Actuators and sensors. Part 1 презентация
Содержание
- 2. outline Motivation, why robots need sensors? Difference between actuators and sensors
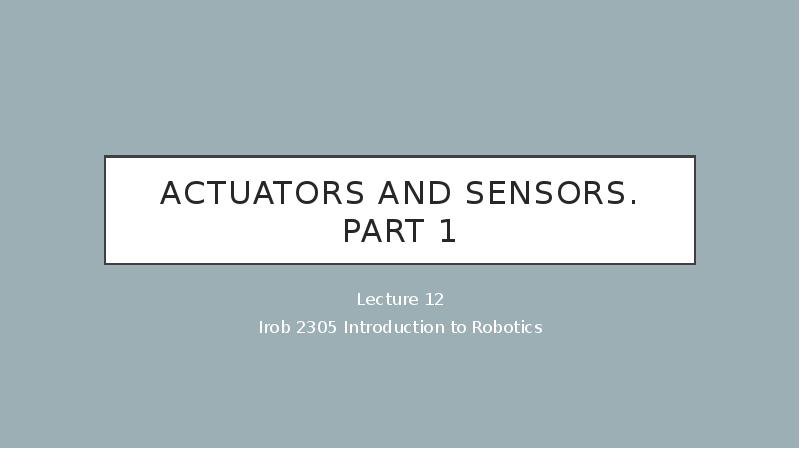
- 3. Sensors in Robotics are primarily used for two different purposes: Sensors
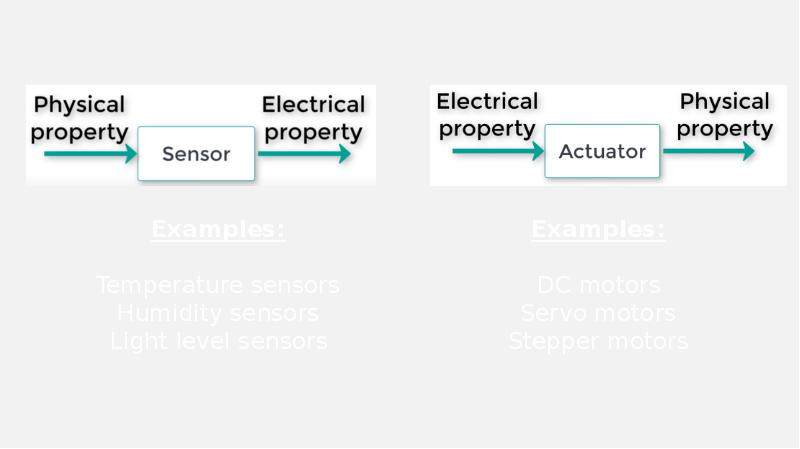
- 5. Any kind of device that converts one kind of energy into
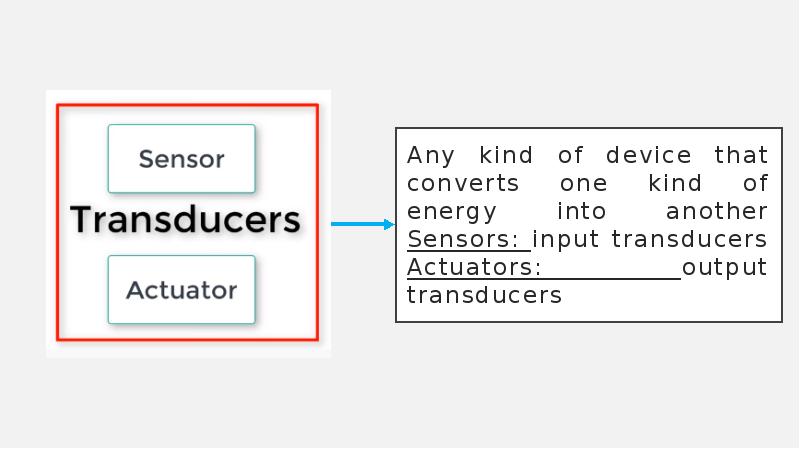
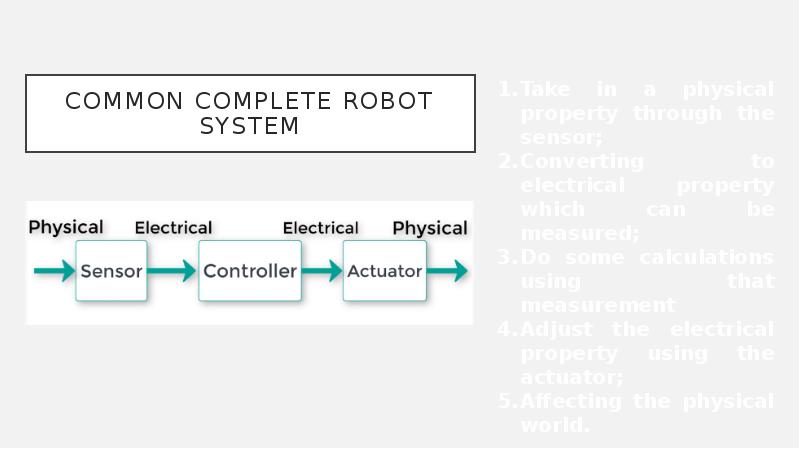
- 6. Common complete robot system
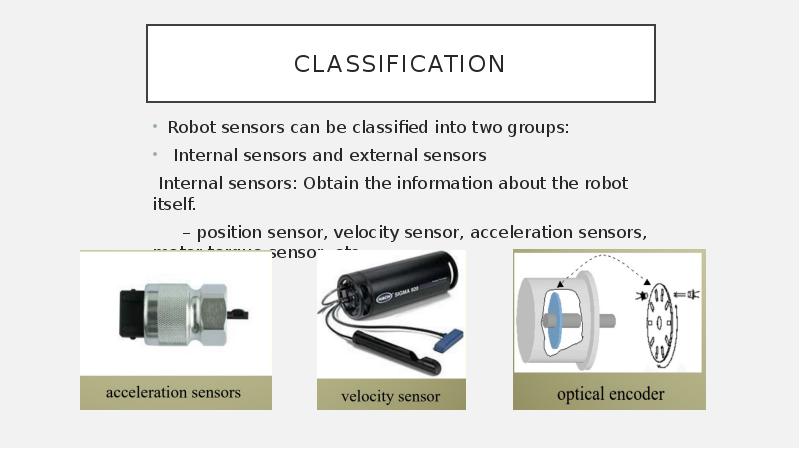
- 7. classification Robot sensors can be classified into two groups: Internal sensors
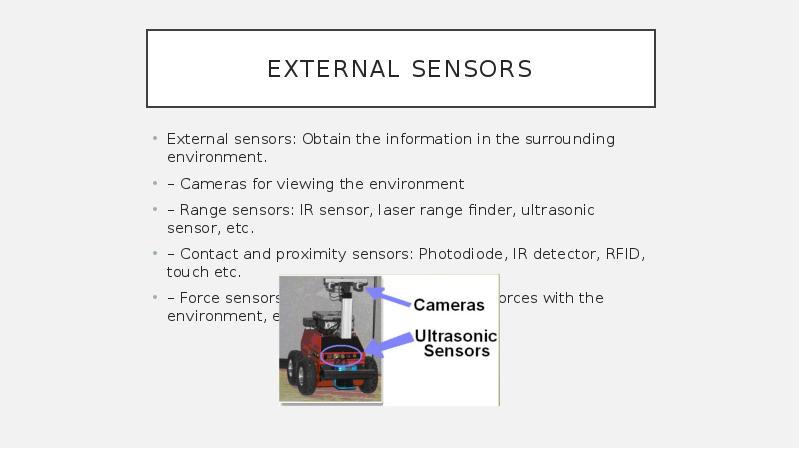
- 8. External sensors External sensors: Obtain the information in the surrounding environment.
- 9. Evaluation Criteria for Sensors Evaluation Criteria for Sensors 1. Sensitivity -
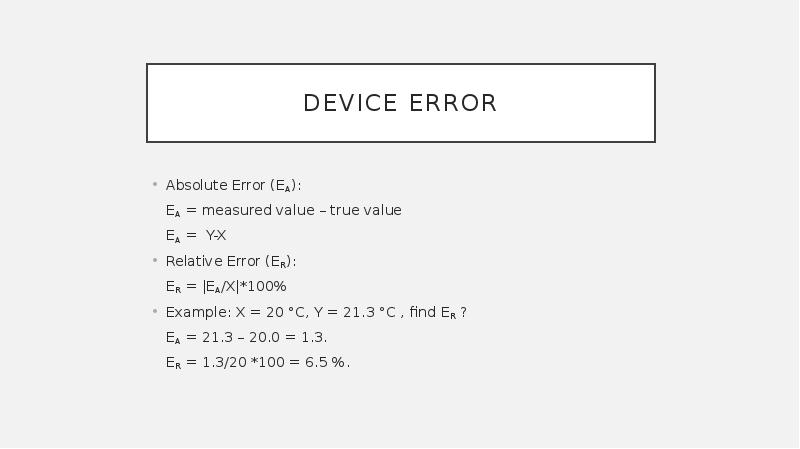
- 11. Device error Absolute Error (EA): EA = measured value – true
- 12. Tolerance (Limiting Error)
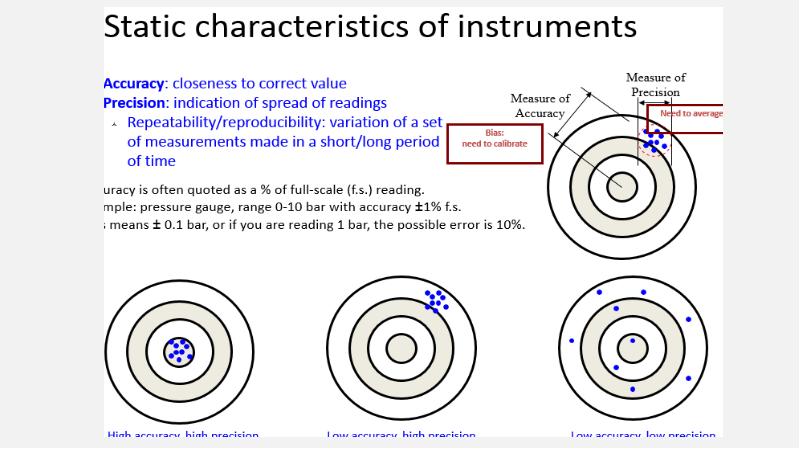
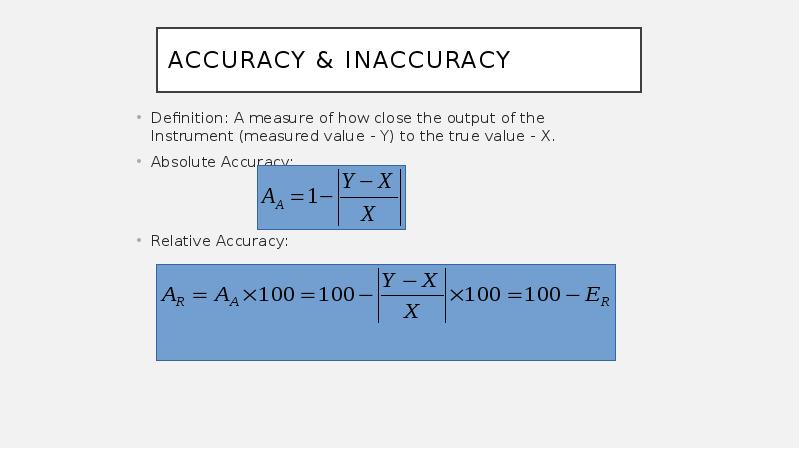
- 13. Accuracy & Inaccuracy Definition: A measure of how close the output
- 14. Example: X = 20 °C, Y = 21.3 °C , find
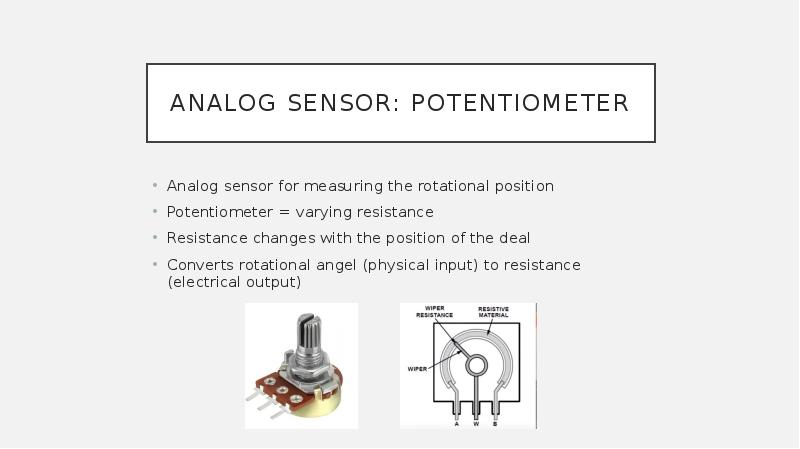
- 15. Analog sensor: Potentiometer Analog sensor for measuring the rotational position Potentiometer
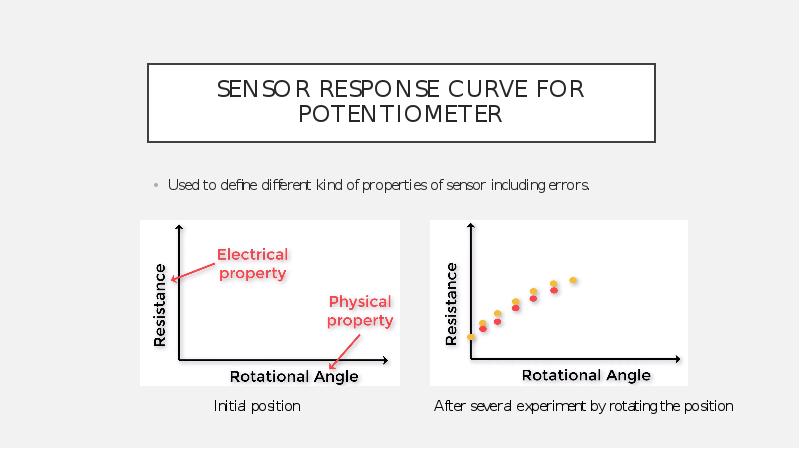
- 16. Sensor response curve for potentiometer Used to define different kind of
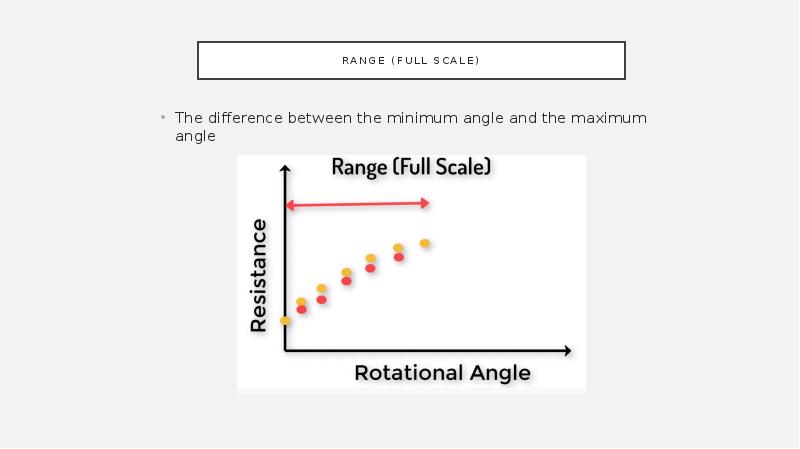
- 17. Range (full scale) The difference between the minimum angle and the
- 18. Nonlinearity error
- 19. Sensitivity The amount of change in the output -> results from
- 20. Next: wide range of sensors
- 21. Скачать презентацию







Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























