Lecture 5. Principles of Macroeconomics презентация
Содержание
- 2. In this Lecture:
- 3. Intertemporal decisions They involve a trade off across periods of time:
- 4. Our model Two period model: today and tomorrow For simplicity: income
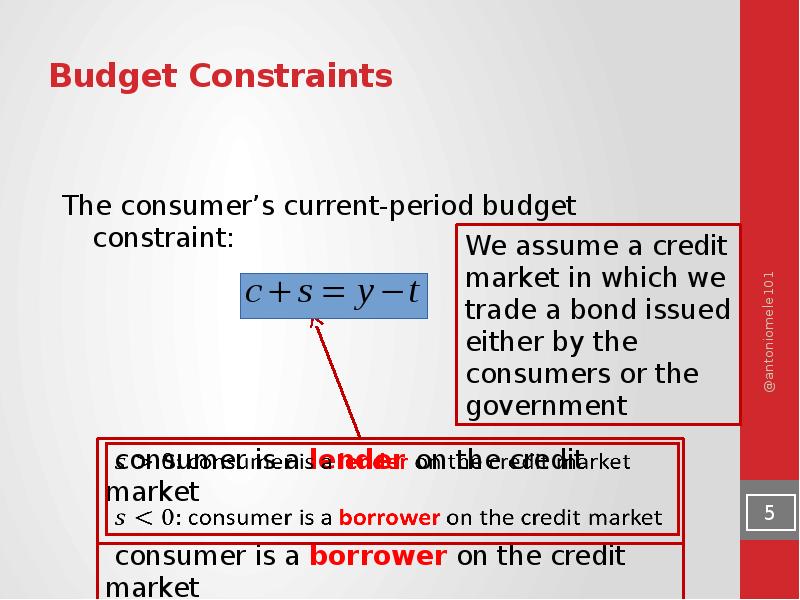
- 5. Budget Constraints
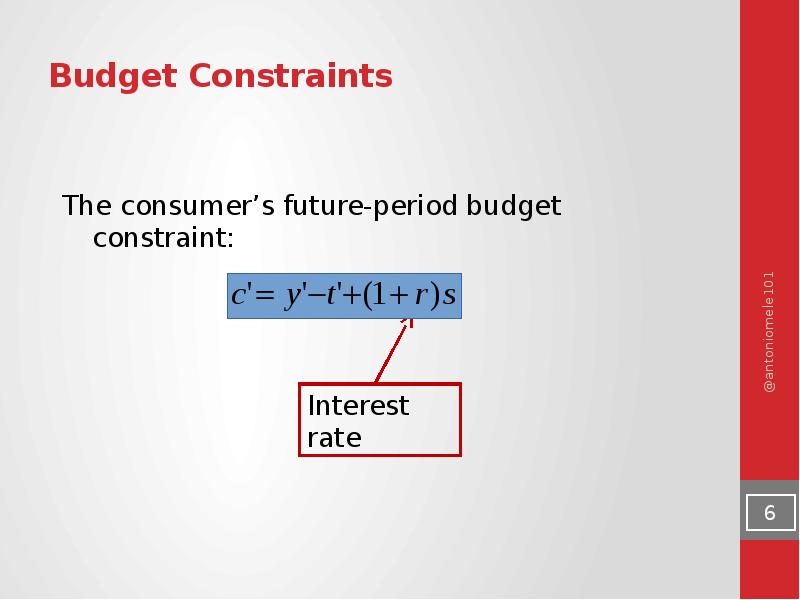
- 6. Budget Constraints
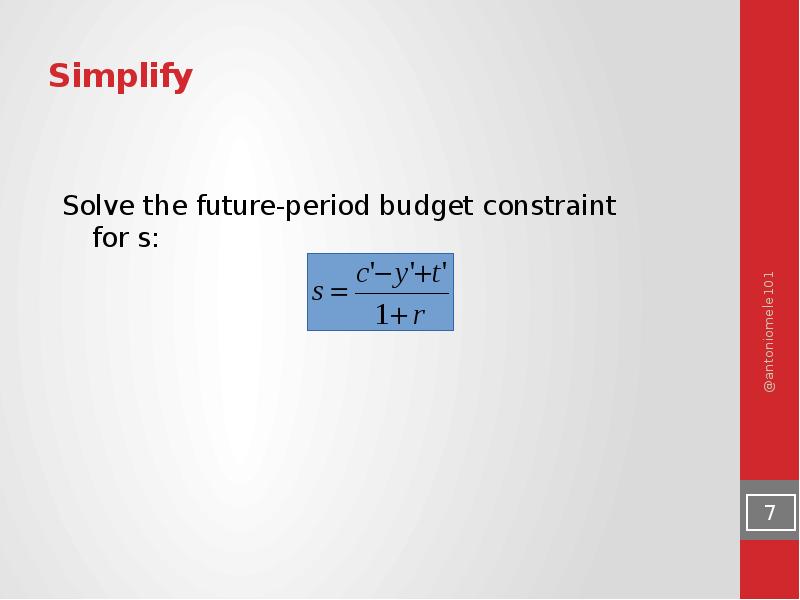
- 7. Simplify
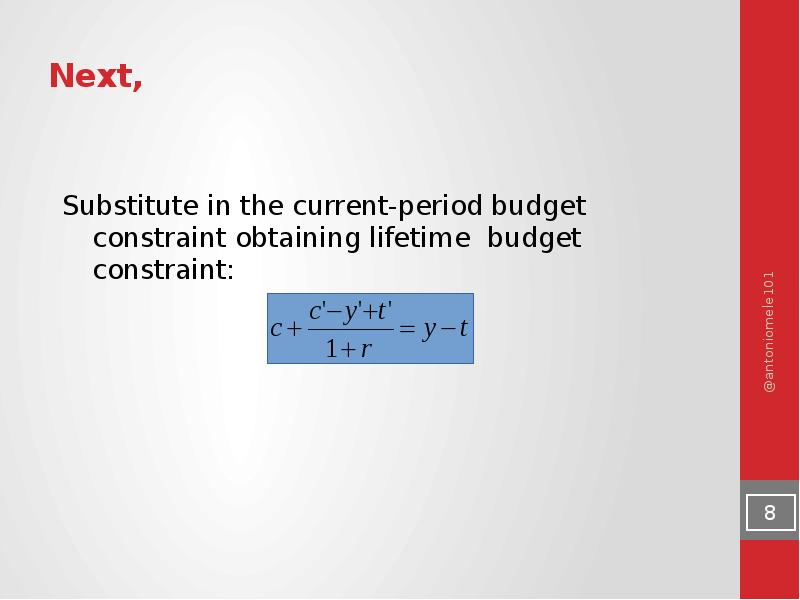
- 8. Next,
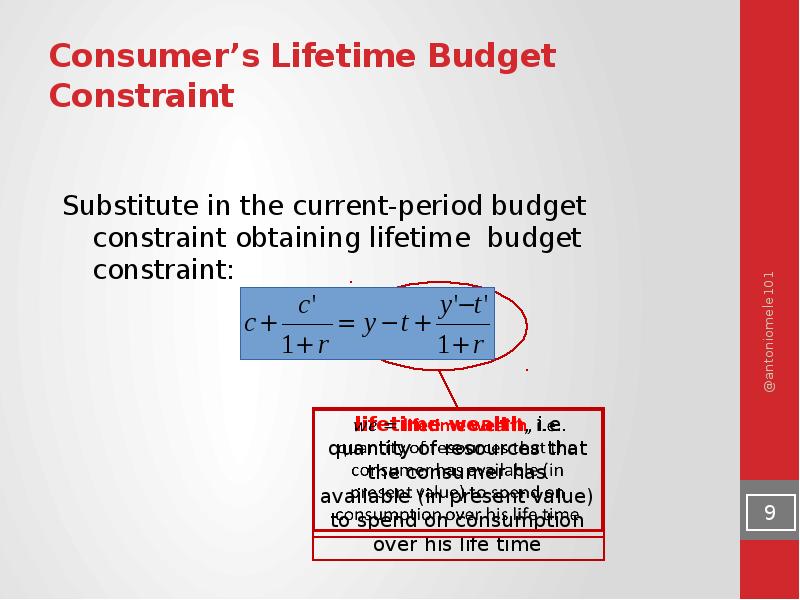
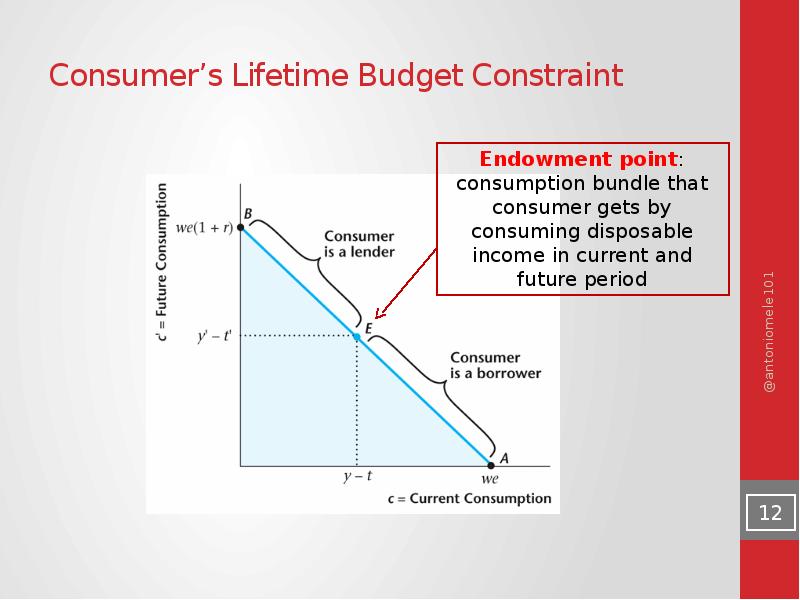
- 9. Consumer’s Lifetime Budget Constraint
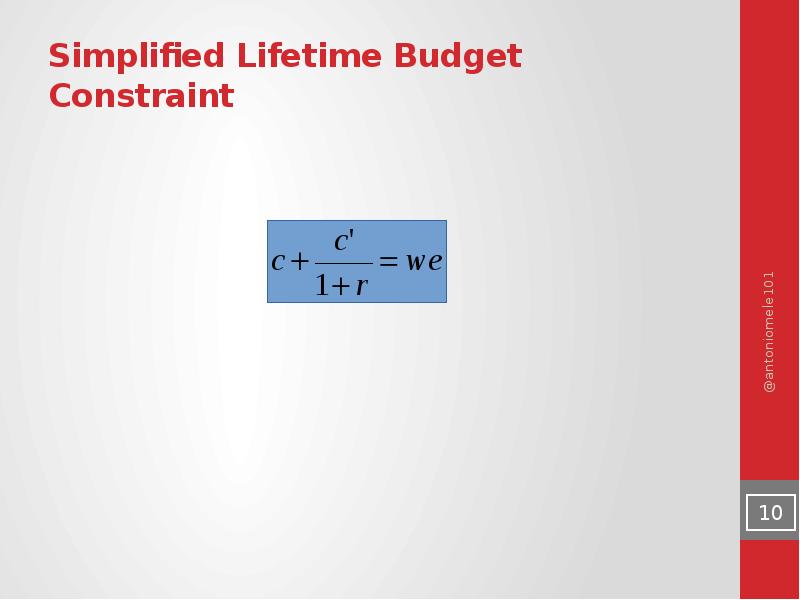
- 10. Simplified Lifetime Budget Constraint
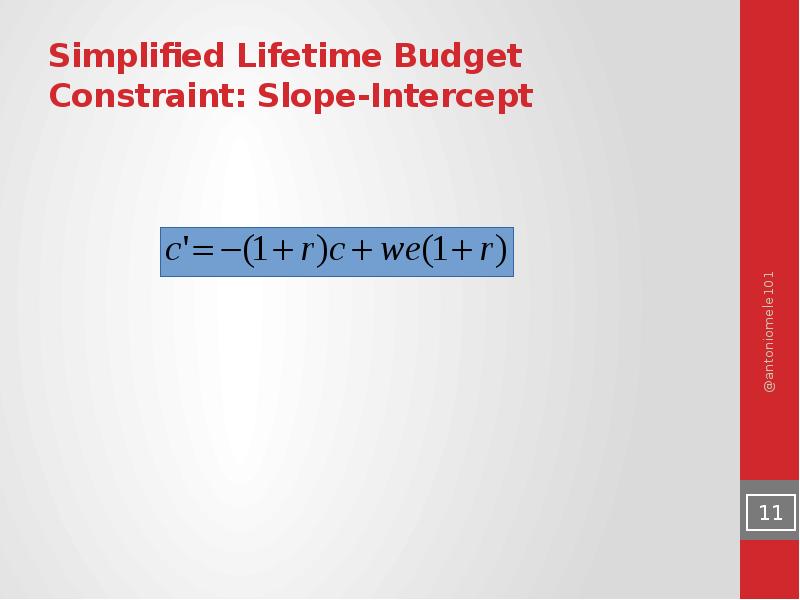
- 11. Simplified Lifetime Budget Constraint: Slope-Intercept
- 12. Consumer’s Lifetime Budget Constraint
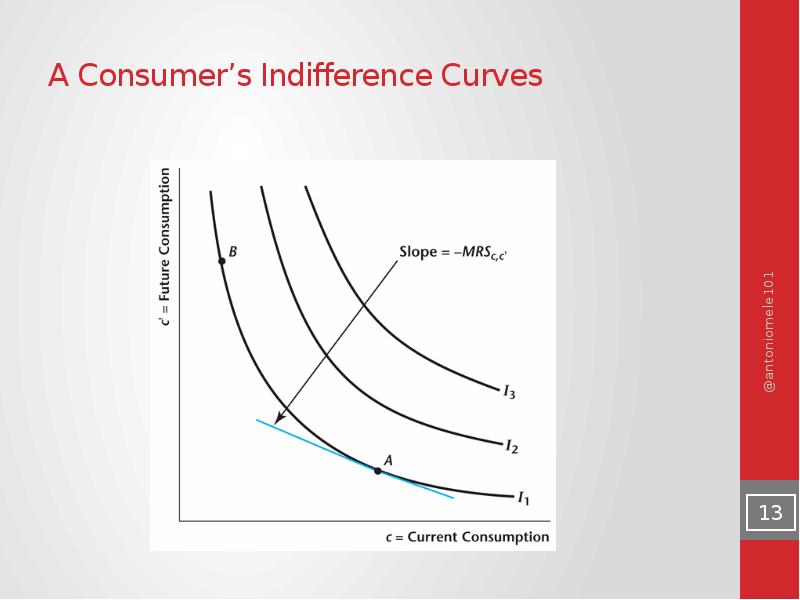
- 13. A Consumer’s Indifference Curves
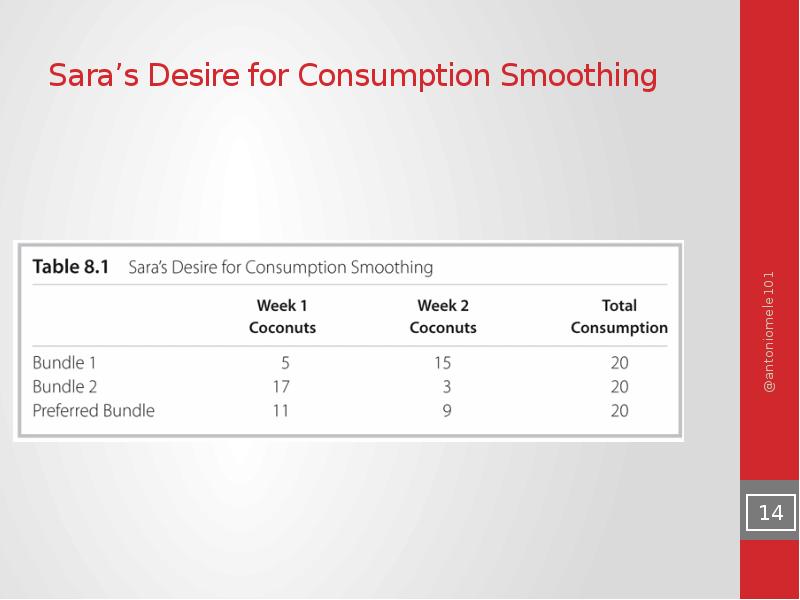
- 14. Sara’s Desire for Consumption Smoothing
- 15. Optimization
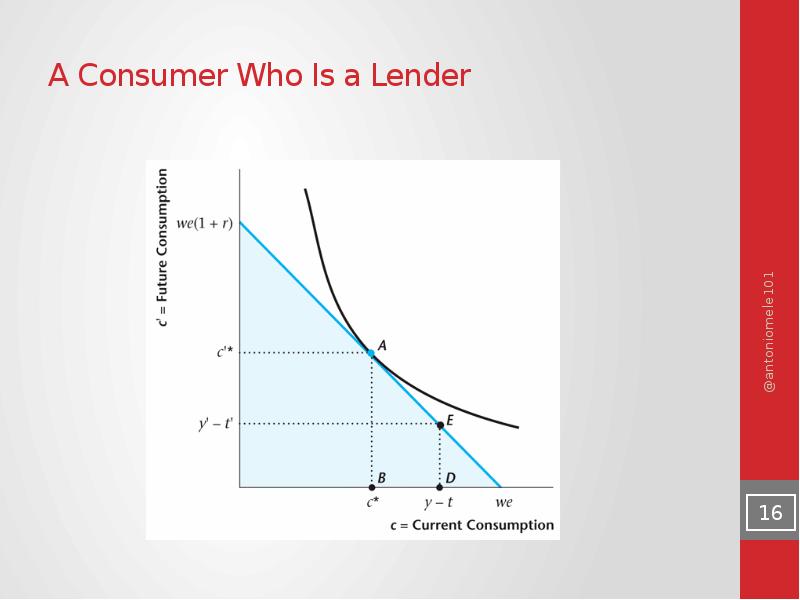
- 16. A Consumer Who Is a Lender
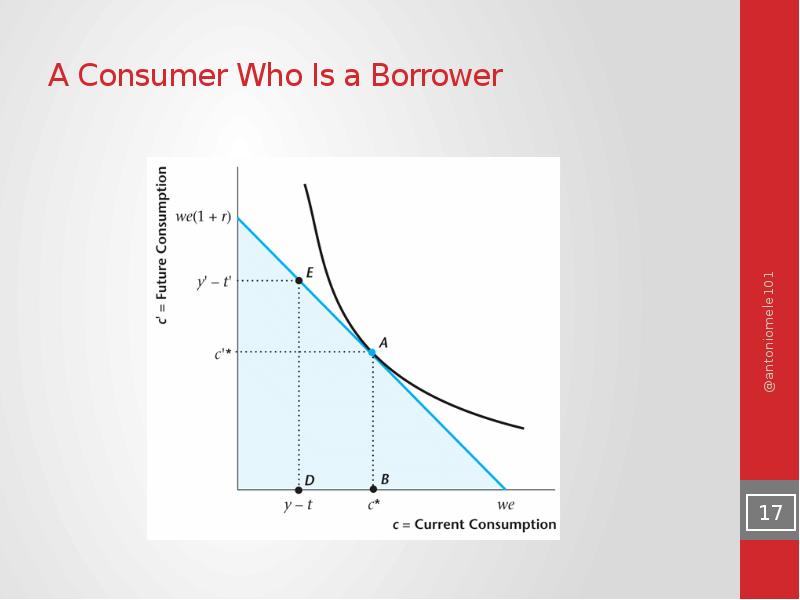
- 17. A Consumer Who Is a Borrower
- 18. An Increase in Current Income for the Consumer
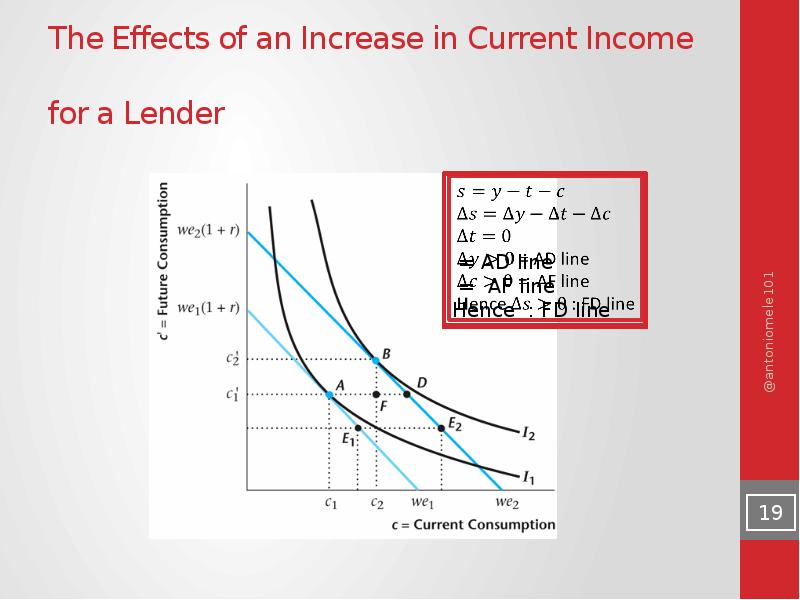
- 19. The Effects of an Increase in Current Income for a Lender
- 20. Observed Consumption-Smoothing Behavior
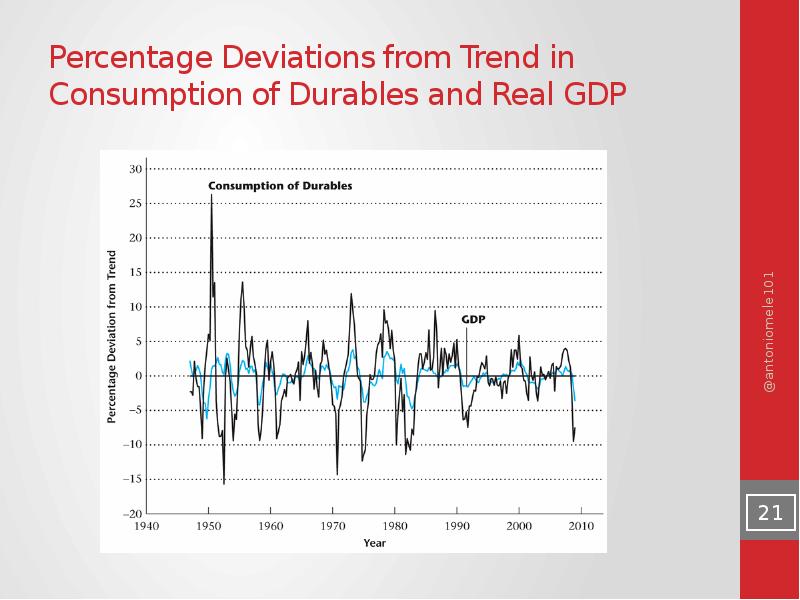
- 21. Percentage Deviations from Trend in Consumption of Durables and Real GDP
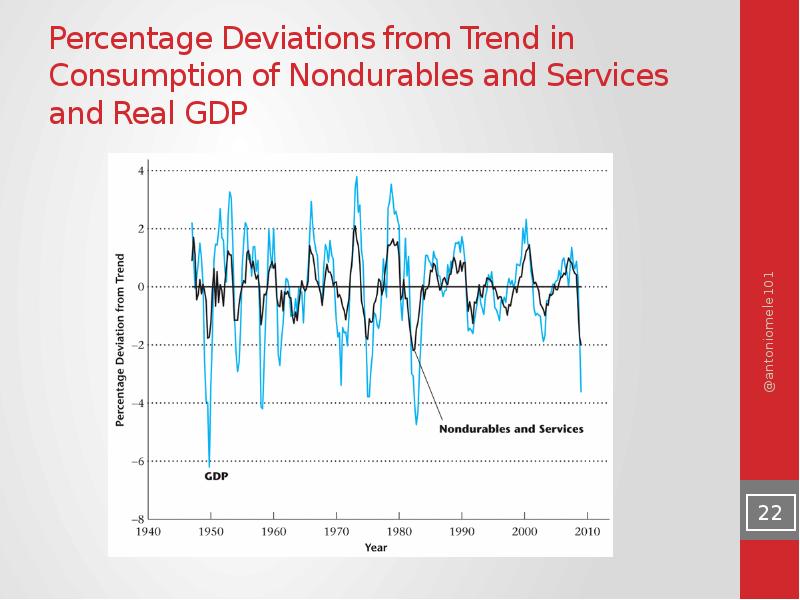
- 22. Percentage Deviations from Trend in Consumption of Nondurables and Services and
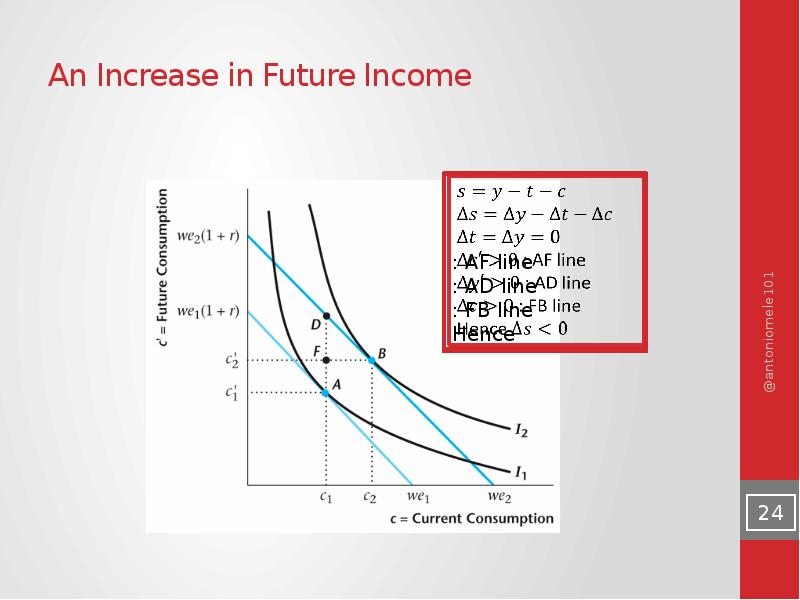
- 23. An Increase in Future Income for the Consumer
- 24. An Increase in Future Income
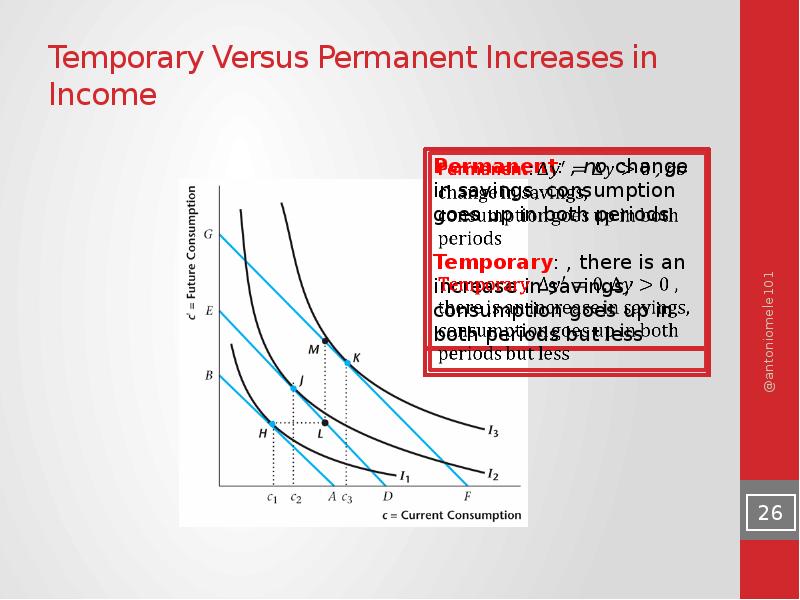
- 25. Temporary and Permanent Increases in Income
- 26. Temporary Versus Permanent Increases in Income
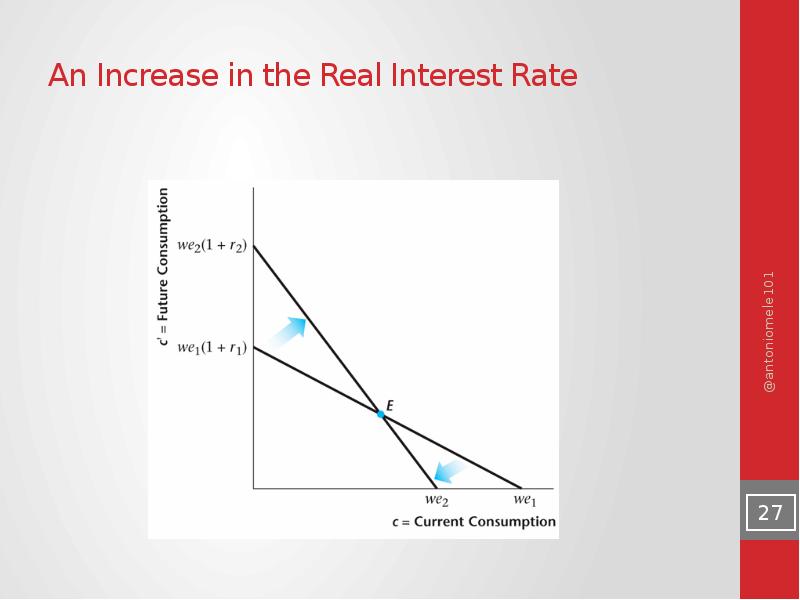
- 27. An Increase in the Real Interest Rate
- 28. An Increase in the Market Real Interest Rate
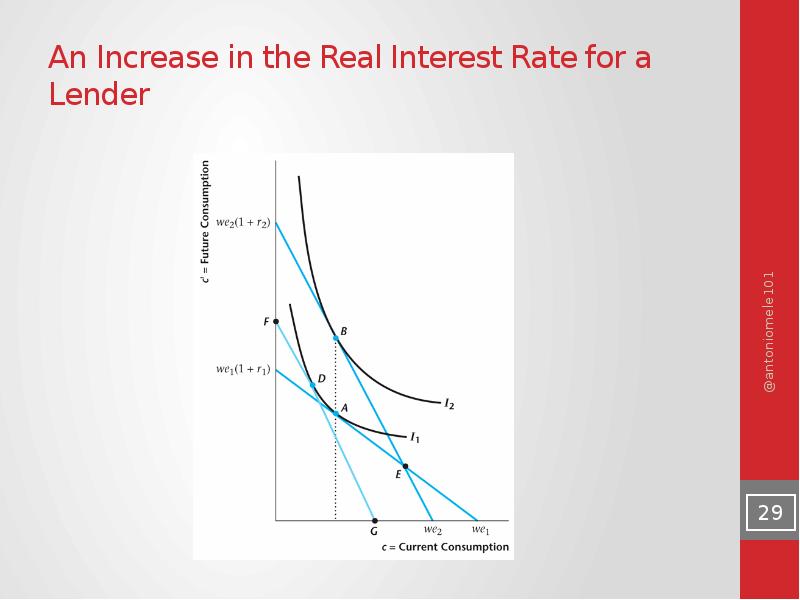
- 29. An Increase in the Real Interest Rate for a Lender
- 30. Effects of an Increase in the Real Interest Rate for a
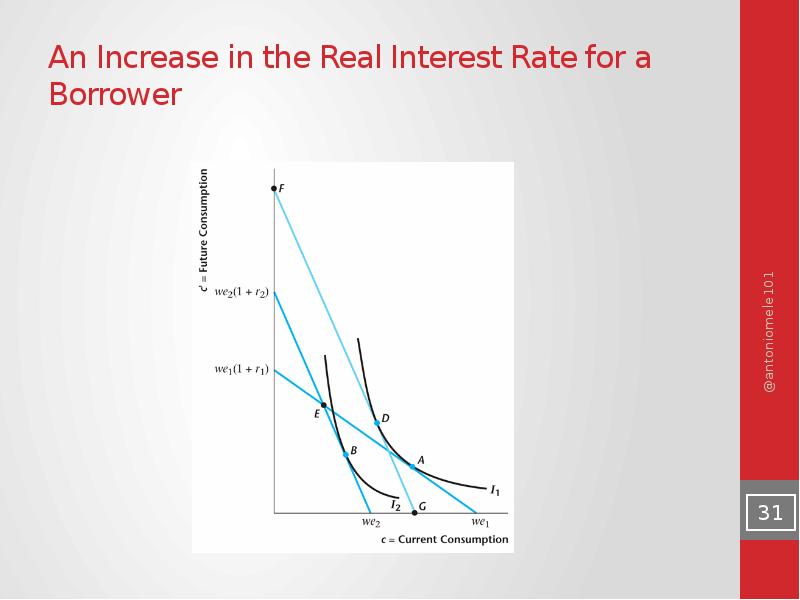
- 31. An Increase in the Real Interest Rate for a Borrower
- 32. Effects of an Increase in the Real Interest Rate for a
- 33. Introducing the government Government buys G, financed either with taxes or
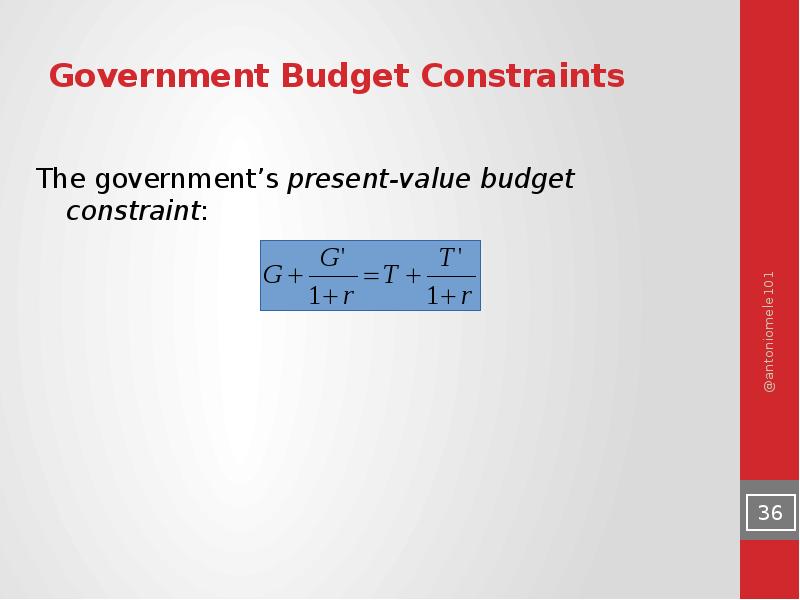
- 34. Government Budget Constraints
- 35. Government Budget Constraints
- 36. Government Budget Constraints
- 37. Competitive equilibrium Each consumer chooses current and future consumption and savings
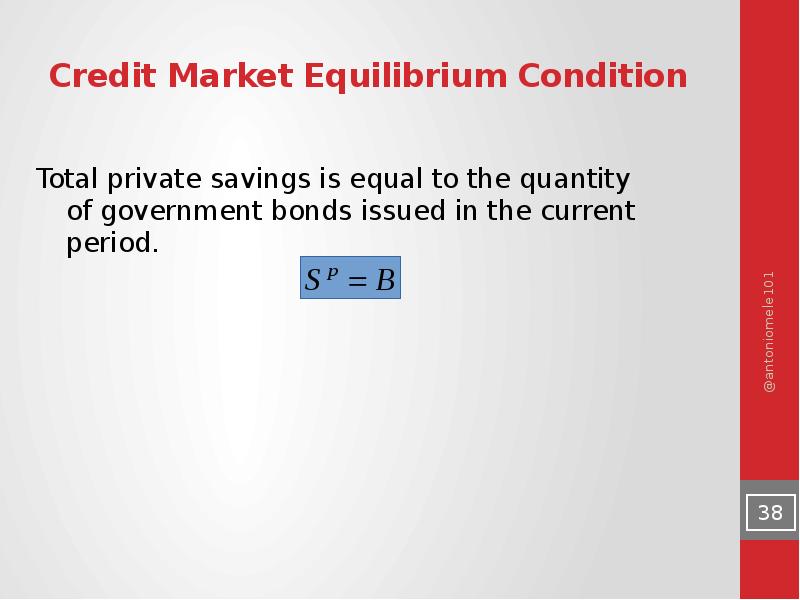
- 38. Credit Market Equilibrium Condition
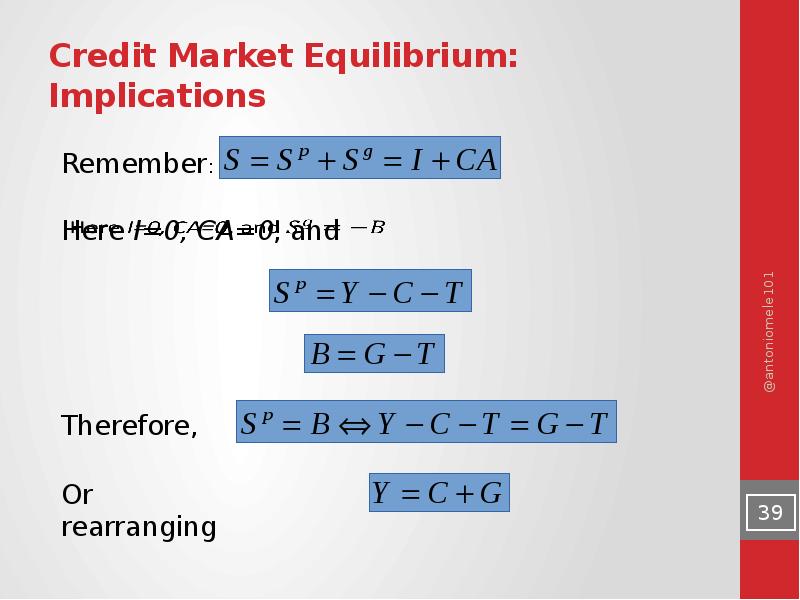
- 39. Credit Market Equilibrium: Implications
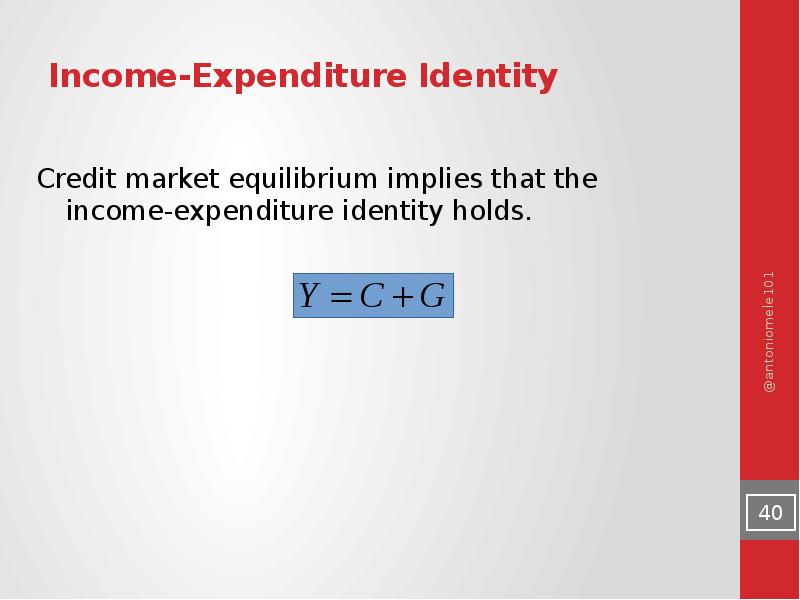
- 40. Income-Expenditure Identity
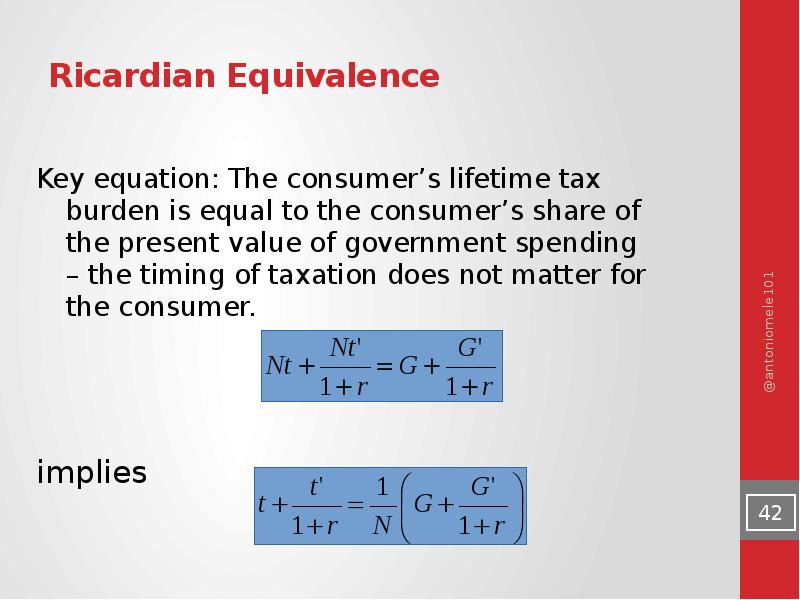
- 41. Ricardian Equivalence
- 42. Ricardian Equivalence
- 43. Ricardian Equivalence
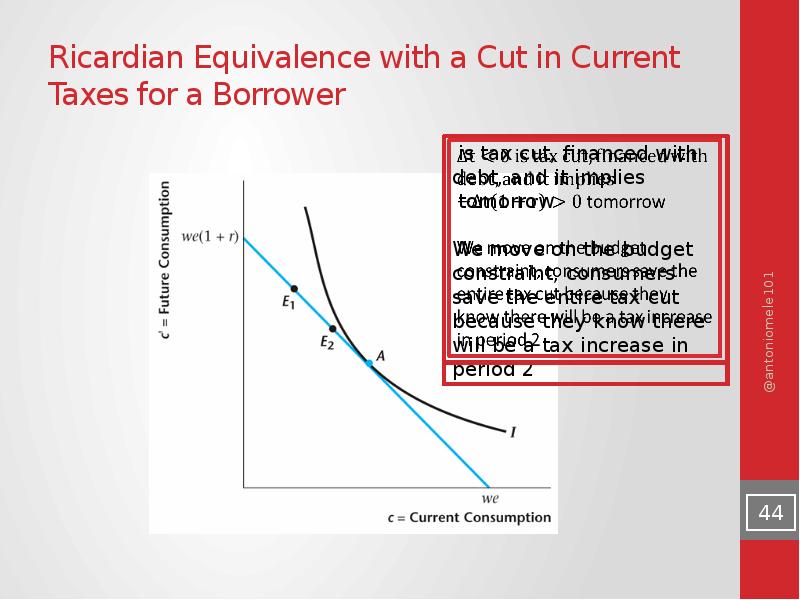
- 44. Ricardian Equivalence with a Cut in Current Taxes for a Borrower
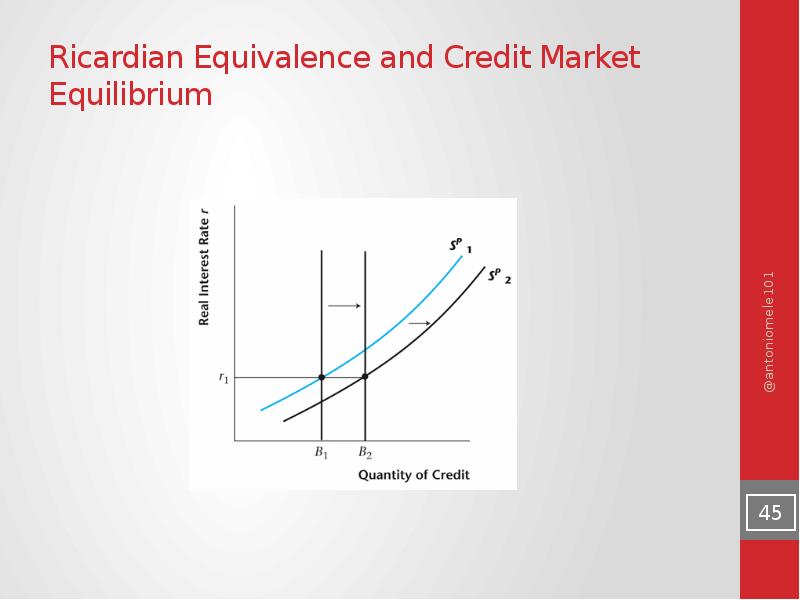
- 45. Ricardian Equivalence and Credit Market Equilibrium
- 46. Discussion of the assumptions Ricardian equivalence theorems says government debt represents
- 47. Readings Savings are generally a good idea http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C_8TGTKdrlY The cost of
- 48. Скачать презентацию




















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Lecture 5. Principles of Macroeconomics можно ниже:
Похожие презентации