Energy and power, solar astronomy. (Lecture 4) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Energy Units - Calorie Calorie (cal) = heat to increase by
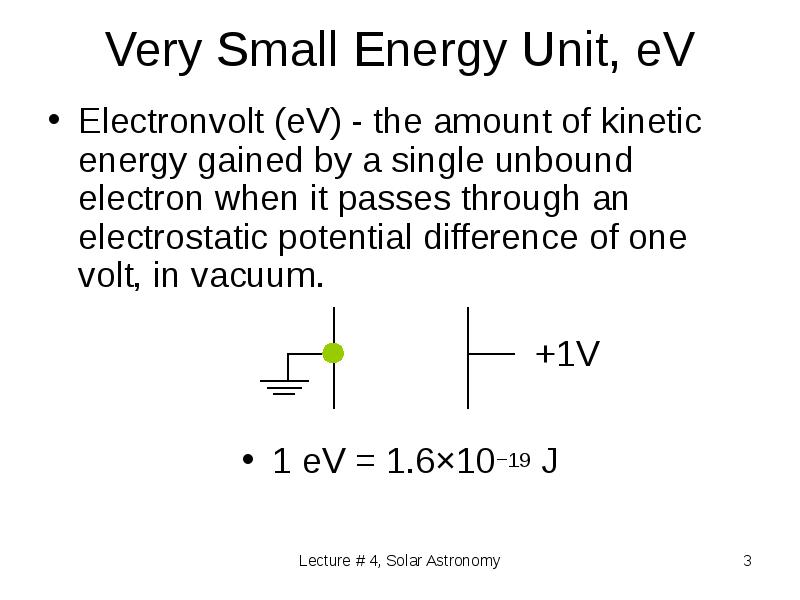
- 3. Very Small Energy Unit, eV Electronvolt (eV) - the amount of
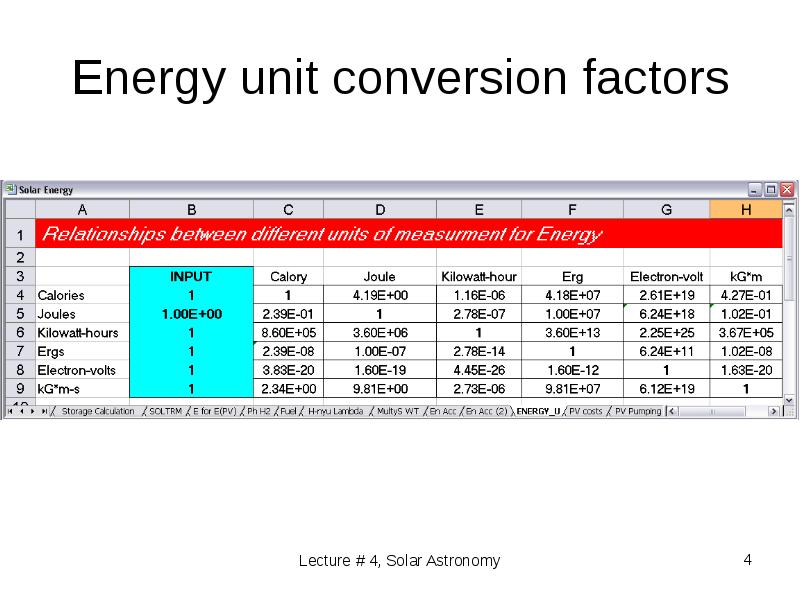
- 4. Energy unit conversion factors
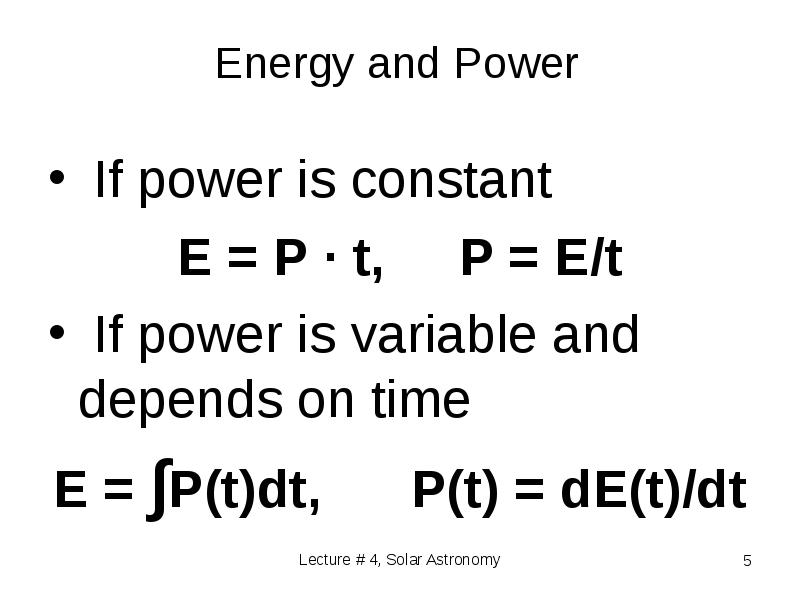
- 5. Energy and Power If power is constant E = P
- 6. Power Units Watt (W) = using one J in one second.
- 7. Power vs. Energy Thus, power is the rate of the energy
- 8. Solar Energy The SUN: Fusion in the sun – the process
- 9. The light: particle, wave Particle and wave Light speed, c =
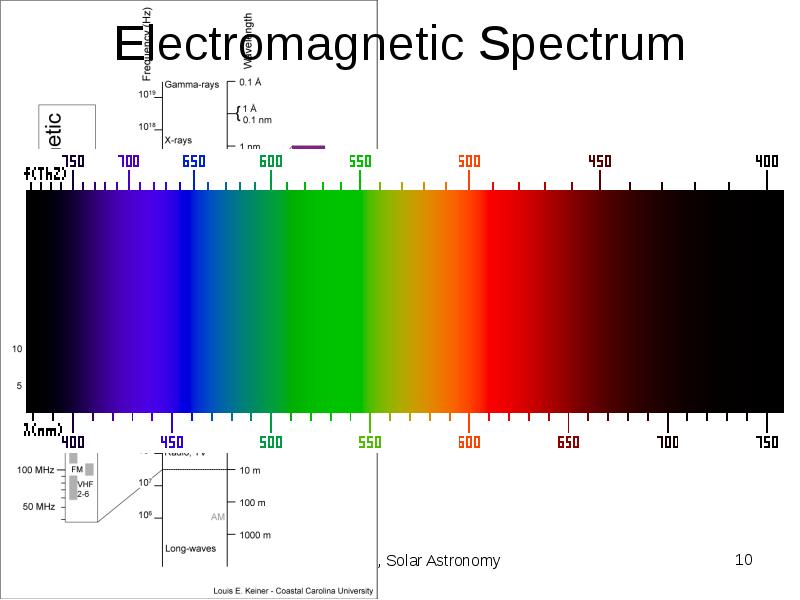
- 10. Electromagnetic Spectrum
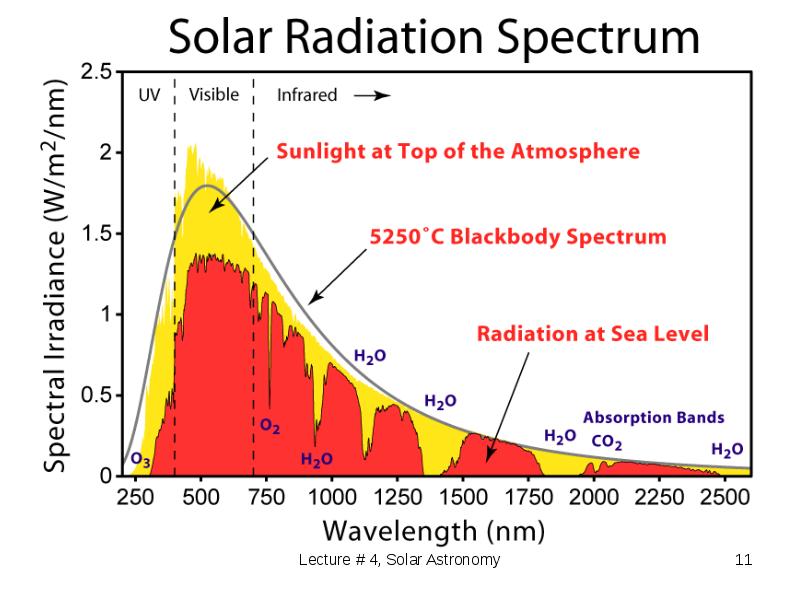
- 11. Sun Spectrum
- 12. The Sun Sun has a capacity of 3.86×1026 W 3.86×108 EJ/s
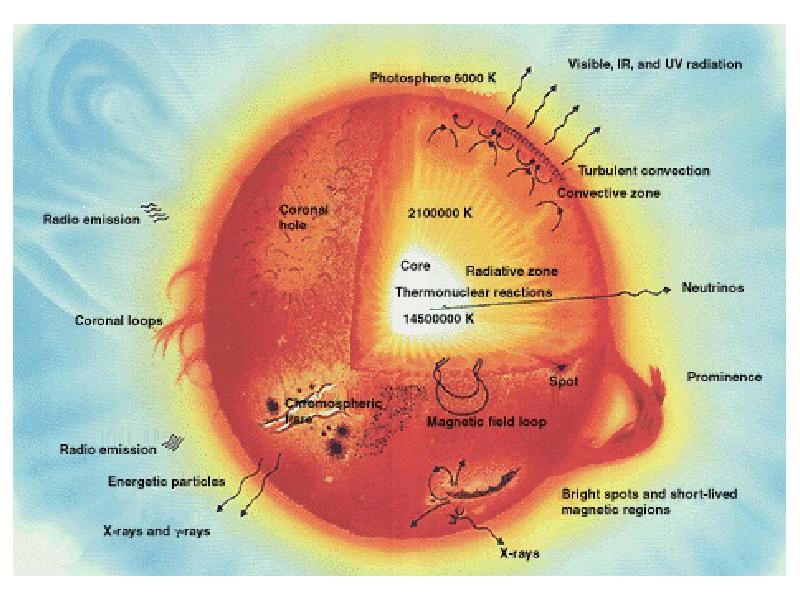
- 13. How this energy is generated?
- 14. How this energy is generated? About 74% of the Sun's mass
- 15. How this energy is generated? The Sun has a surface temperature
- 16. How this energy is generated? The Sun diameter: 1.4 106 km
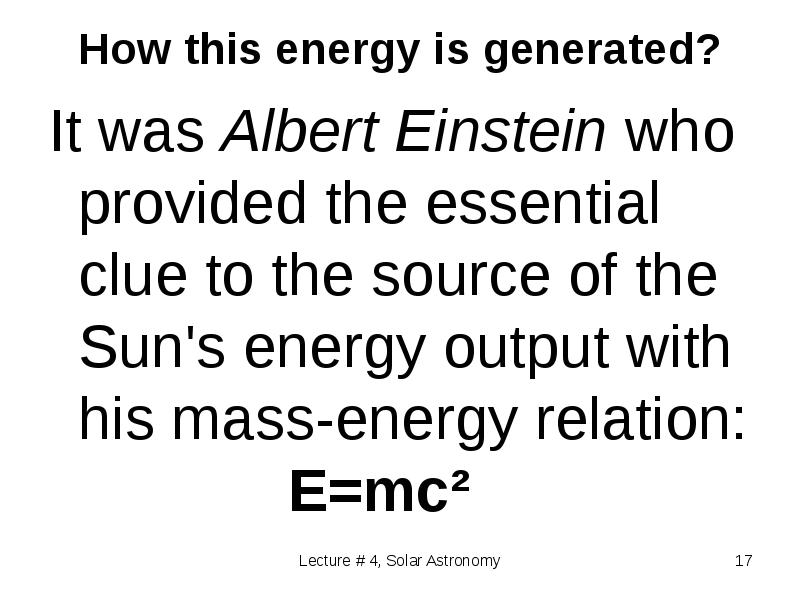
- 17. How this energy is generated? It was Albert Einstein who provided
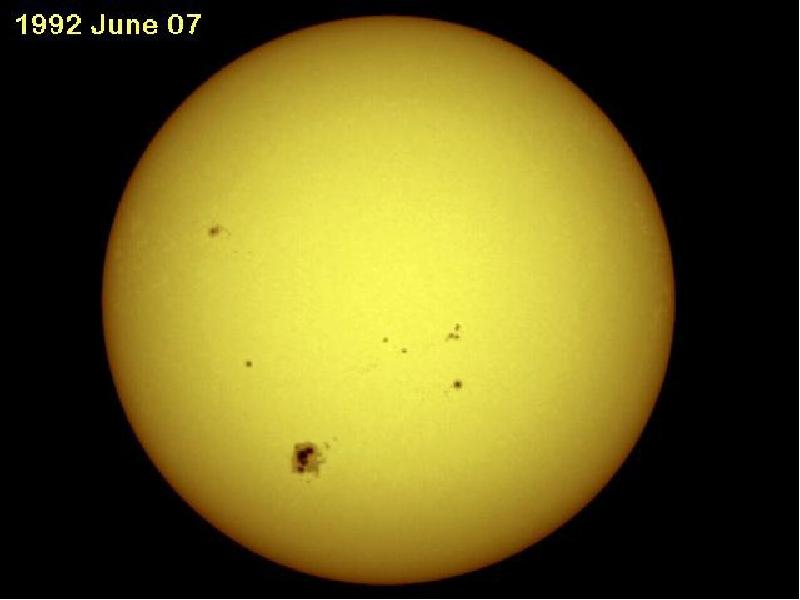
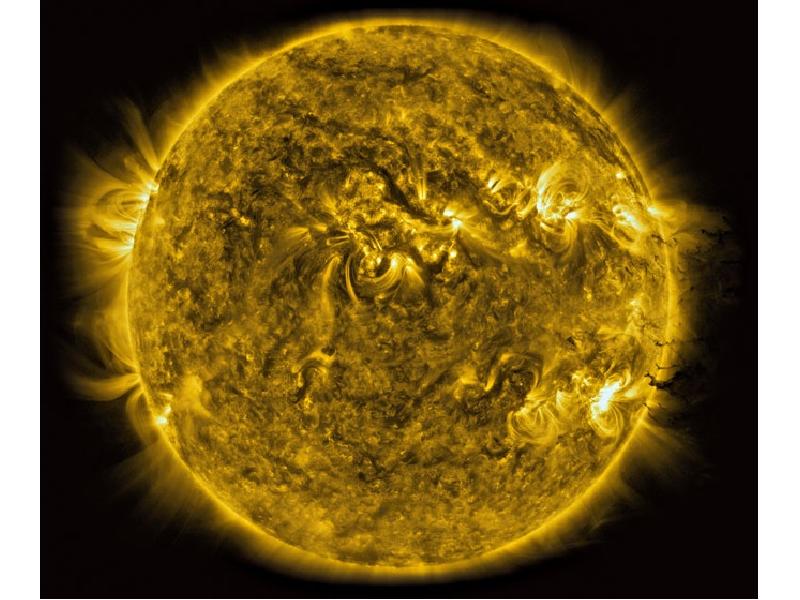
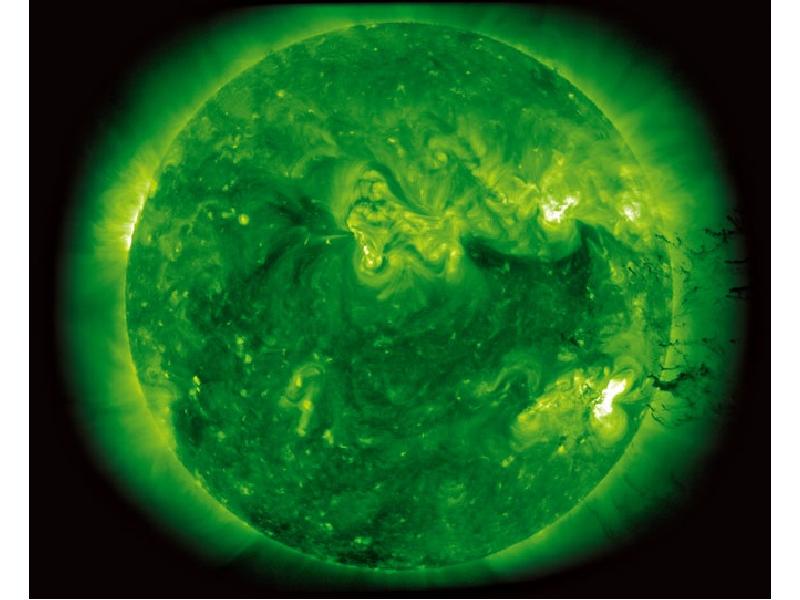
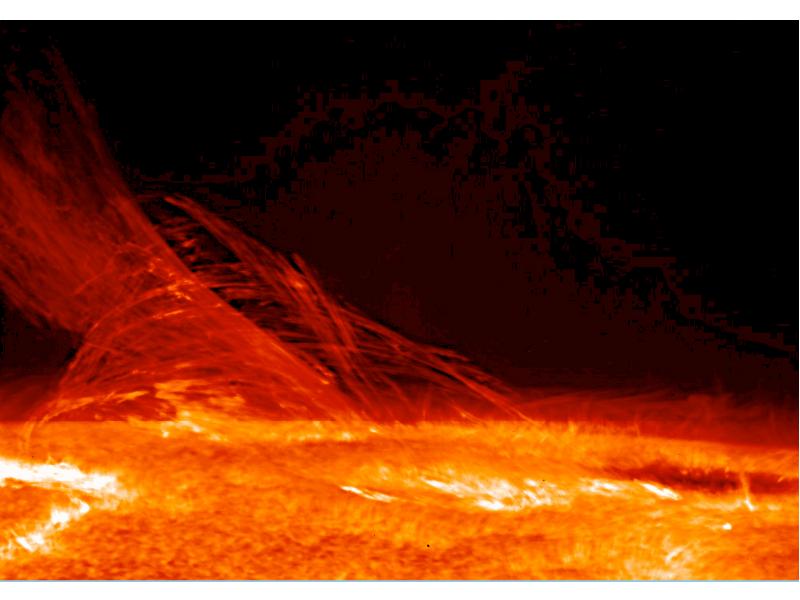
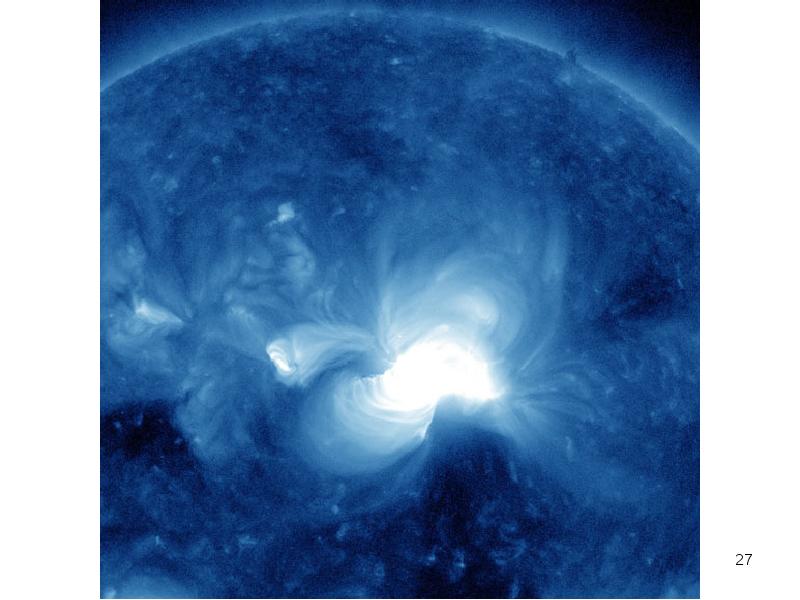
- 20. The Sun
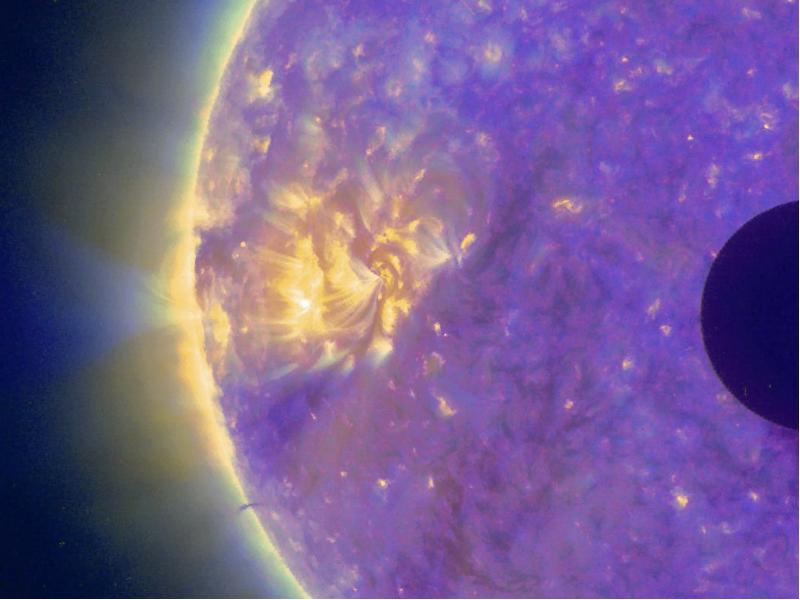
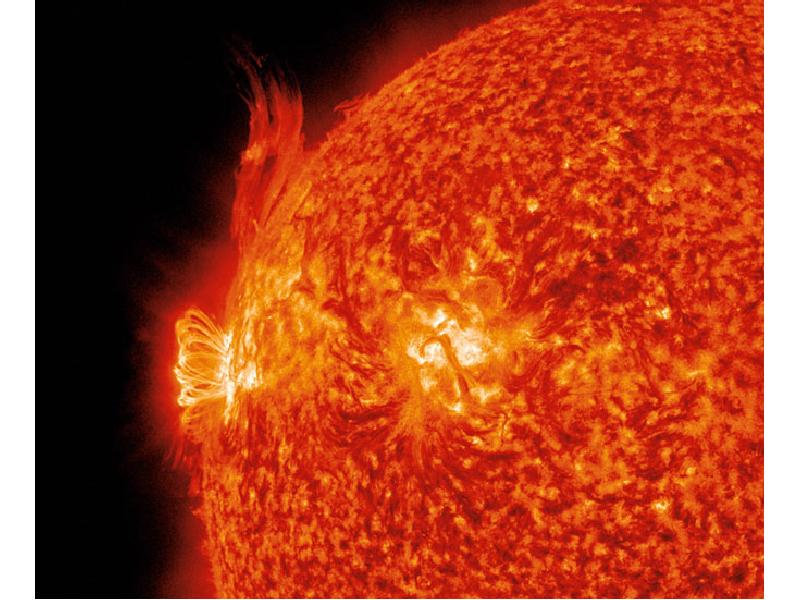
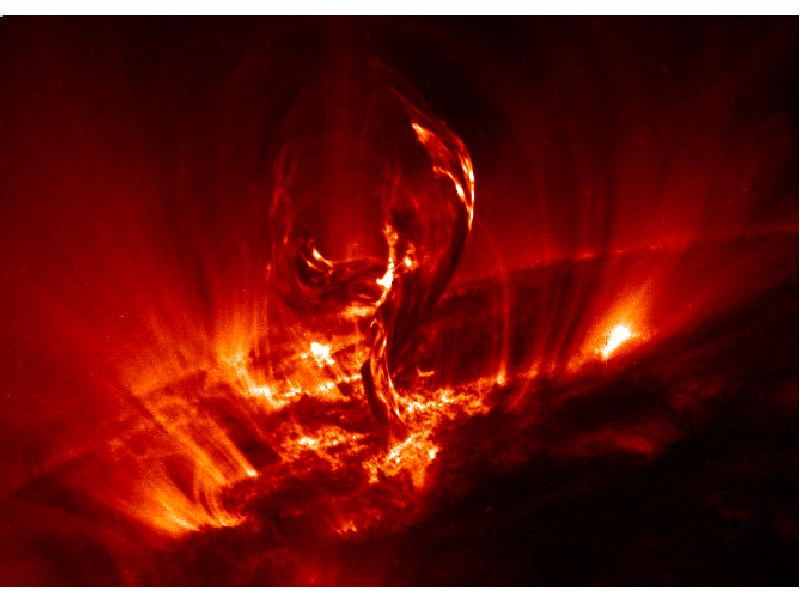
- 24. NASA caption: Giant magnetic loops dance on the sun’s horizon in
- 28. Sun surface videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipvfwPqh3V4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0WW1HN0iG0M https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lpzCSZ7Eerc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nmDZhQAIeXM
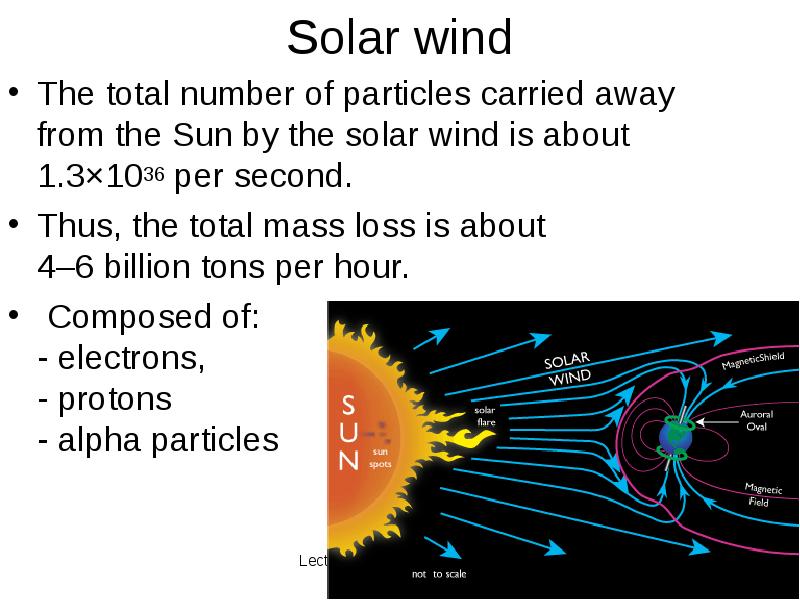
- 29. Solar wind The total number of particles carried away from the
- 30. Elementary particles flow from Sun – Solar Wind http://www.independent.co.uk/travel/europe/watch-this-beautiful-timelapse-of-the-northern-lights-over-norway-9735690.html http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-28690559 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sBWPCvdv8Bk
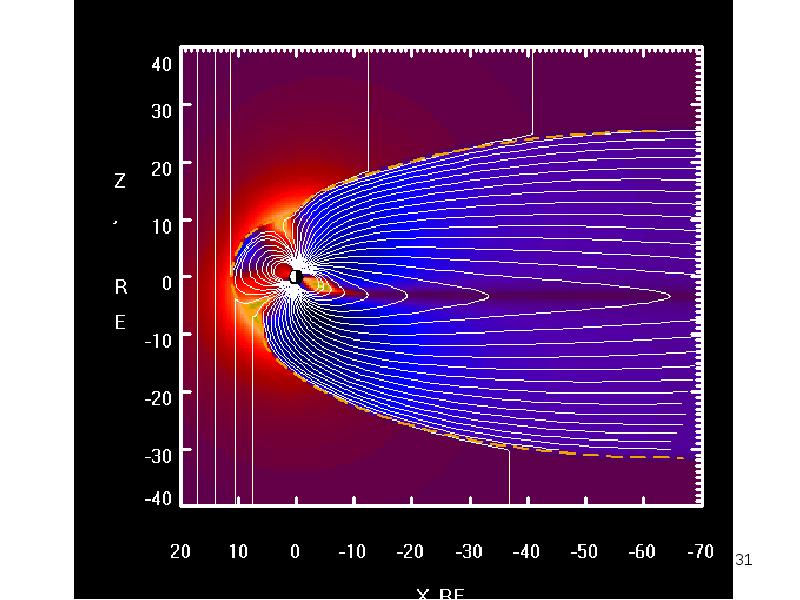
- 31. Solar Wind
- 32. Aurora Borealis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hsMW7zbzsUs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vdb9IndsSXk https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pjgvGiEHlNs
- 33. How this energy is generated? In 1920 Sir Arthur Eddington proposed
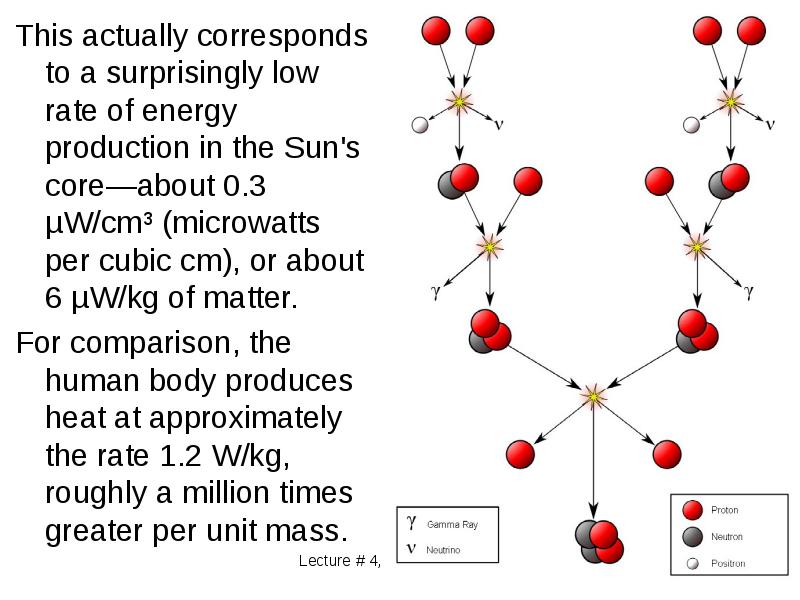
- 34. This actually corresponds to a surprisingly low rate of energy production
- 36. How this energy is generated?
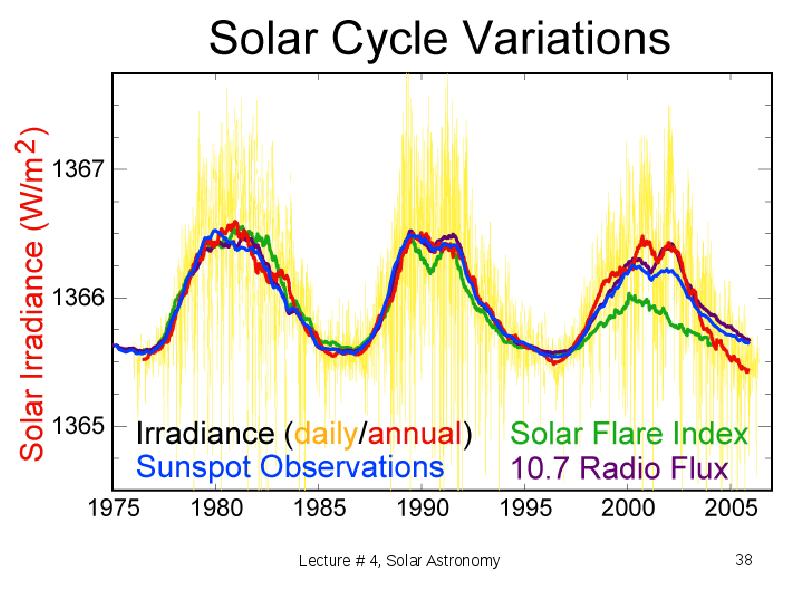
- 37. 1.5 The future of energy resources Solar Constant = 1366 W/sq.m.
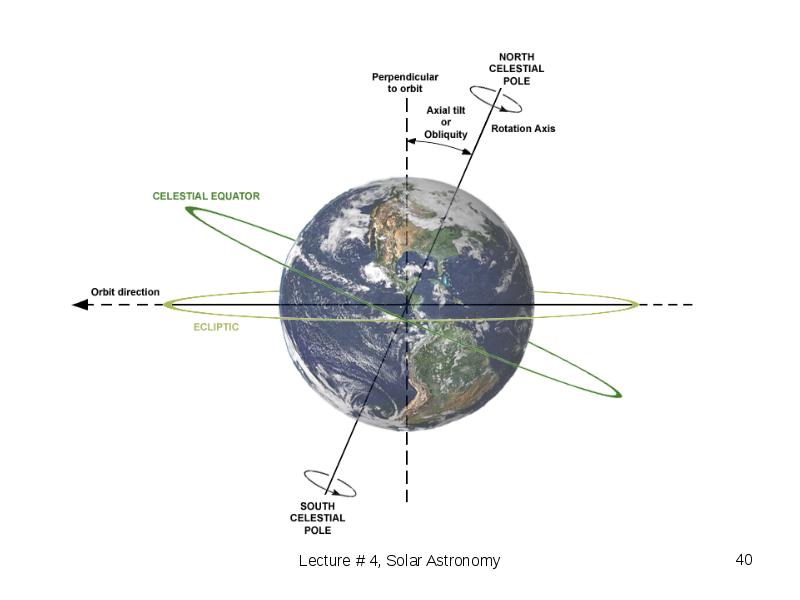
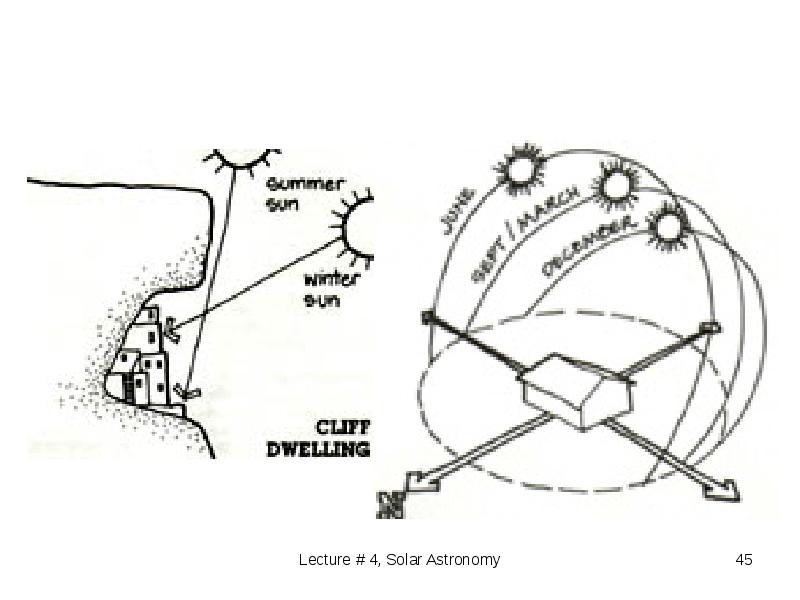
- 39. Earth's rotation Earth's rotation tilts about 23.5 degrees on its
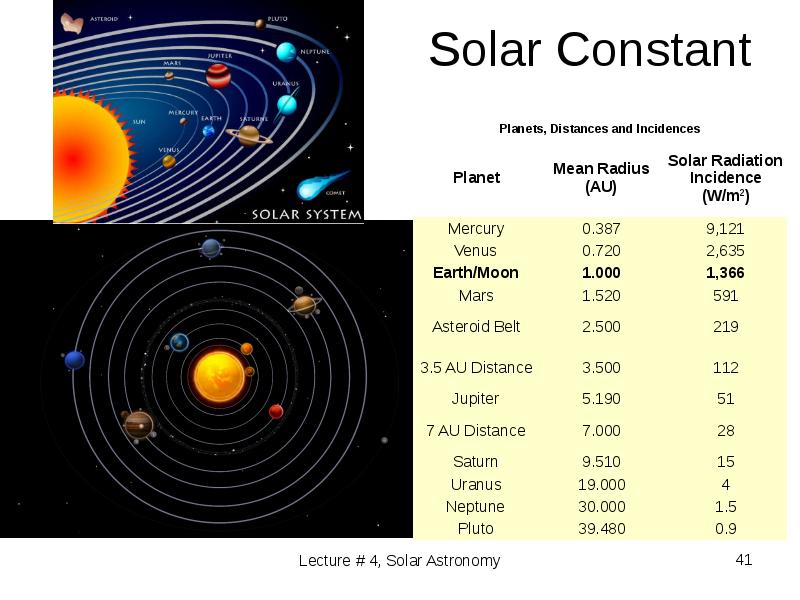
- 41. Solar Constant
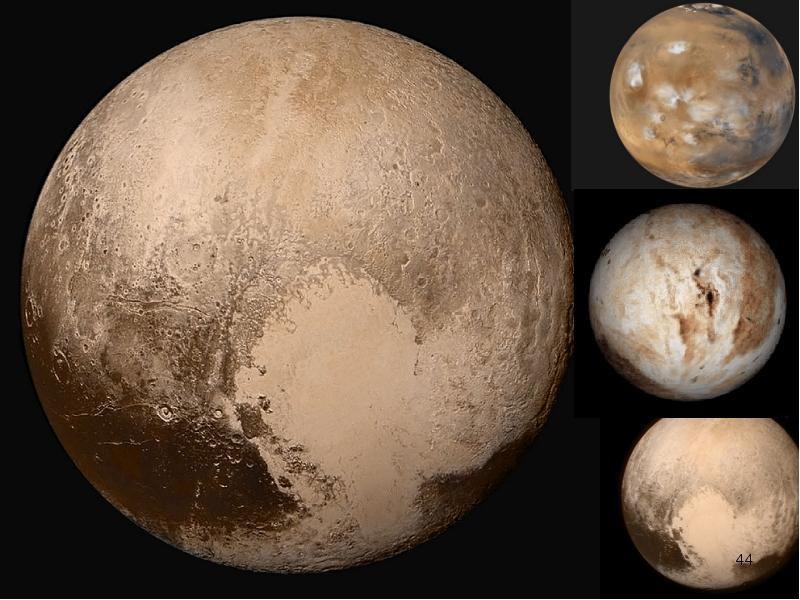
- 42. Now: go to the article http://www.wired.com/2015/07/pluto-new-horizons-2/
- 44. Solar radiation bouncing atmosphere the theoretical daily-average insolation at the top
- 46. Airmass In astronomy, airmass is the optical path length through Earth's
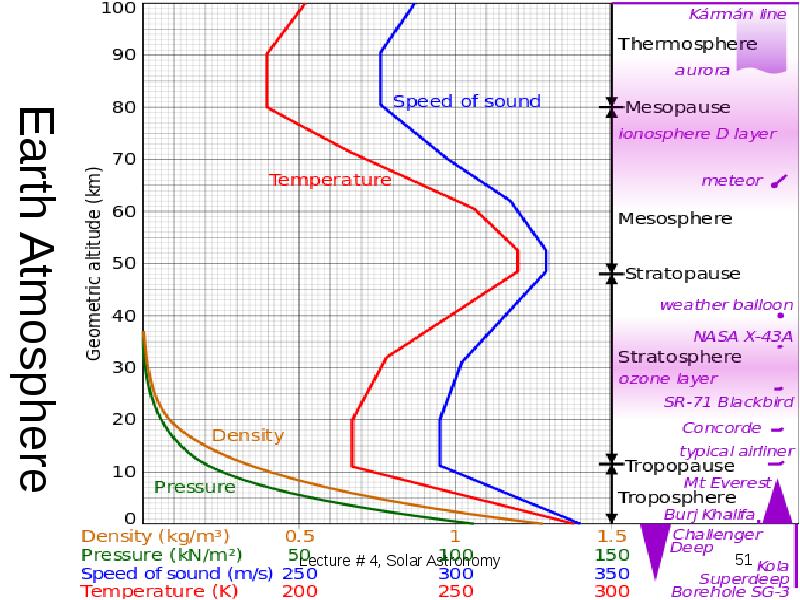
- 47. Earth Atmosphere
- 48. Rayleigh scattering
- 49. Airmass “Airmass” normally indicates relative airmass, the path length relative to
- 50. Airmass Atmosphere height = 8.5 ÷ 11 km. Earth's mean radius
- 51. Earth Atmosphere
- 52. Numbers to remember Solar constant = 1366W/m2 Attenuation at AM1
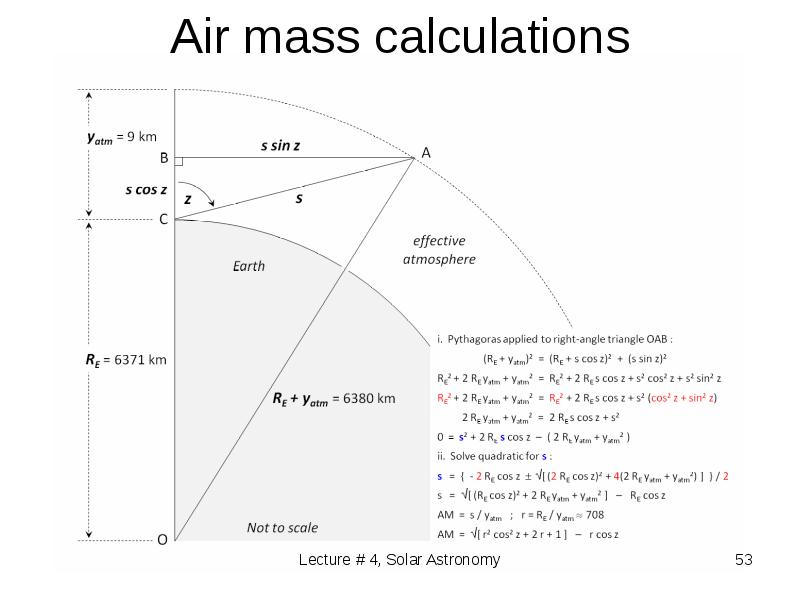
- 53. Air mass calculations
- 54. Notion of the Cost per peak watt installed “Peak Watt” =
- 55. Скачать презентацию































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Energy and power, solar astronomy. (Lecture 4) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации