Introduction to CFX. Workshop 1 Mixing T-Junction презентация
Содержание
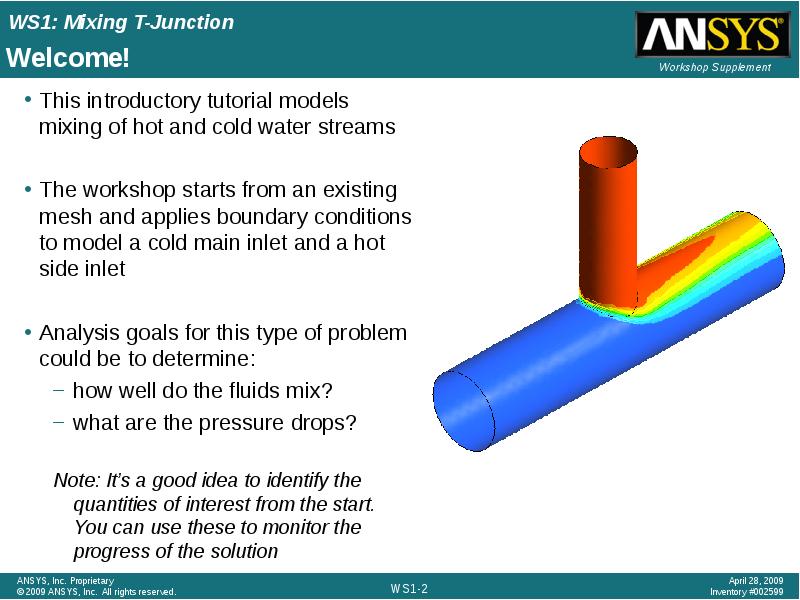
- 2. Welcome! This introductory tutorial models mixing of hot and cold water
- 3. Pre-processing Goals Launch CFX-Pre from Workbench Use pre-defined materials Define the
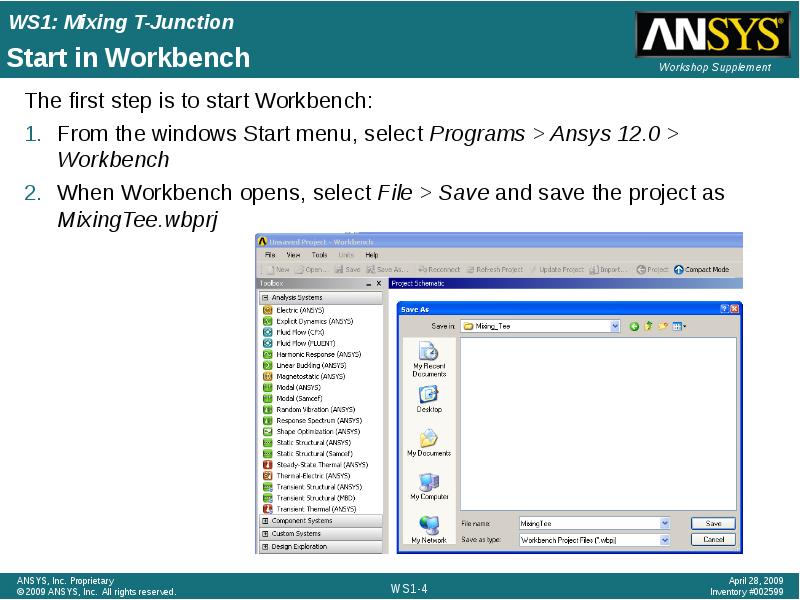
- 4. Start in Workbench The first step is to start Workbench: From
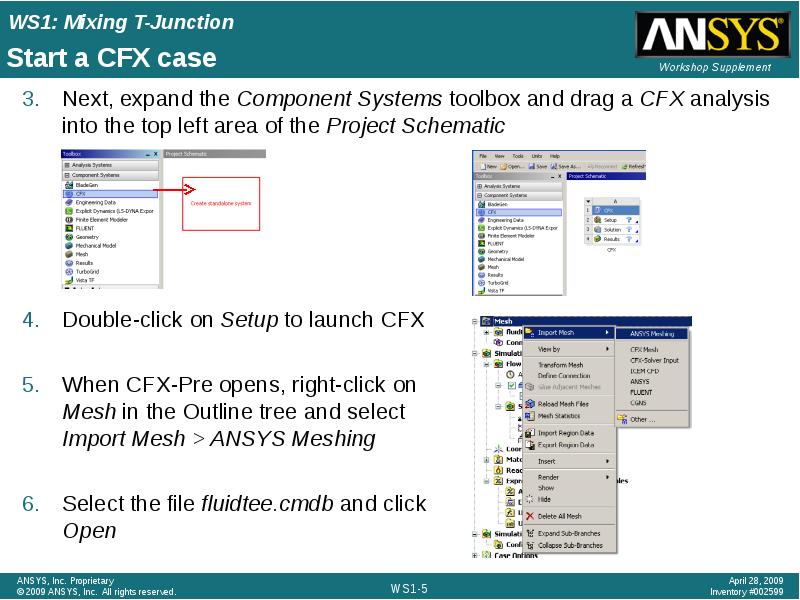
- 5. Start a CFX case Next, expand the Component Systems toolbox and
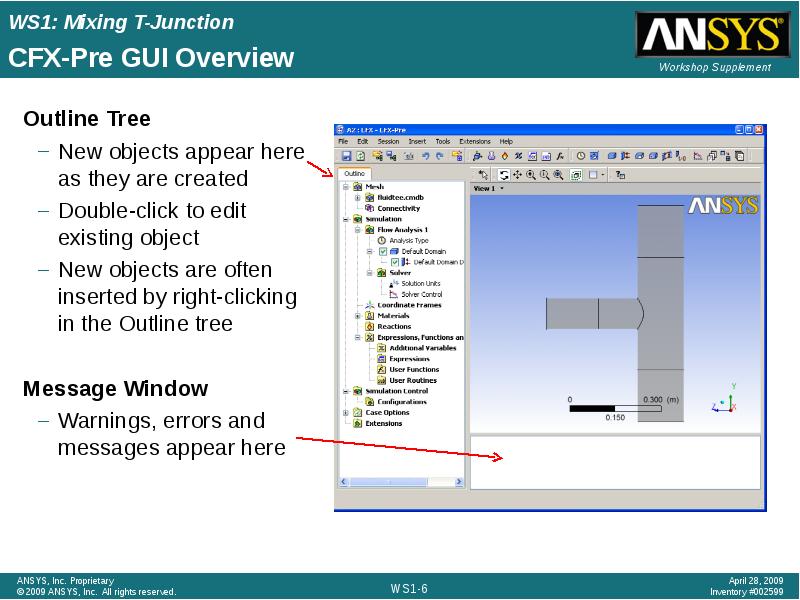
- 6. CFX-Pre GUI Overview Outline Tree New objects appear here as they
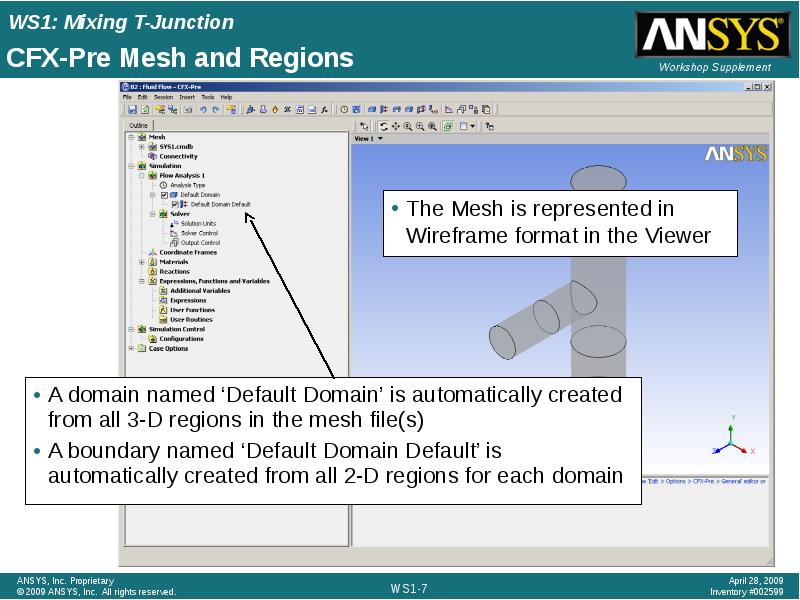
- 7. CFX-Pre Mesh and Regions A domain named ‘Default Domain’ is automatically
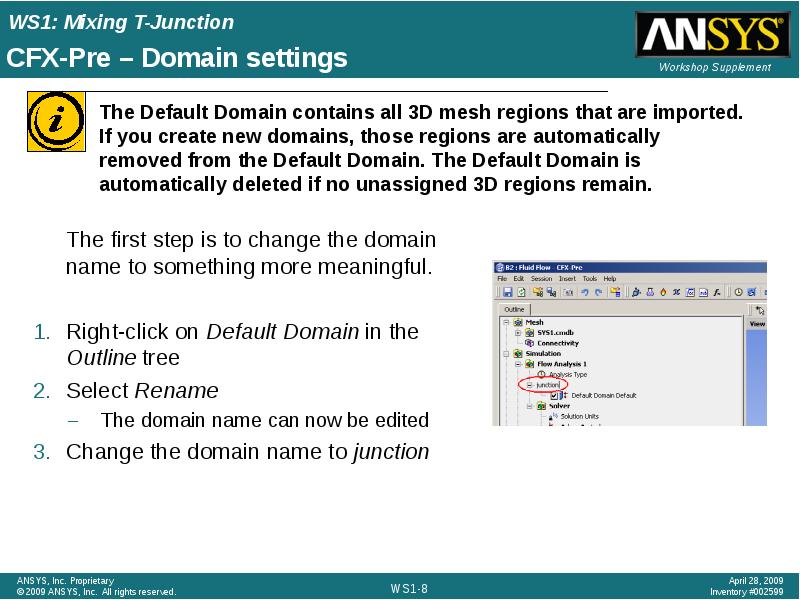
- 8. CFX-Pre – Domain settings The first step is to change the
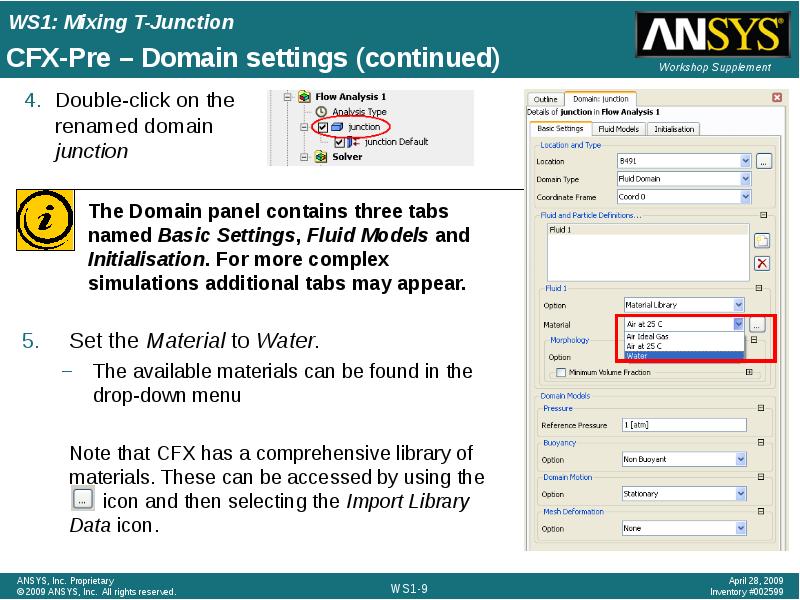
- 9. CFX-Pre – Domain settings (continued) Double-click on the renamed domain junction
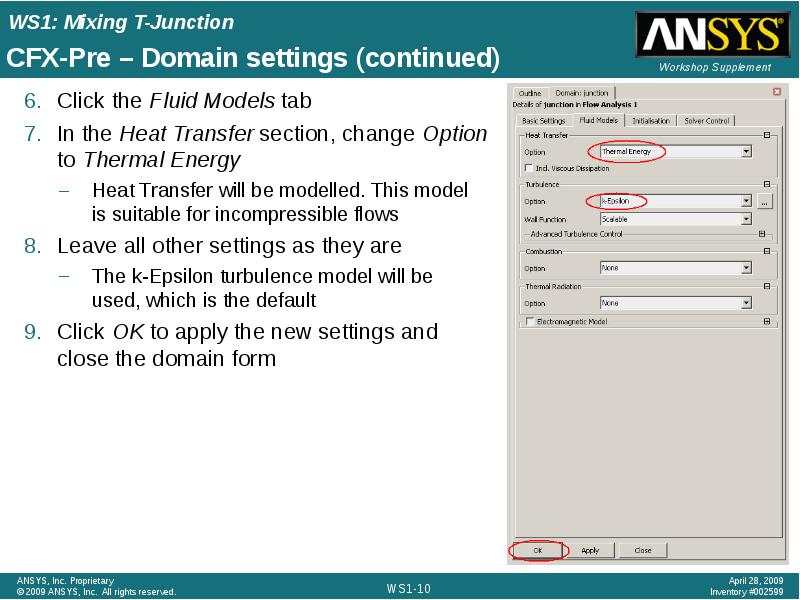
- 10. CFX-Pre – Domain settings (continued) Click the Fluid Models tab In
- 11. Boundary Conditions
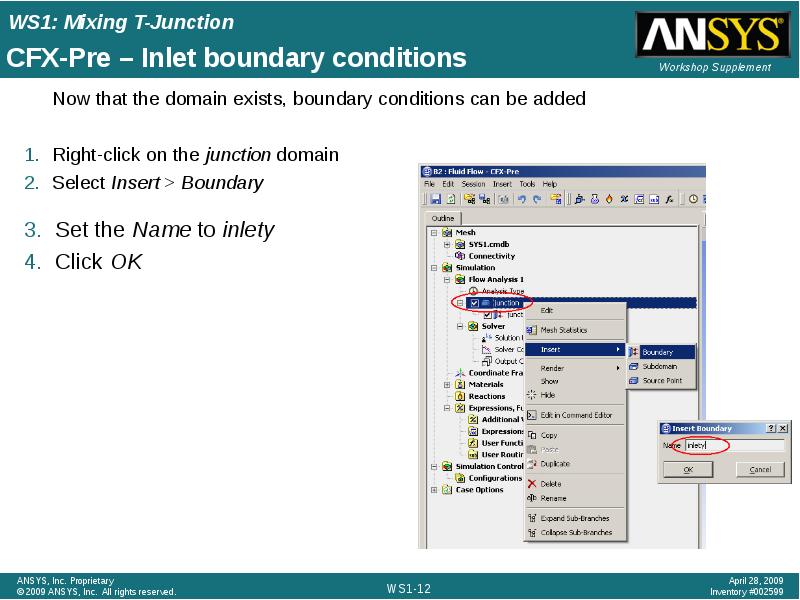
- 12. CFX-Pre – Inlet boundary conditions Now that the domain exists, boundary
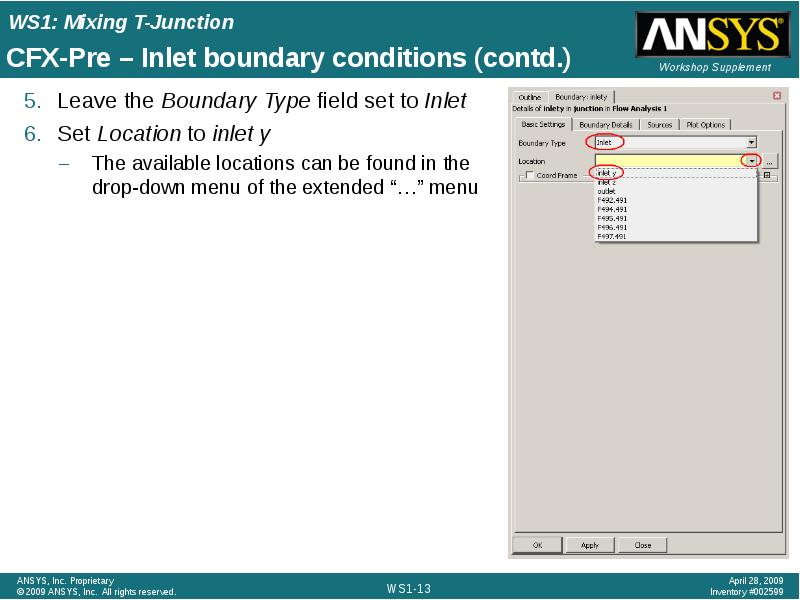
- 13. CFX-Pre – Inlet boundary conditions (contd.) Leave the Boundary Type field
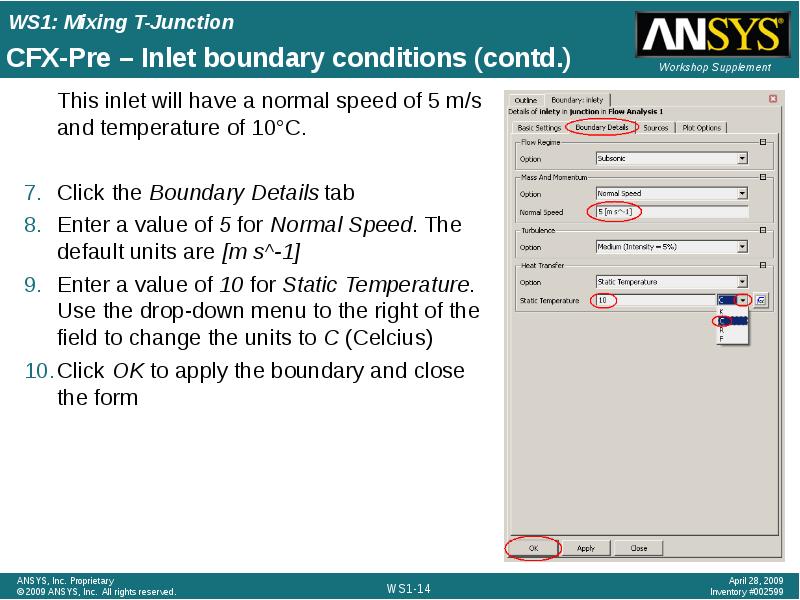
- 14. CFX-Pre – Inlet boundary conditions (contd.) This inlet will have a
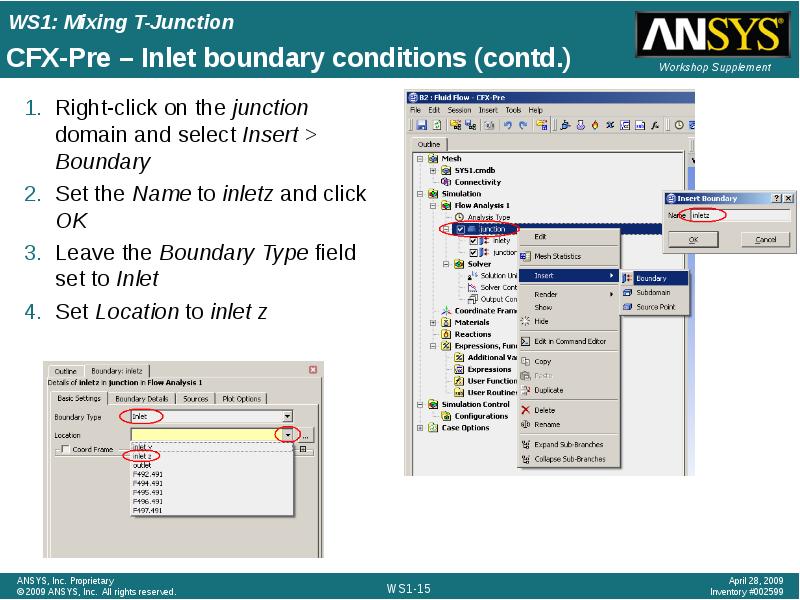
- 15. CFX-Pre – Inlet boundary conditions (contd.)
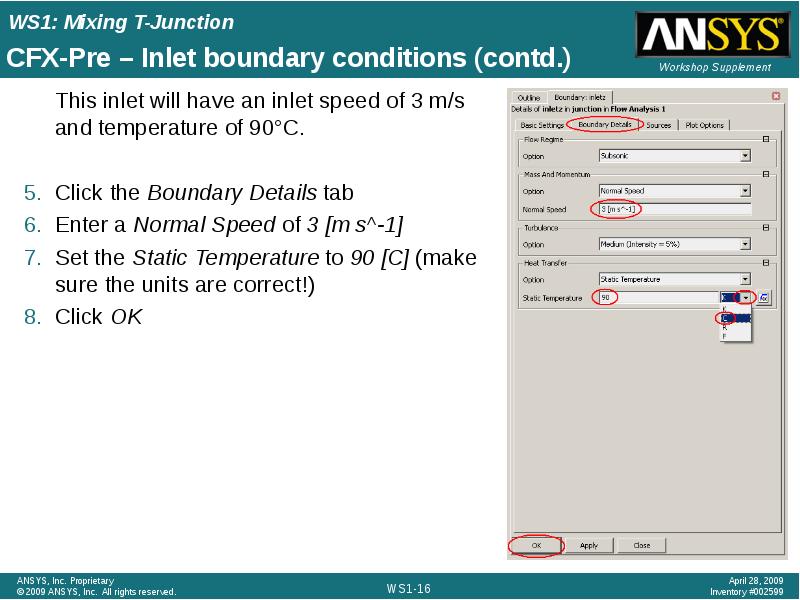
- 16. CFX-Pre – Inlet boundary conditions (contd.) This inlet will have an
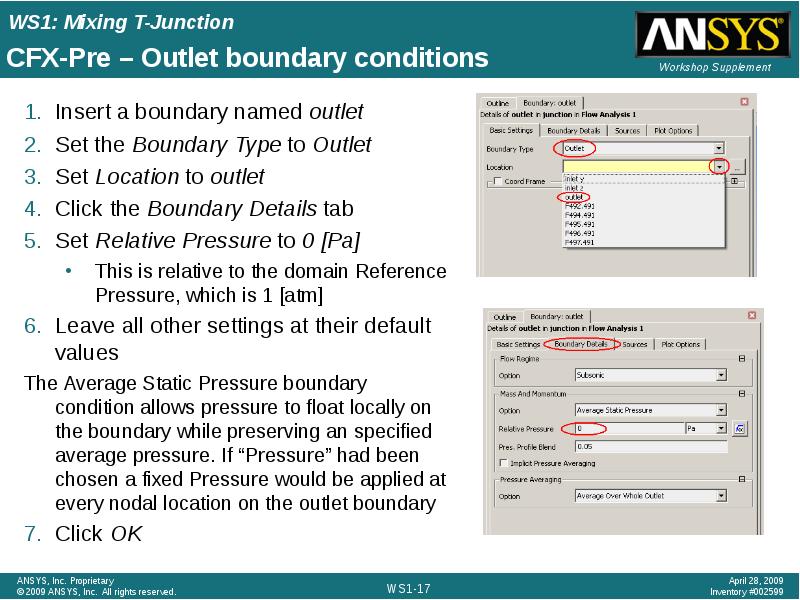
- 17. CFX-Pre – Outlet boundary conditions
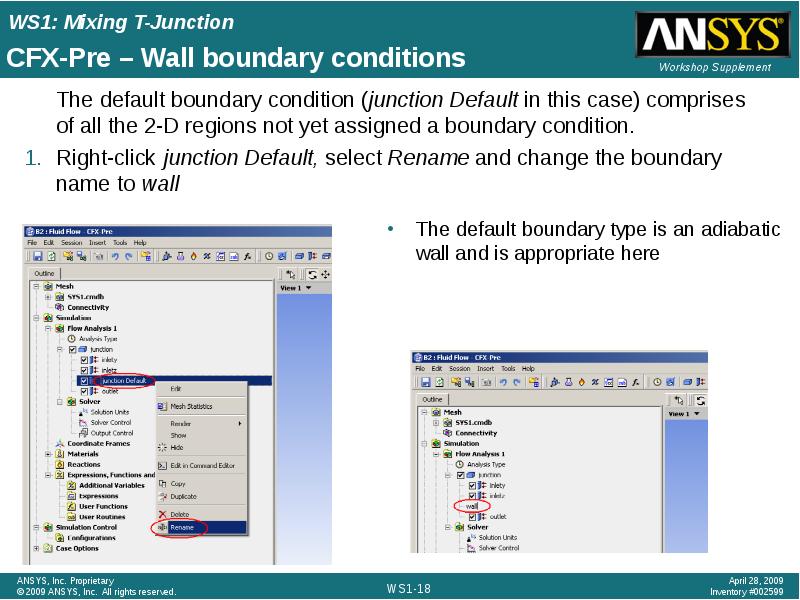
- 18. CFX-Pre – Wall boundary conditions The default boundary condition (junction Default
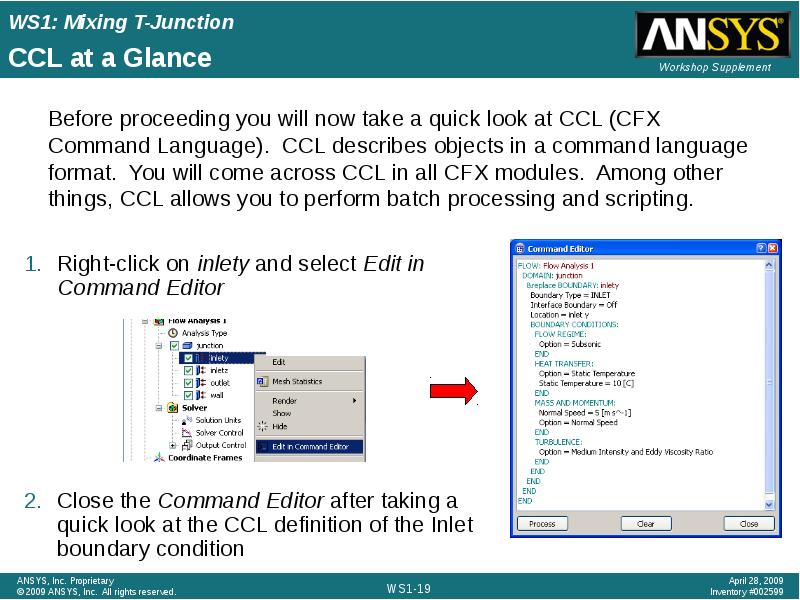
- 19. CCL at a Glance Right-click on inlety and select Edit in
- 20. Initialisation Automatic: This will use a previous solution if provided, otherwise
- 21. Solver Control Double-click on Solver Control from the Outline tree The
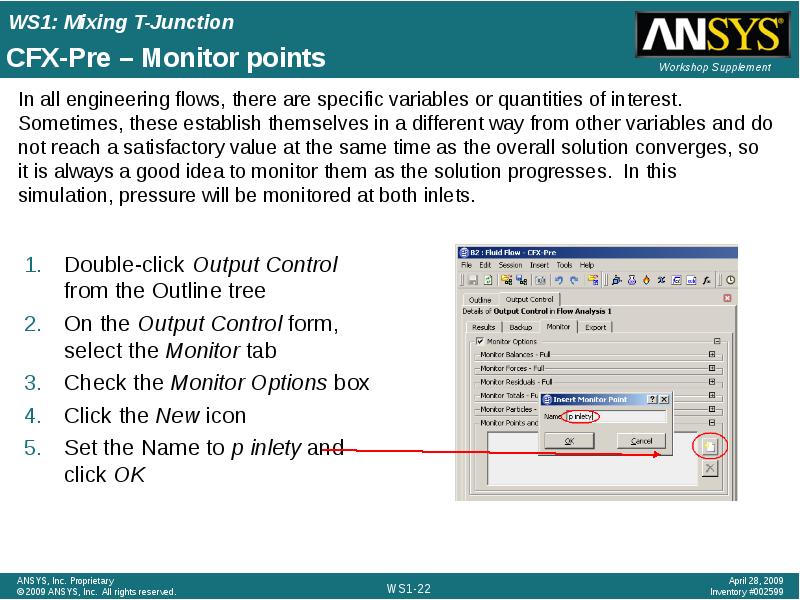
- 22. CFX-Pre – Monitor points Double-click Output Control from the Outline tree
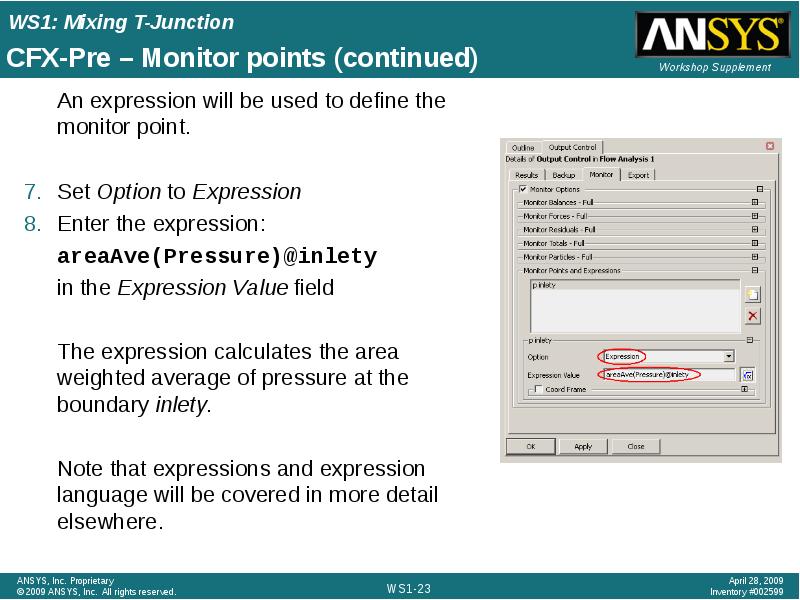
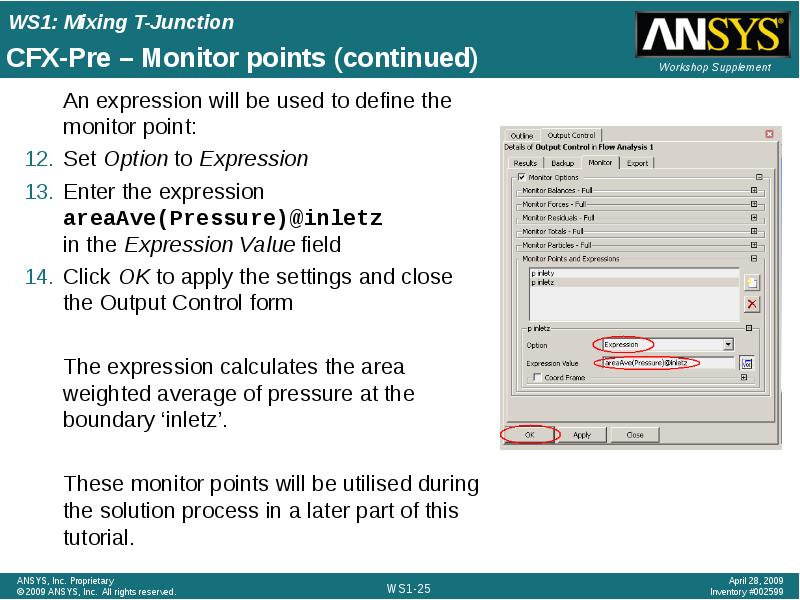
- 23. CFX-Pre – Monitor points (continued) An expression will be used to
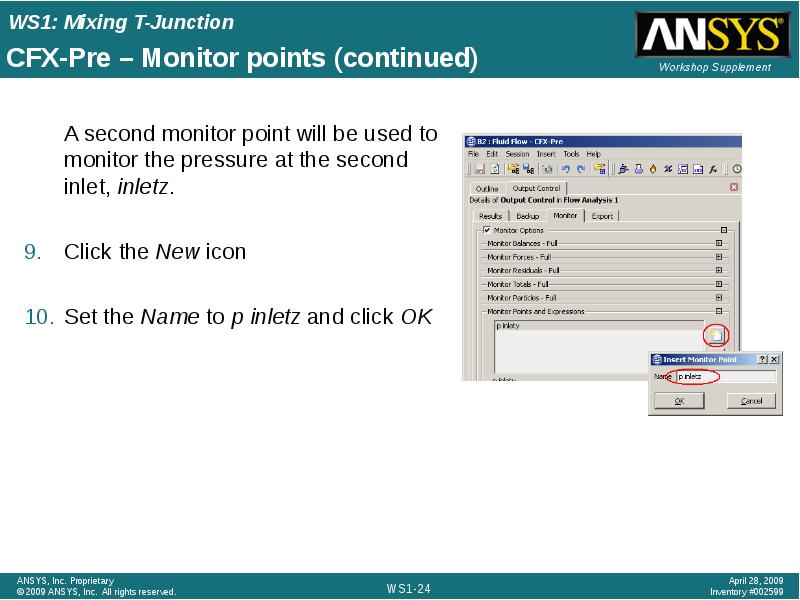
- 24. CFX-Pre – Monitor points (continued) A second monitor point will be
- 25. CFX-Pre – Monitor points (continued) An expression will be used to
- 26. Solution Goals Launch CFX-Pre from Workbench. Use pre-defined materials. Define the
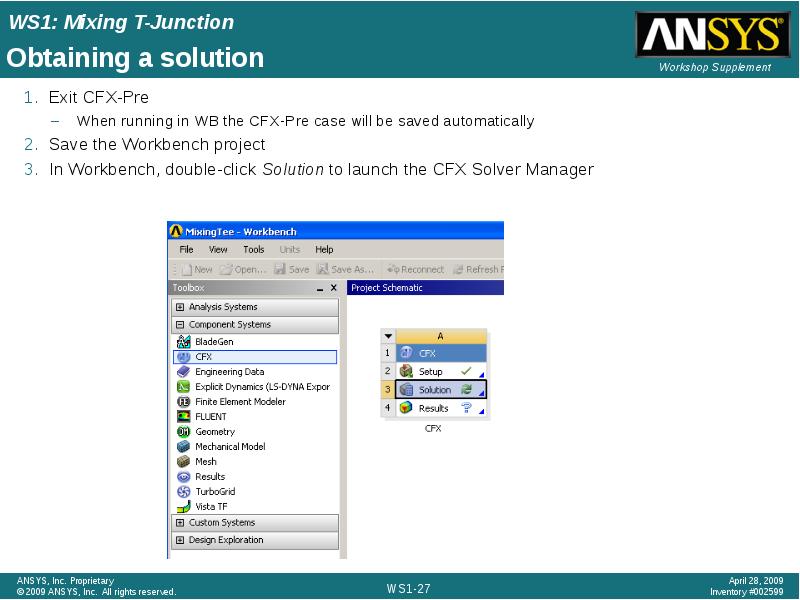
- 27. Obtaining a solution Exit CFX-Pre When running in WB the CFX-Pre
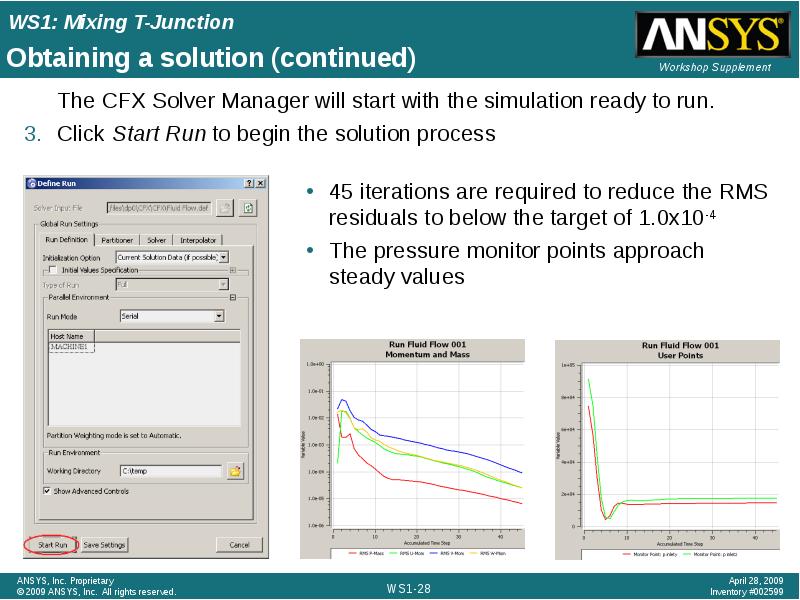
- 28. Obtaining a solution (continued) The CFX Solver Manager will start with
- 29. Post-processing Goals Launch CFX-Pre from Workbench. Use pre-defined materials. Define the
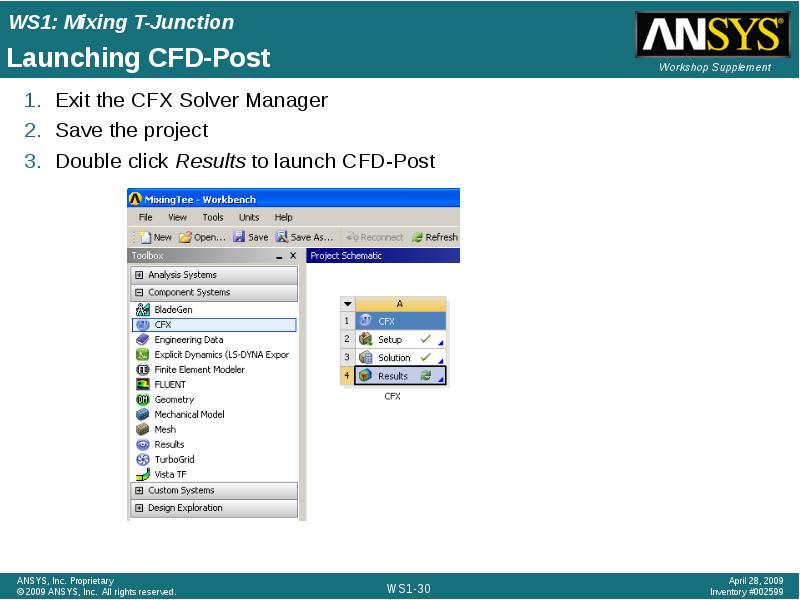
- 30. Launching CFD-Post Exit the CFX Solver Manager Save the project Double
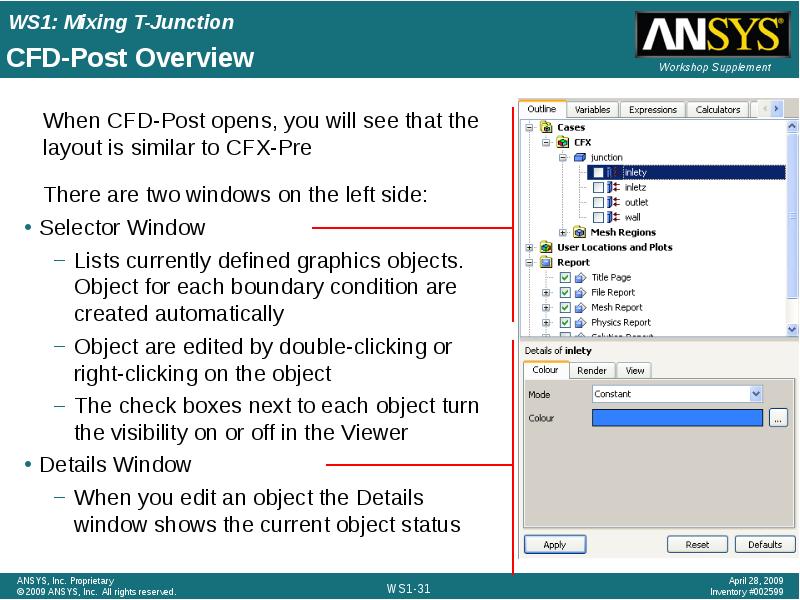
- 31. CFD-Post Overview Selector Window Lists currently defined graphics objects. Object for
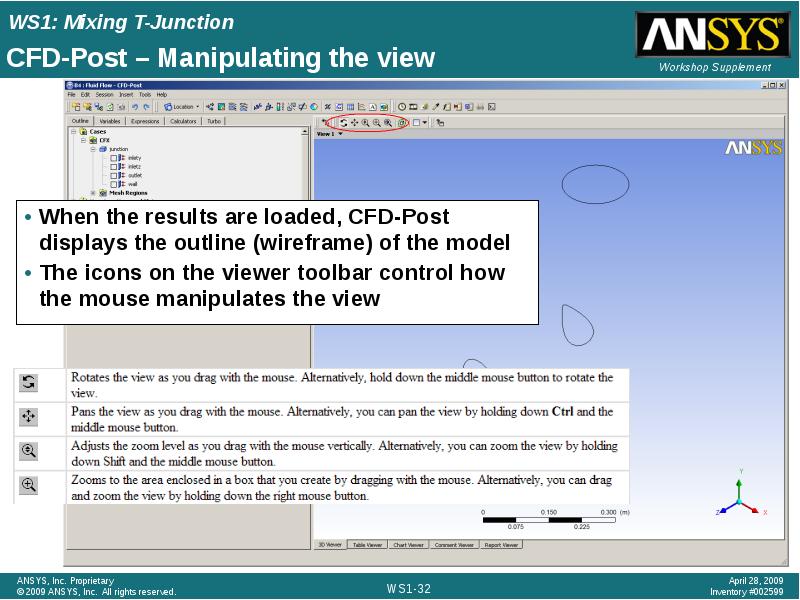
- 32. CFD-Post – Manipulating the view When the results are loaded, CFD-Post
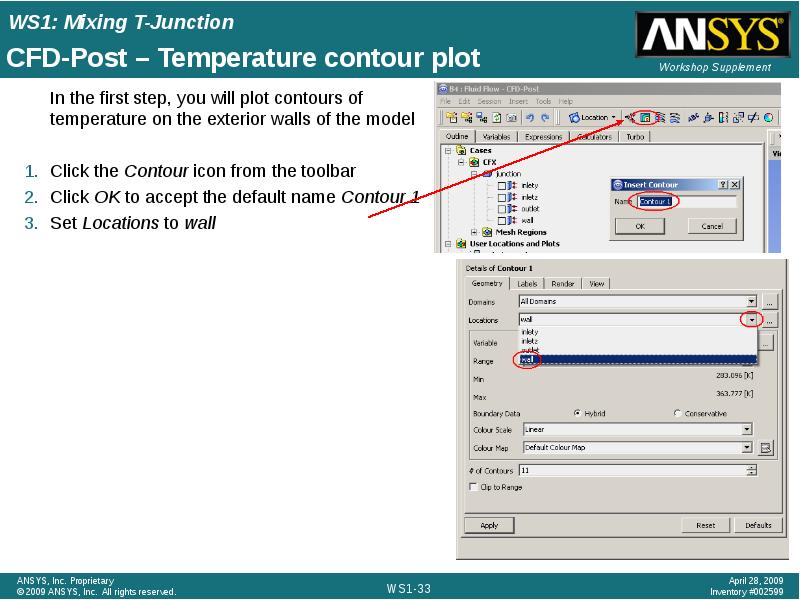
- 33. CFD-Post – Temperature contour plot In the first step, you will
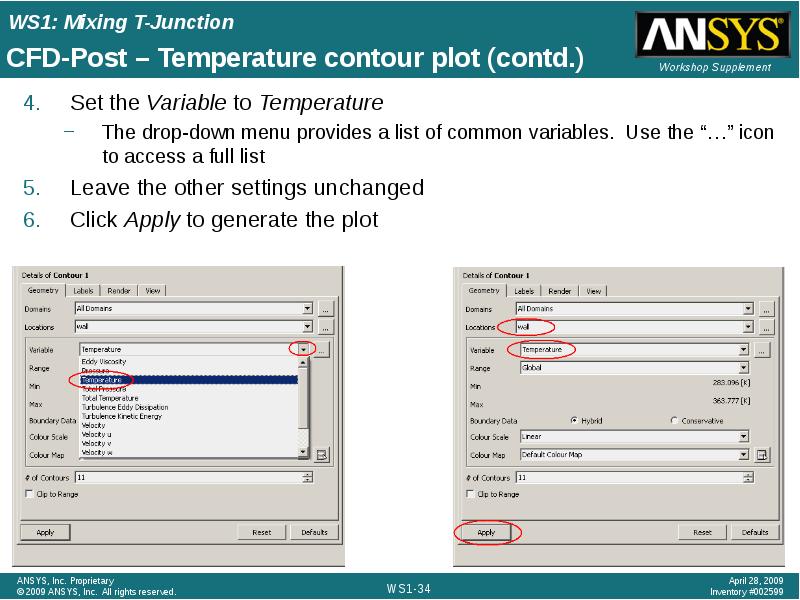
- 34. CFD-Post – Temperature contour plot (contd.)
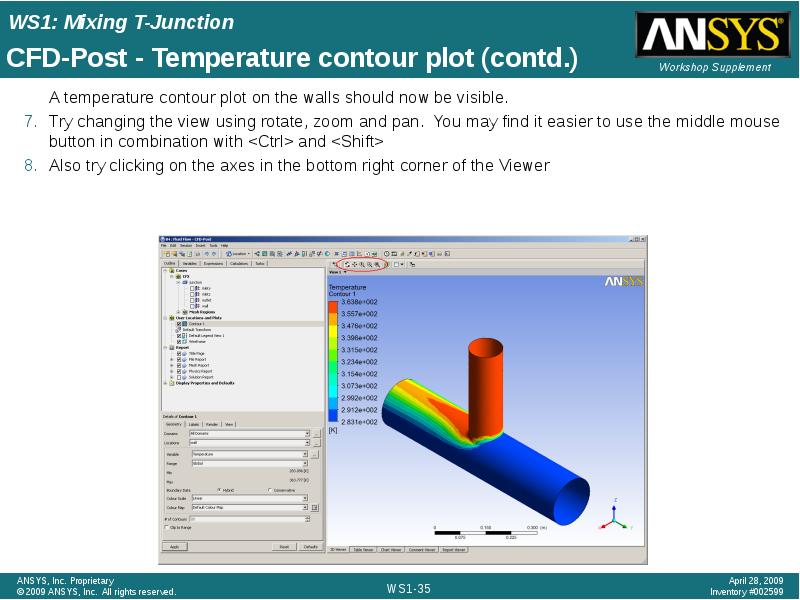
- 35. CFD-Post - Temperature contour plot (contd.) A temperature contour plot on
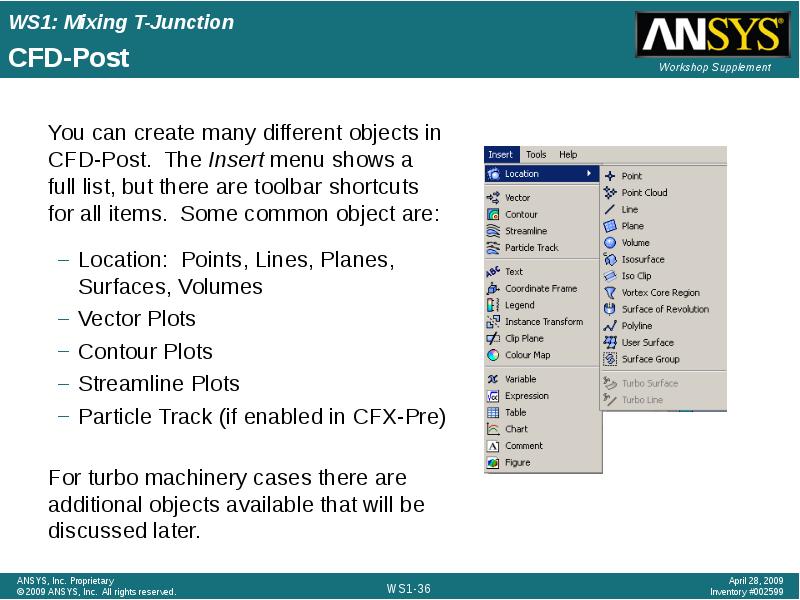
- 36. CFD-Post Location: Points, Lines, Planes, Surfaces, Volumes Vector Plots Contour Plots
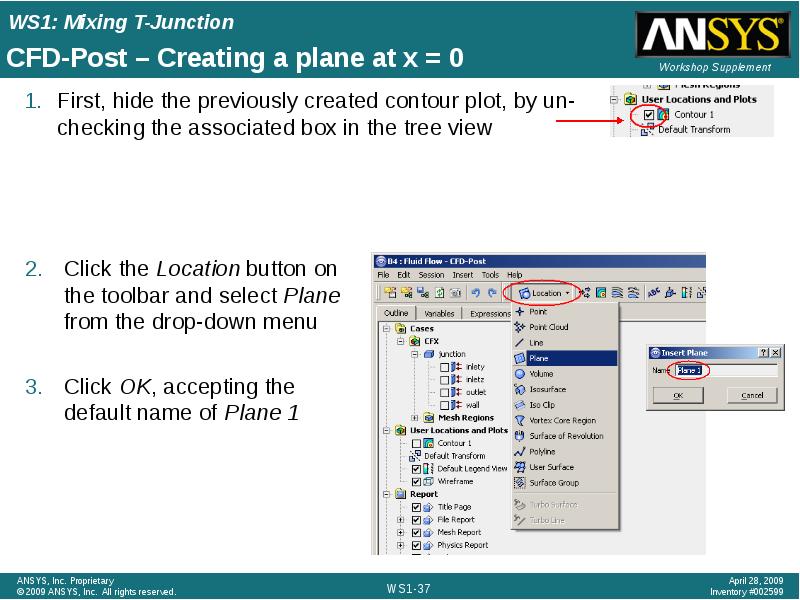
- 37. CFD-Post – Creating a plane at x = 0 First, hide
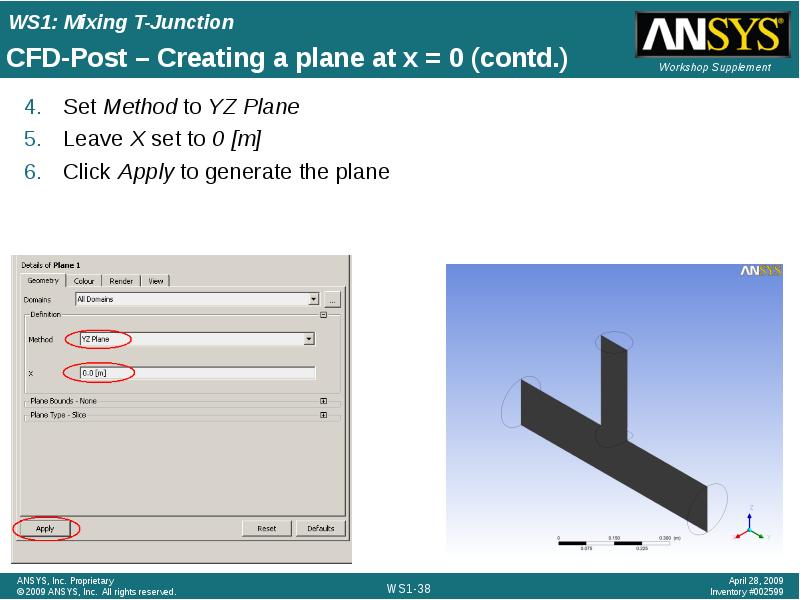
- 38. CFD-Post – Creating a plane at x = 0 (contd.)
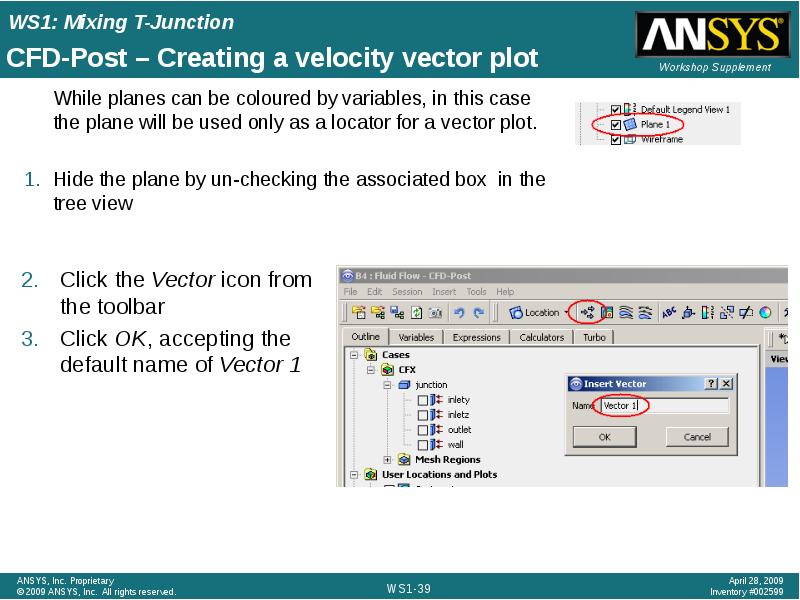
- 39. CFD-Post – Creating a velocity vector plot While planes can be
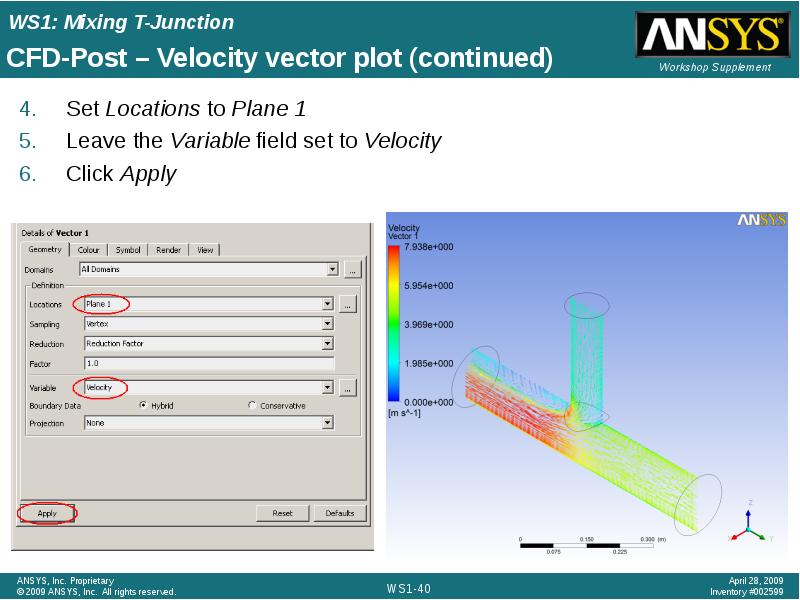
- 40. CFD-Post – Velocity vector plot (continued)
- 41. CFD-Post – Aligning the view Given that the vector plot is
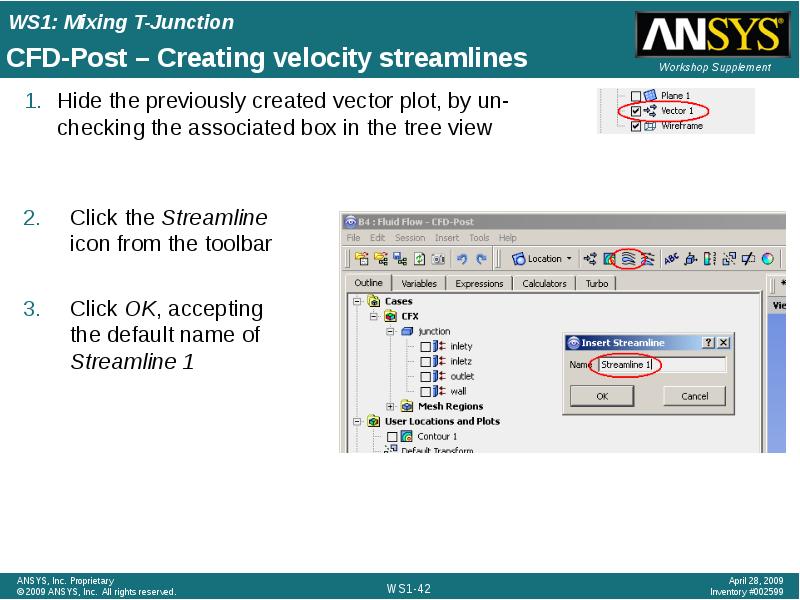
- 42. CFD-Post – Creating velocity streamlines Hide the previously created vector plot,
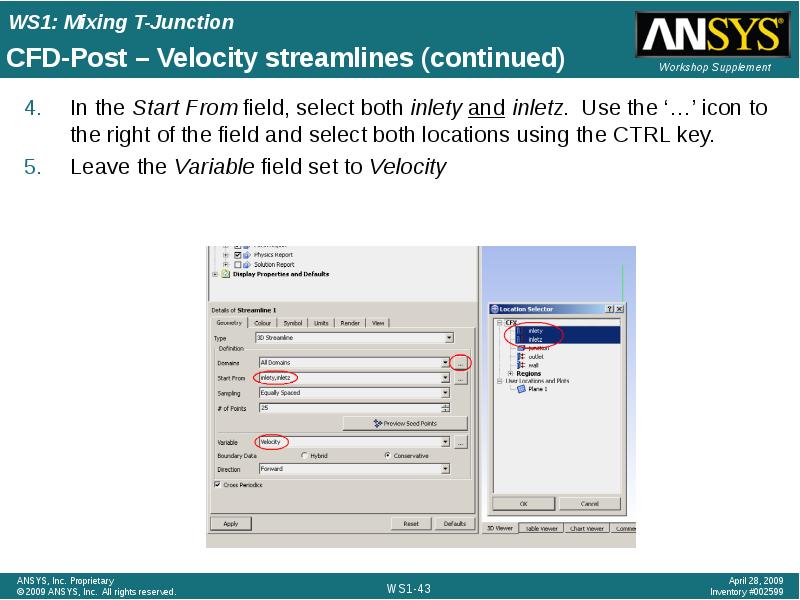
- 43. CFD-Post – Velocity streamlines (continued)
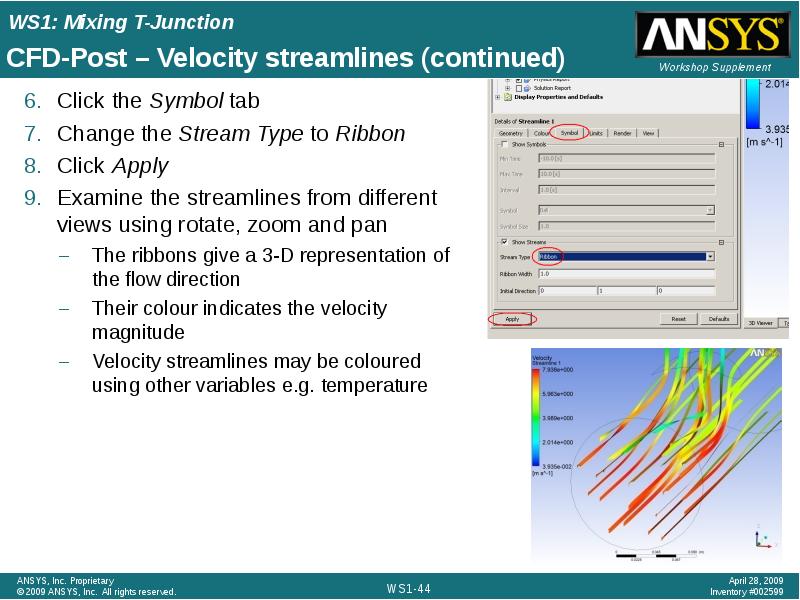
- 44. CFD-Post – Velocity streamlines (continued) Click the Symbol tab Change the
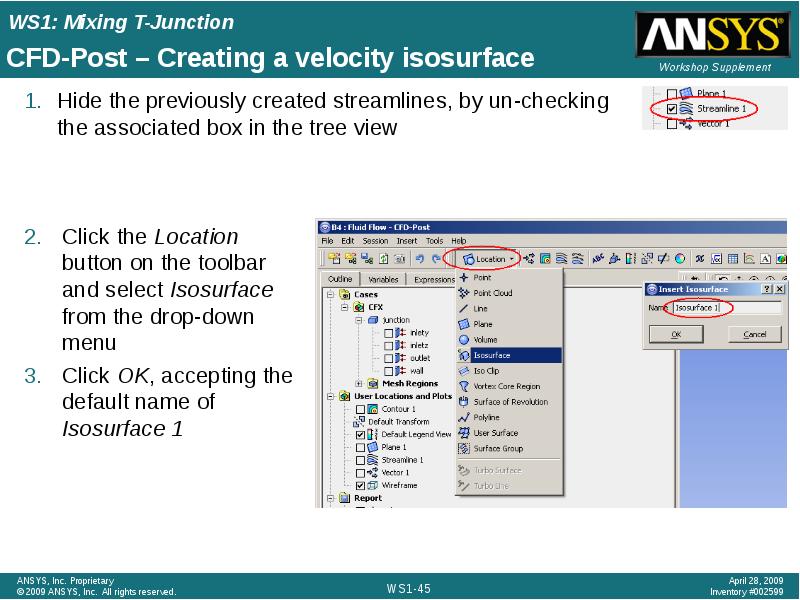
- 45. CFD-Post – Creating a velocity isosurface Hide the previously created streamlines,
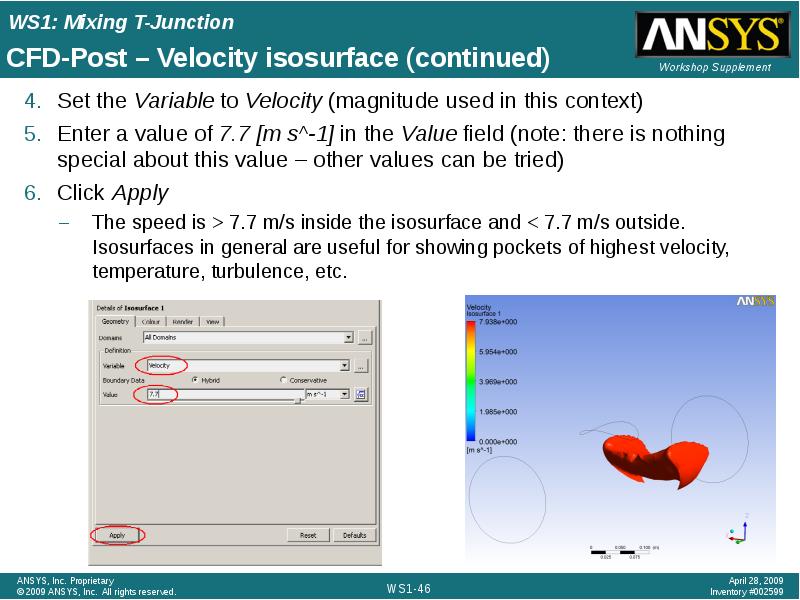
- 46. CFD-Post – Velocity isosurface (continued) Set the Variable to Velocity (magnitude
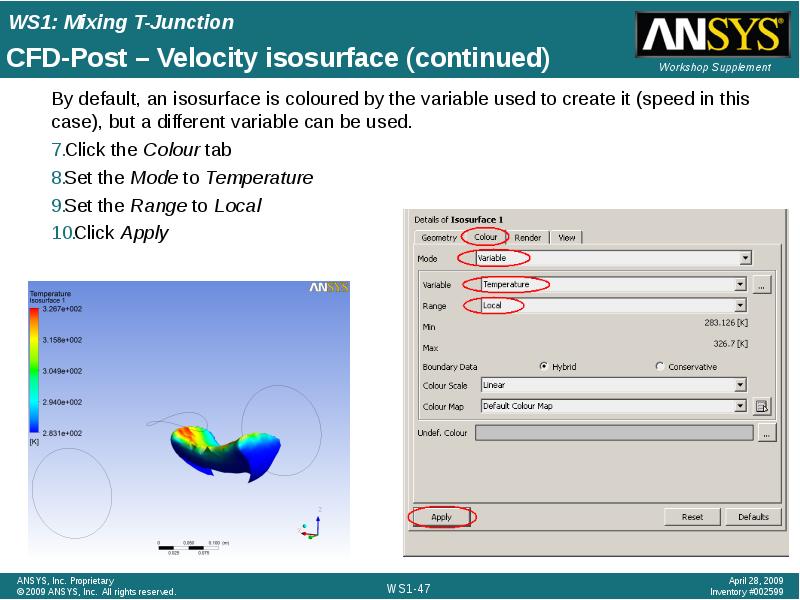
- 47. CFD-Post – Velocity isosurface (continued) By default, an isosurface is coloured
- 48. Скачать презентацию






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Introduction to CFX. Workshop 1 Mixing T-Junction можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























