Geographical investigations – student guide: extreme weather презентация
Содержание
- 2. Overview Overview Requirements of the specification What is extreme weather? Investigating
- 3. 1. Overview Unit 2 has four components, but you are only
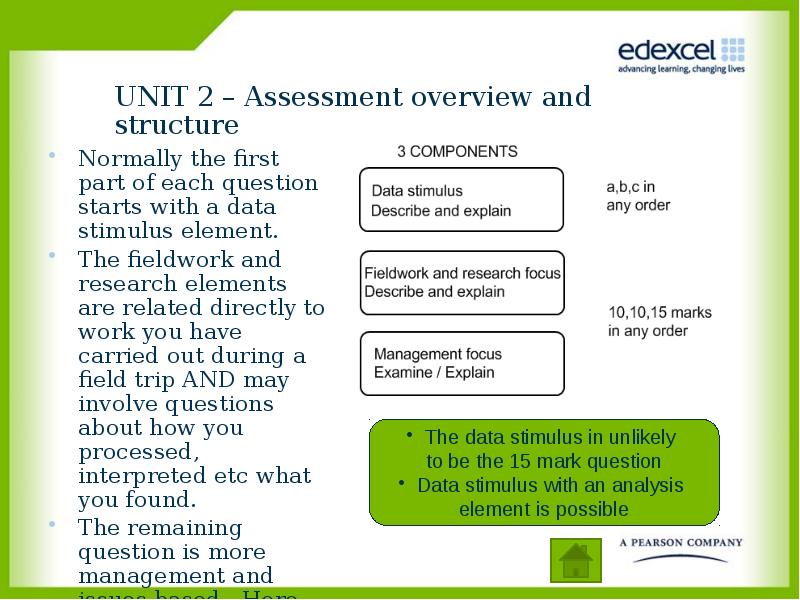
- 4. UNIT 2 – Assessment overview and structure Normally the first part
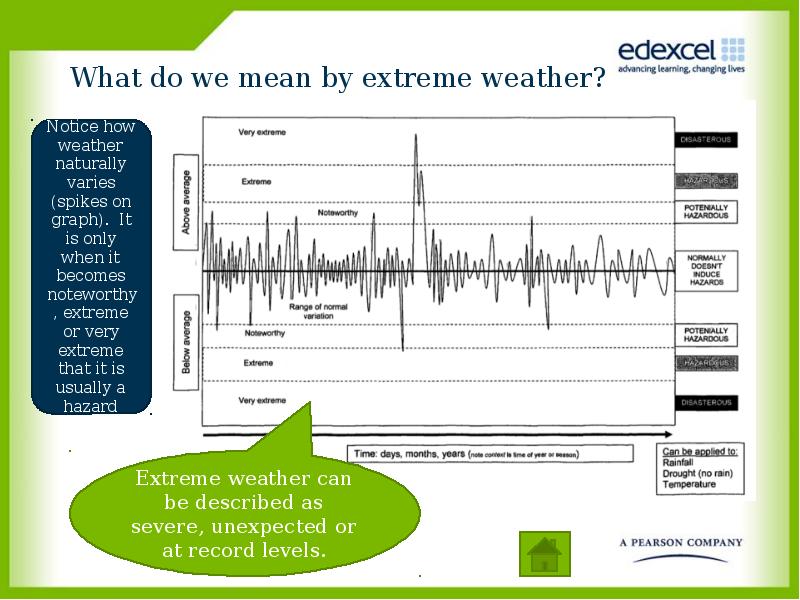
- 5. What do we mean by extreme weather?
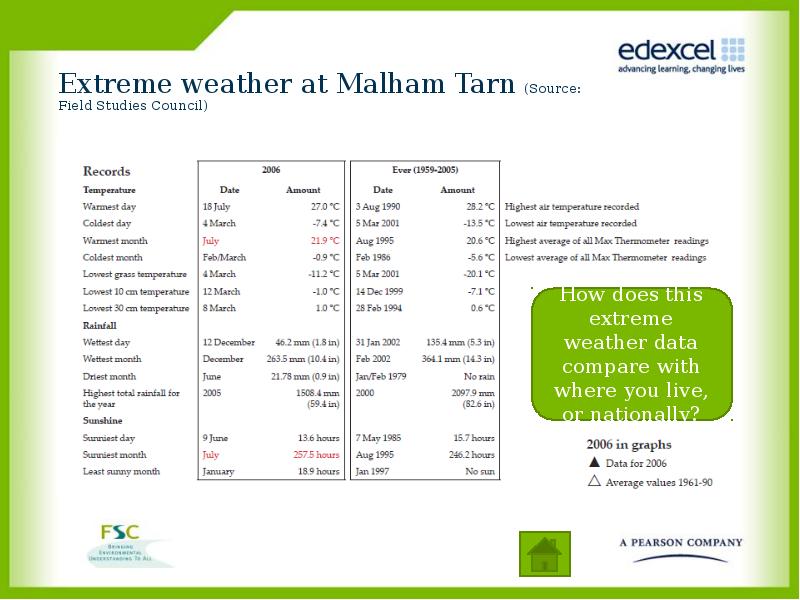
- 6. Extreme weather at Malham Tarn (Source: Field Studies Council)
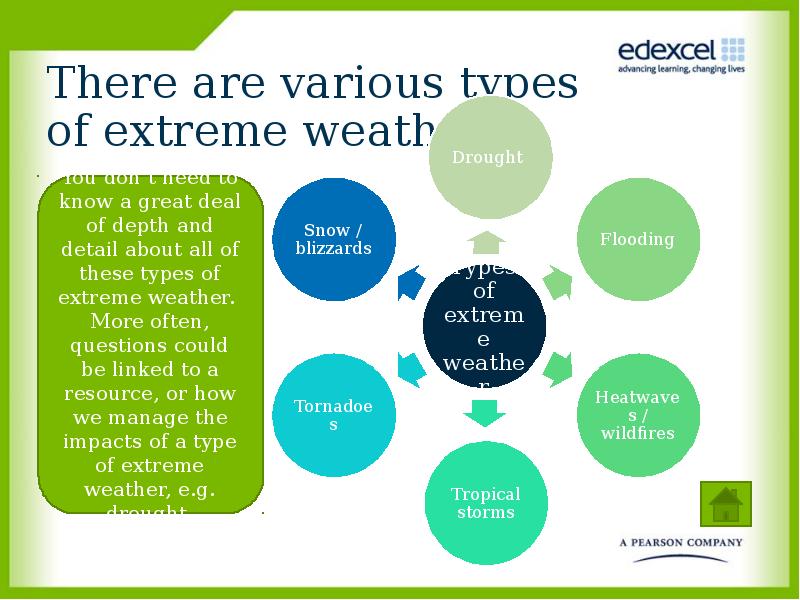
- 7. There are various types of extreme weather
- 8. How can extreme weather events be classified? An immediate disastrous
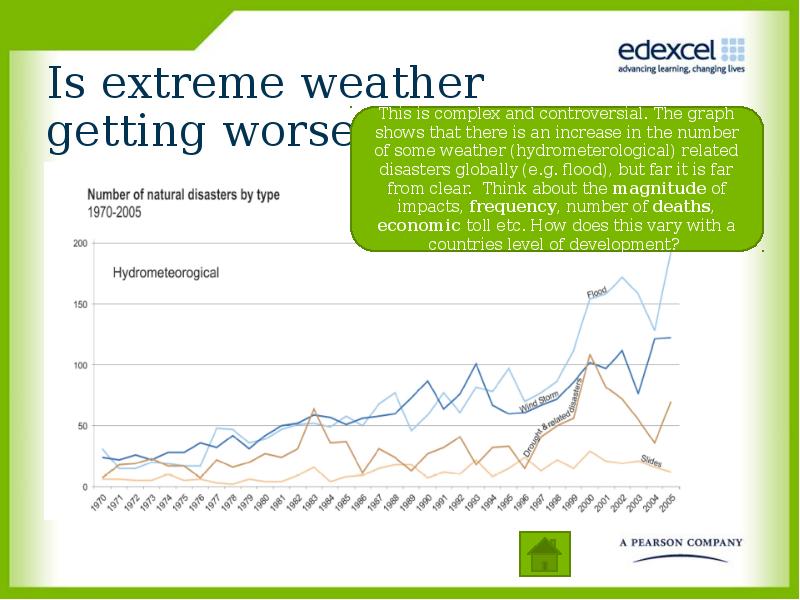
- 9. Is extreme weather getting worse?
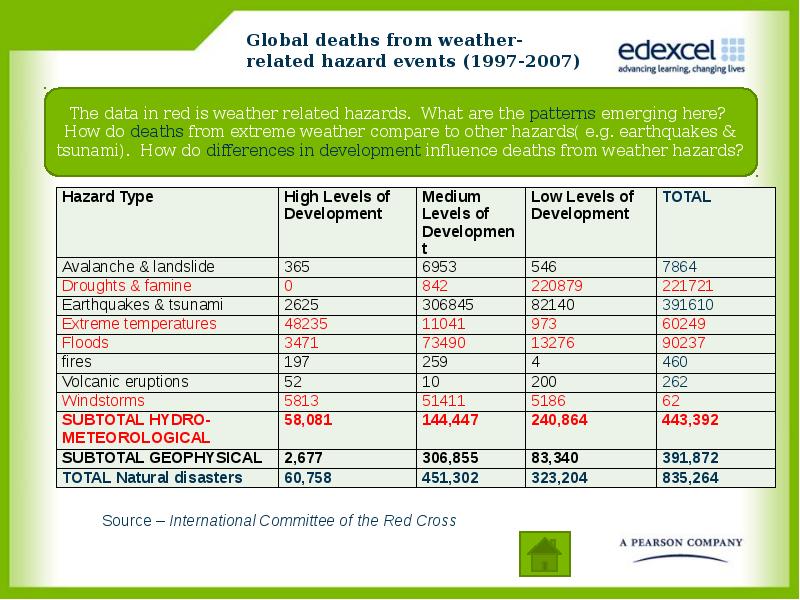
- 10. Global deaths from weather-related hazard events (1997-2007)
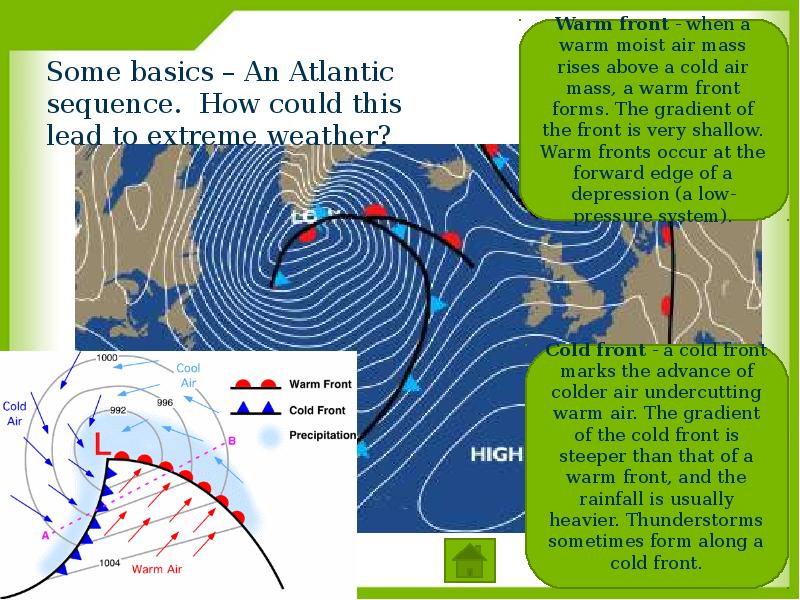
- 11. Some basics – An Atlantic sequence. How could this lead to
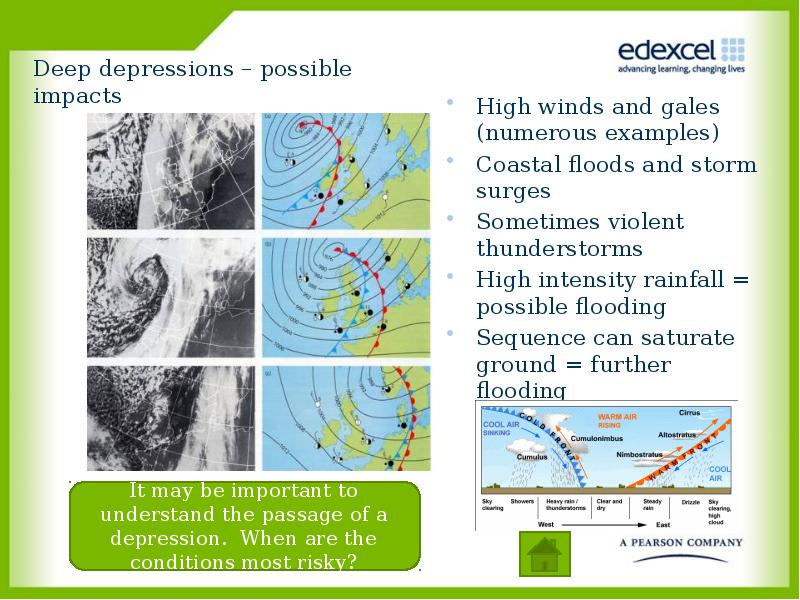
- 12. Deep depressions – possible impacts High winds and gales (numerous examples)
- 13. Winter and summer anticyclones Winter smog forms as pollutants are trapped
- 14. Risks associated with hurricanes Hurricanes are predictable in terms of their
- 15. There are other types of extreme weather that need to be
- 16. Thinking about fieldwork and research
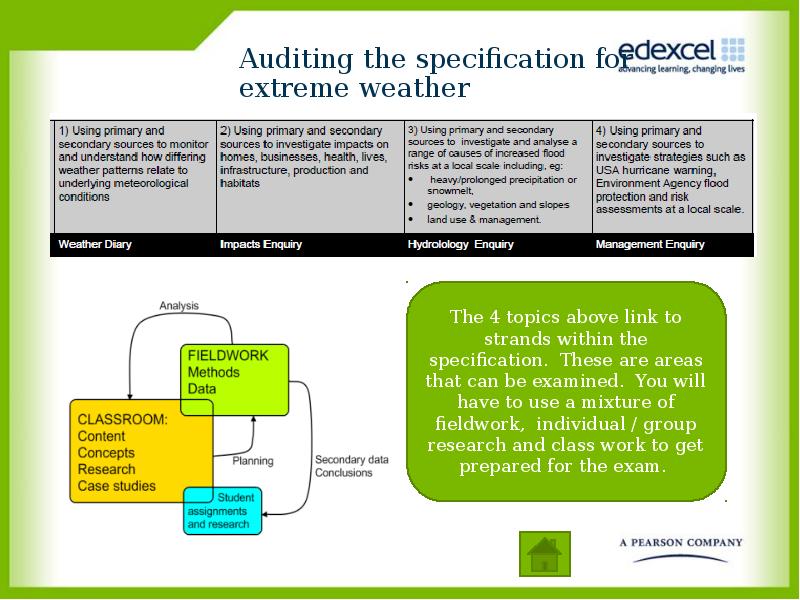
- 17. Auditing the specification for extreme weather
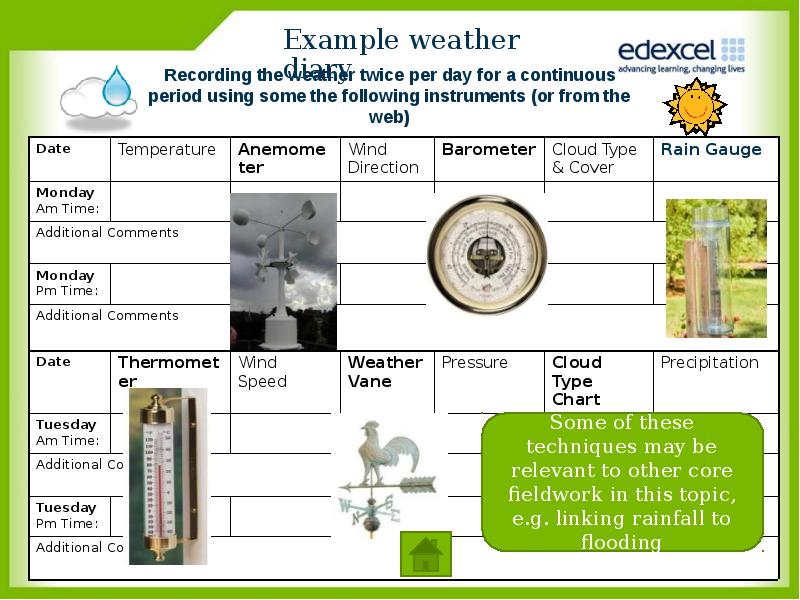
- 18. How show I go about a weather diary?
- 20. Скачать презентацию









Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Geographical investigations – student guide: extreme weather можно ниже:
Похожие презентации