Monopolistic competition. (Lecture 17) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Monopolistic Competition Imperfect competition refers to those market structures that fall
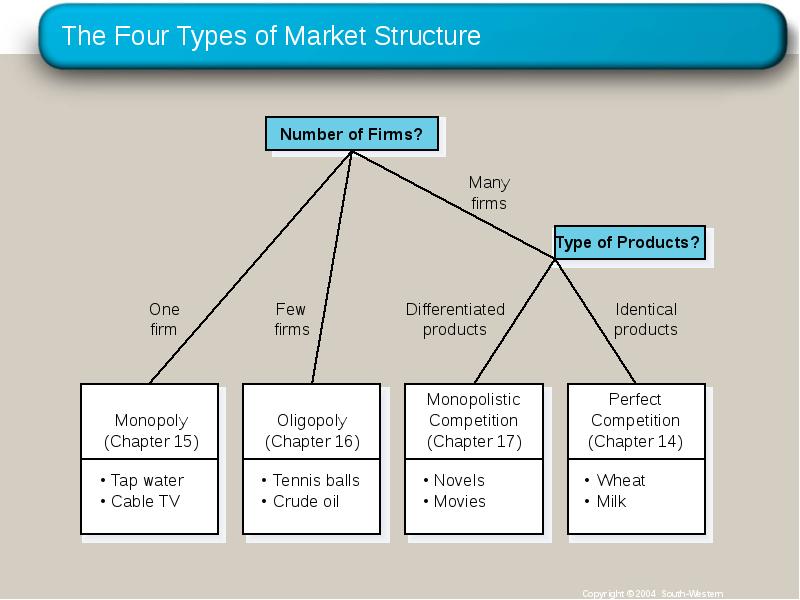
- 3. The Four Types of Market Structure
- 4. Monopolistic Competition Types of Imperfectly Competitive Markets Monopolistic Competition Many firms
- 5. Monopolistic Competition Markets that have some features of competition and some
- 6. Monopolistic Competition Attributes of Monopolistic Competition Many sellers Product differentiation Free
- 7. Monopolistic Competition Many Sellers There are many firms competing for
- 8. Monopolistic Competition Product Differentiation Each firm produces a product that
- 9. Monopolistic Competition Free Entry or Exit Firms can enter or
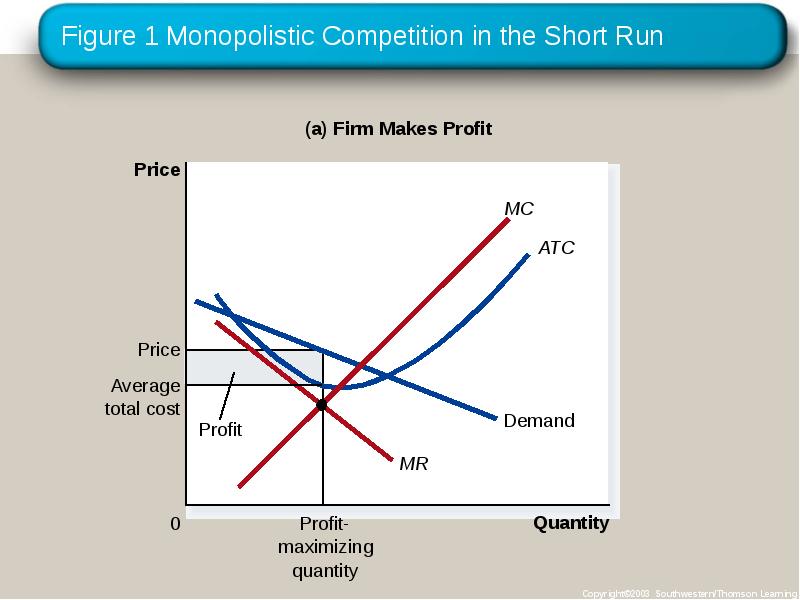
- 10. COMPETITION WITH DIFFERENTIATED PRODUCTS The Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short
- 11. Figure 1 Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run
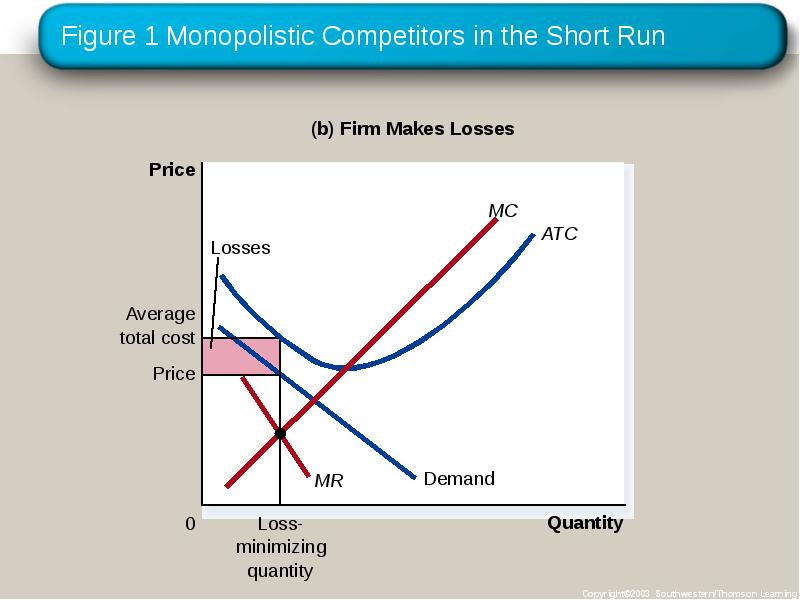
- 12. COMPETITION WITH DIFFERENTIATED PRODUCTS The Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short
- 13. Figure 1 Monopolistic Competitors in the Short Run
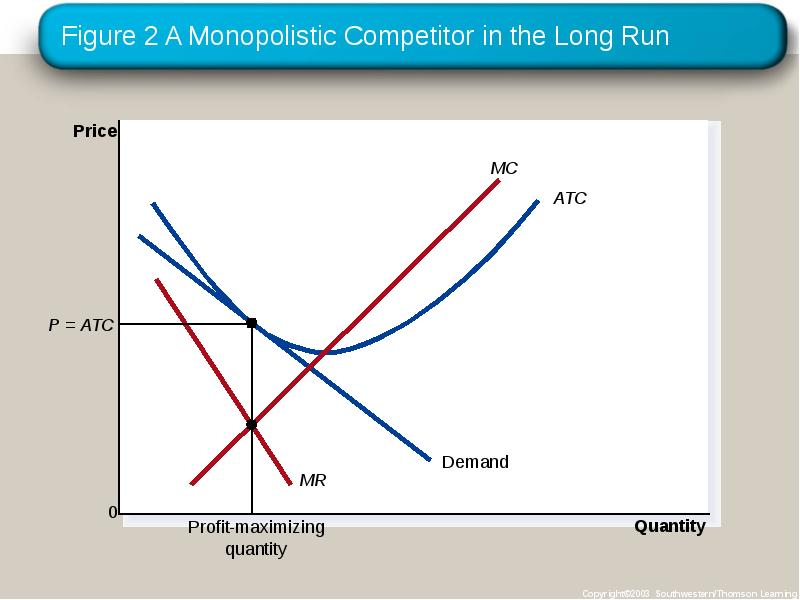
- 14. The Long-Run Equilibrium Firms will enter and exit until the firms
- 15. Figure 2 A Monopolistic Competitor in the Long Run
- 16. Long-Run Equilibrium Two Characteristics As in a monopoly, price exceeds
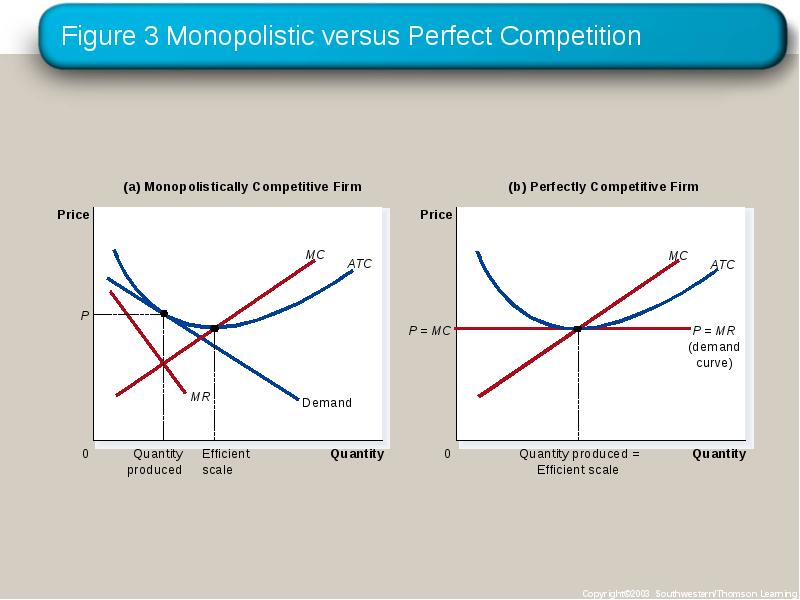
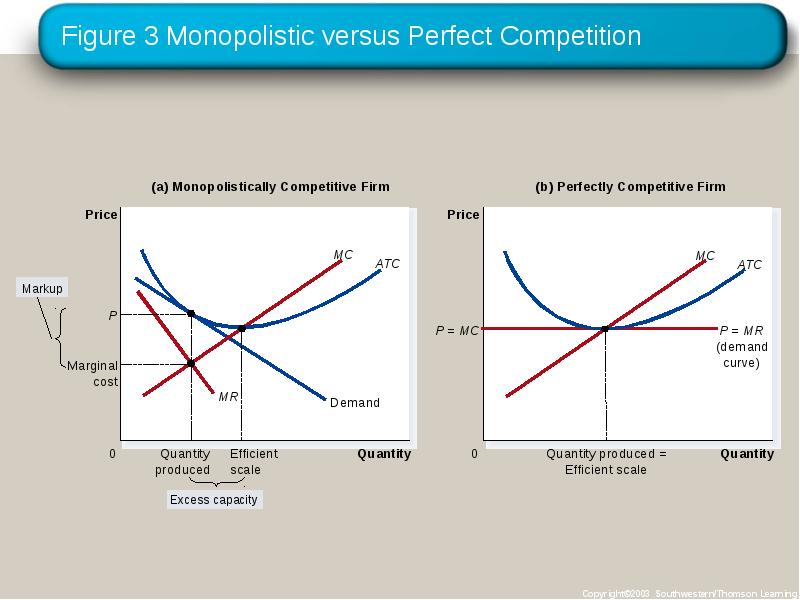
- 17. Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition There are two noteworthy differences between monopolistic
- 18. Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition Excess Capacity There is no excess capacity
- 19. Figure 3 Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition
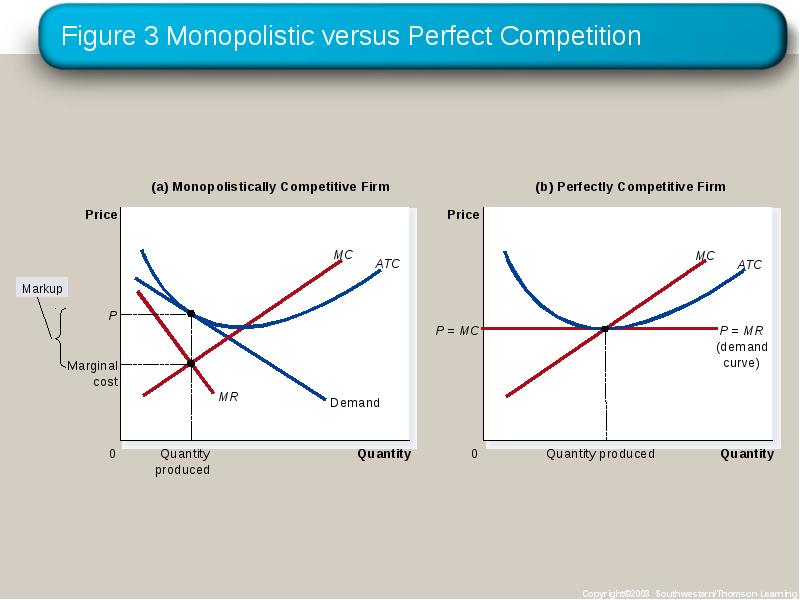
- 20. Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition Markup Over Marginal Cost For a competitive
- 21. Figure 3 Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition
- 22. Figure 3 Monopolistic versus Perfect Competition
- 23. Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society Monopolistic competition does not
- 24. Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society There is the normal
- 25. Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society Another way in which
- 26. Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society Externalities of entry include:
- 27. Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society The product-variety externality:
- 28. ADVERTISING When firms sell differentiated products and charge prices above marginal
- 29. ADVERTISING Firms that sell highly differentiated consumer goods typically spend between
- 30. ADVERTISING Critics of advertising argue that firms advertise in order to
- 31. ADVERTISING Defenders argue that advertising provides information to consumers They also
- 32. Brand Names Critics argue that brand names cause consumers to perceive
- 33. Brand Names Economists have argued that brand names may be a
- 34. Summary A monopolistically competitive market is characterized by three attributes: many
- 35. Summary Monopolistic competition does not have all of the desirable properties
- 36. Summary The product differentiation inherent in monopolistic competition leads to the
- 37. Скачать презентацию





























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Monopolistic competition. (Lecture 17) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации