Economics of pricing and decision making. (Seminar 1) презентация
Содержание
- 2. The guessing game Each of you have to declare a number
- 3. `
- 4. The guessing game Discussion Bounded rationality People do not naturally use
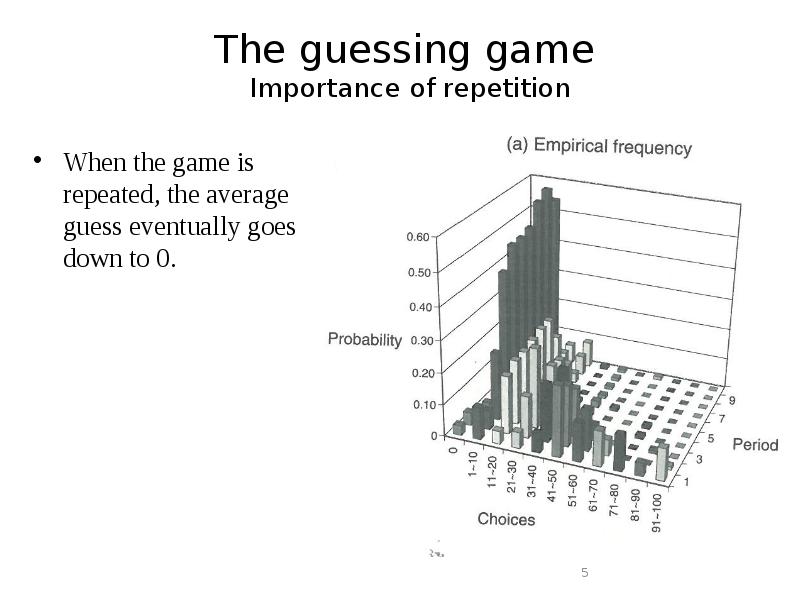
- 5. The guessing game Importance of repetition When the game is repeated,
- 6. Q1 V W X Y Z A 9,5 8,7 5,6 3,6 9,2 B 2,5 7,6 3,5 8,5 0,8 C 7,3 1,4 5,2 4,1 9,7 D 5,0 1,6 8,9 0,0 0,9 E 4,4 3,8 9,6 2,9 1,2
- 7. Q1 V W X Y Z A 9,5 8,7 5,6 3,6 9,2 B 2,5 7,6 3,5 8,5 0,8 C 7,3 1,4 5,2 4,1 9,7 D 5,0 1,6 8,9 0,0 0,9 E 4,4 3,8 9,6 2,9 1,2
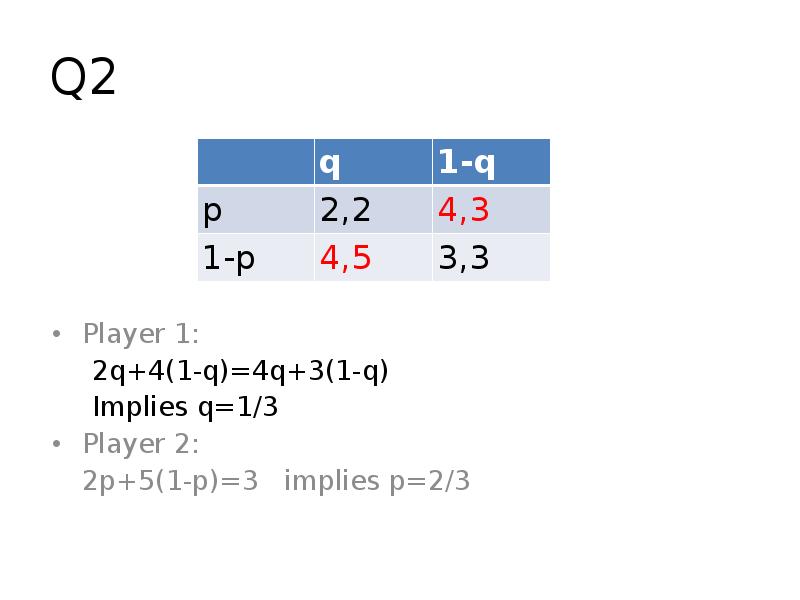
- 8. Q2 Player 1: 2q+4(1-q)=4q+3(1-q) Implies q=1/3 Player 2: 2p+5(1-p)=3 implies p=2/3
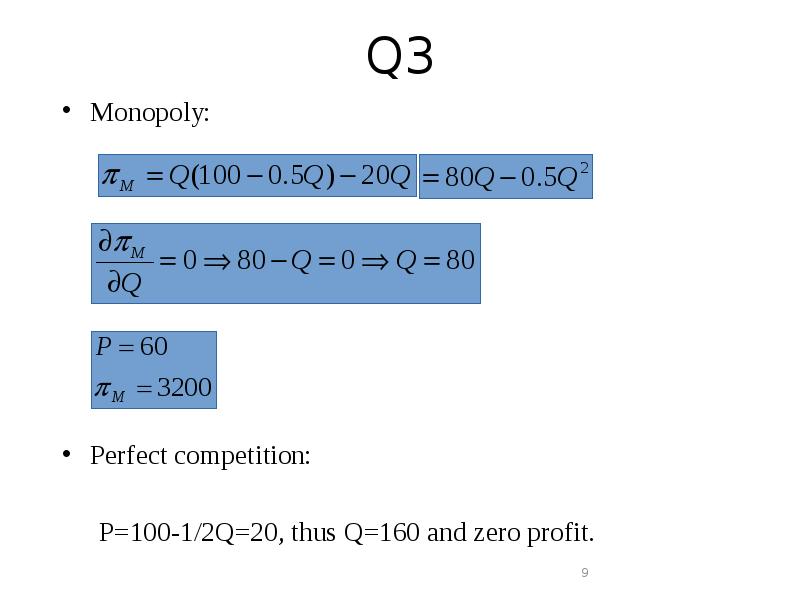
- 9. Q3 Monopoly: Perfect competition: P=100-1/2Q=20, thus Q=160 and zero profit.
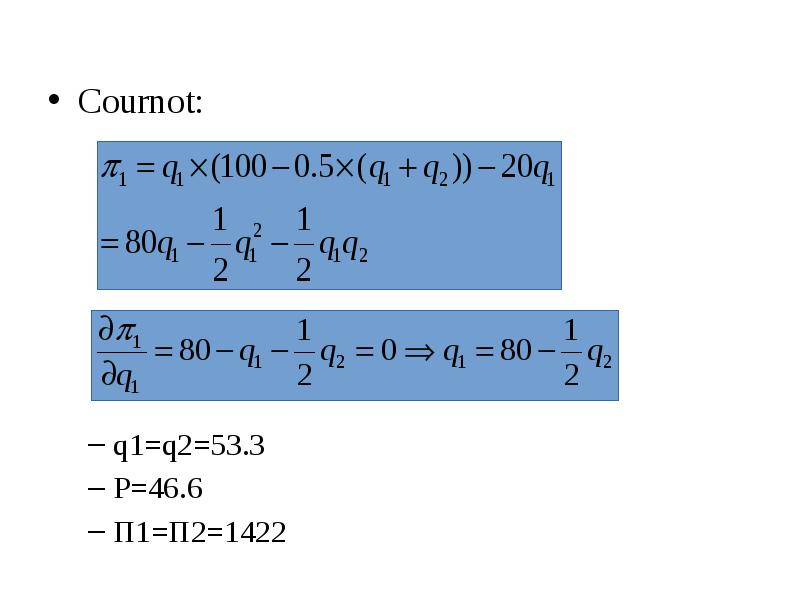
- 10. Cournot: Cournot: q1=q2=53.3 P=46.6 Π1=Π2=1422
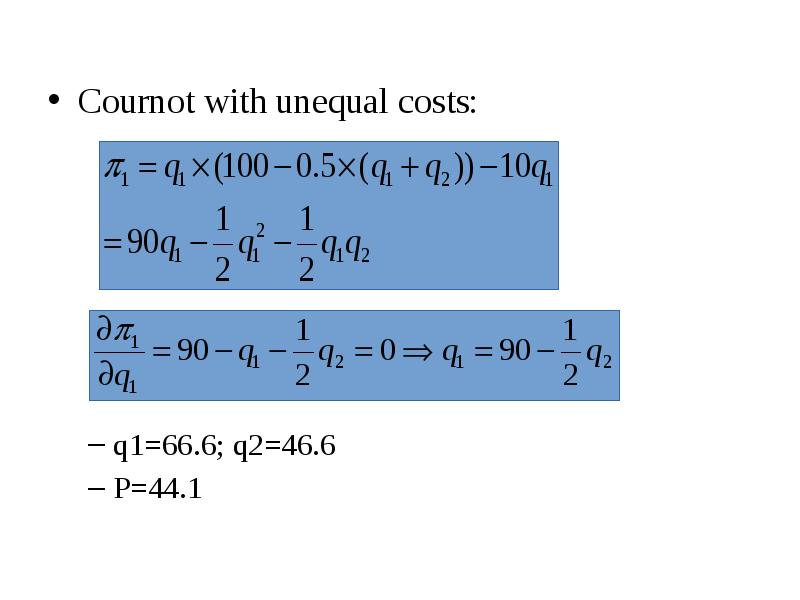
- 11. Cournot with unequal costs: Cournot with unequal costs: q1=66.6; q2=46.6 P=44.1
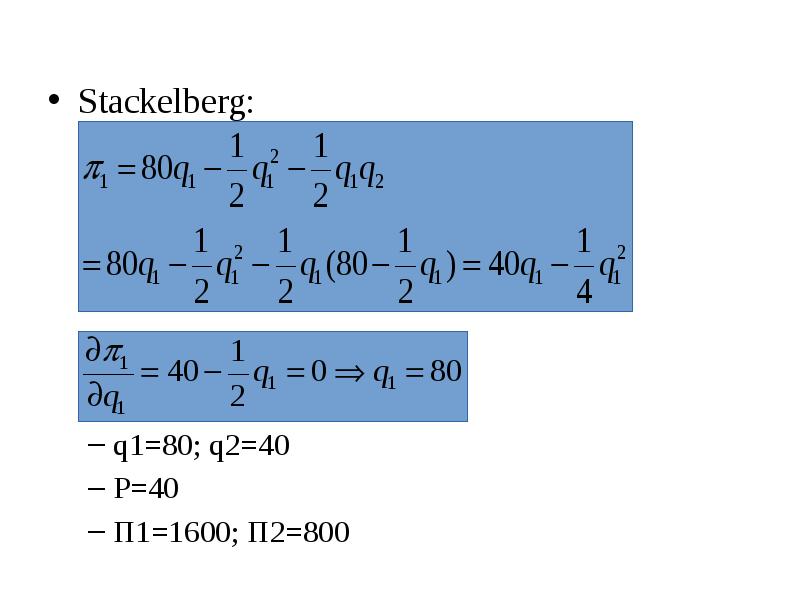
- 12. Stackelberg: Stackelberg: q1=80; q2=40 P=40 Π1=1600; Π2=800
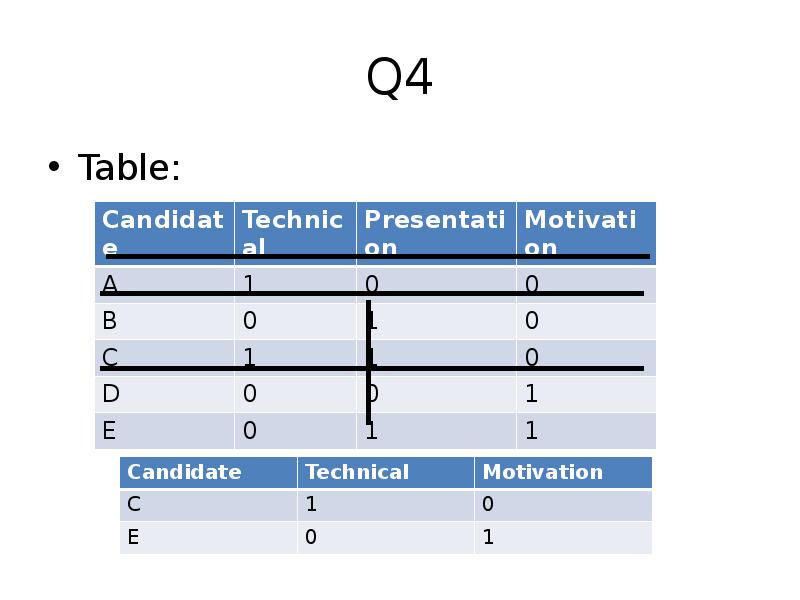
- 13. Q4 Table:
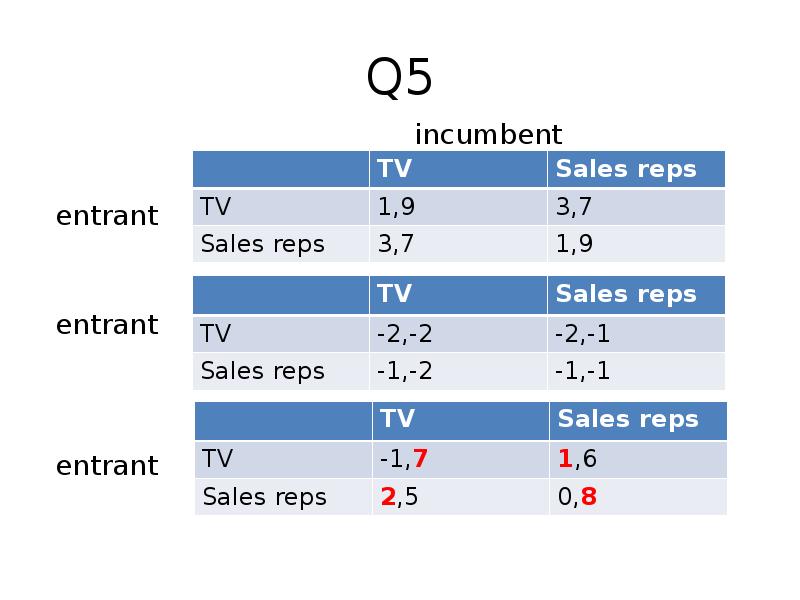
- 14. Q5
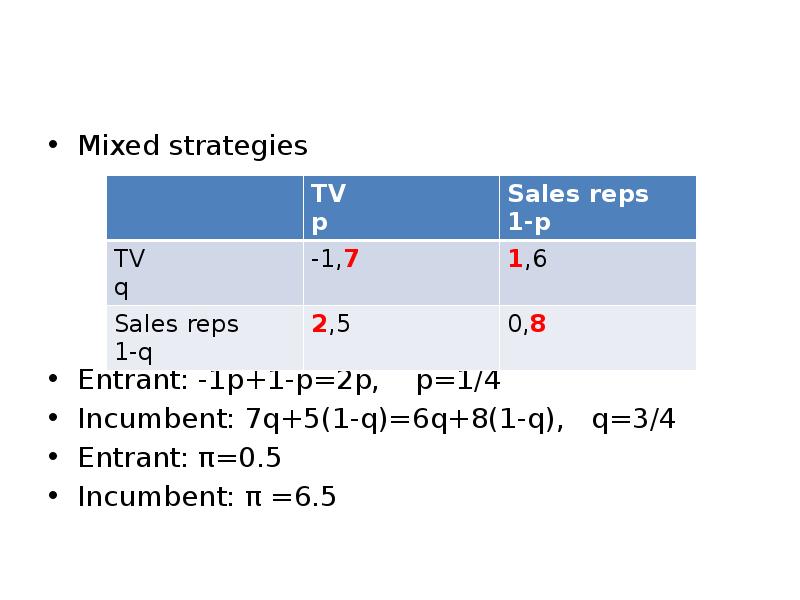
- 15. Mixed strategies Mixed strategies Entrant: -1p+1-p=2p, p=1/4 Incumbent: 7q+5(1-q)=6q+8(1-q), q=3/4 Entrant:
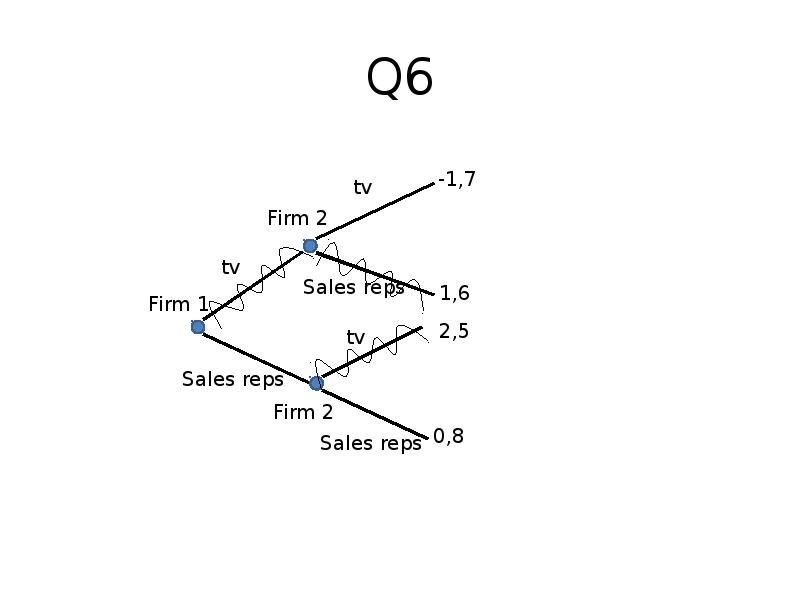
- 16. Q6
- 17. Скачать презентацию




Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Economics of pricing and decision making. (Seminar 1) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации