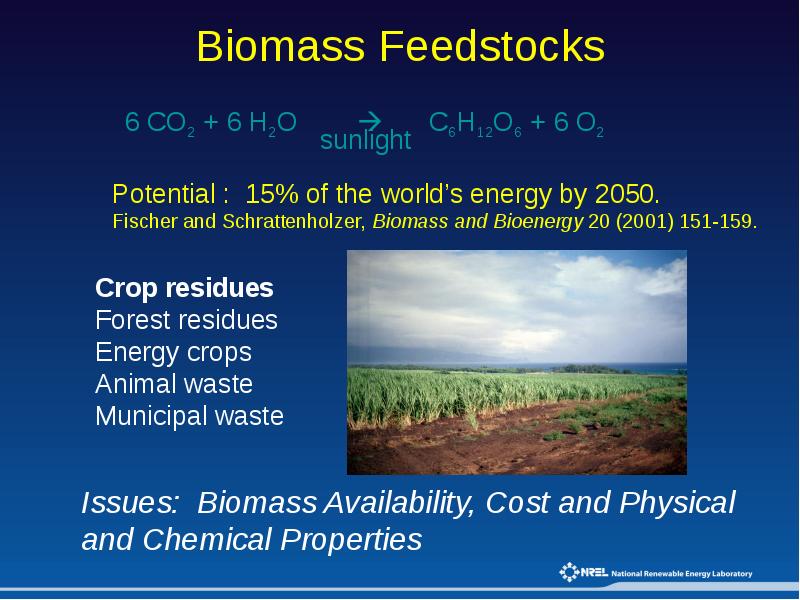
Biomass Feedstocks презентация
Содержание
- 3. Biodiesel (B100) ASTM PS 121 Biodiesel Fuel Standard similar to
- 4. Handles Just Like Diesel No engine modifications required for B20, if
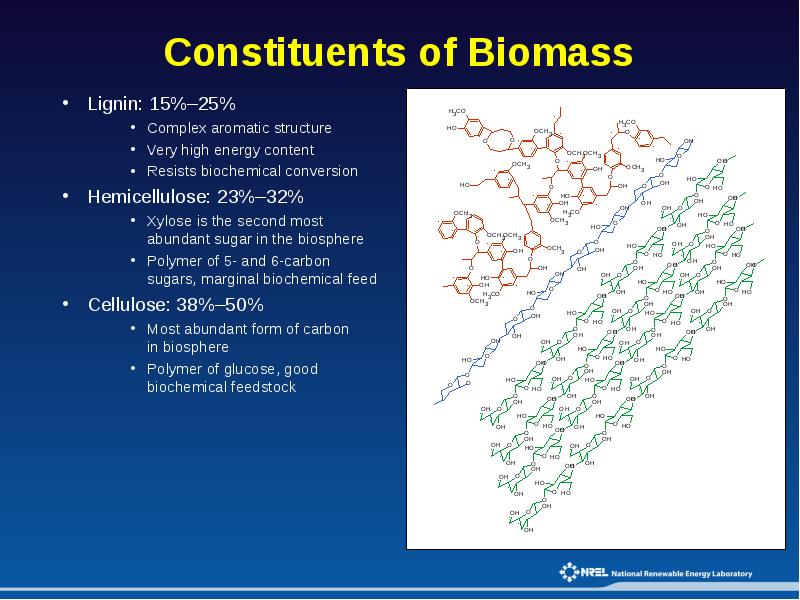
- 8. Constituents of Biomass Lignin: 15%–25% Complex aromatic structure Very high energy
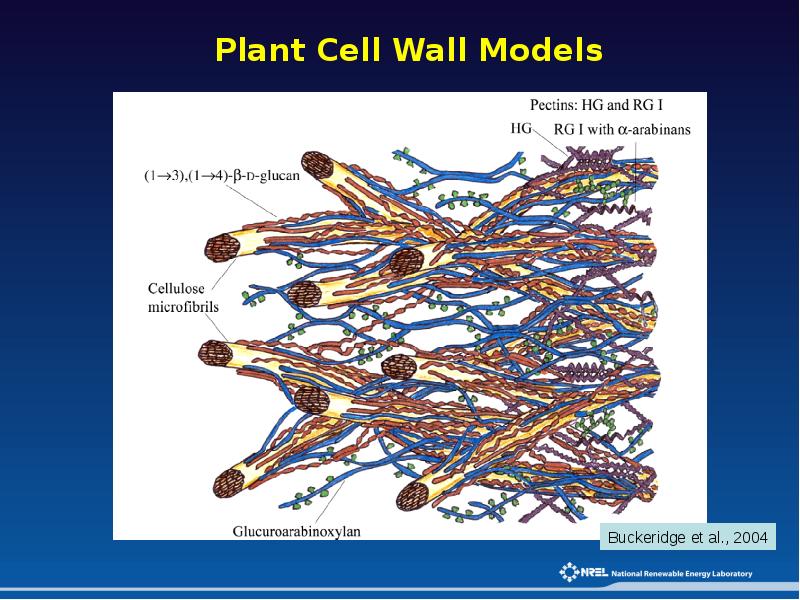
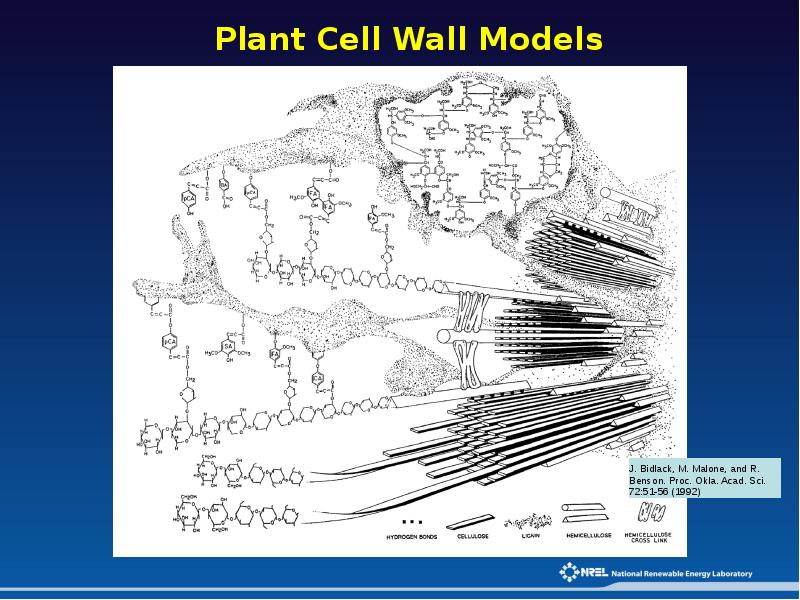
- 9. Plant Cell Wall Models
- 10. Plant Cell Wall Models
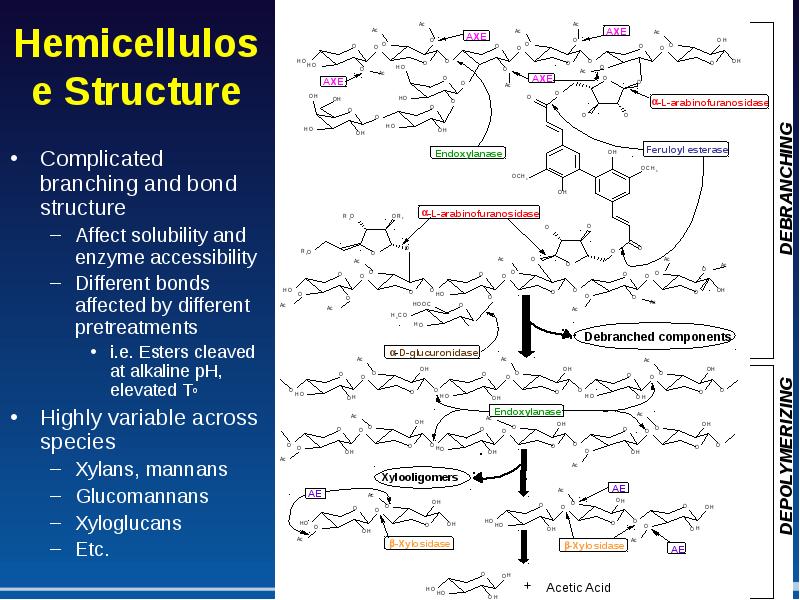
- 11. Hemicellulose Structure Complicated branching and bond structure Affect solubility and enzyme
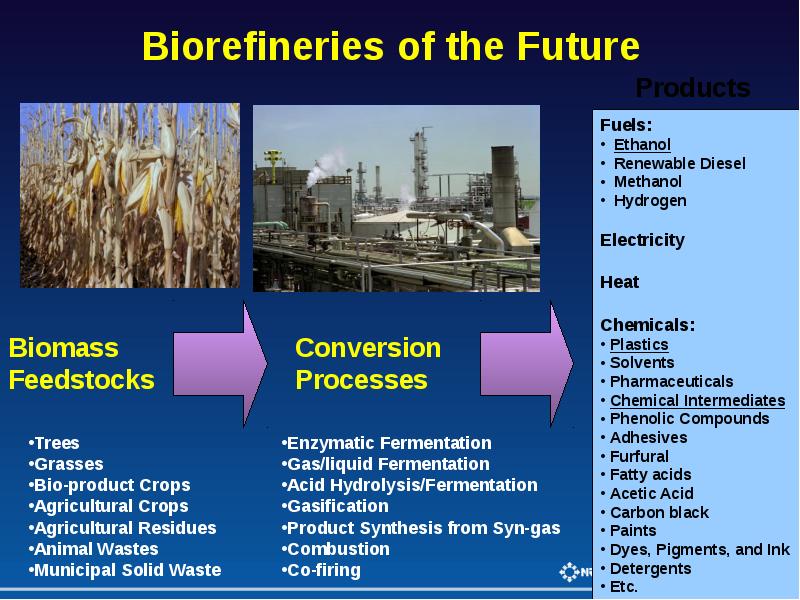
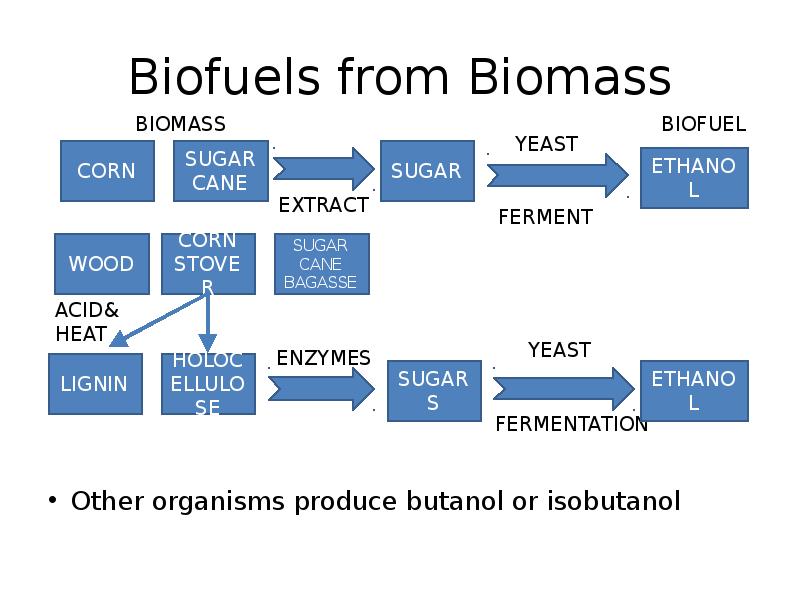
- 12. Biofuels from Biomass Other organisms produce butanol or isobutanol
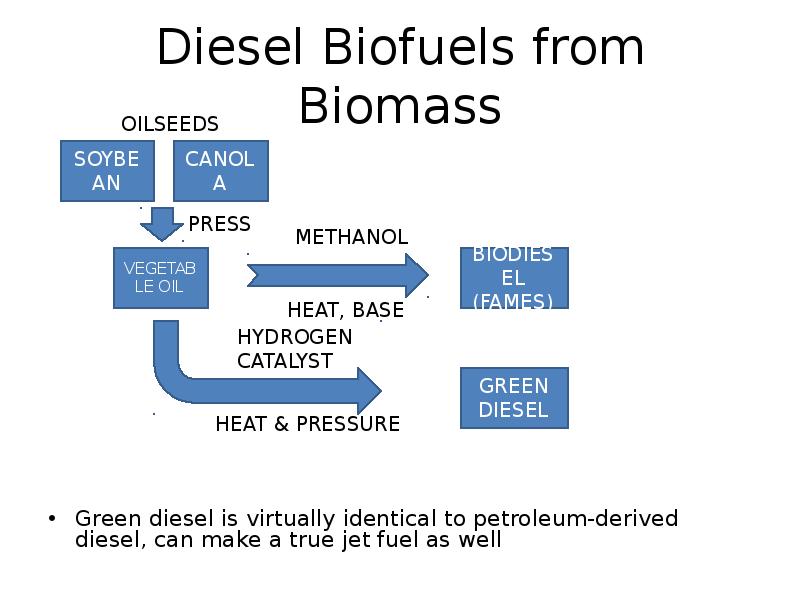
- 13. Diesel Biofuels from Biomass Green diesel is virtually identical to petroleum-derived
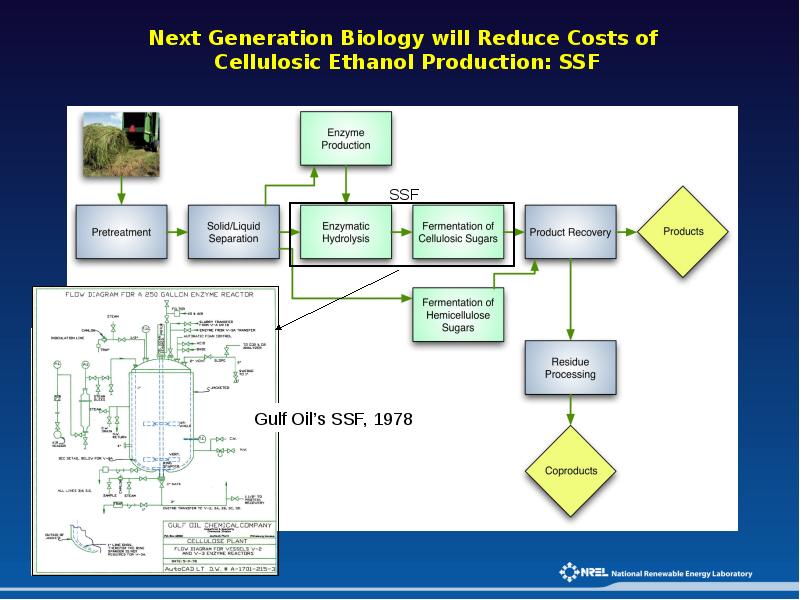
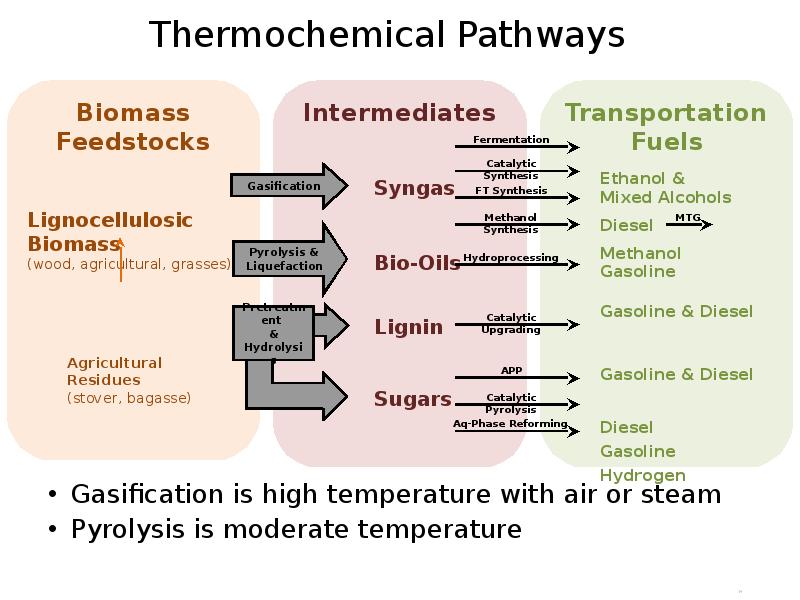
- 14. Thermochemical Pathways Gasification is high temperature with air or steam
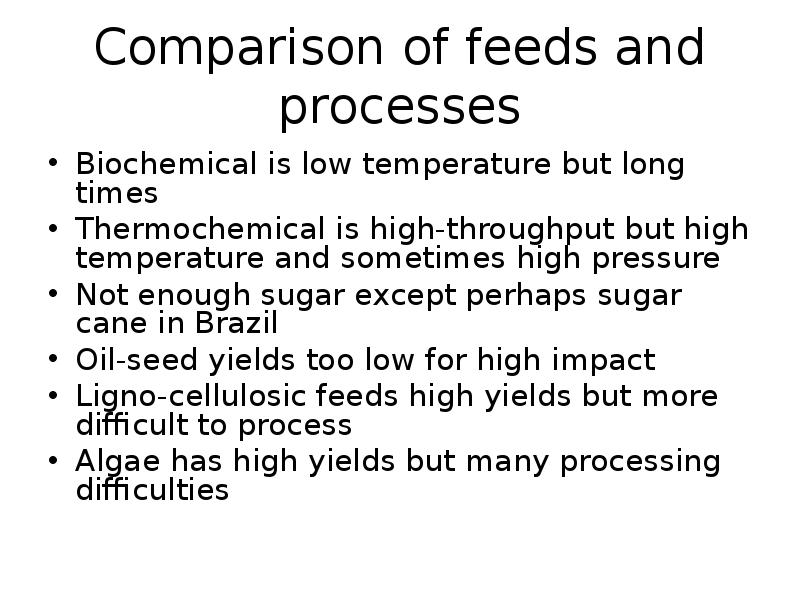
- 15. Comparison of feeds and processes Biochemical is low temperature but long
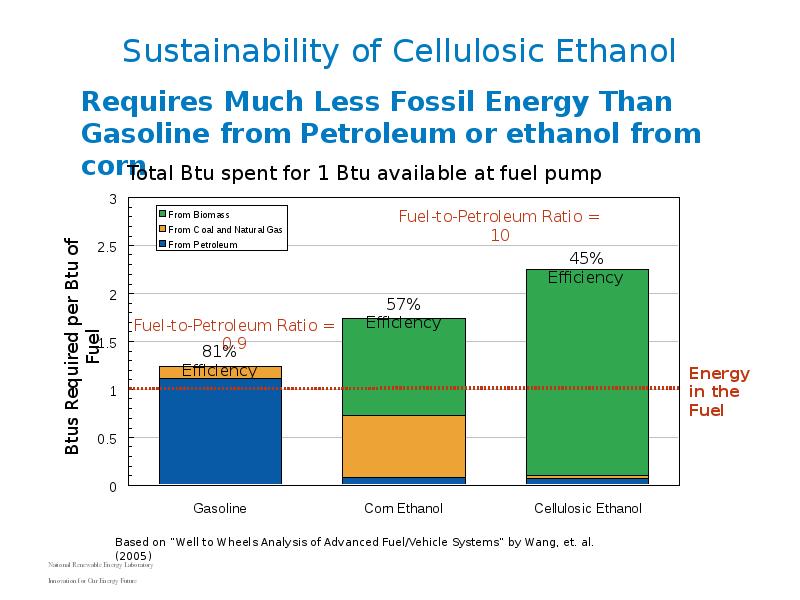
- 16. Sustainability of Cellulosic Ethanol
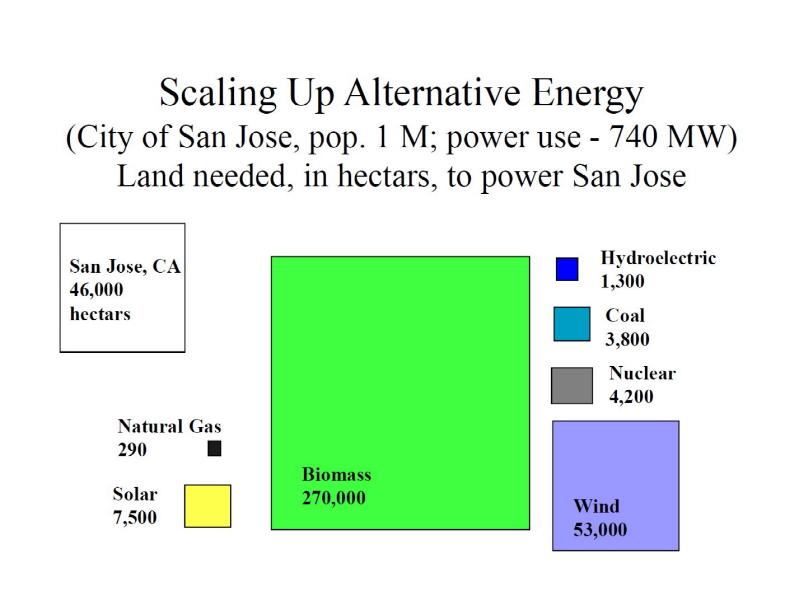
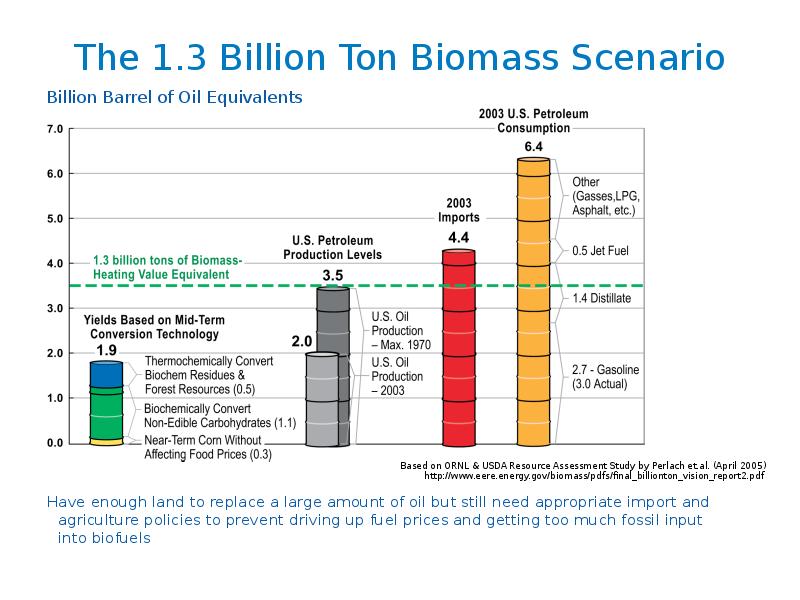
- 17. Is there enough land? If biomass competes with food crops for
- 19. The 1.3 Billion Ton Biomass Scenario
- 20. When will the fuels come? Corn ethanol and biodiesel are here
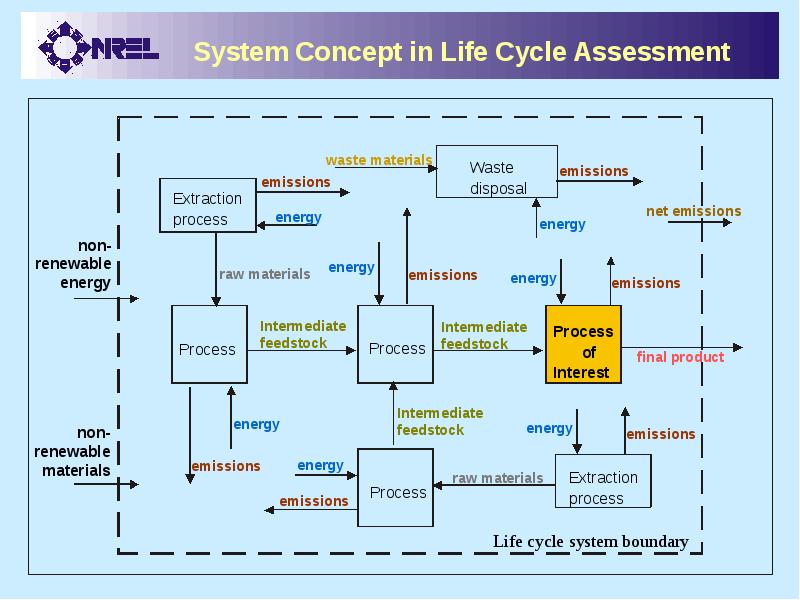
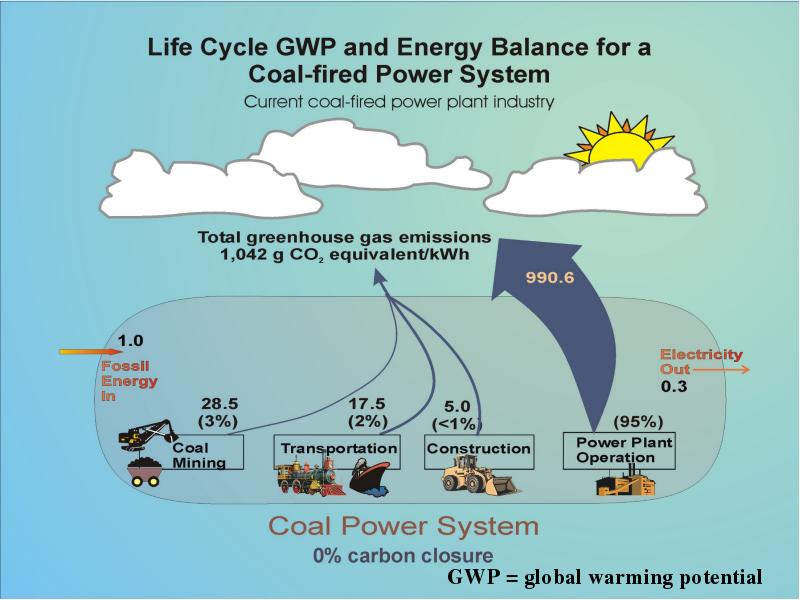
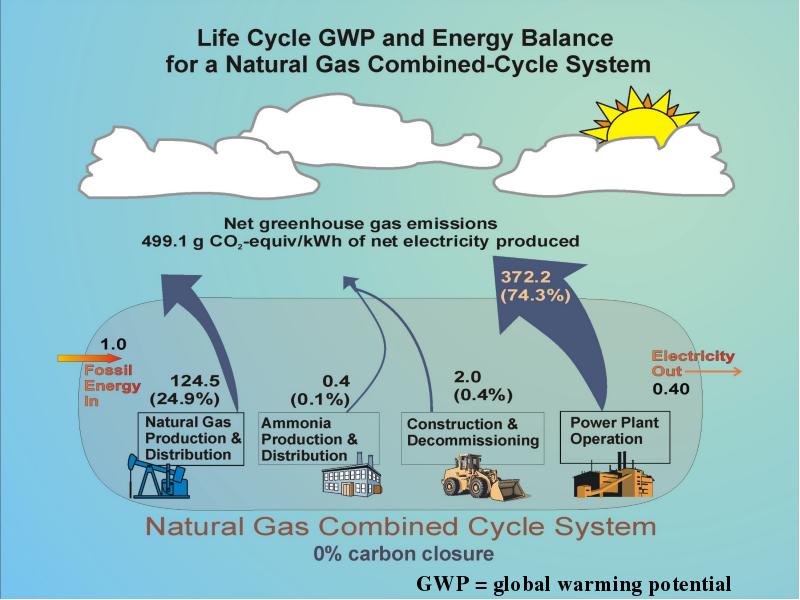
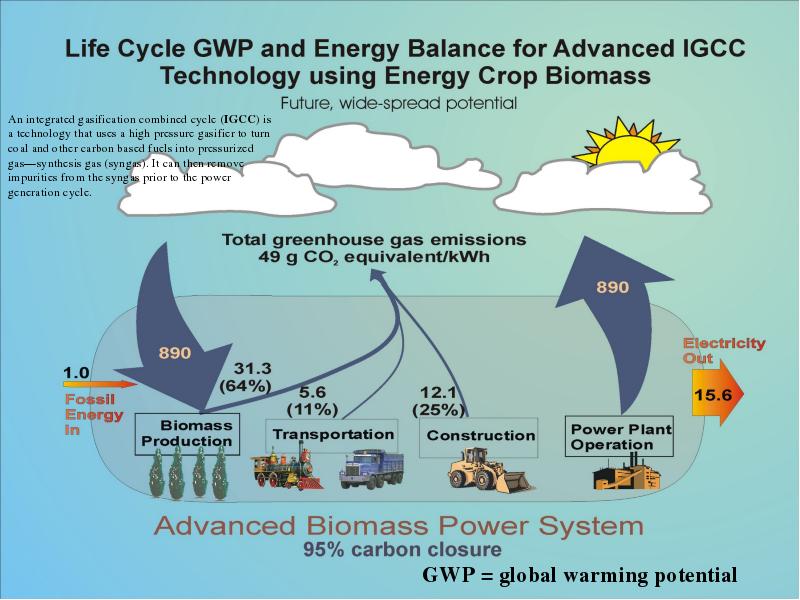
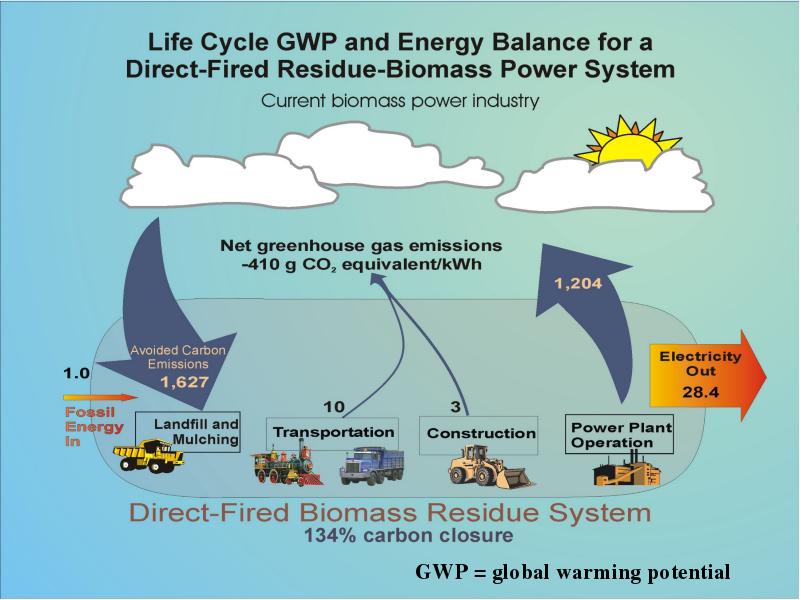
- 21. Life Cycle Assessment: Definition LCA Is a systematic analytical method Used
- 27. Summary Energy is the driver of everything we do in today’s
- 28. Скачать презентацию


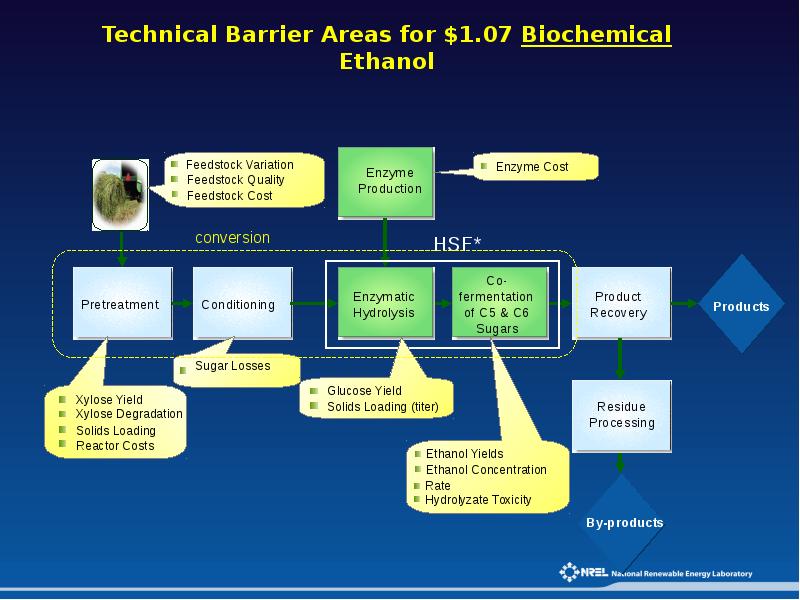
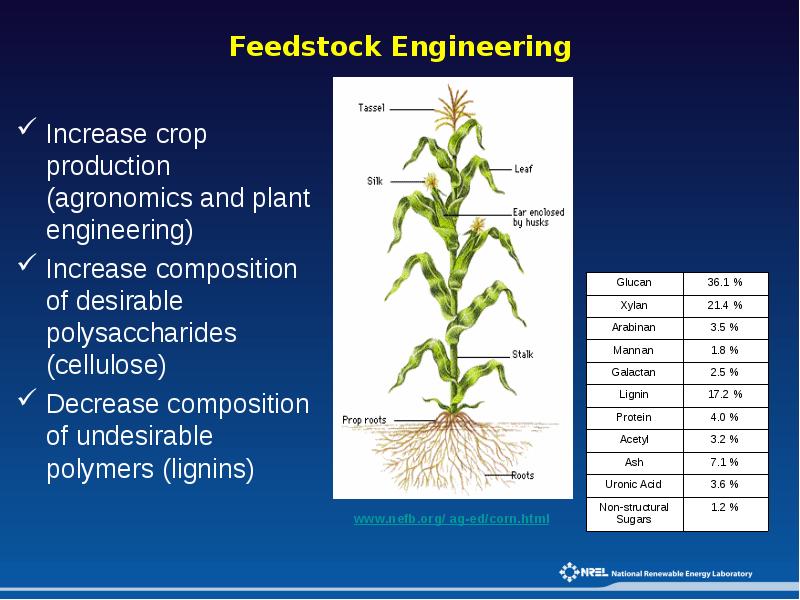




Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации