Vir al hepatitises (VH) Group of clinical similar vir al diseases of the man презентация
Содержание
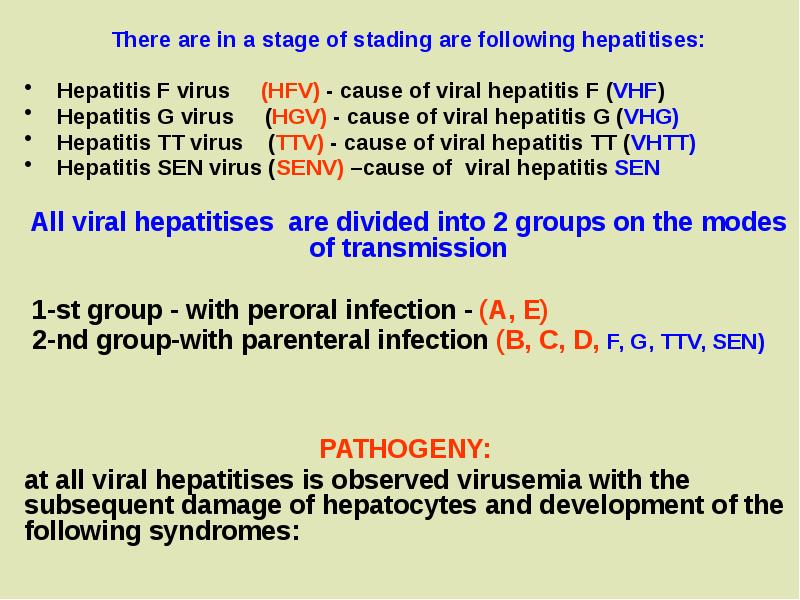
- 2. There are in a stage of stading are following hepatitises:
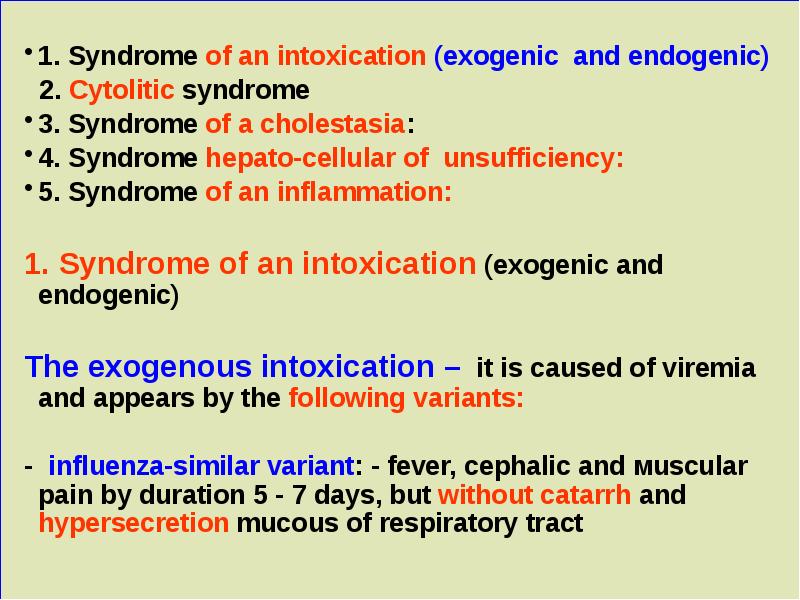
- 3. 1. Syndrome of an intoxication (exogenic and endogenic) 2. Cytolitic
- 4. - arthralgia variant: - ostealgia or arthralgia often in evening time
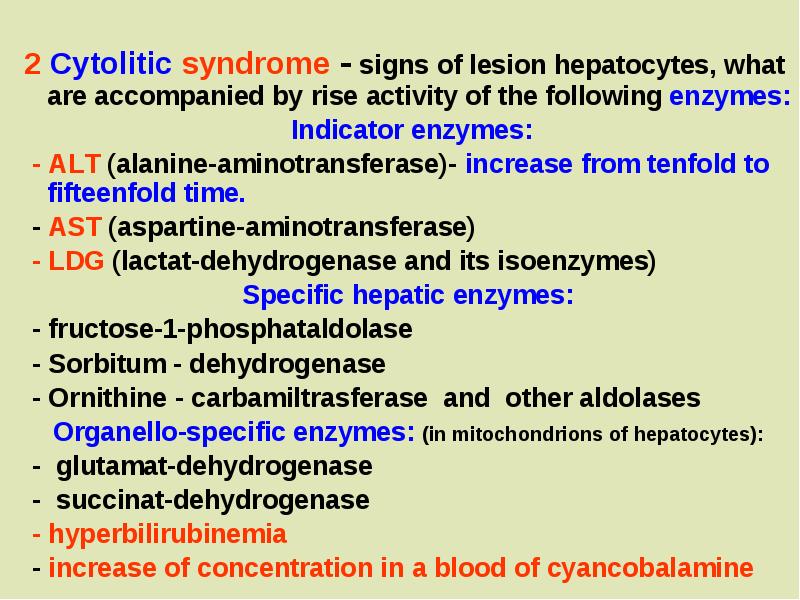
- 5. 2 Cytolitic syndrome - signs of lesion hepatocytes, what are accompanied
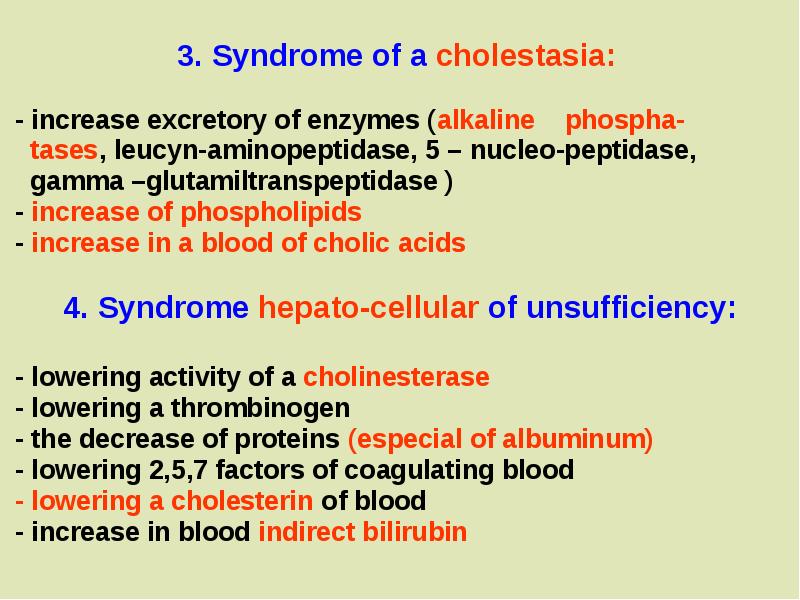
- 6. 3. Syndrome of a cholestasia: - increase excretory of
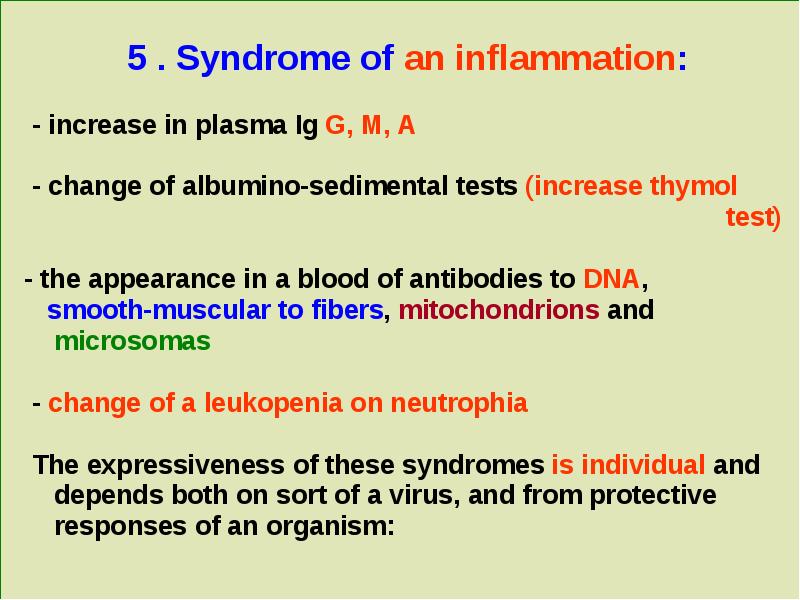
- 8. 5 . Syndrome of an inflammation: - increase in plasma
- 9. Viral hepatitis may proceed as: Acute cyclic form of disease
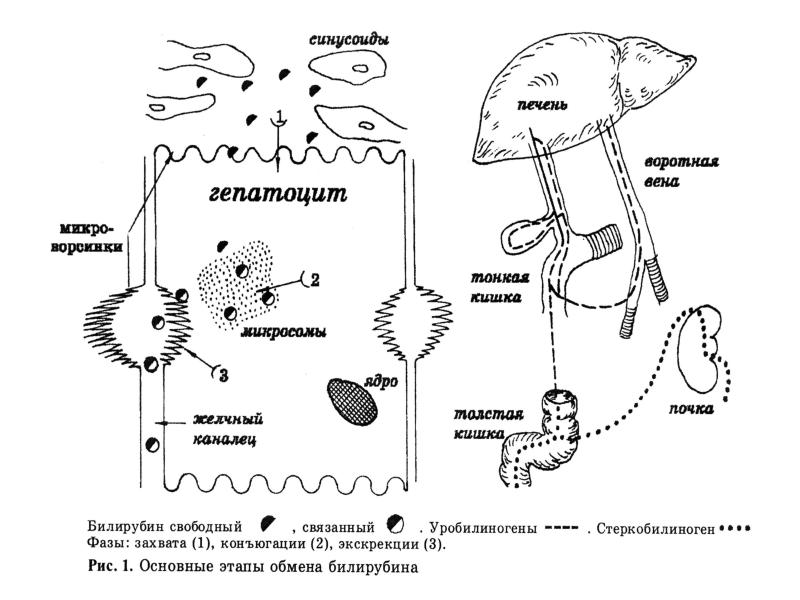
- 10. PATHOMORPHOLOGY - at all hepatitises to change in liver,
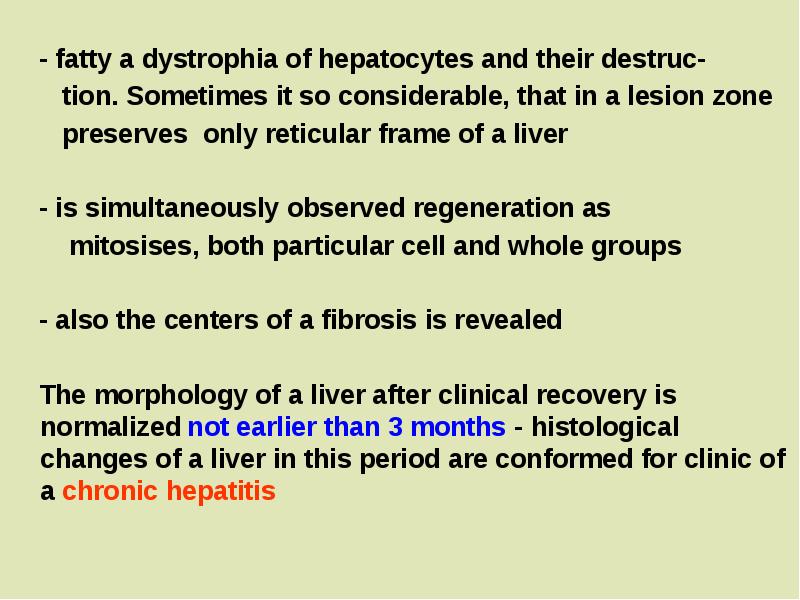
- 11. - fatty a dystrophia of hepatocytes and their destruc- tion.
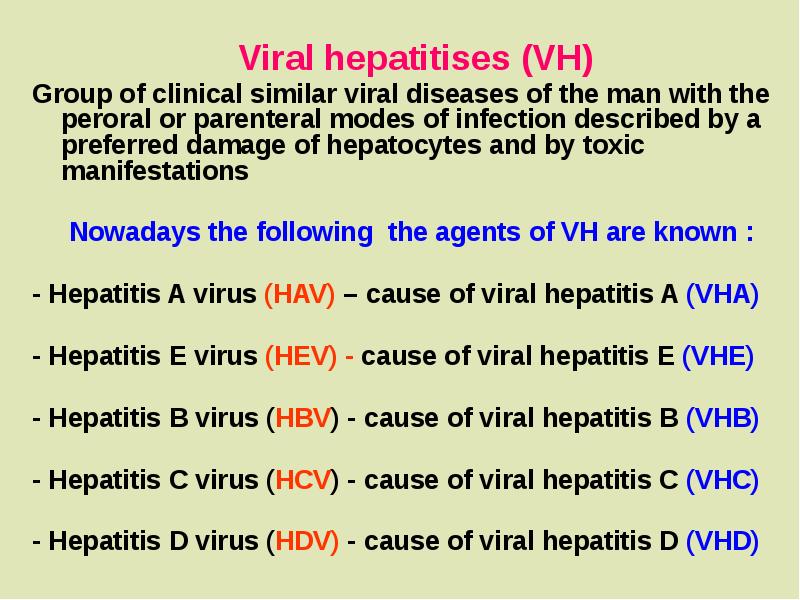
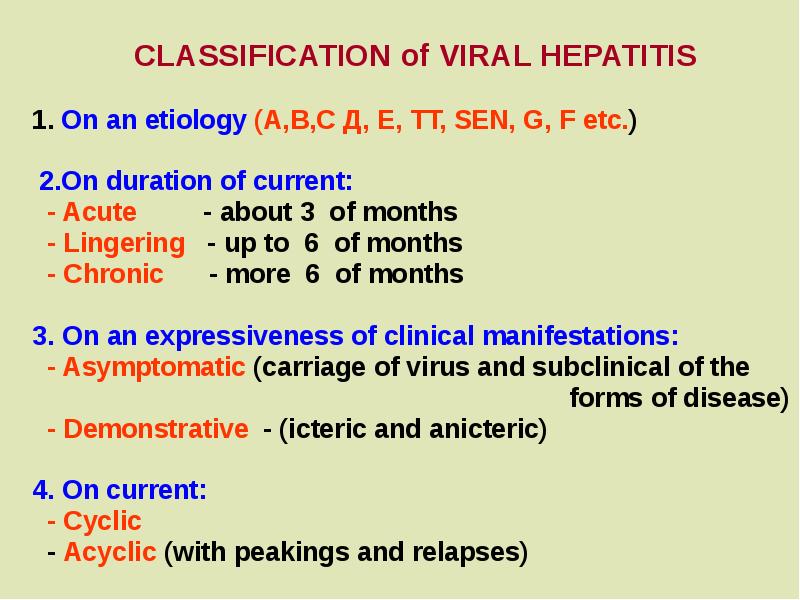
- 12. CLASSIFICATION of VIRAL HEPATITIS 1. On an etiology (A,B,C Д,
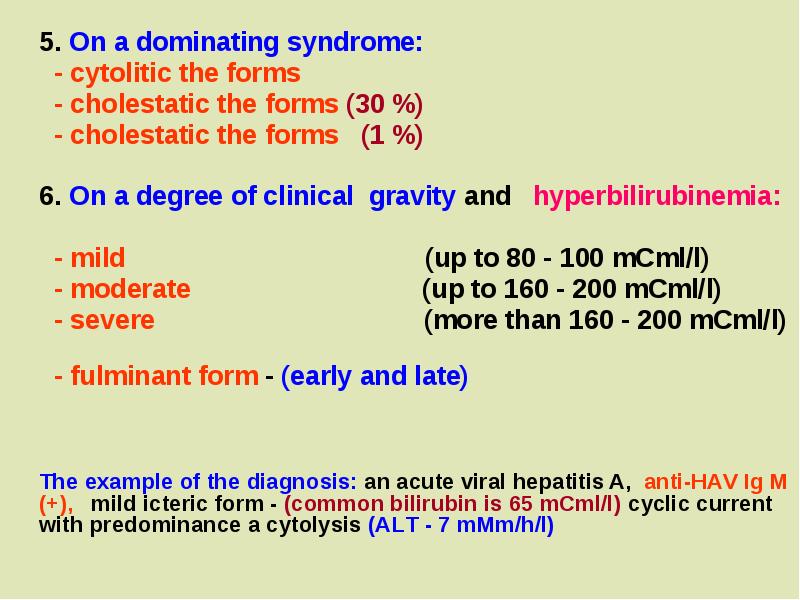
- 13. 5. On a dominating syndrome: - cytolitic the forms -
- 14. Common pathogeny of viral hepatitis
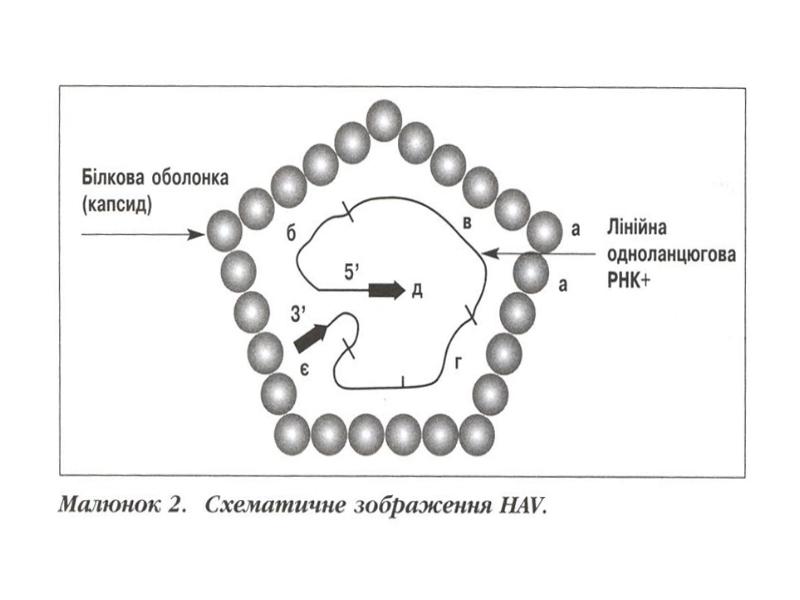
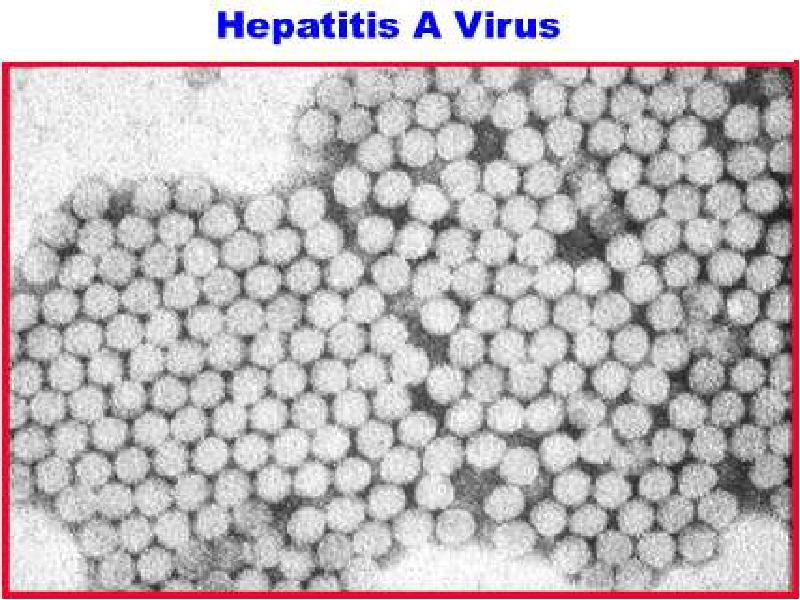
- 15. VIRAL HEPATITIS A (VHA) VIRAL HEPATITIS A (VHA)
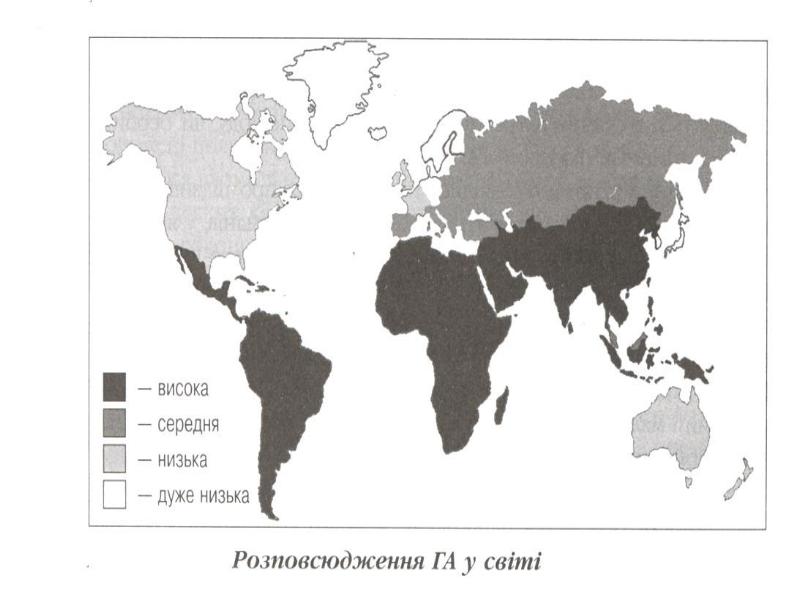
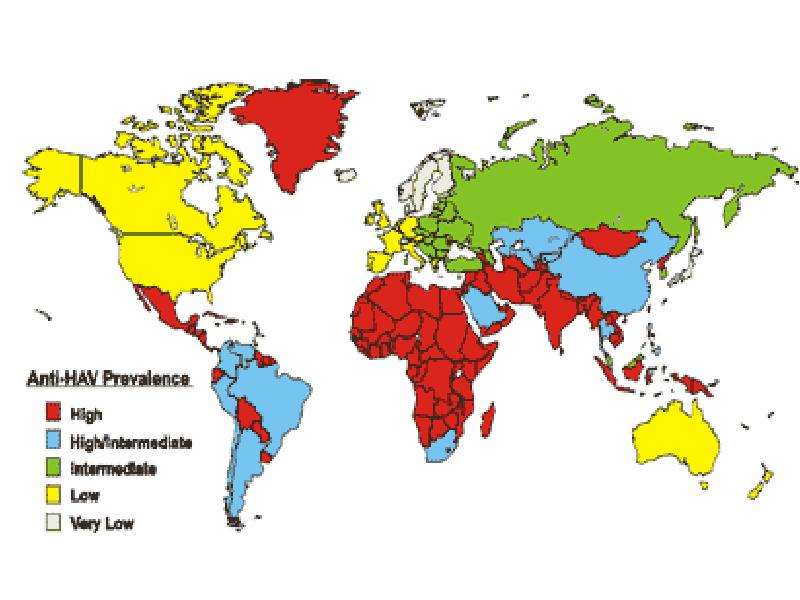
- 18. EPIDEMIOLOGY- it is antroponosis The sourse - the patient with
- 21. CLINIC: Incubation 15 - 50 days (30 days) Prodromal
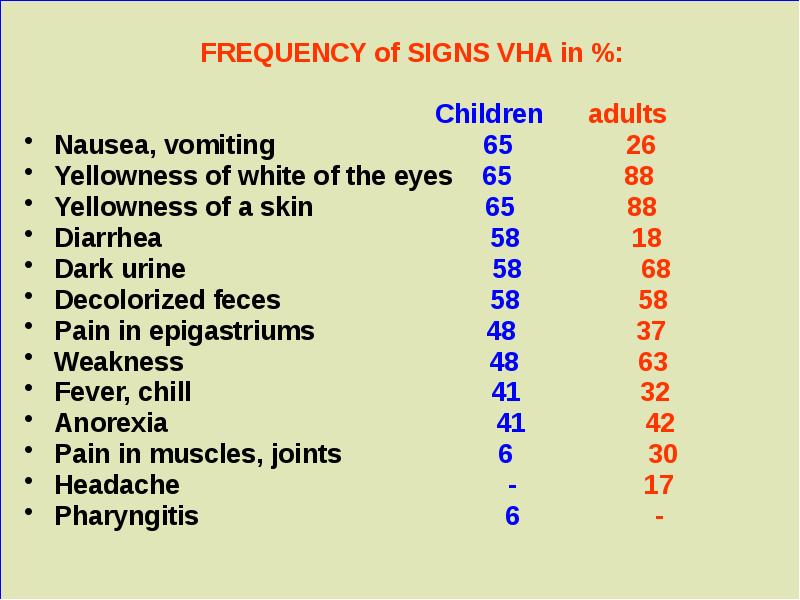
- 22. FREQUENCY of SIGNS VHA in %:
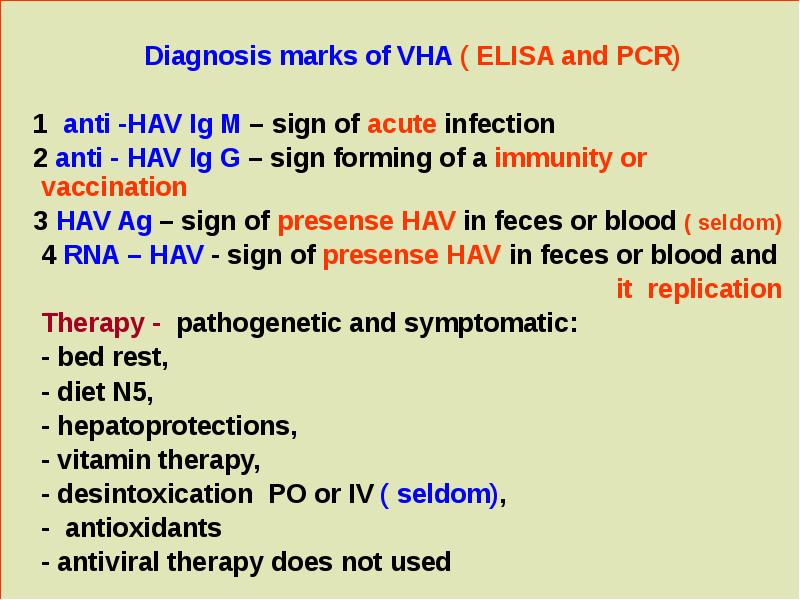
- 30. Diagnosis marks of VHA ( ELISA and PCR) 1 anti
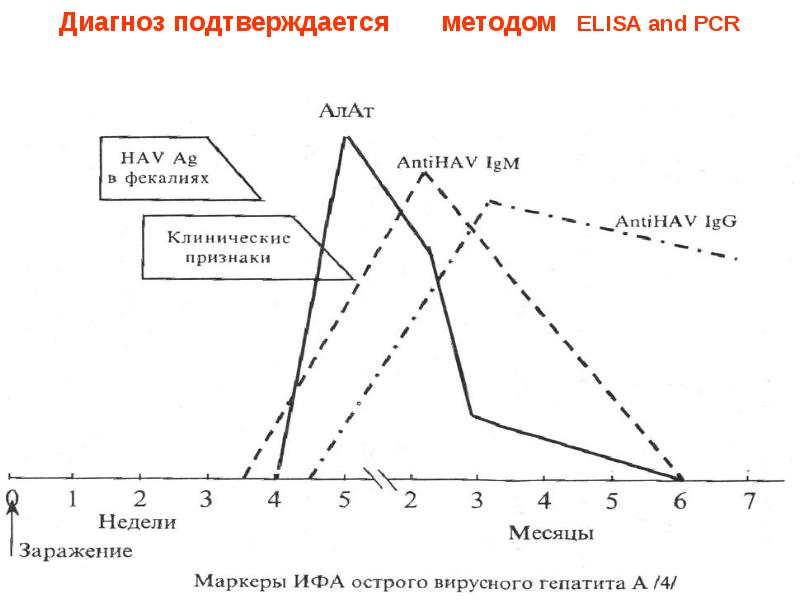
- 31. Диагноз подтверждается методом ELISA and PCR
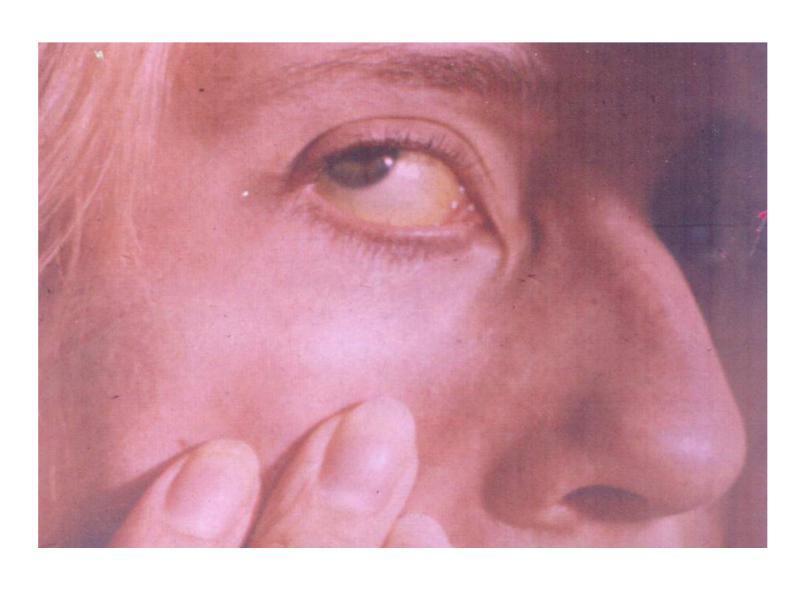
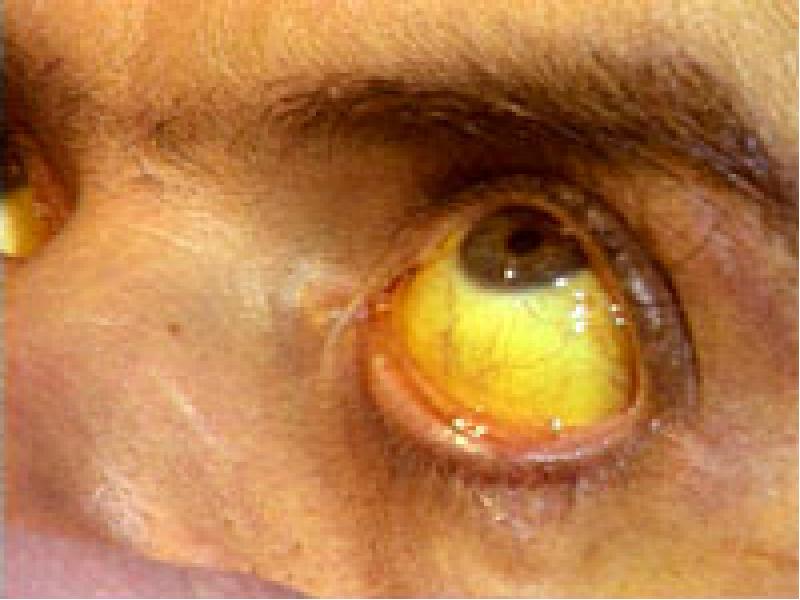
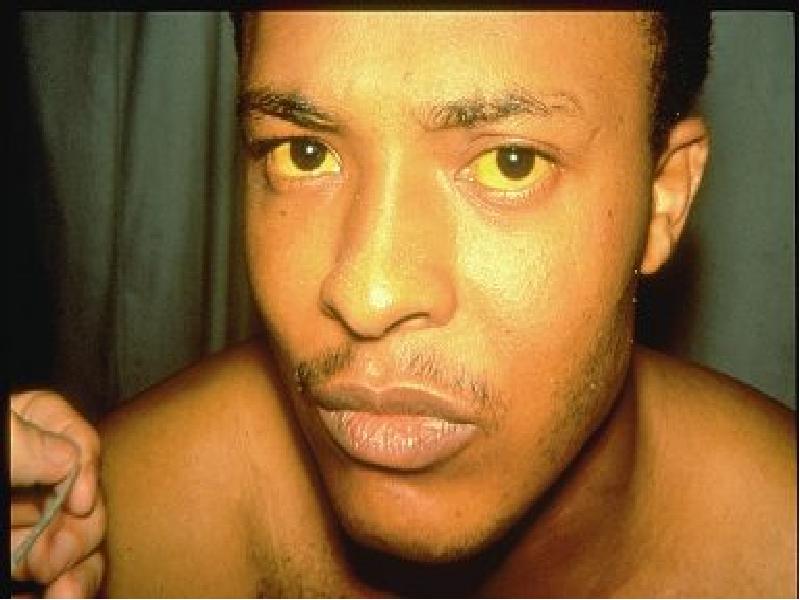
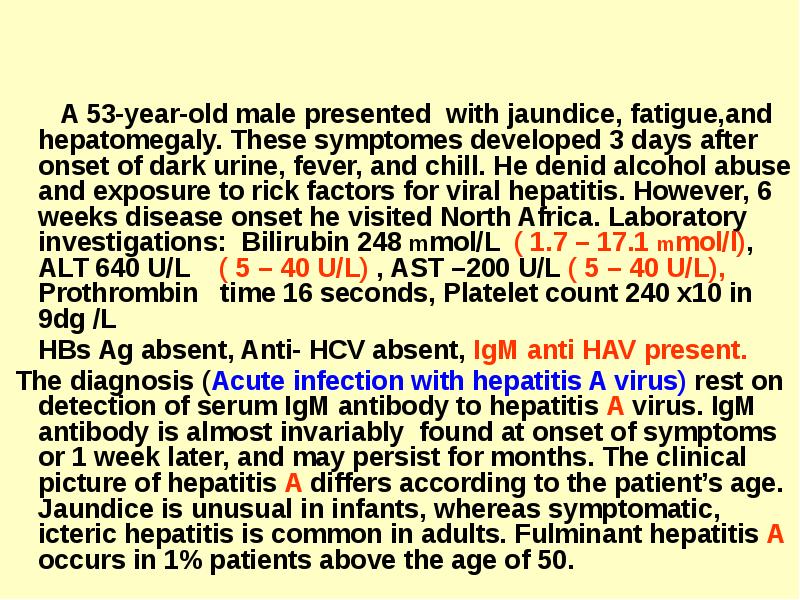
- 32. A 53-year-old male presented with jaundice, fatigue,and hepatomegaly. These symptomes developed
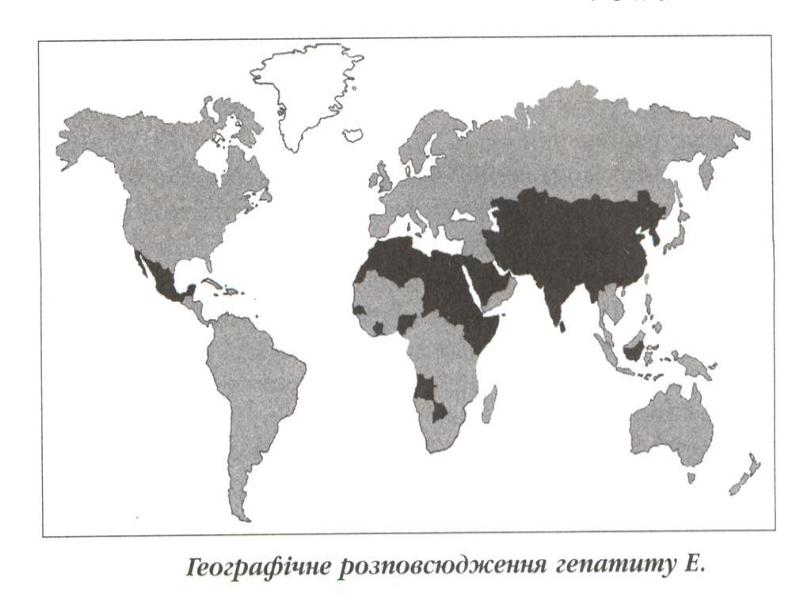
- 33. VIRAL HEPATITIS Е (VHE) The agent - shallow spherical Calicinoviruses
- 35. The seasonal prevalence - is more often in period
- 36. fever – sign is nonconstant with appearance of an icterus aggravation
- 37. Lethality no more than 0,4 % The pregnant women in 3td
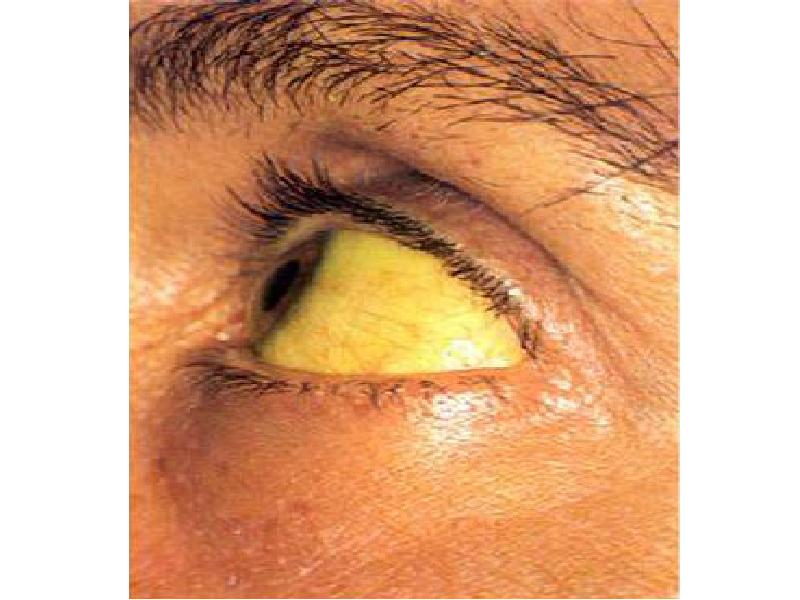
- 38. A 39-year-old Chinese businessman travelling to Italy presents fatigue, anorexia, jaundice,
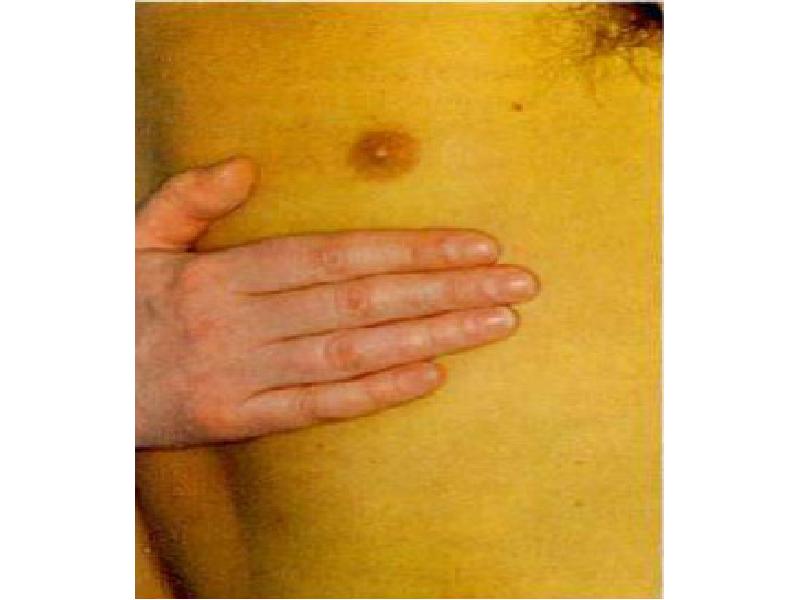
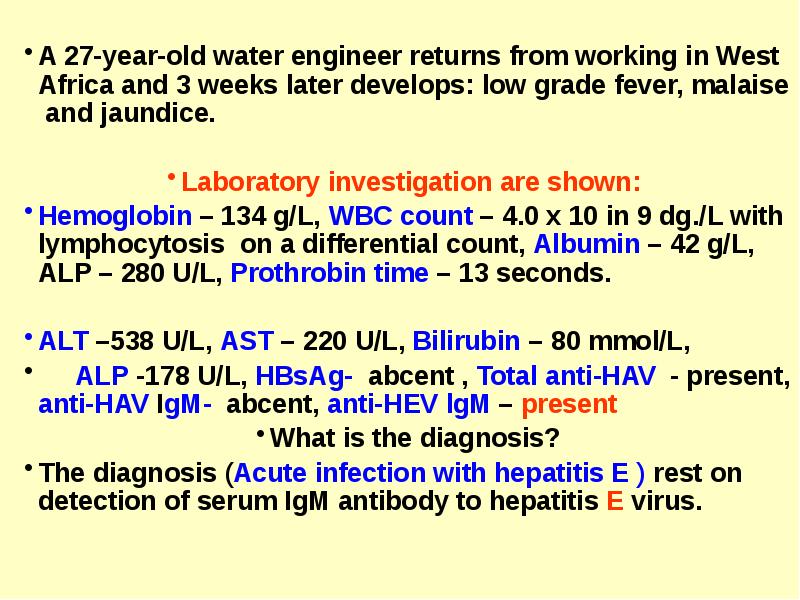
- 39. A 27-year-old water engineer returns from working in West Africa and
- 40. Therapy - pathogenetic and symptomatic: bed rest, diet N5, hepatoprotections, vitamin
- 41. Appearance encephalopathy with an oppression of consciousness, degree expressivenesses which is
- 43. Скачать презентацию















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Vir al hepatitises (VH)
Group of clinical similar vir al diseases of the man можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























