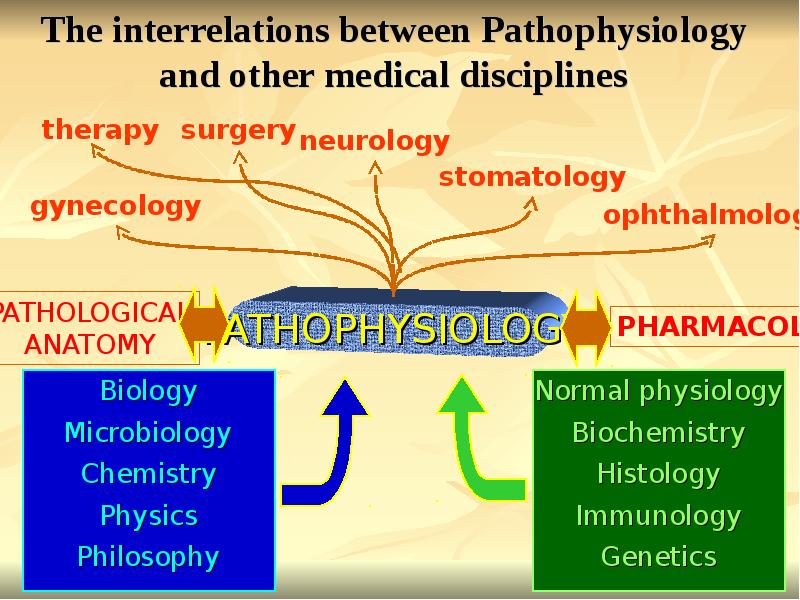
Pathophysiology. (Subject 1) презентация
Содержание
- 3. Head of Pathophysiology Department KOLESNIK Yuri Mikhailovich Rector of
- 4. Pathophysiology PATHOS – disease PHYSIS – essence LOGOS – knowledge
- 5. Pathophysiology tasks Creation of the disease general conception (general nosology) Study
- 6. Experimental therapy Working out of new methods of diseases treatment
- 7. The main methods of Pathophysiology Experimental modelling of: pathologic processes on
- 8. Pathophysiological experiment It includes four stages: Planning the experiment; Carrying out
- 9. The main methods of Pathophysiology Clinical examination of various diseases with
- 10. Scientific work of department neuro-endocrine mechanisms of endocrine pancreas regulation
- 11. Pathogenesis is the study of general mechanisms of diseases onset and
- 12. The role of etiologic factor in disease development Etiologic factor can
- 13. The main link of pathogenesis The main link of pathogenesis
- 14. The role of local and general changes in the organism
- 15. The role of pathogenic and adaptive reactions during disease development Pathogenesis
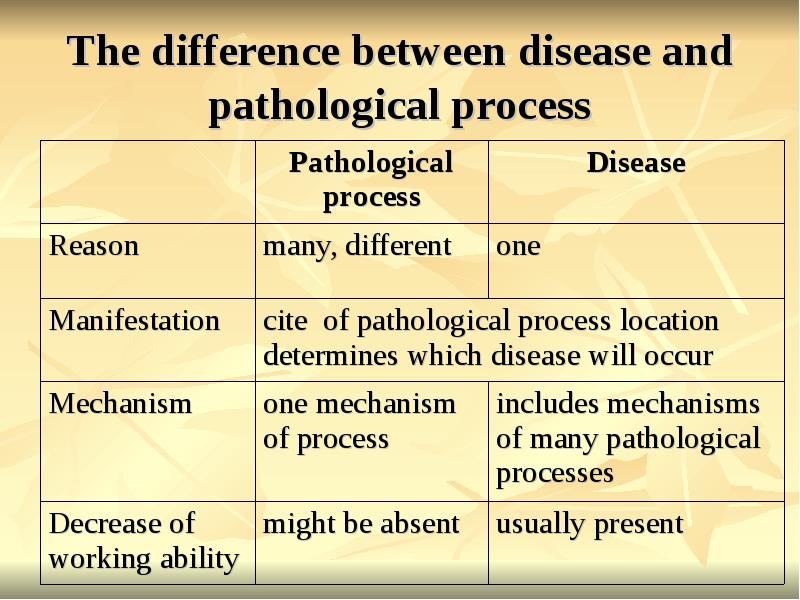
- 16. The difference between disease and pathological process
- 17. Civilization (lifestyle) diseases Positive consequences of civilization: resistance to infections, increased
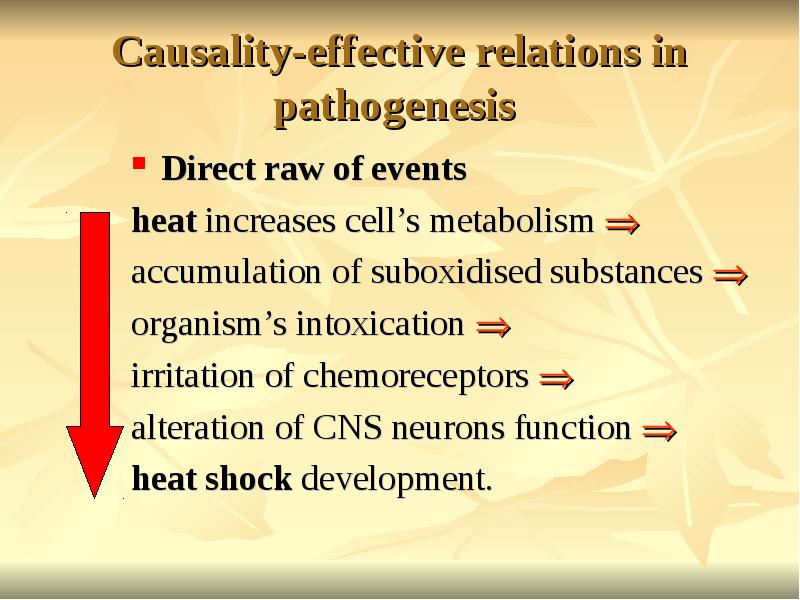
- 18. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Direct raw of events heat
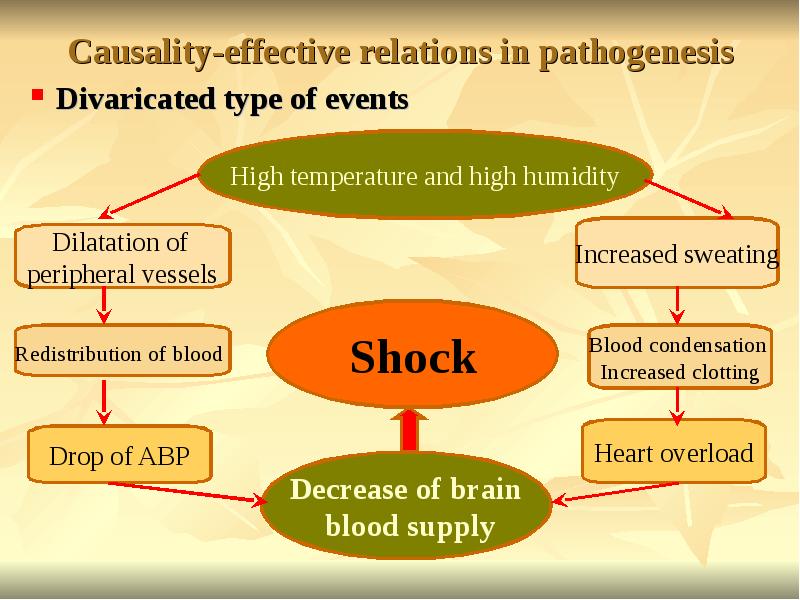
- 19. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Divaricated type of events
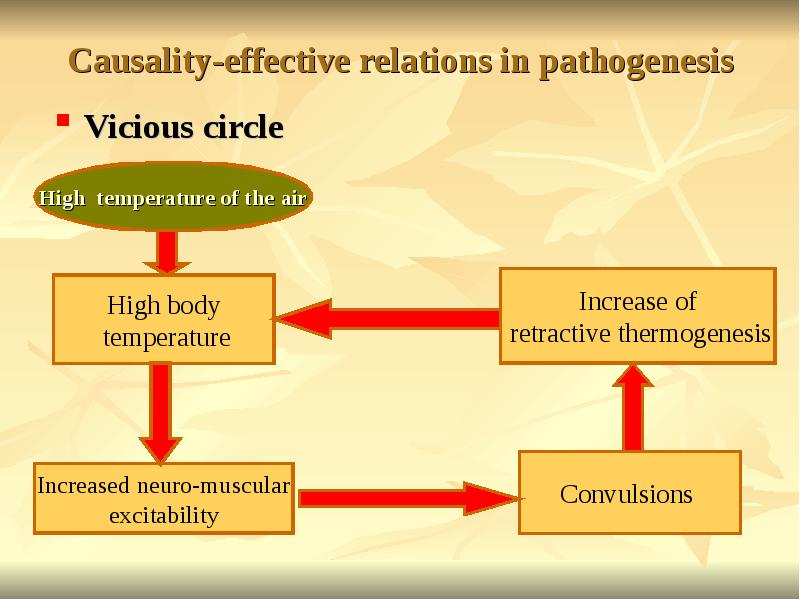
- 20. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Vicious circle
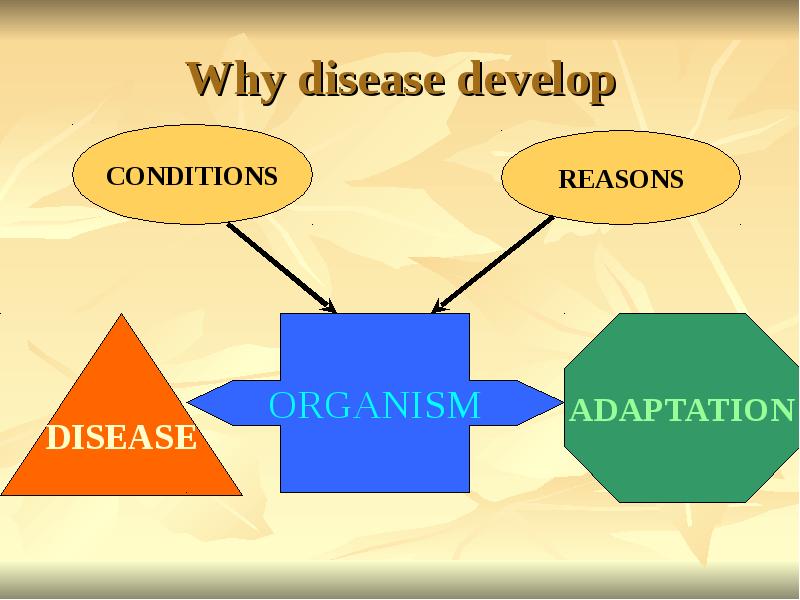
- 21. Why disease develop
- 22. Organism responce Reactivity - ability to respond to internal and external
- 23. Types of reactivity Levels: normal, increased, low, absent (anergy) Species
- 24. Types of resistance Passive resistance – barrier systems, bactericidial agents,
- 25. Mechanisms of reactivity and resistance formation General mechanisms – influence
- 26. Скачать презентацию



















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации