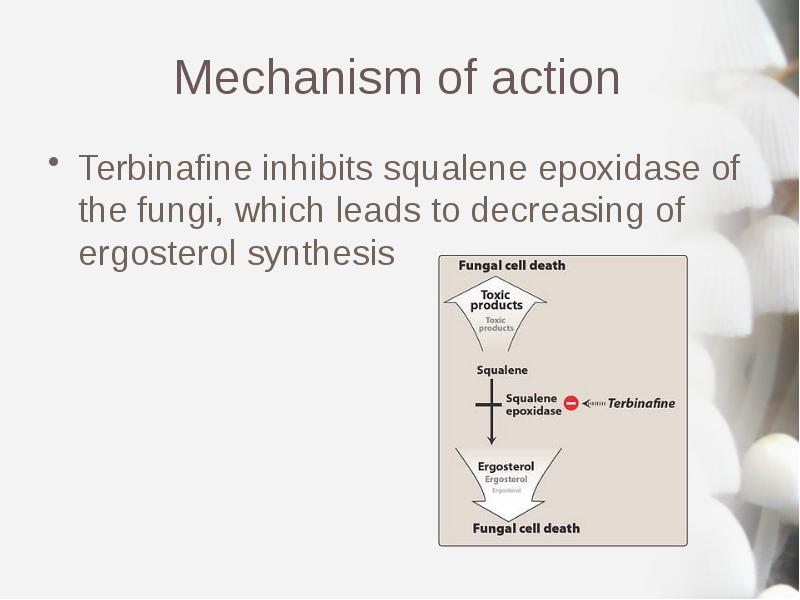
- 18. Mechanism of action Terbinafine inhibits squalene epoxidase of the fungi, which
- 19. Terbinafine Has fungicidal action, mostly active against Trychophyton Half life from
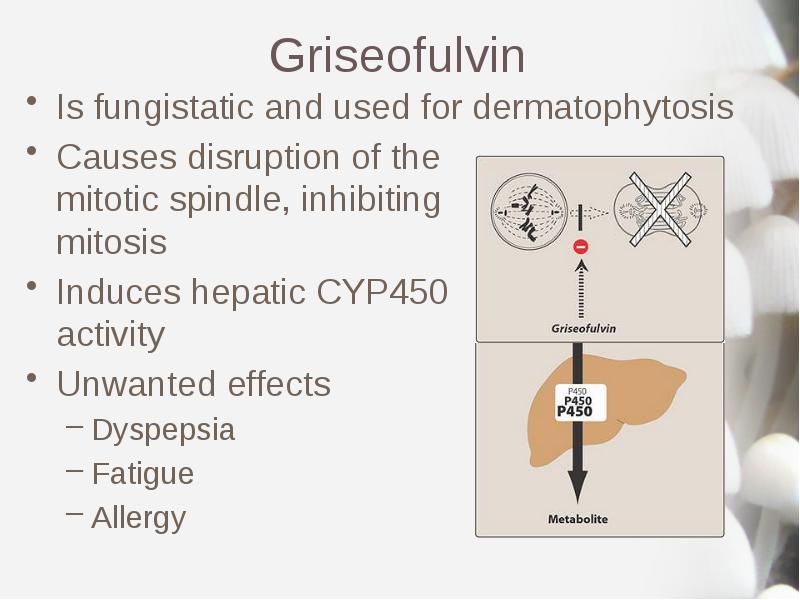
- 20. Griseofulvin Is fungistatic and used for dermatophytosis Causes disruption of the
- 22. Скачать презентацию









Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации