Lecture 1. TCP/IP Overview and History презентация
Содержание
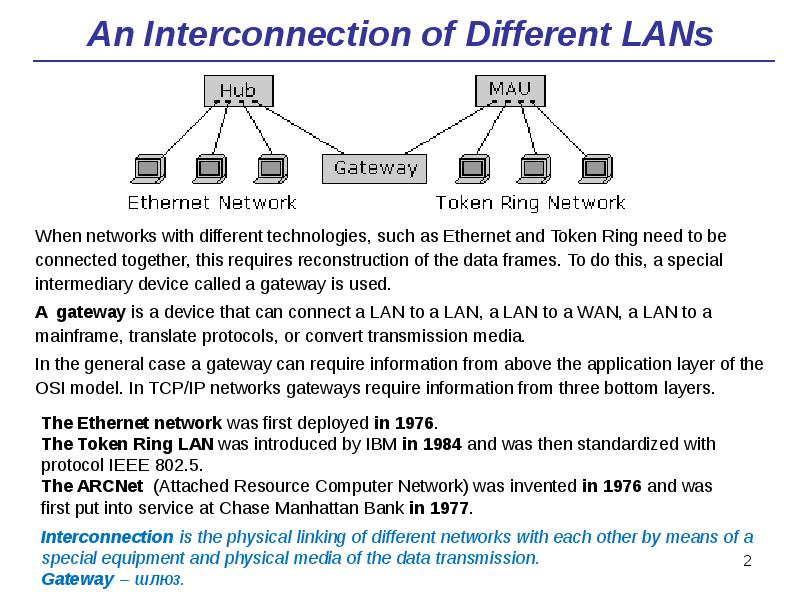
- 2. An Interconnection of Different LANs
- 3. Advanced Research Projects Agency - ARPA
- 4. Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO)
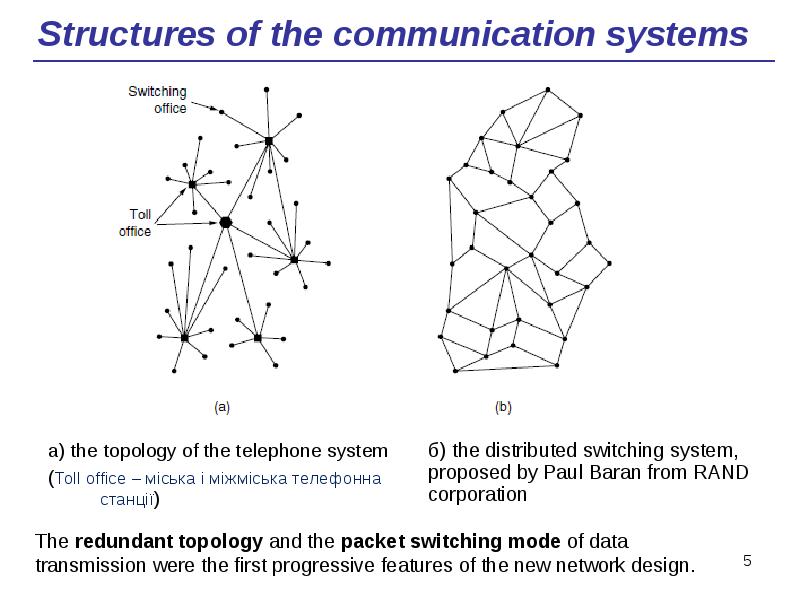
- 5. Structures of the communication systems а) the topology of the telephone
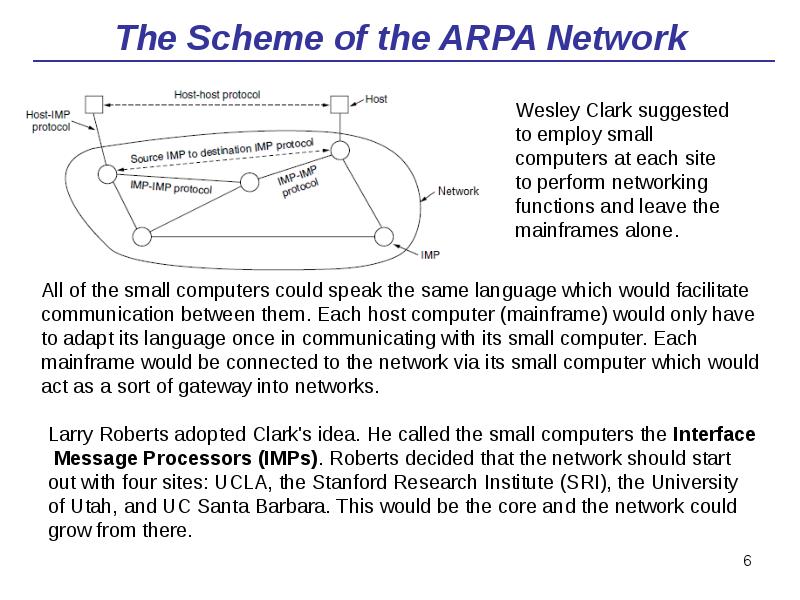
- 6. The Scheme of the ARPA Network
- 7. IMP - Interface Message Processor
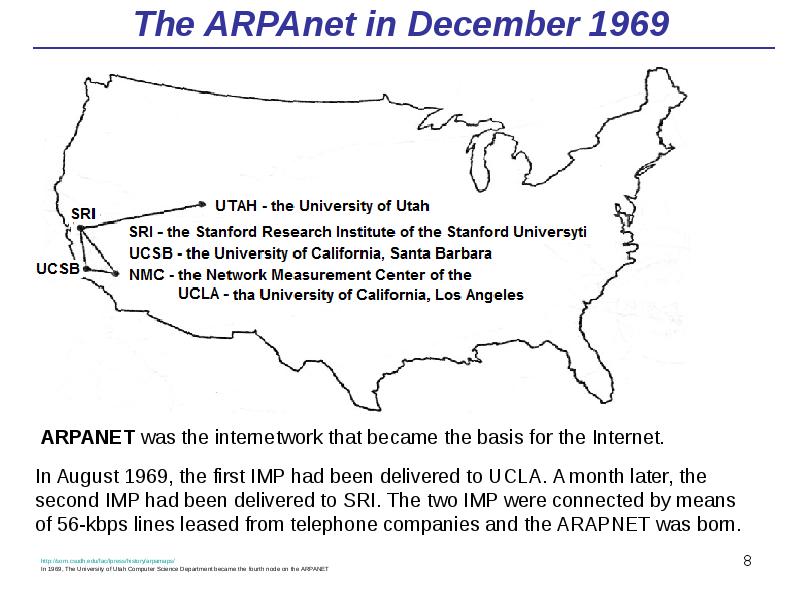
- 8. The ARPAnet in December 1969 http://som.csudh.edu/fac/lpress/history/arpamaps/ In 1969, The University of
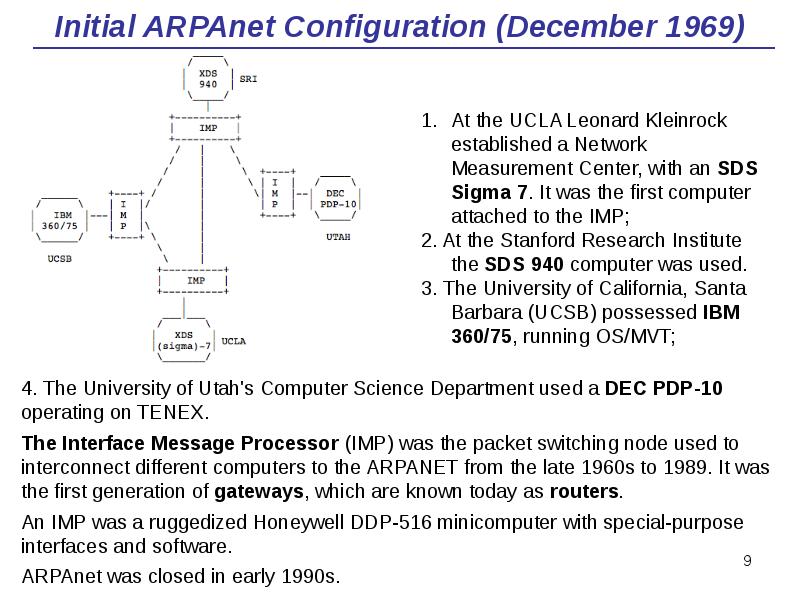
- 9. Initial ARPAnet Configuration (December 1969)
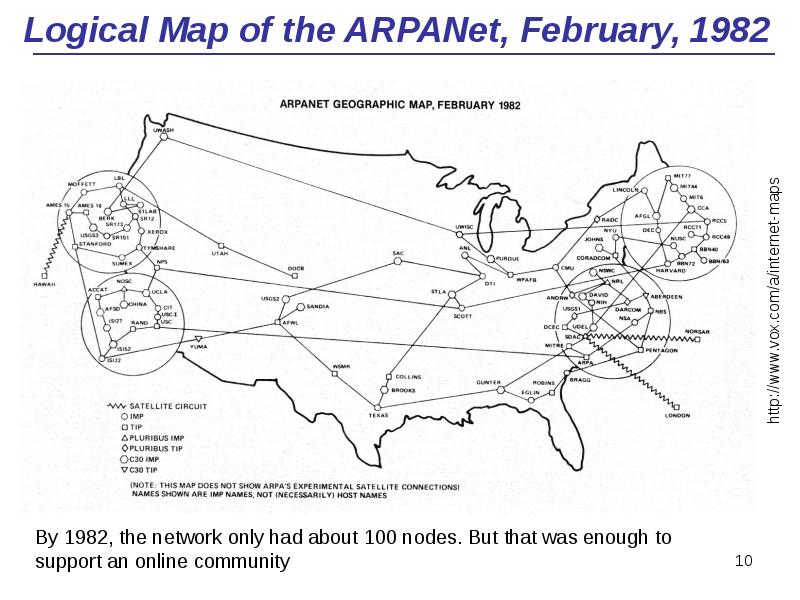
- 10. Logical Map of the ARPANet, February, 1982
- 11. Pioneers of Computer Networking
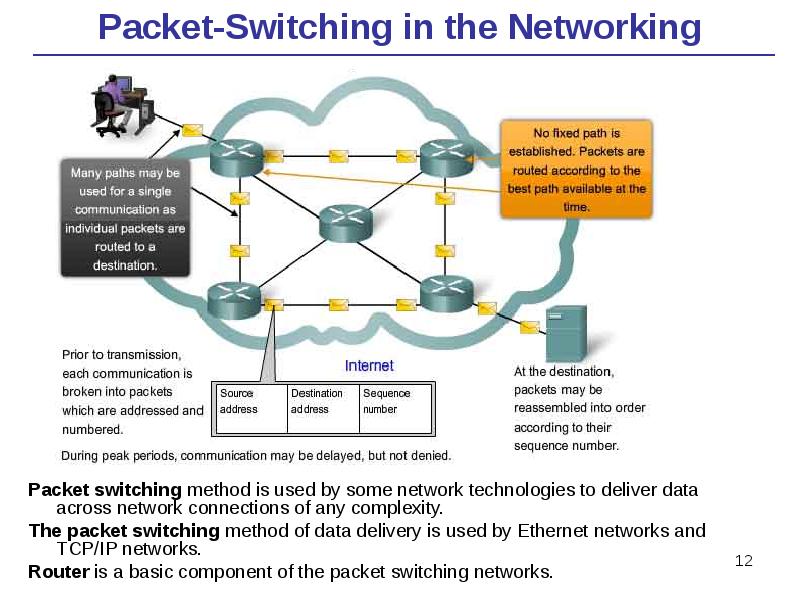
- 12. Packet-Switching in the Networking Packet switching method is used by some
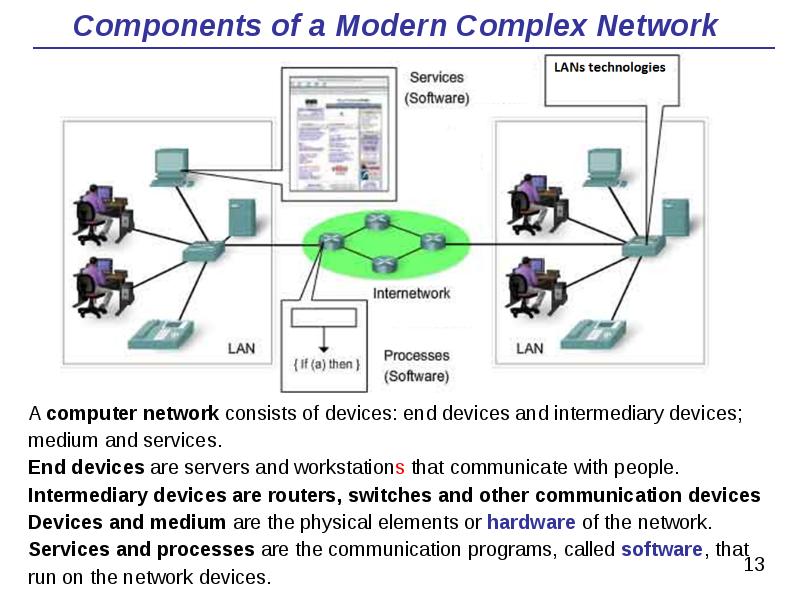
- 13. Components of a Modern Complex Network
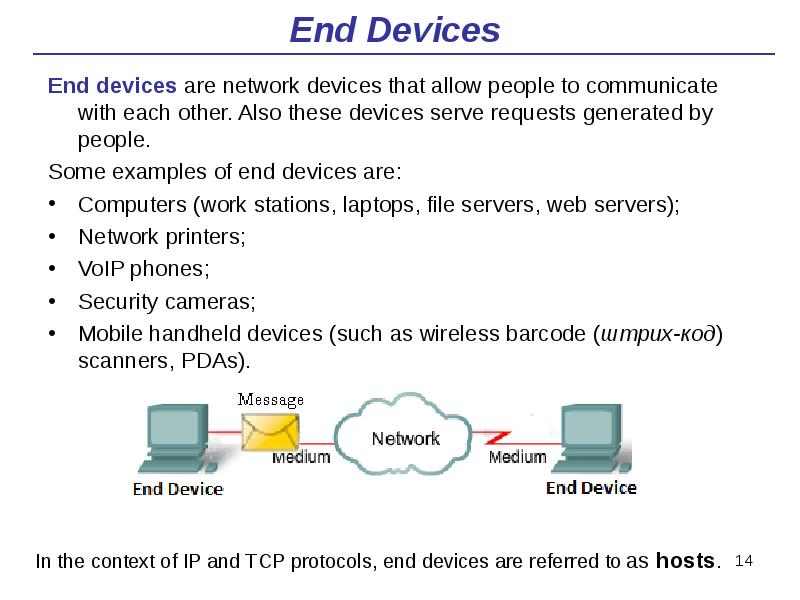
- 14. End Devices End devices are network devices that allow people
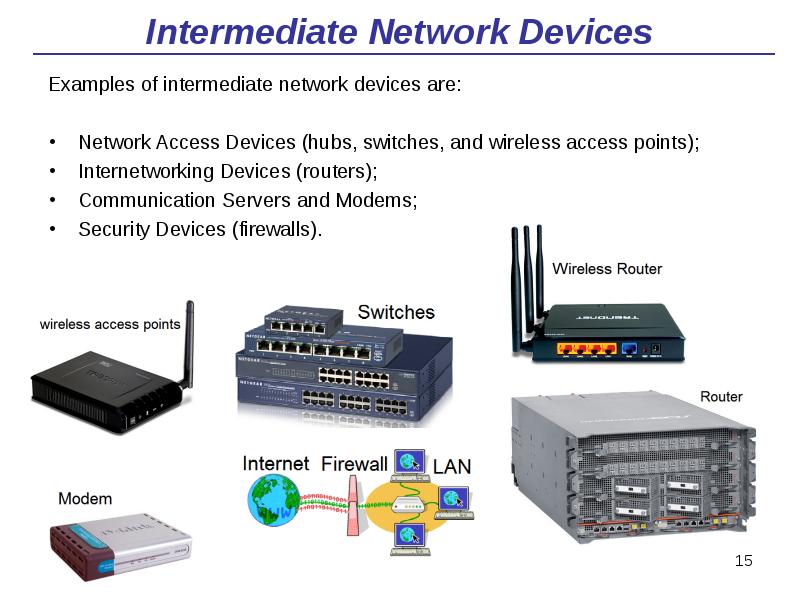
- 15. Intermediate Network Devices Examples of intermediate network devices are: Network Access
- 16. List of Functions of Intermediate Network Devices Processes running on the
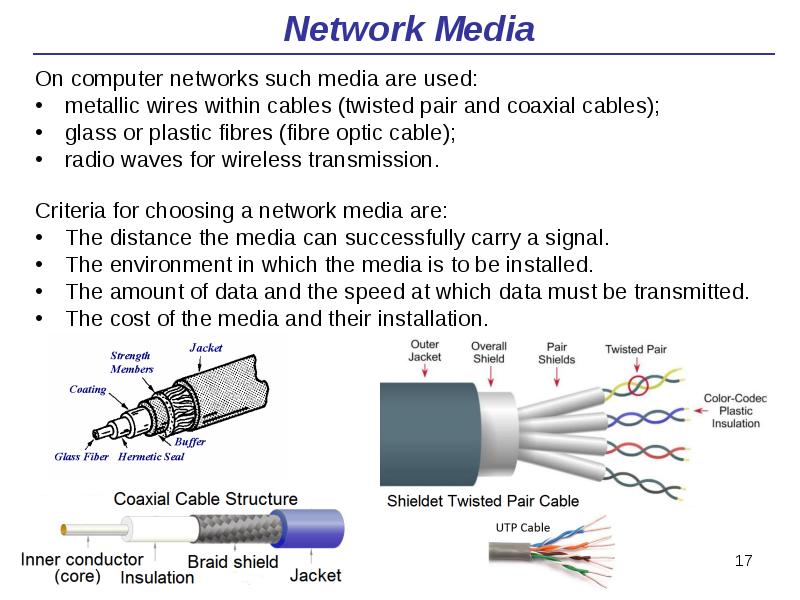
- 17. Network Media On computer networks such media are used: metallic
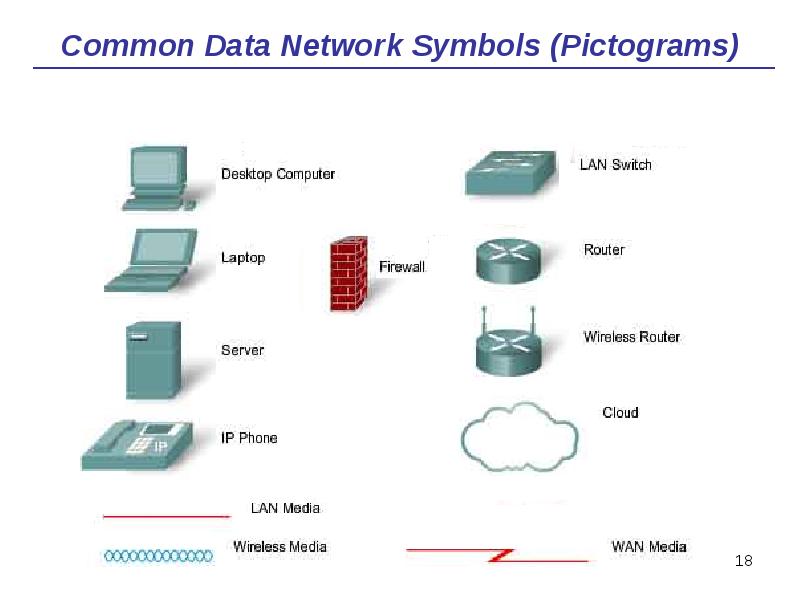
- 18. Common Data Network Symbols (Pictograms)
- 19. Definition of some Network Concepts A communication is a process of
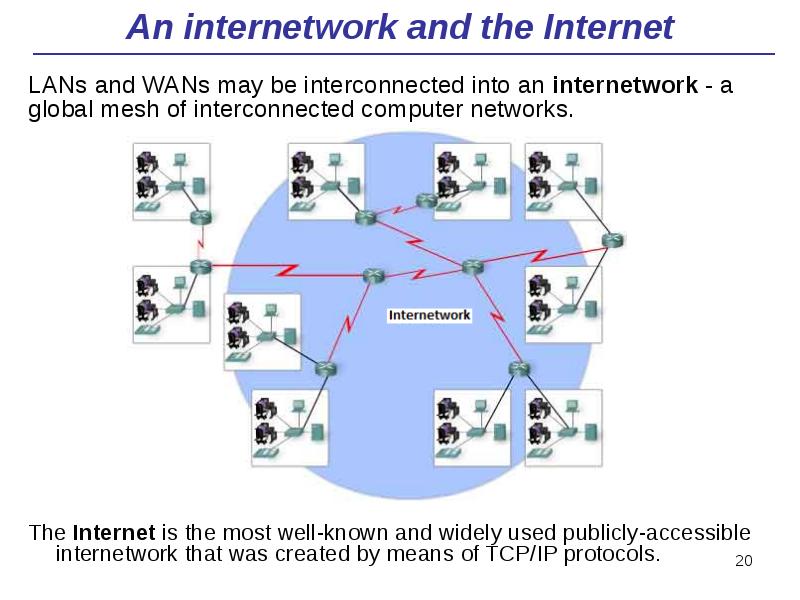
- 20. An internetwork and the Internet The Internet is the most well-known
- 21. Definition of the term “Protocol” In computer networking a protocol is
- 22. Protocol Stack or Protocol Suite A protocol stack is a set
- 23. Network Protocols Describe: the format or structure of the message
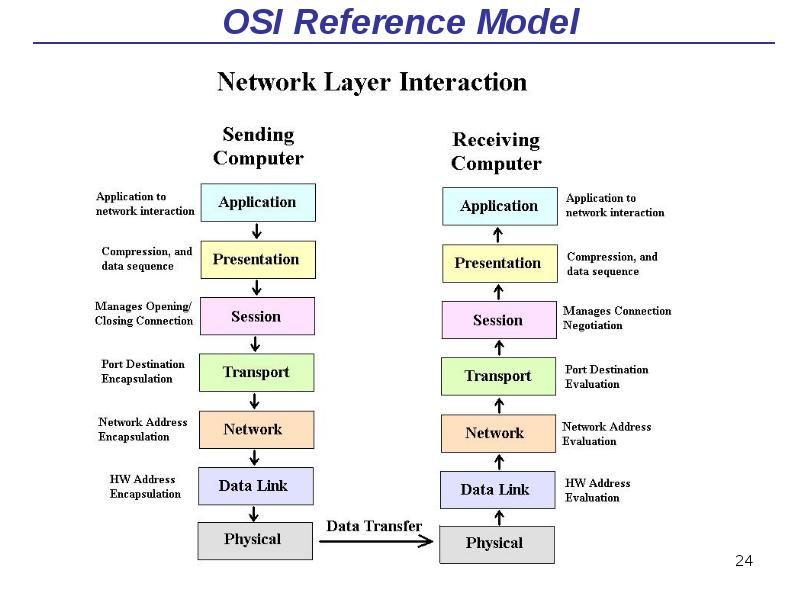
- 24. OSI Reference Model
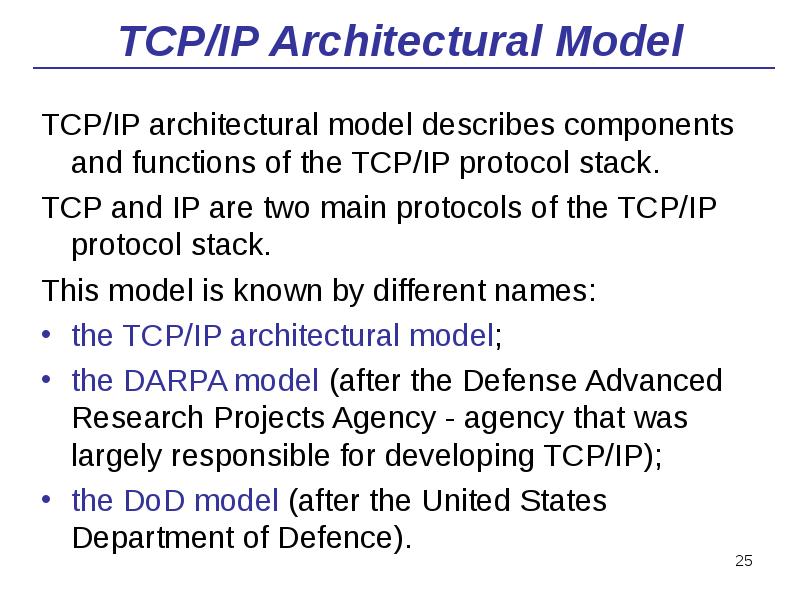
- 25. TCP/IP Architectural Model TCP/IP architectural model describes components and functions of
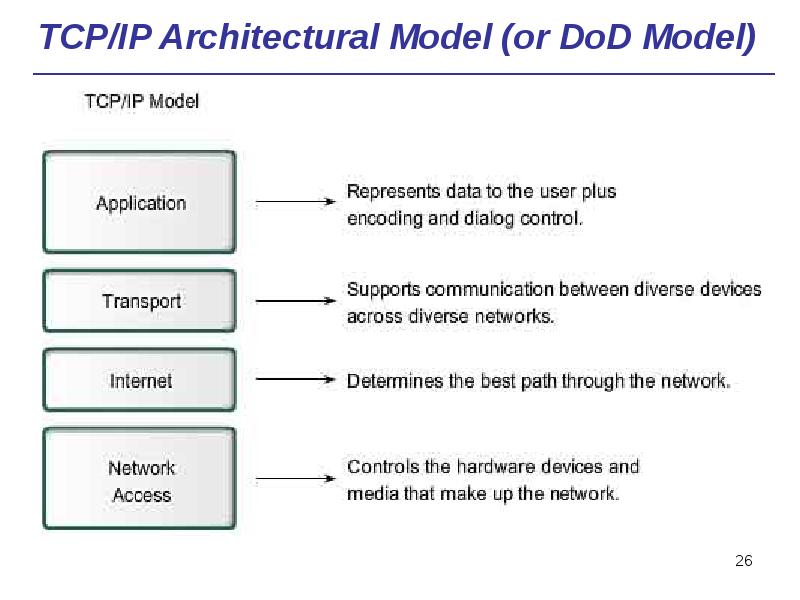
- 26. TCP/IP Architectural Model (or DoD Model)
- 27. The Comparison of the TCP/IP and OSI Models
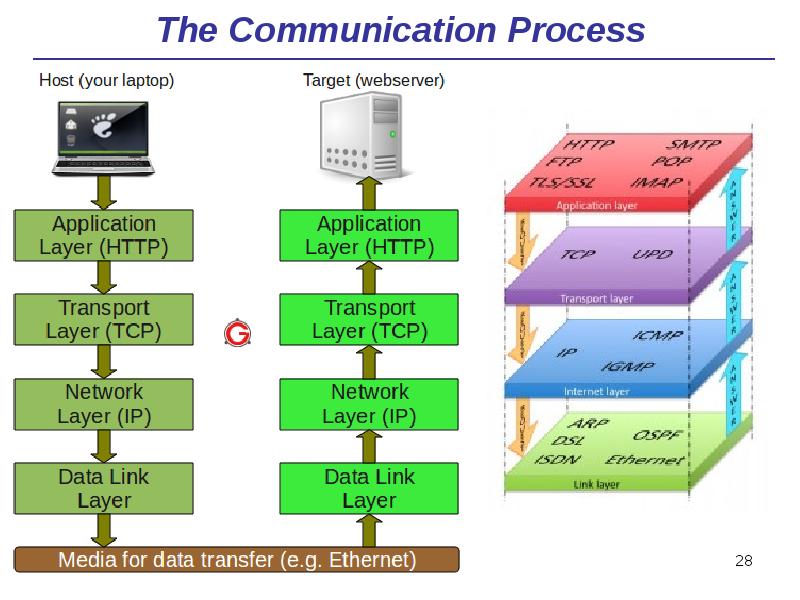
- 28. The Communication Process
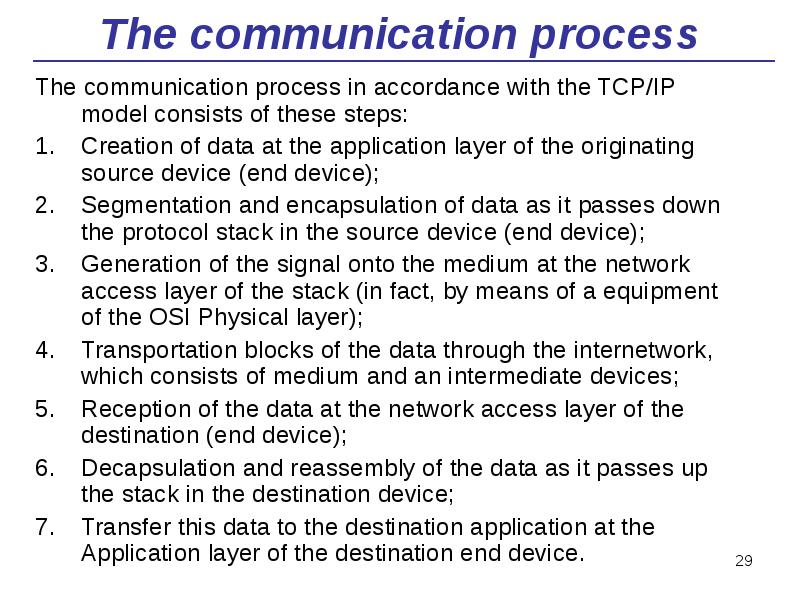
- 29. The communication process The communication process in accordance with the TCP/IP
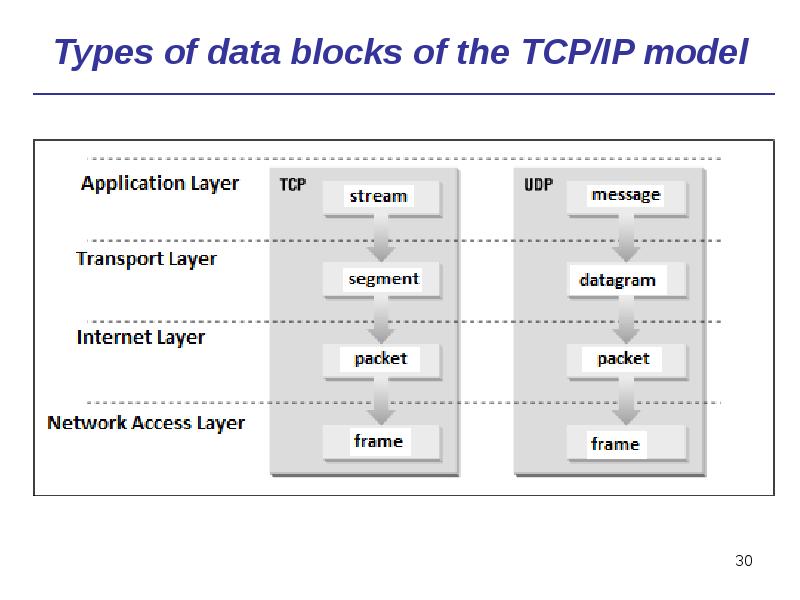
- 30. Types of data blocks of the TCP/IP model
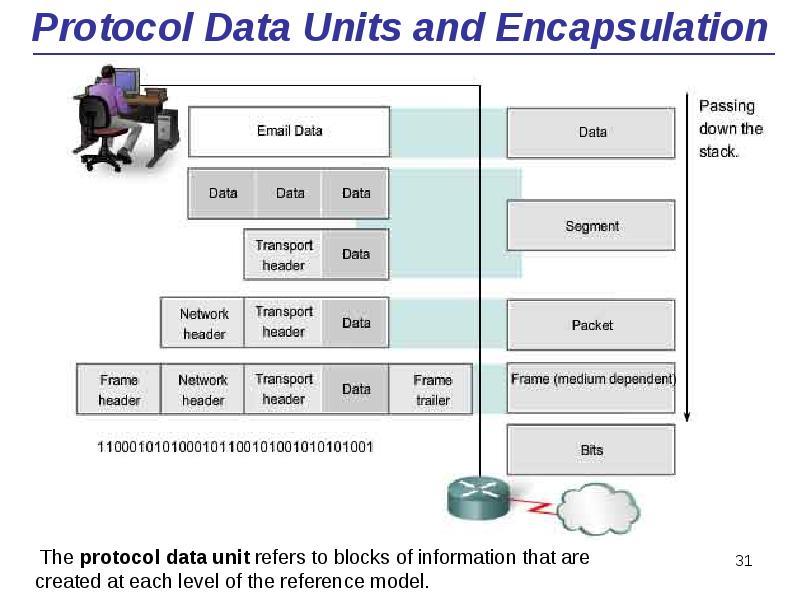
- 31. Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
- 32. Questions for self check What does the abbreviation ARPA mean? Tell
- 33. Скачать презентацию






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Lecture 1. TCP/IP Overview and History можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























