HUMAN LOCOMOTION SYSTEM презентация
Содержание
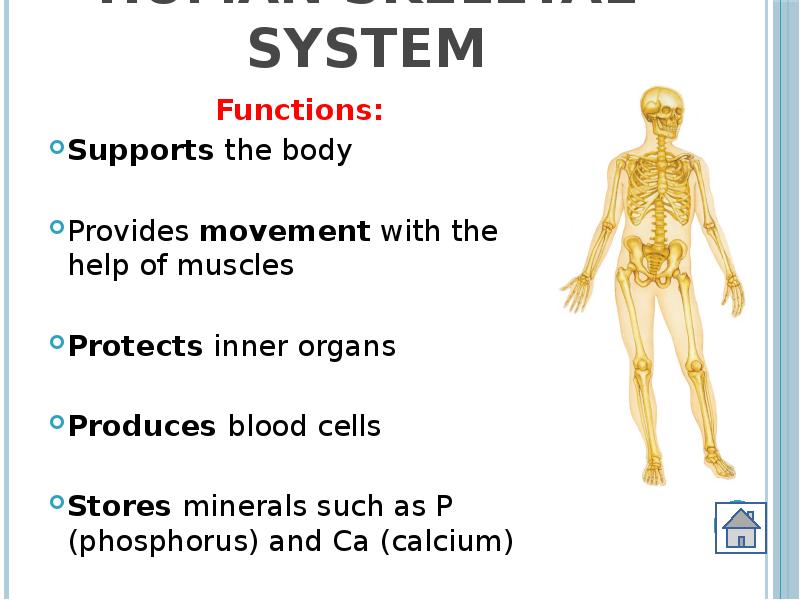
- 2. Human Skeletal System Functions: Supports the body Provides movement with
- 3. Skeletal System Skeletal system is the supportive and protective system of
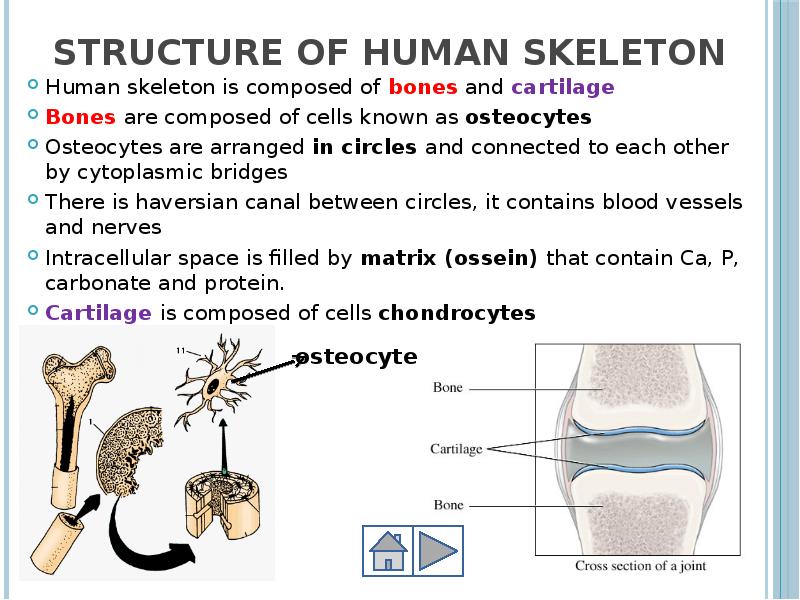
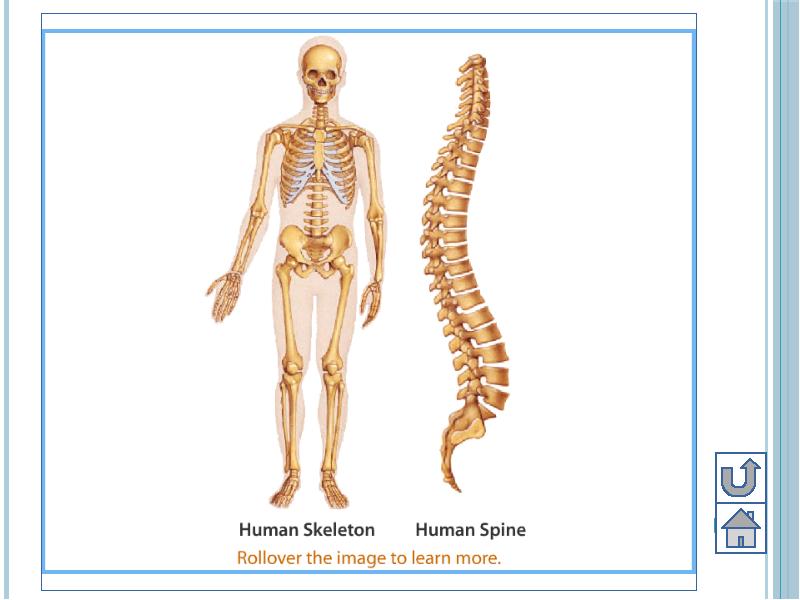
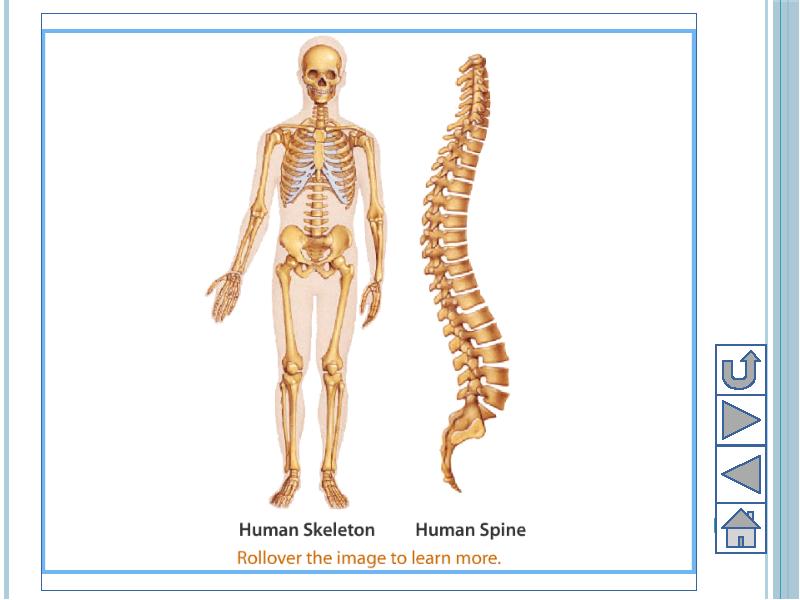
- 4. Structure of human skeleton Human skeleton is composed of bones and
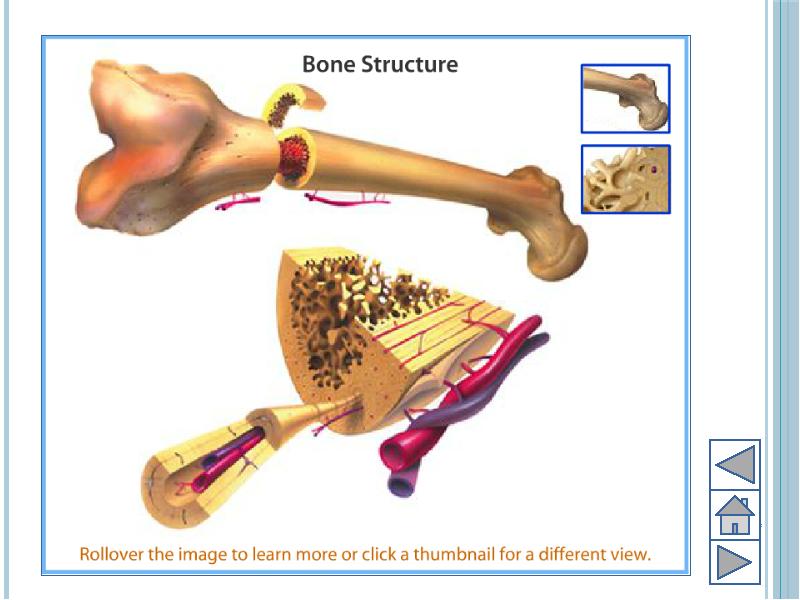
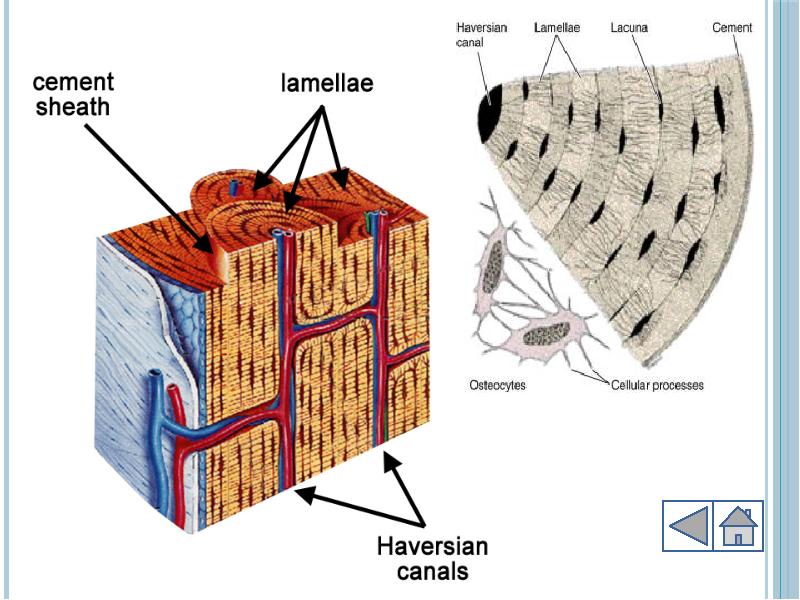
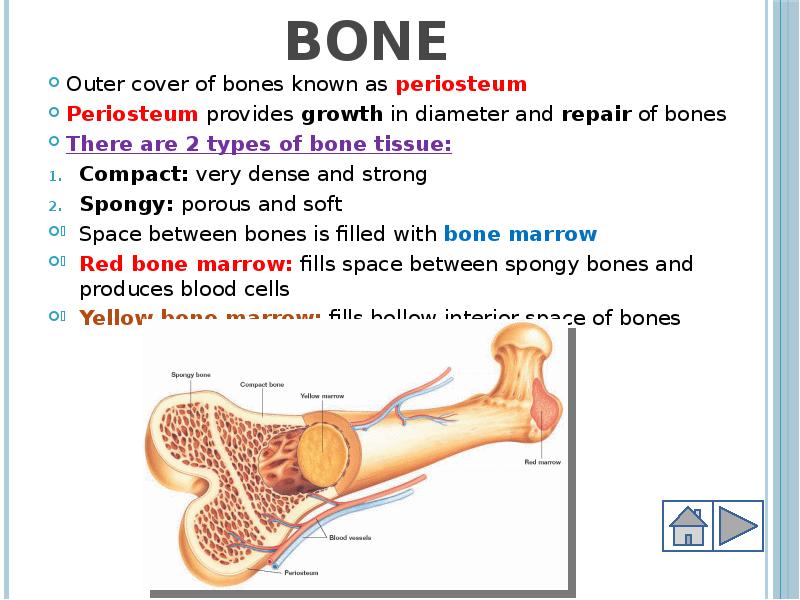
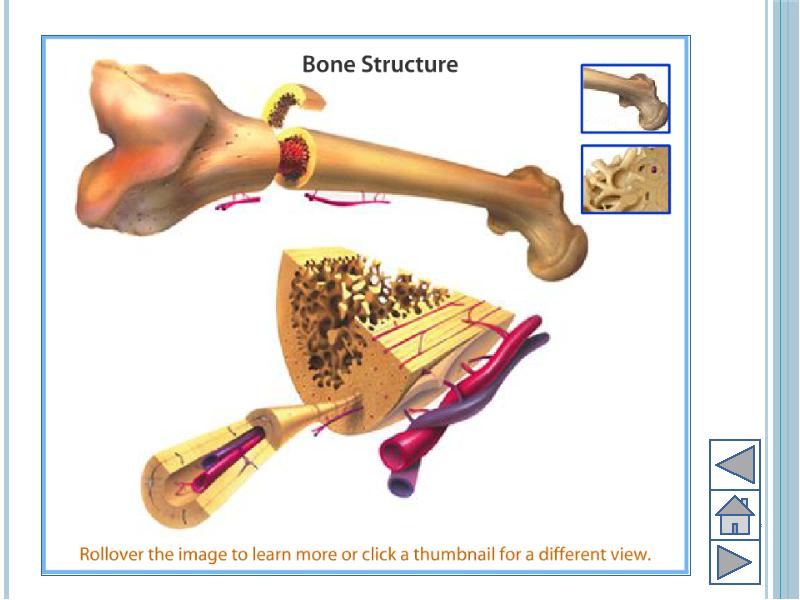
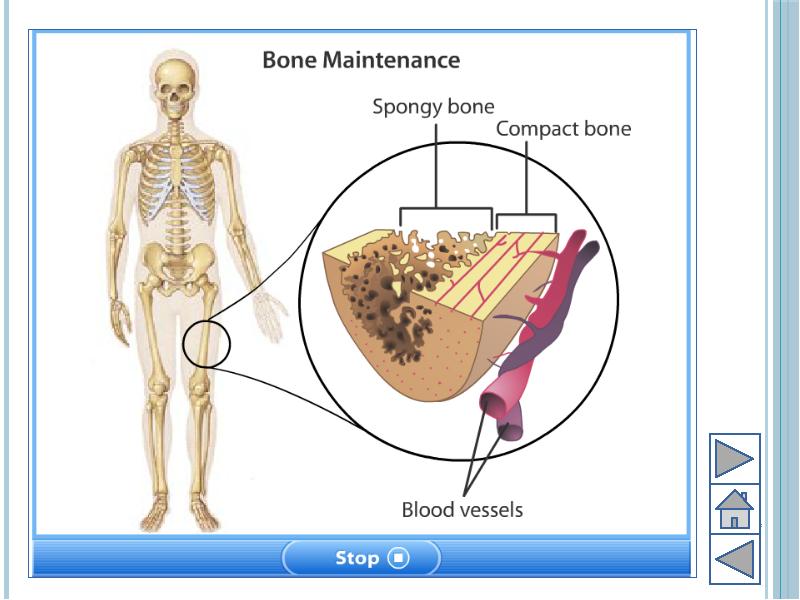
- 7. Bone Outer cover of bones known as periosteum Periosteum provides growth
- 9. Red and Yellow bone marrows
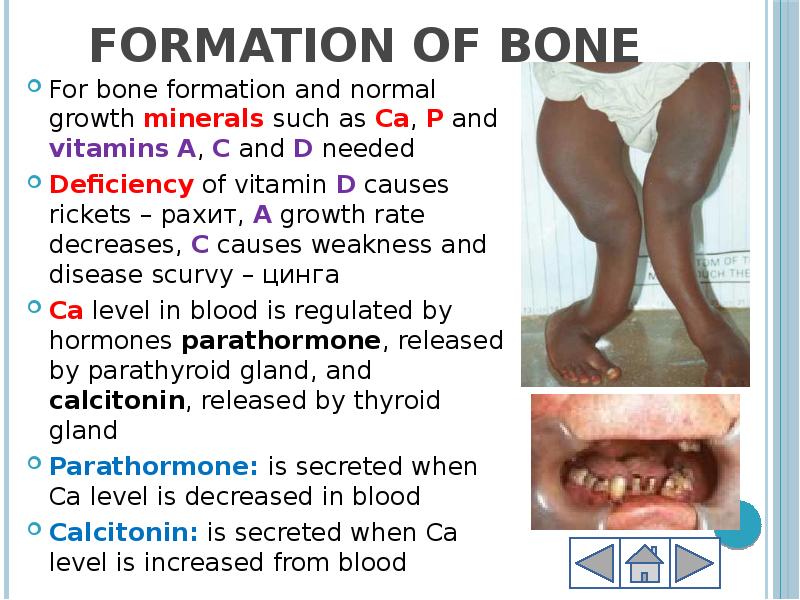
- 10. Formation of bone For bone formation and normal growth minerals such
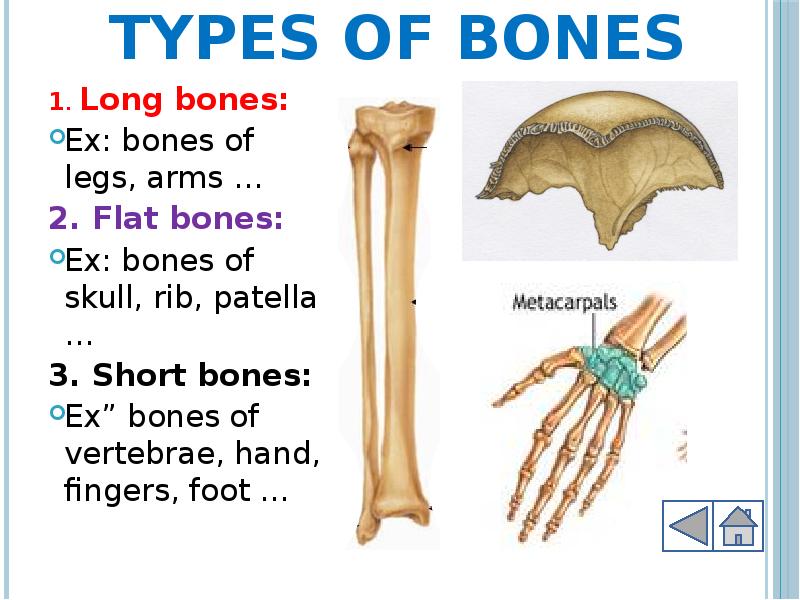
- 12. Types of bones 1. Long bones: Ex: bones of legs, arms
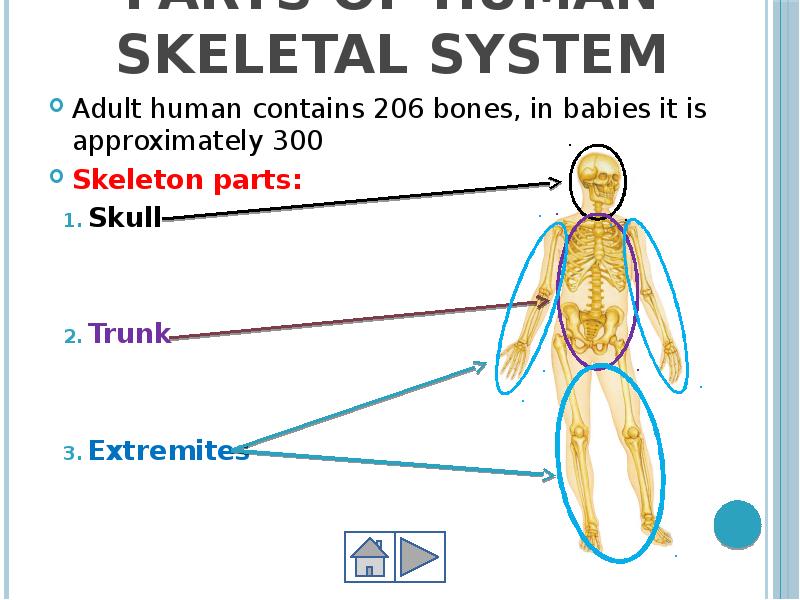
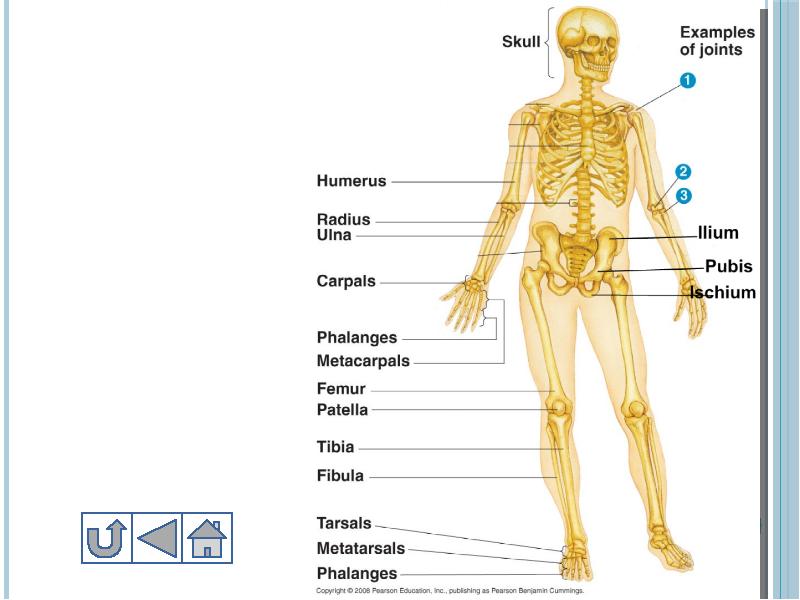
- 13. Parts of Human Skeletal System Adult human contains 206 bones, in
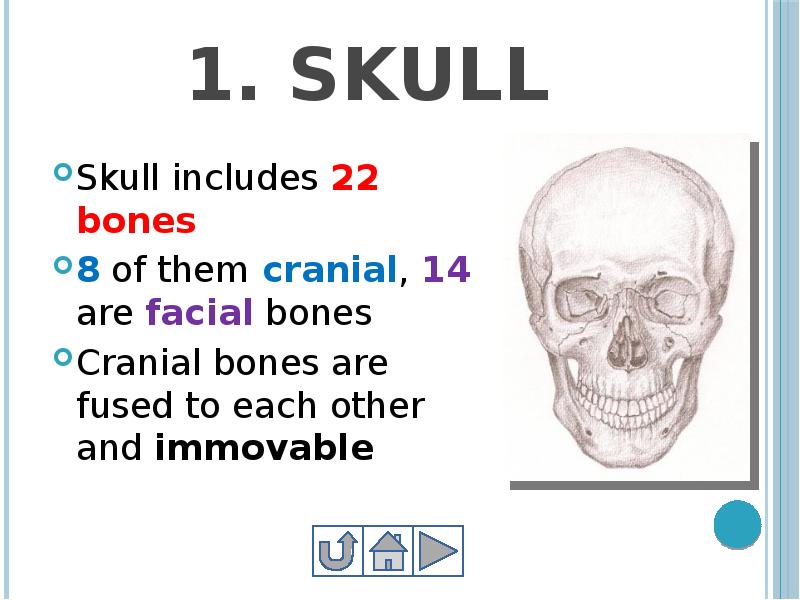
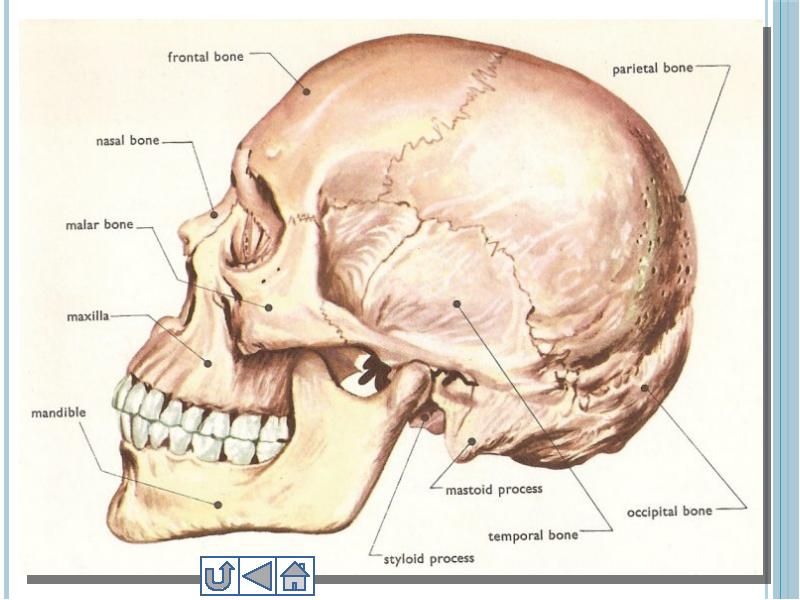
- 15. 1. Skull Skull includes 22 bones 8 of them cranial,
- 17. 2. Trunk Trunk includes vertebral column, ribs, sternum, pelvic girdle and
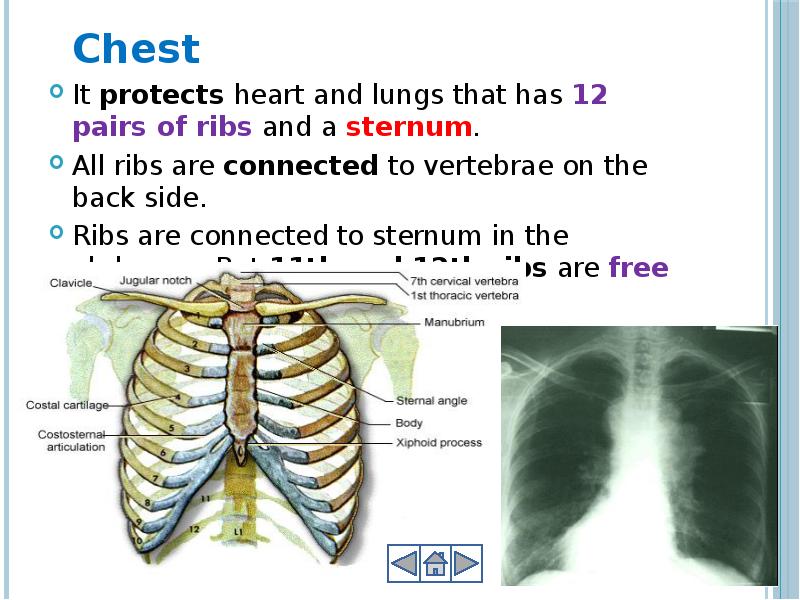
- 19. Chest Chest It protects heart and lungs that has 12 pairs
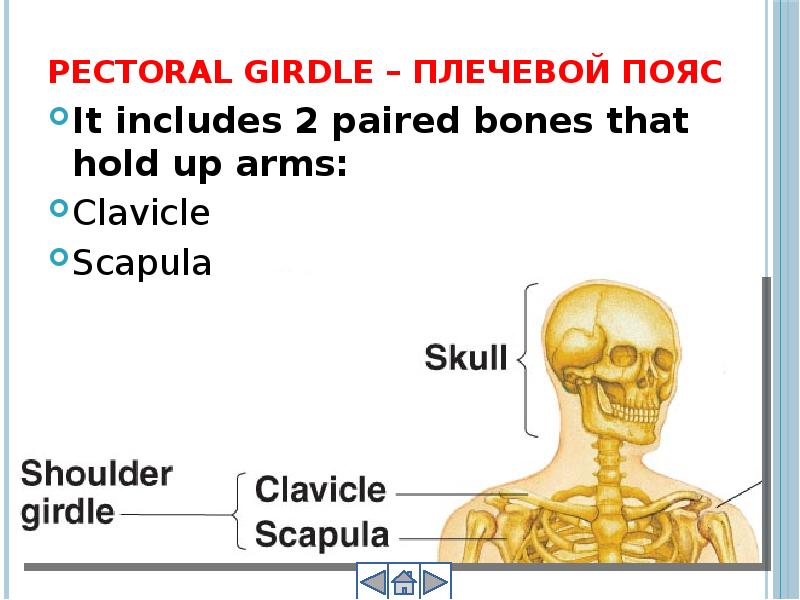
- 20. Pectoral girdle – плечевой пояс It includes 2 paired bones that
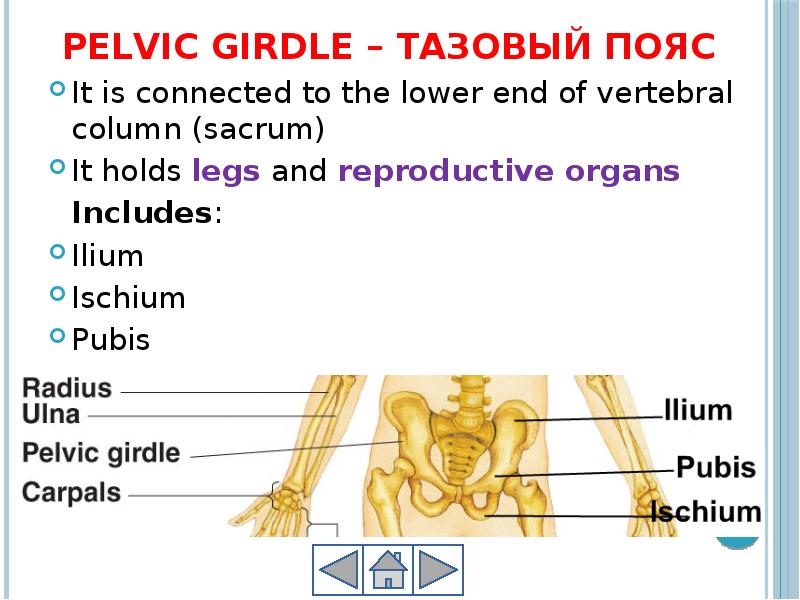
- 21. Pelvic girdle – тазовый пояс It is connected to the lower
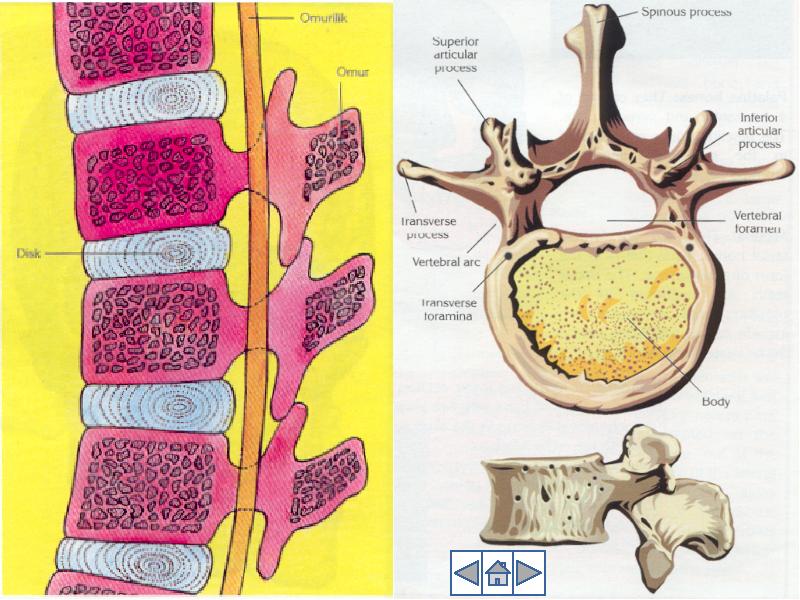
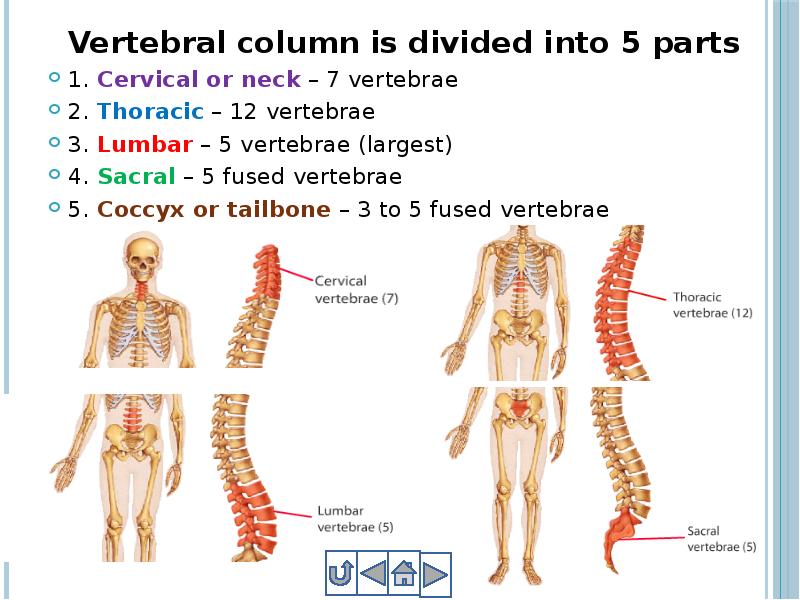
- 22. Vertebral column is divided into 5 parts Vertebral column is divided
- 25. 3. Extremites - конечности Extremites in other words appendages include upper
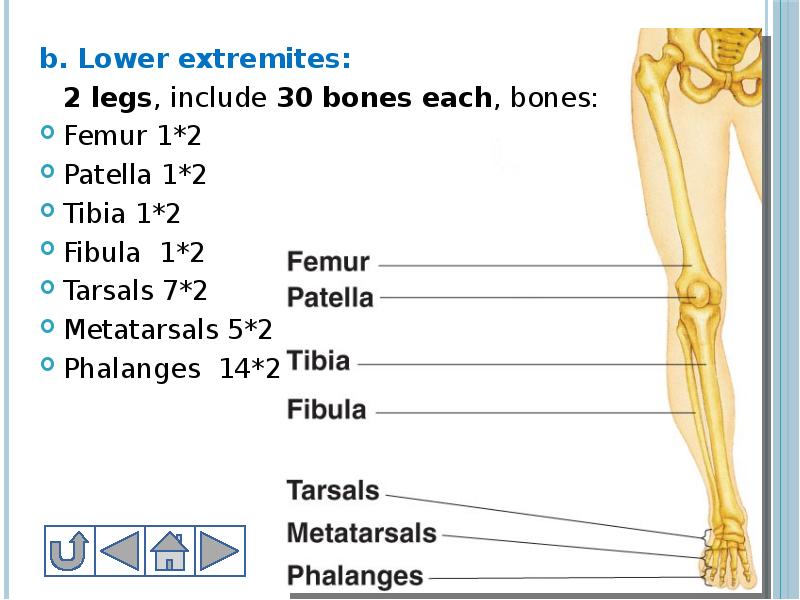
- 26. b. Lower extremites: b. Lower extremites: 2 legs, include 30 bones
- 28. Joints Joint forms the junction between two or more bones There
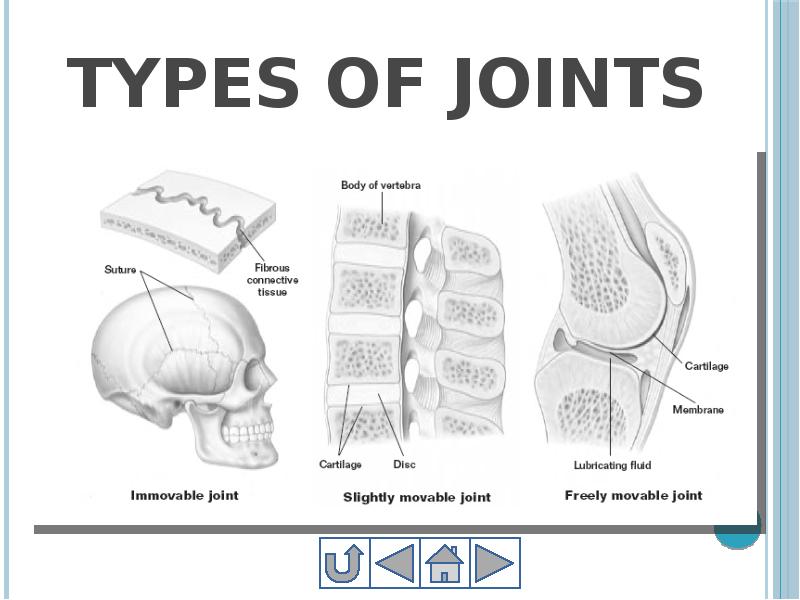
- 29. Types of joints
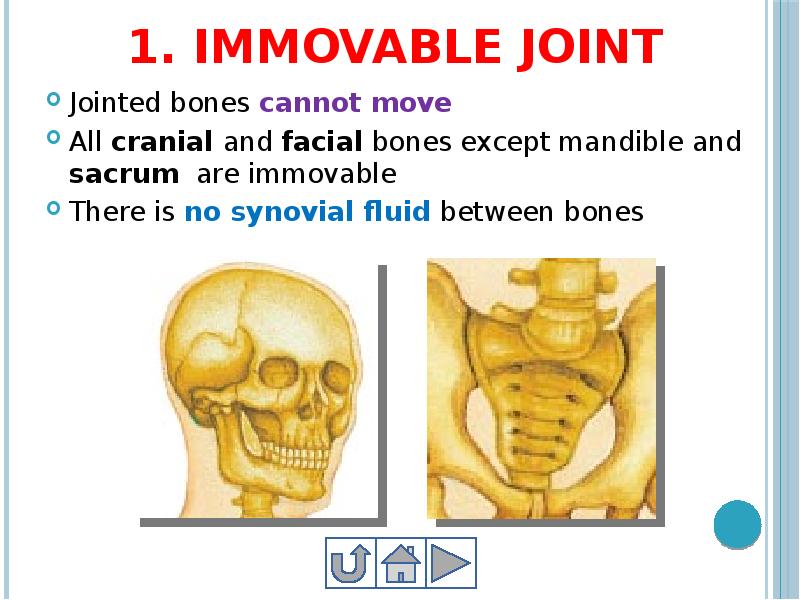
- 30. 1. Immovable joint Jointed bones cannot move All cranial and facial
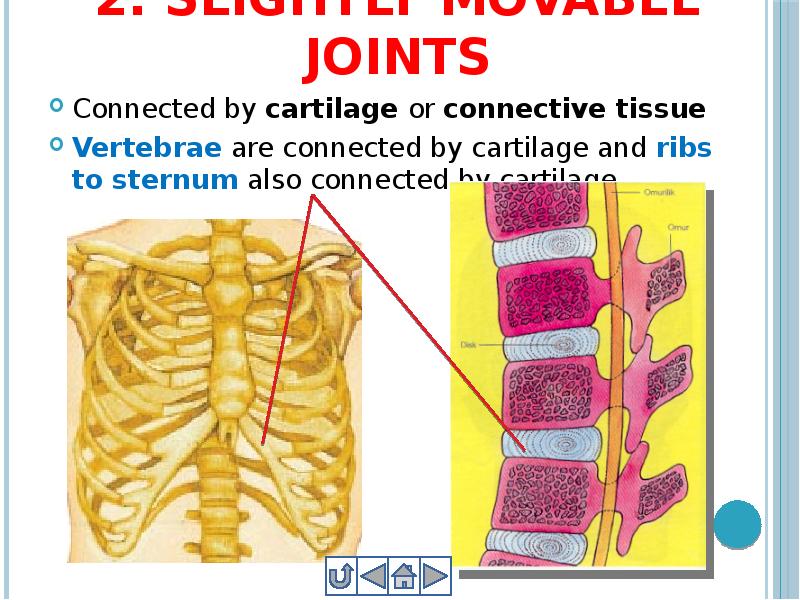
- 31. 2. Slightly movable joints Connected by cartilage or connective tissue Vertebrae
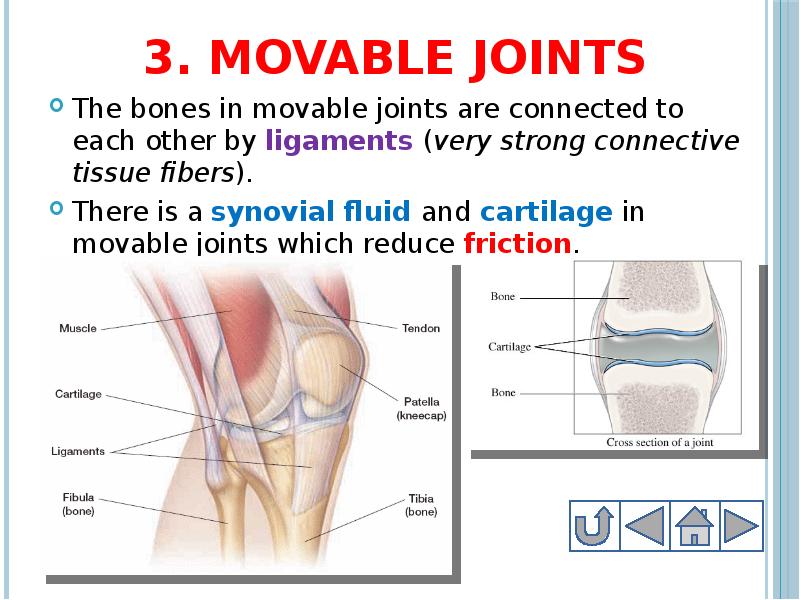
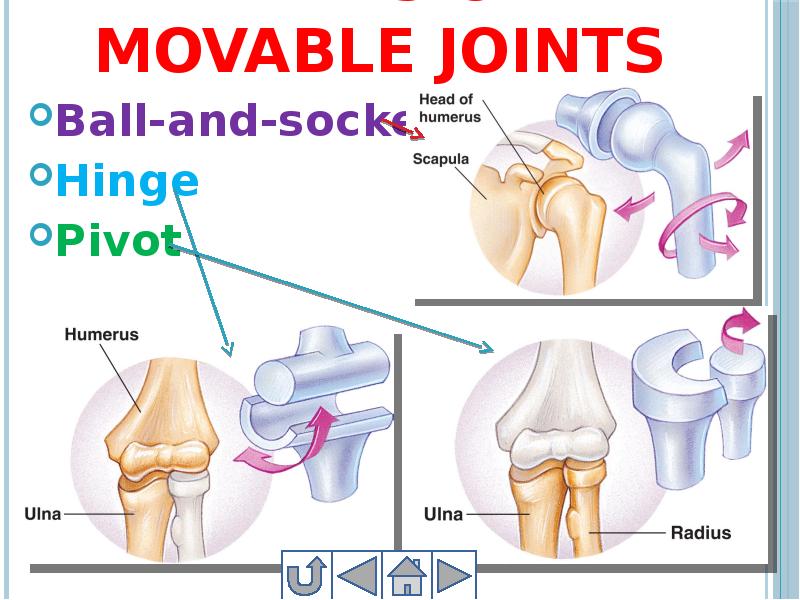
- 32. 3. Movable joints The bones in movable joints are connected to
- 33. Types of movable joints Ball-and-socket Hinge Pivot
- 34. Joints
- 35. Types of joints
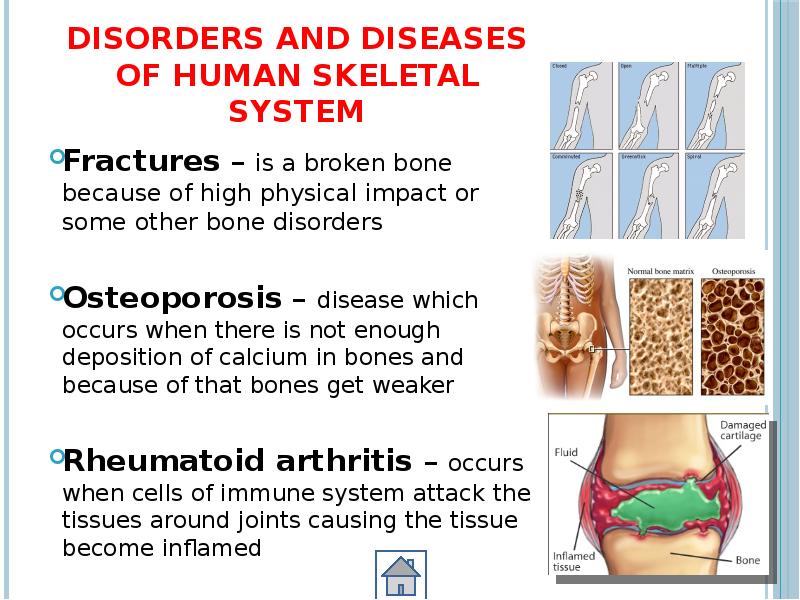
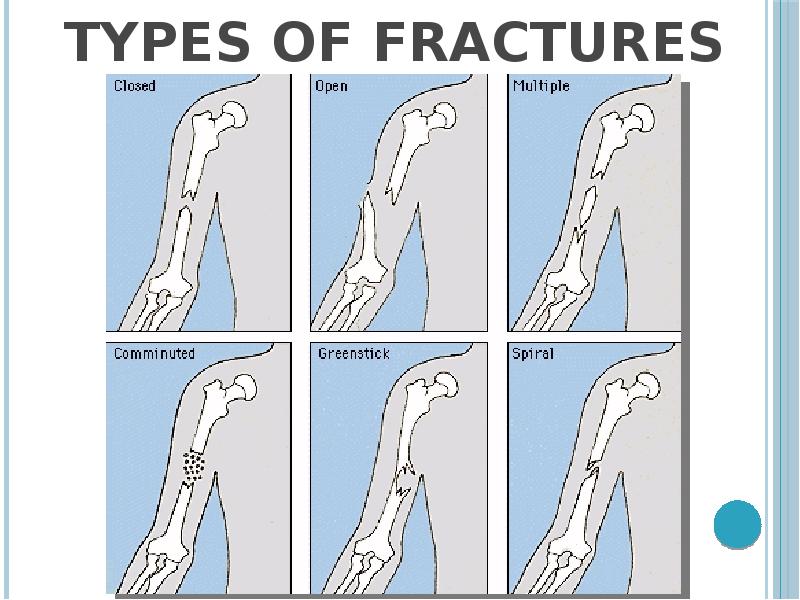
- 36. Disorders and diseases of human skeletal system Fractures – is a
- 37. Types of fractures
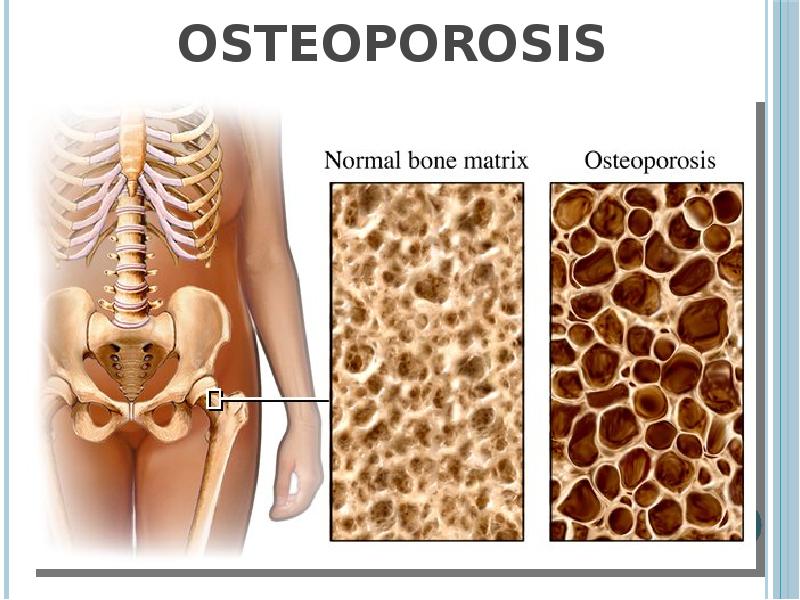
- 38. Osteoporosis
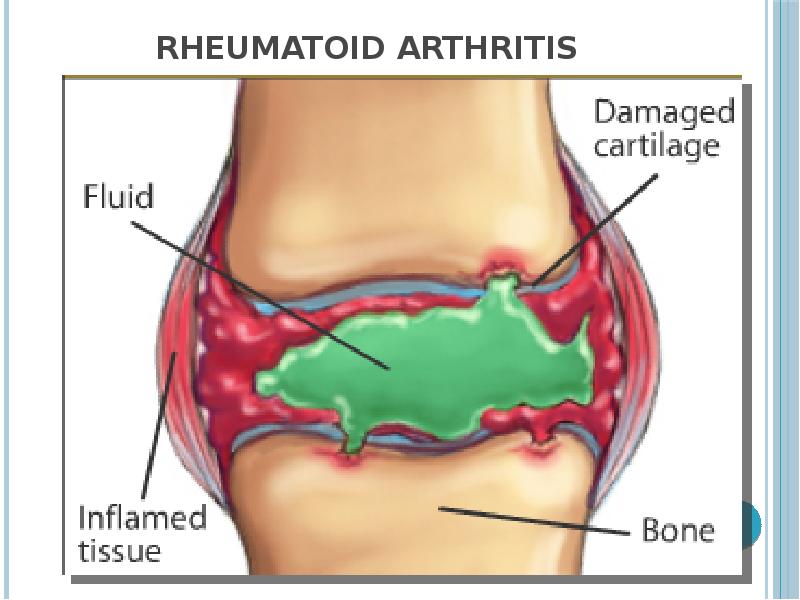
- 39. Rheumatoid arthritis
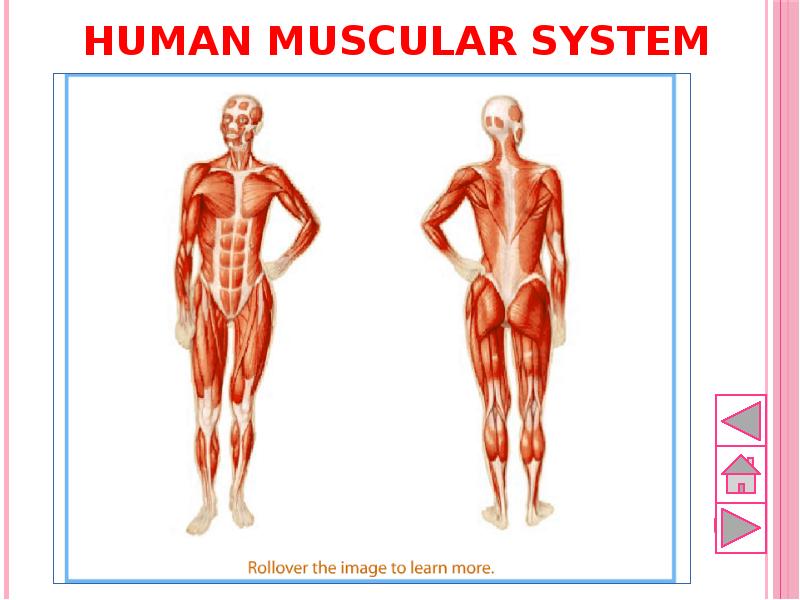
- 40. Muscular system Muscular system helps in the movement of body, inner
- 41. Human muscular system
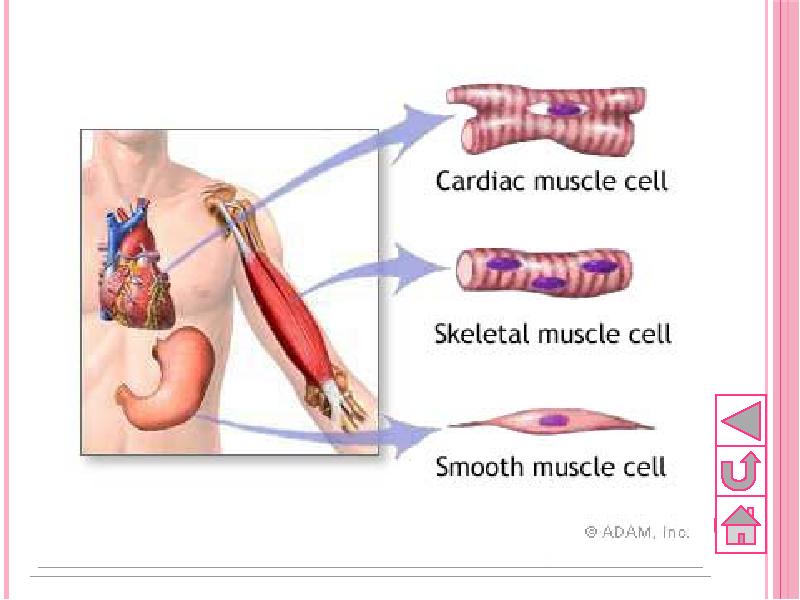
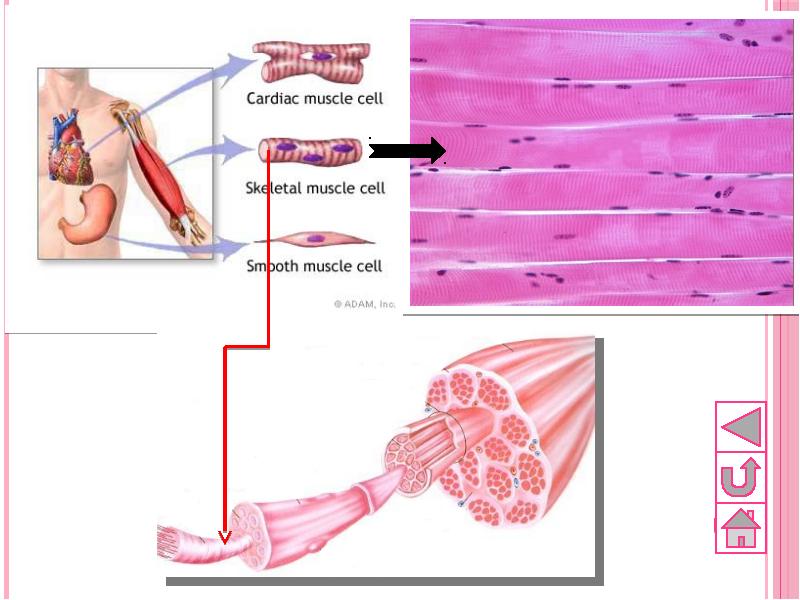
- 43. Types of muscular tissue There are 3 types of muscular tissue,
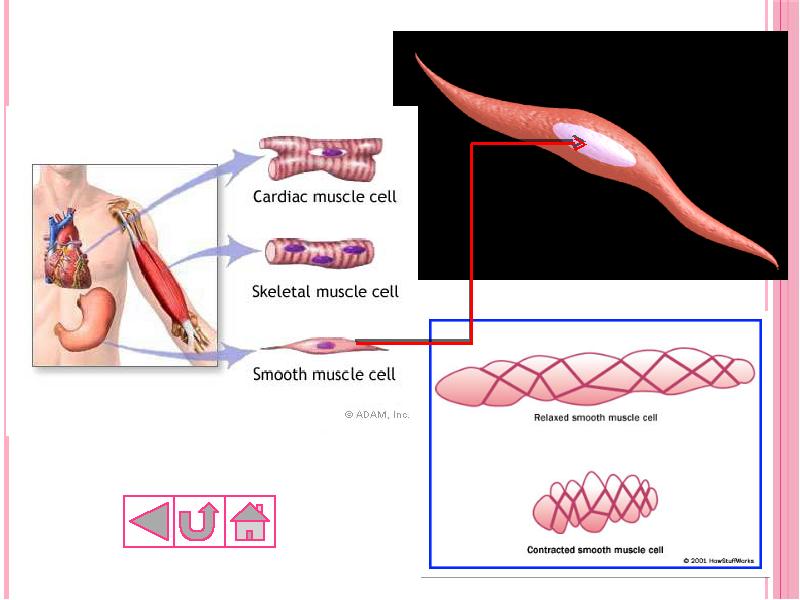
- 45. 1. Smooth muscle Each cell is long, sharp-ended with a single
- 47. 2.Skeletal or striated muscle Cells are long, cylindrical and multinuclear, i.e.
- 49. Skeletal muscles cover the skeleton Skeletal muscles cover the skeleton They
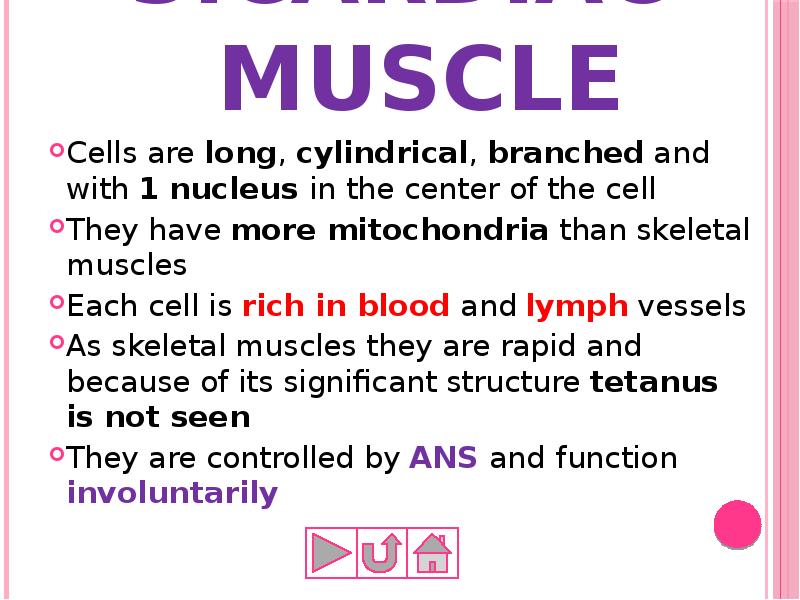
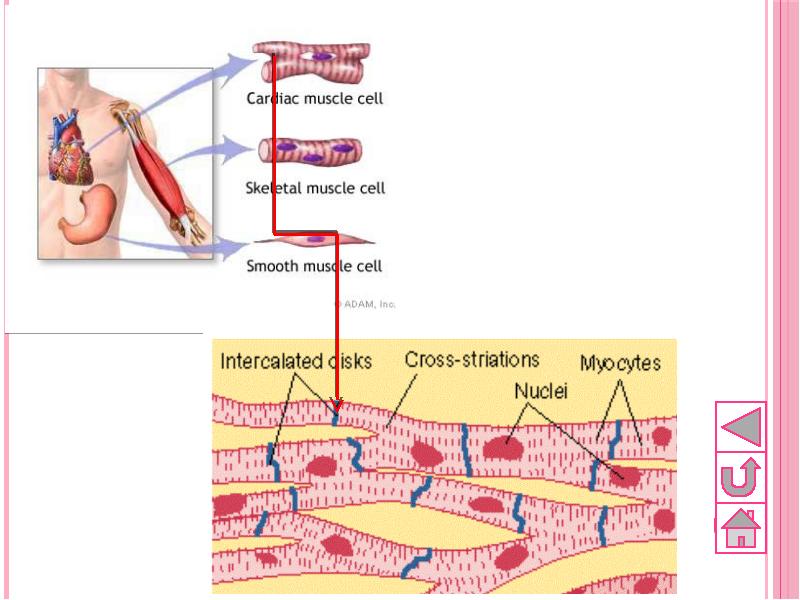
- 51. 3.Cardiac muscle Cells are long, cylindrical, branched and with 1 nucleus
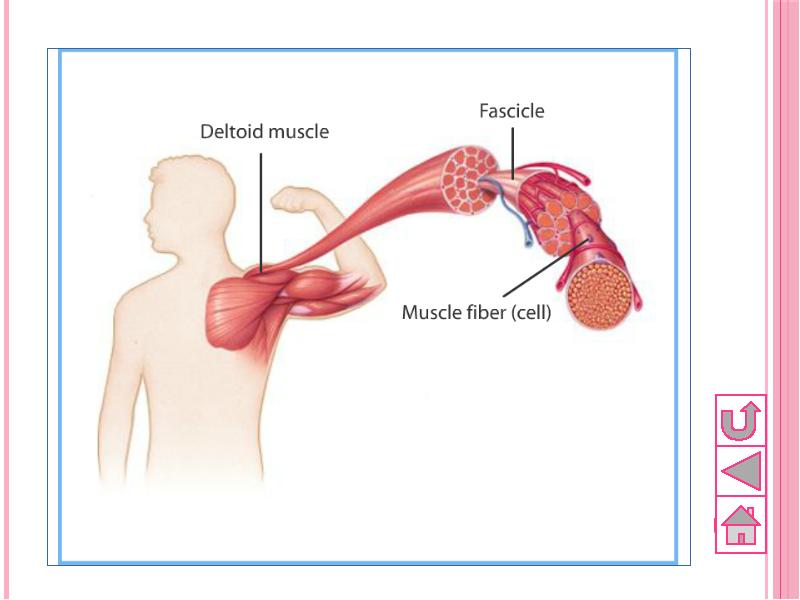
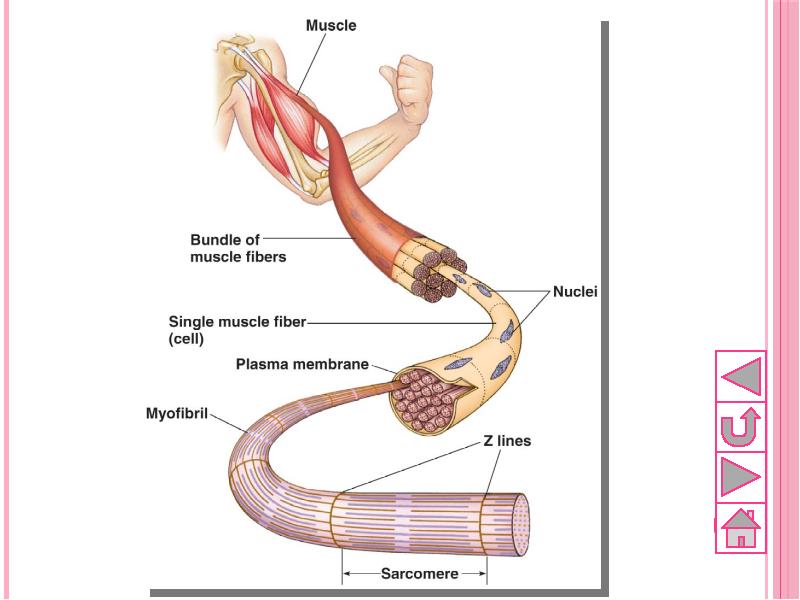
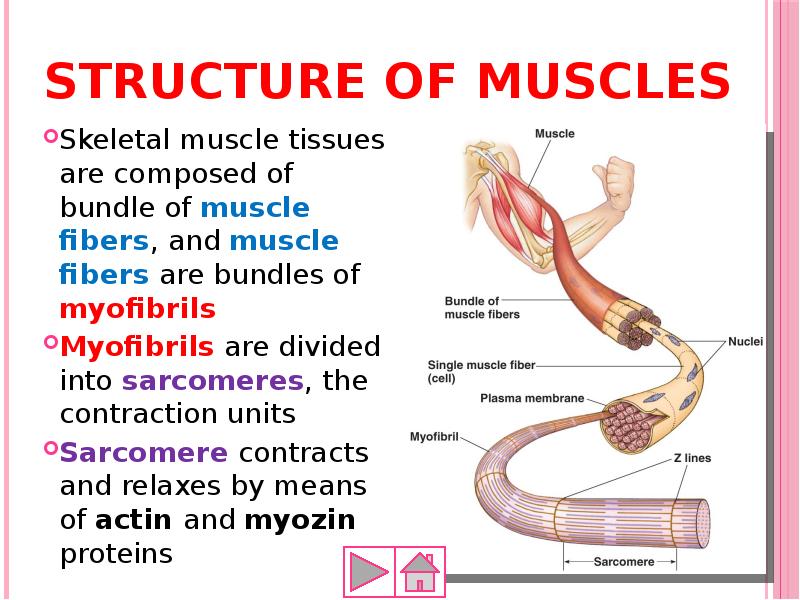
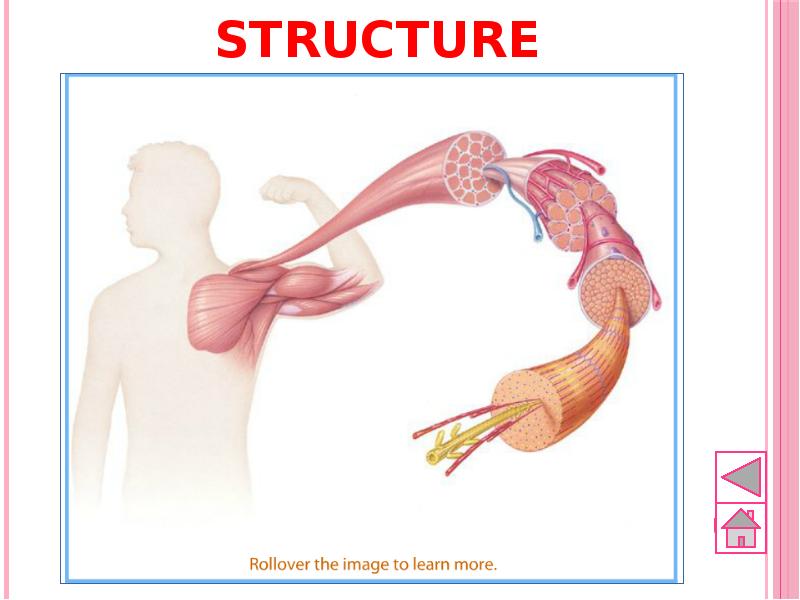
- 53. Structure of muscles Skeletal muscle tissues are composed of bundle of
- 54. Skeletal muscle structure
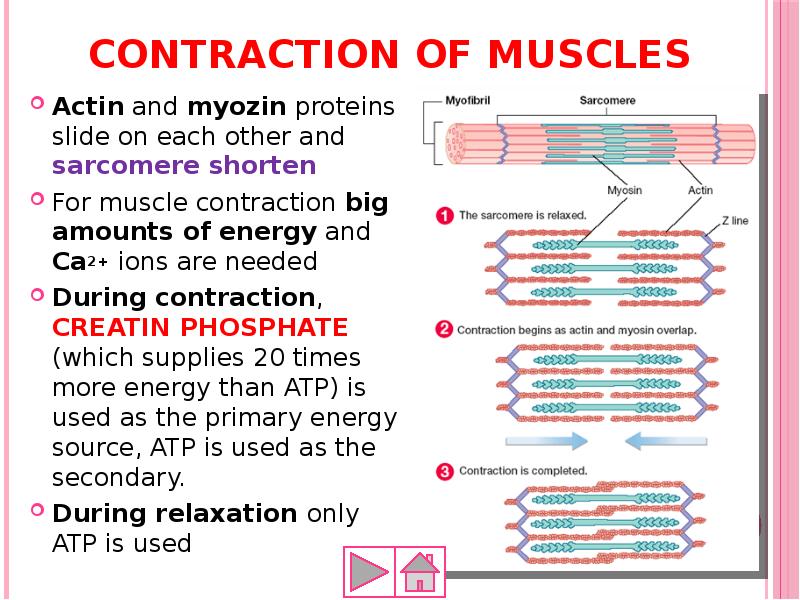
- 55. Contraction of muscles Actin and myozin proteins slide on each other
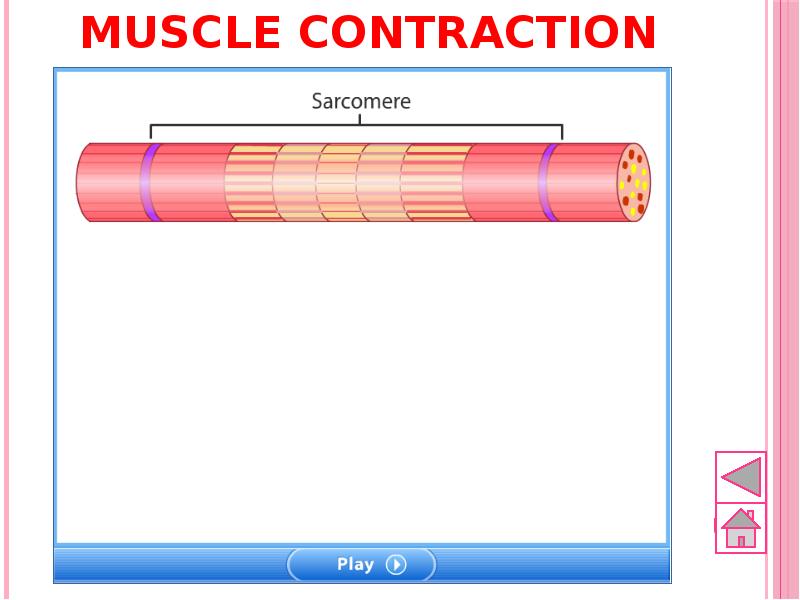
- 56. Muscle contraction
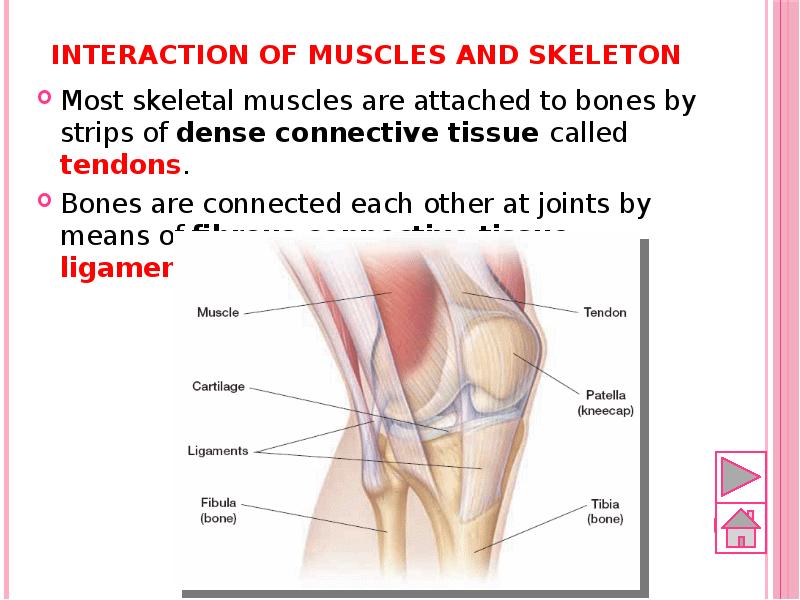
- 57. Interaction of muscles and skeleton Most skeletal muscles are attached to
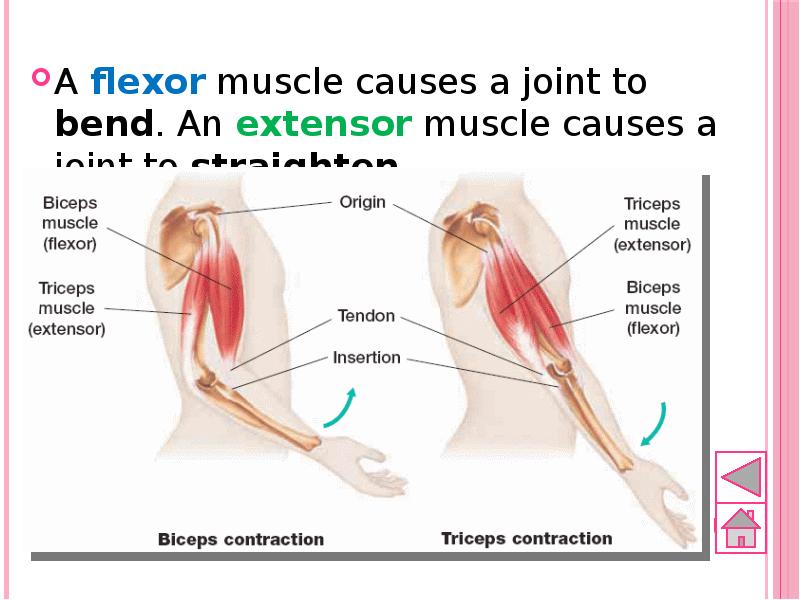
- 58. A flexor muscle causes a joint to bend. An extensor muscle
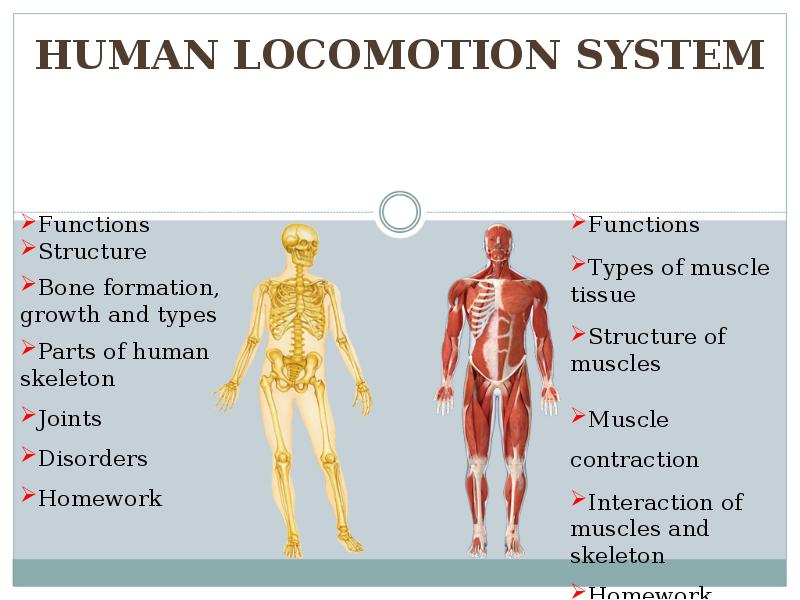
- 59. Locomotion system outlines: 1. Skeletal system Functions Structure Bone formation,
- 60. Locomotion system objectives Explain the general function of skeletal system.
- 61. Locomotion system key terms
- 62. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























