Hypoxia. (Subject 7) презентация
Содержание
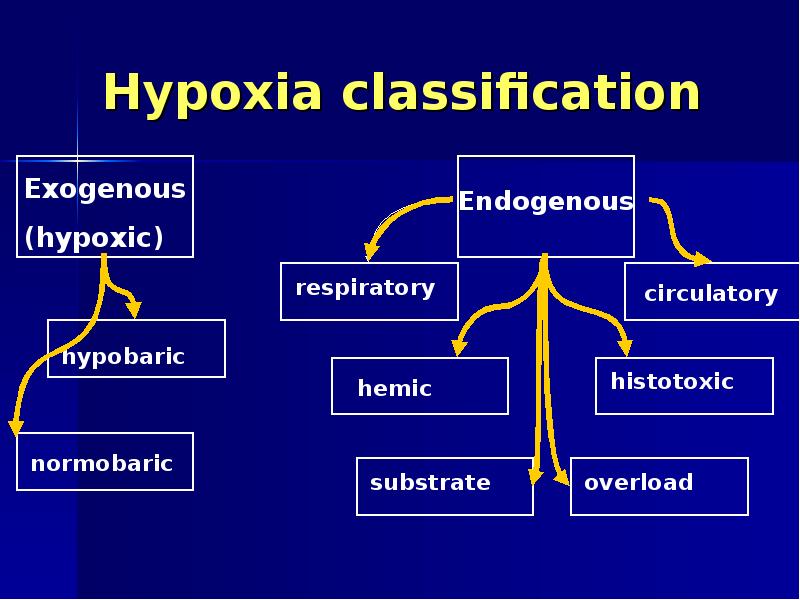
- 2. Hypoxia classification
- 3. Hypoxia classification Due to time of development Fulminant (immediate) –several seconds
- 4. Hypoxia classification Due to prevalence of clinical symptoms: local and general.
- 5. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia hypobaric type atmospheric pressure+ partial oxygen pressure
- 6. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia normobaric type Normal atmospheric pressure + oxygen %
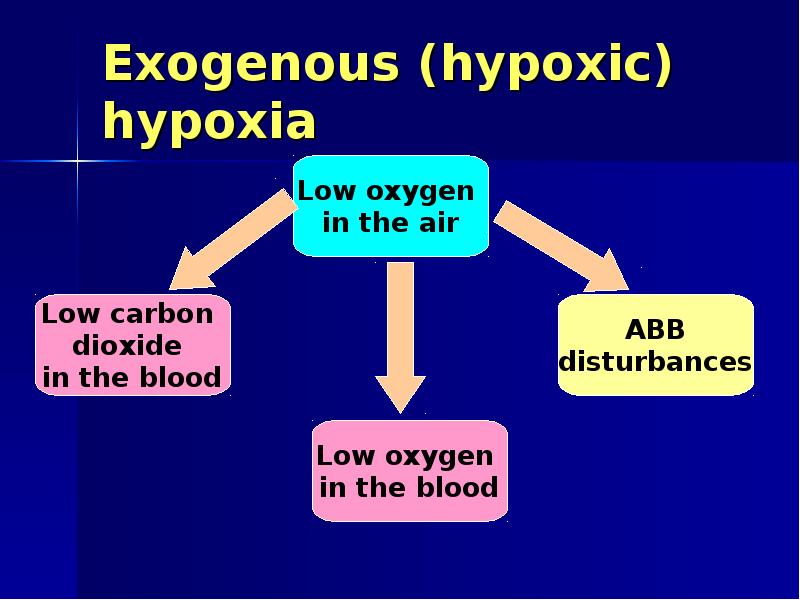
- 7. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
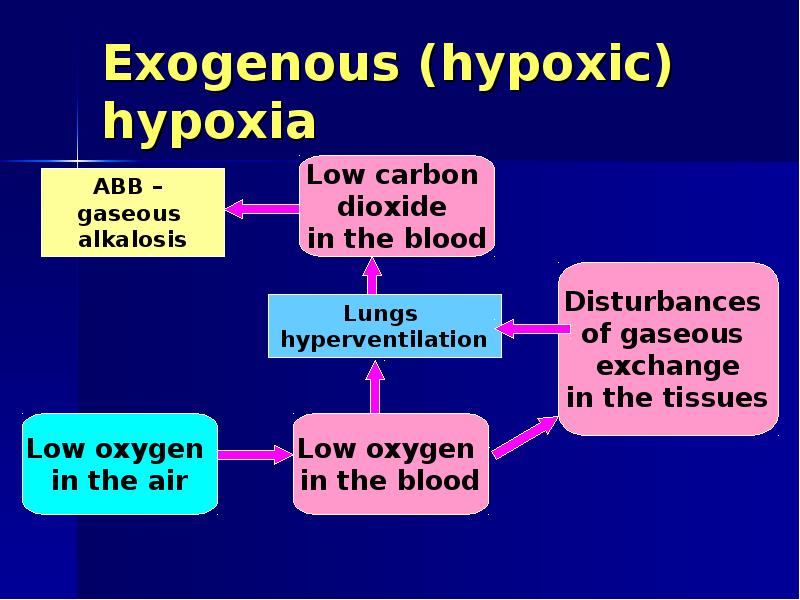
- 8. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
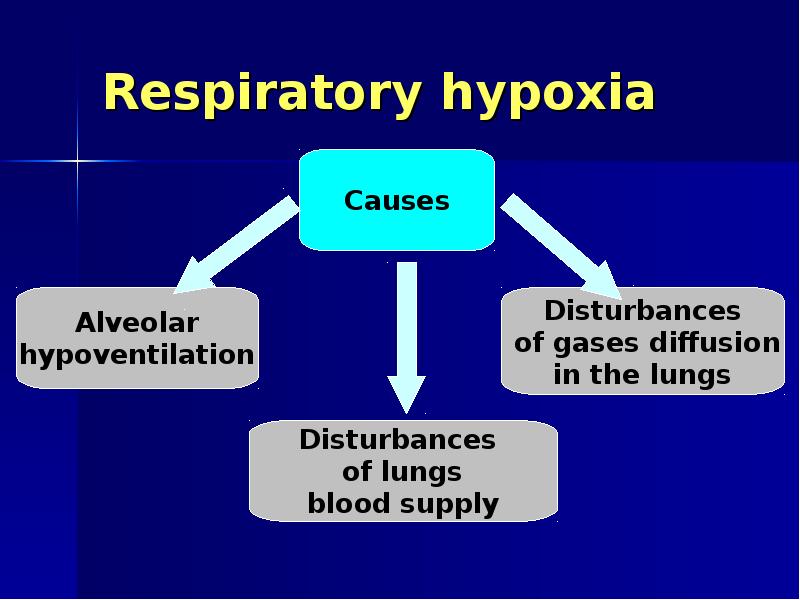
- 9. Respiratory hypoxia
- 10. Respiratory hypoxia Alveolar hypoventilation reasons: Obstructive violations (lung edema, tumors or
- 11. Respiratory hypoxia Disturbances of lungs blood supply - heart failure, decreased
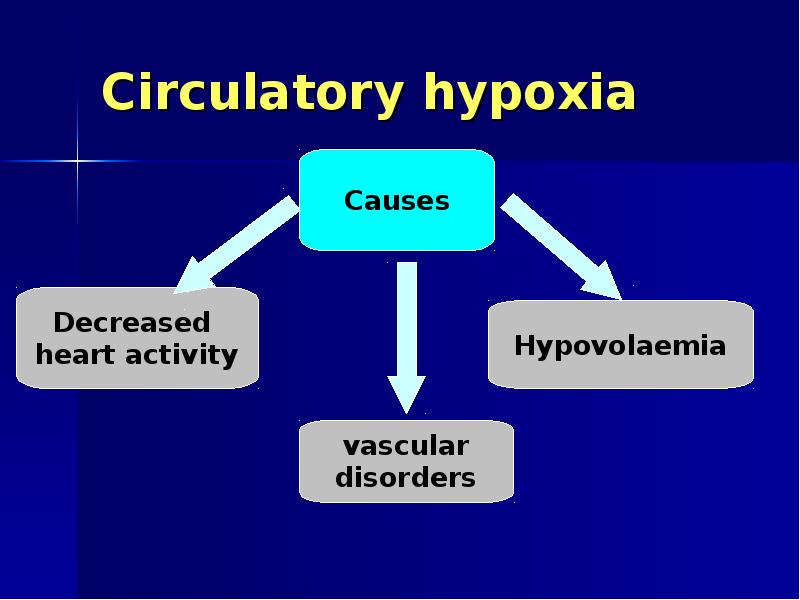
- 12. Circulatory hypoxia
- 13. Circulatory hypoxia - systemic Decrease of heart activity - myocardial infarction,
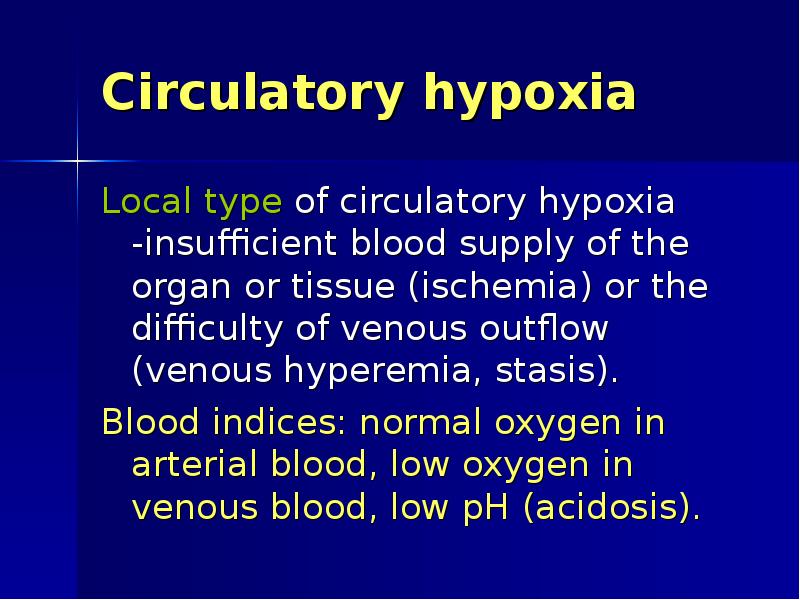
- 14. Circulatory hypoxia Local type of circulatory hypoxia -insufficient blood supply of
- 15. Hemic hypoxia Anemic type – accompanying different anemias. Inactivation type -
- 16. Hemic hypoxia The reasons of anemia: chronic bleedings, erythrocytes hemolysis,
- 17. Hemic hypoxia Carbon monoxide poisoning: CO has the affinity to Hb
- 18. Histotoxic hypoxia The inability of cells to utilize oxygen Causes:
- 19. Histotoxic hypoxia Cyanide poisoning Cyanide ions bind to the Fe atom
- 20. Histotoxic hypoxia Disturbance of respiratory enzymes synthesis results from vitamins deficiency
- 21. Histotoxic hypoxia Dissociation of oxidation and phosphorylation processes in respiratory chain:
- 22. Overload hypoxia Occur during physical overload of certain organ or tissue.
- 23. Substrate hypoxia Deficiency of the substrate to be oxidized - glucose
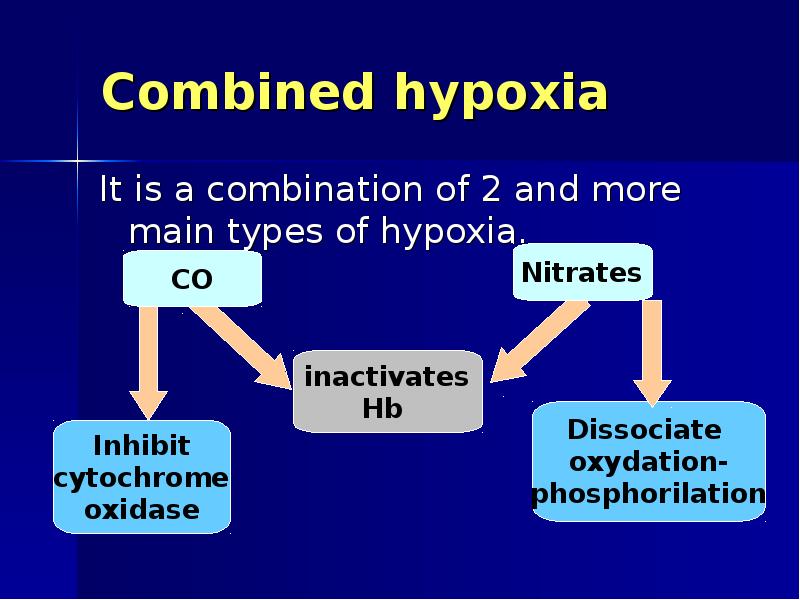
- 24. Combined hypoxia It is a combination of 2 and more main
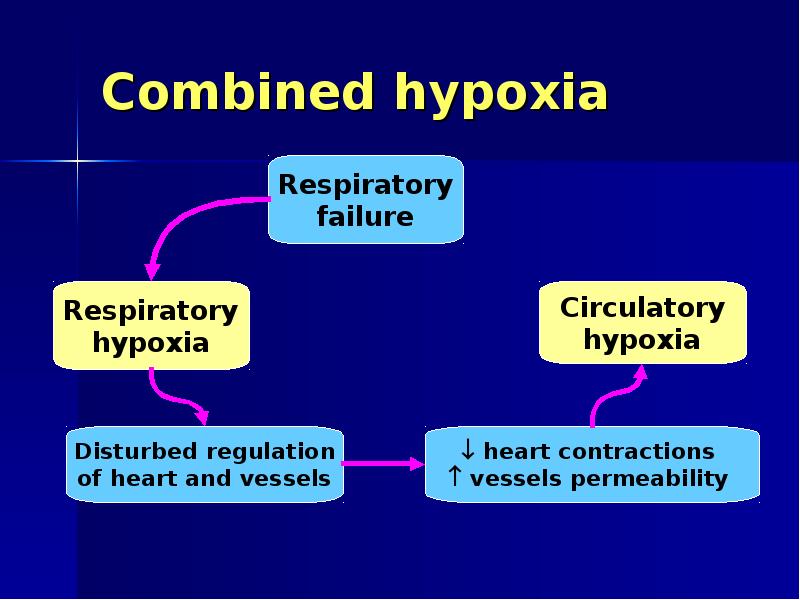
- 25. Combined hypoxia
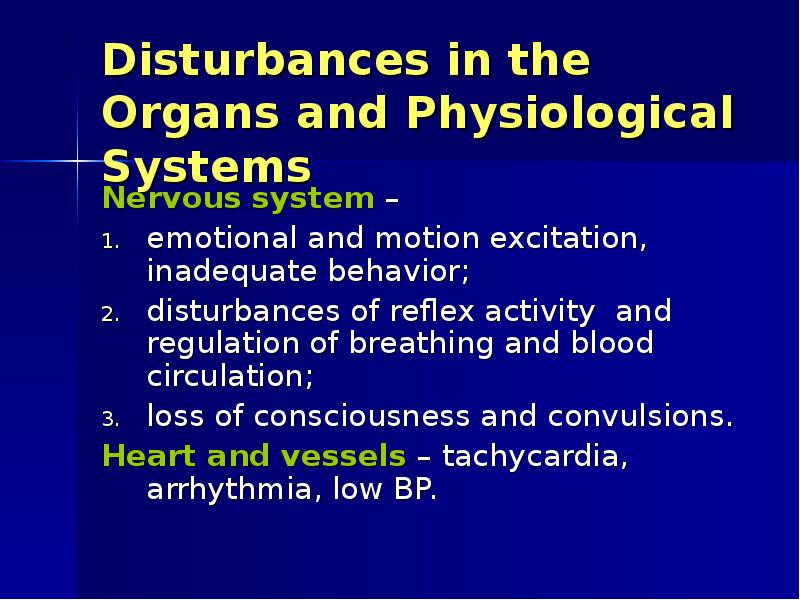
- 26. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems Nervous system –
- 27. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems Lungs - irregular breathing;
- 28. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems GIT organs (chronic hypoxia)
- 29. Adaptation to hypoxia The reactions of urgent adaptation (protective-adaptive) manifest in
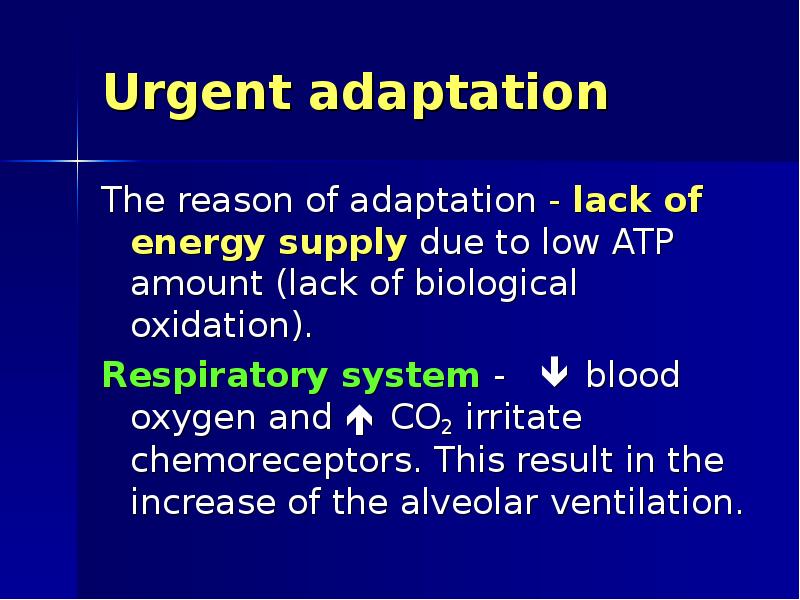
- 30. Urgent adaptation The reason of adaptation - lack of energy supply
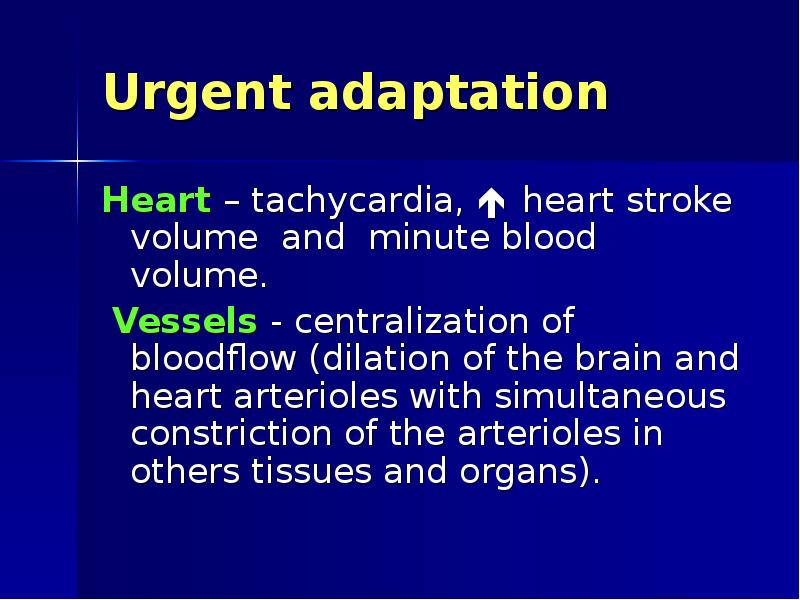
- 31. Urgent adaptation Heart – tachycardia, heart stroke volume and minute
- 32. Urgent adaptation Blood - activation of RBC outflow from the bone
- 33. Adaptation to hypoxia Urgent reactions - activation of the oxygen transport
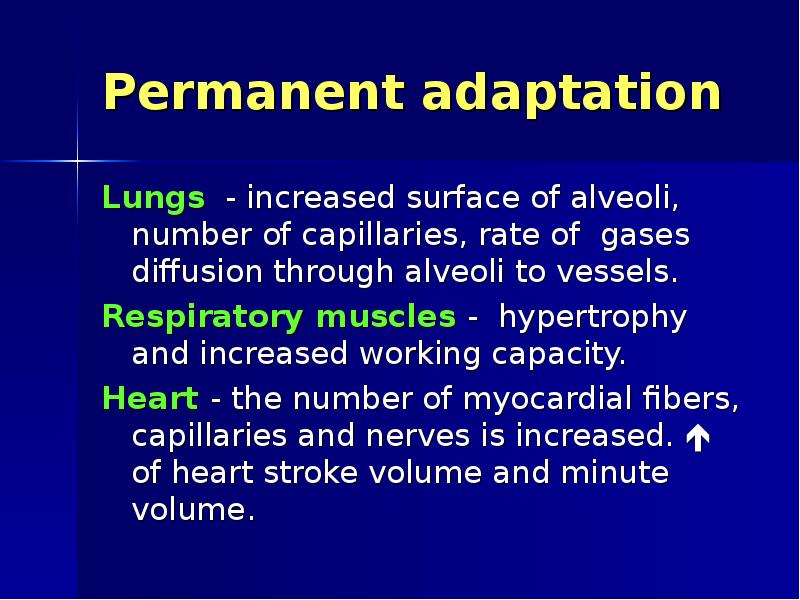
- 34. Permanent adaptation Lungs - increased surface of alveoli, number of capillaries,
- 35. Permanent adaptation Number of the vessels in all organs and tissues
- 36. Clinical application of hypoxia Intermittent hypoxia - repeated episodes of hypoxia
- 37. Clinical application of hypoxia Interval Hypoxic Training is used for the
- 38. Clinical application of hypoxia Adaptation to hypoxia provides resistance to other
- 39. Скачать презентацию


























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации