Jets in flight презентация
Содержание
- 3. Lesson Objectives Understand the Engineering Design Process Comprehend the basic principles
- 4. Navy Aviation
- 5. Lesson Goal Apply the principles of flight and the engineering design
- 6. Lesson Organization Part 1: Understanding and applying the basic principles of
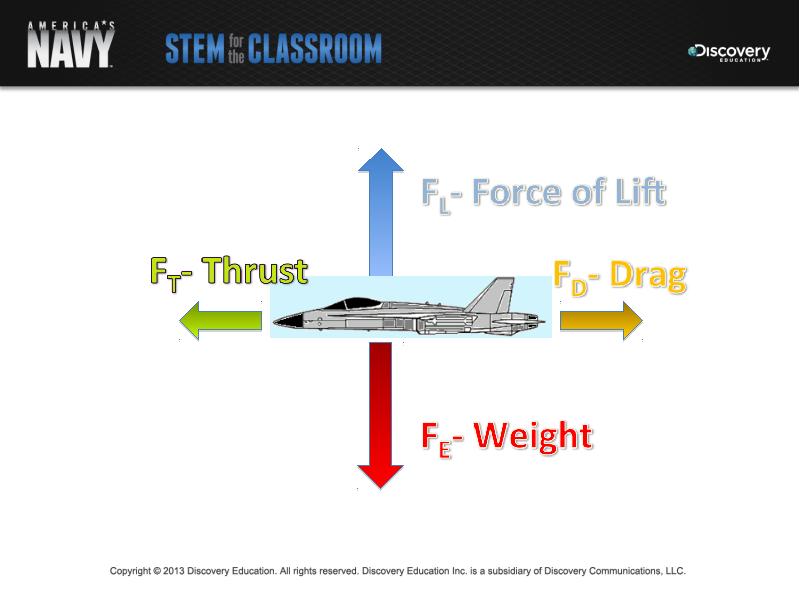
- 10. Part 1: The Principles of Flight Forces acting on an aircraft
- 12. Flight is achieved by shifting the balance between the opposing forces
- 13. Thrust is produced in one of two ways: Thrust is produced
- 14. Lift is the upward force created as air passes over and
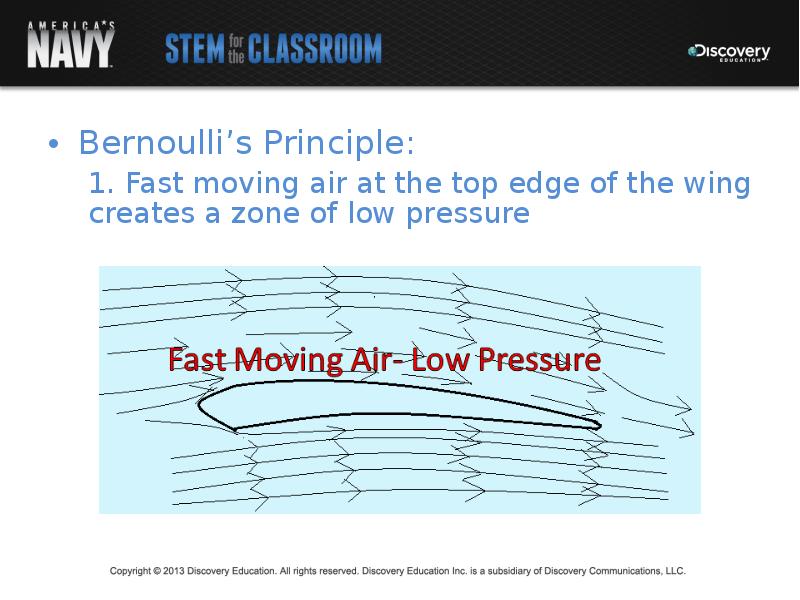
- 15. Bernoulli’s Principle: Bernoulli’s Principle: 1. Fast moving air at the top
- 16. Bernoulli’s Principle: Bernoulli’s Principle: 2. Slow moving air along the bottom
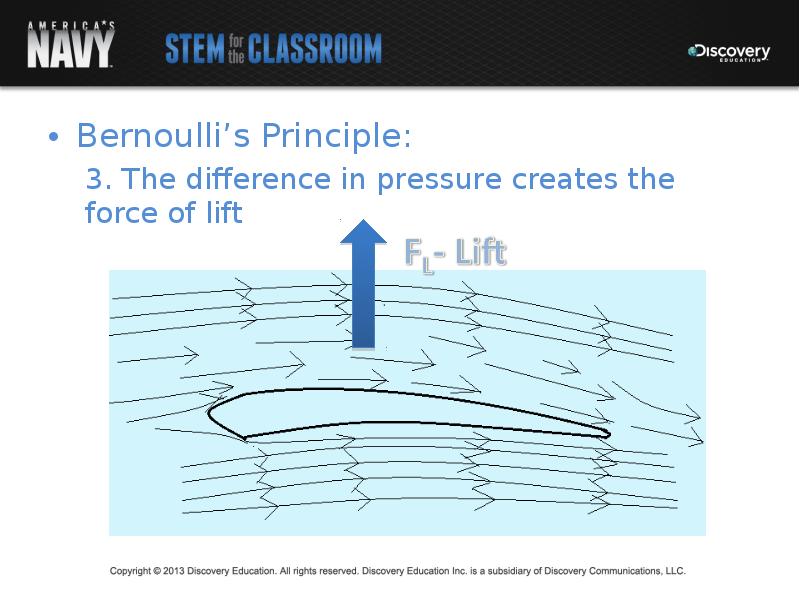
- 17. Bernoulli’s Principle: Bernoulli’s Principle: 3. The difference in pressure creates the
- 18. Lift Momentum: additional upward force is generated incoming air deflects off
- 23. Part 2: Designing a Prototype You are an engineer tasked with
- 26. Step 1: Identify the Problem Step 1: Identify the Problem Create
- 27. Step 2: Identify Criteria and Constraints Step 2: Identify Criteria and
- 28. Complete the remaining steps of the engineering design process and demonstrate
- 29. Скачать презентацию

























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации