Physical chemistry of surface phenomena. Basics of adsorptive therapy презентация
Содержание
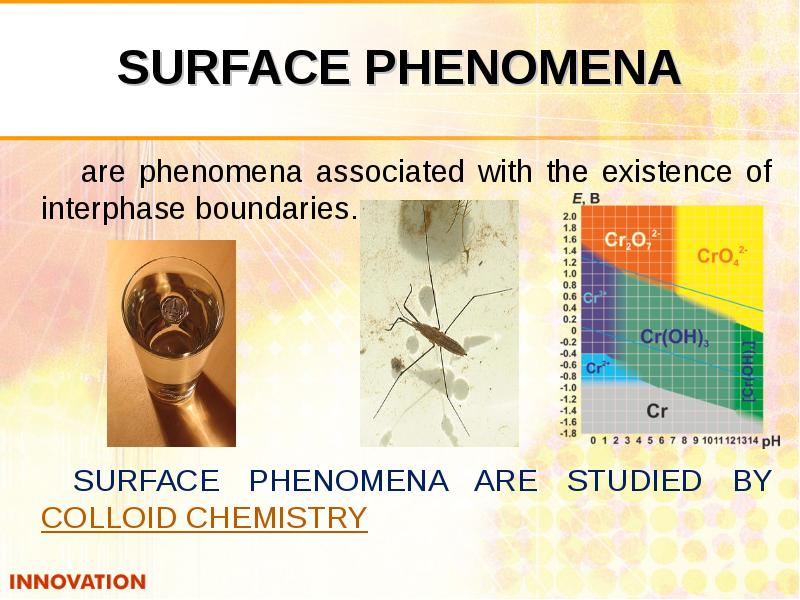
- 2. SURFACE PHENOMENA are phenomena associated with the existence of interphase boundaries.
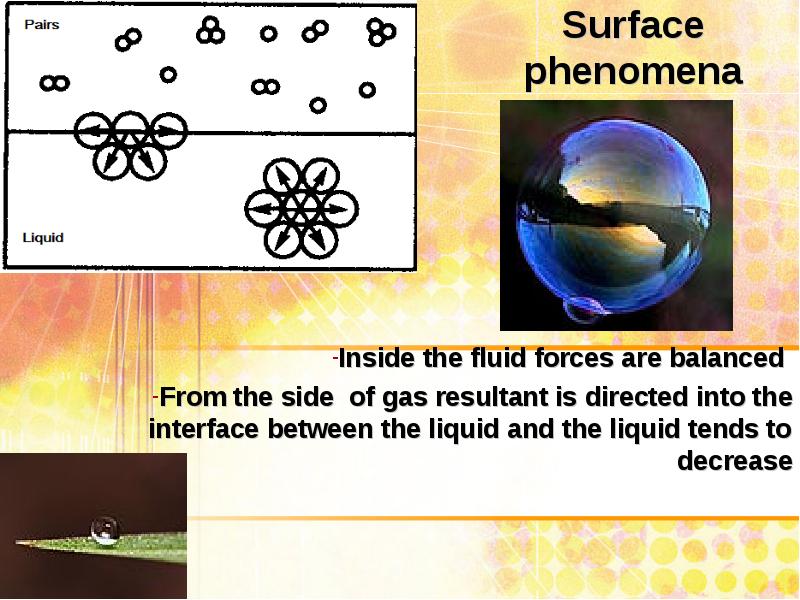
- 3. Surface phenomena Inside the fluid forces are balanced From the
- 4. Surface phenomena The increased surface area of the phase separation is
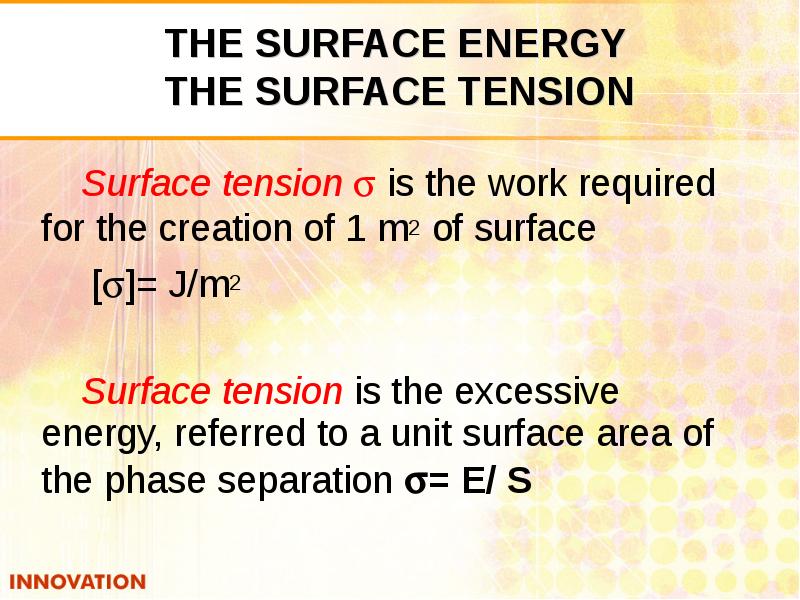
- 5. THE SURFACE ENERGY THE SURFACE TENSION Surface tension is the
- 6. Surface tension Surface tension depends on: the nature of fluid σ(Н2О)=72,8
- 7. SORPTION
- 8. Medical & biological importance: Assimilation of nutrients and drugs
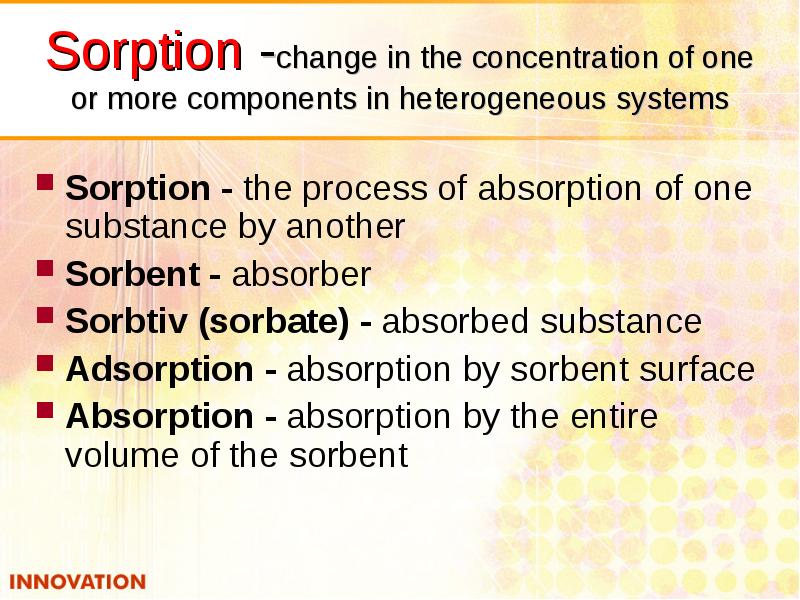
- 9. Sorption -change in the concentration of one or more components in
- 10. Adsorption Adsorption is spontaneous change of component concentration in the surface
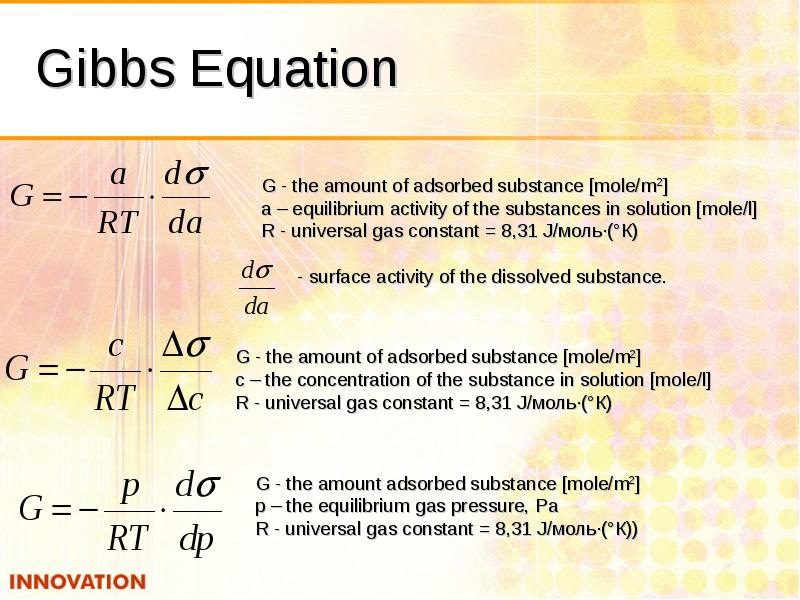
- 11. Gibbs Equation
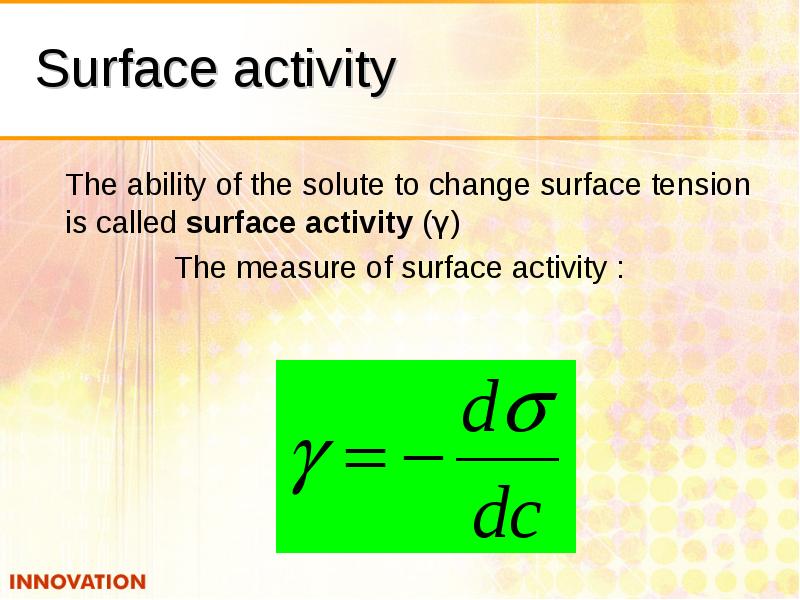
- 12. Surface activity The ability of the solute to change surface tension
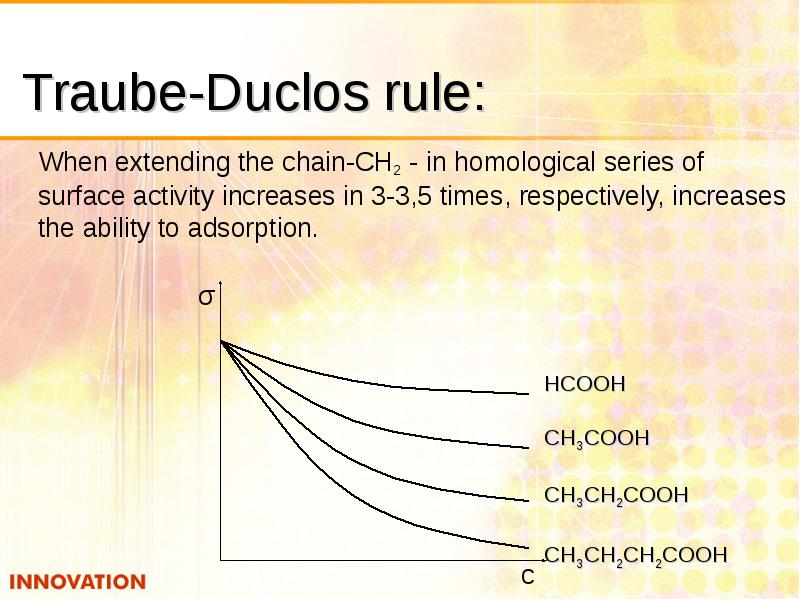
- 13. Traube-Duclos rule: When extending the chain-CH2 - in homological series of
- 14. SAS, SIS, SNS Surface-active substances (SAS): reduce σ solvent. σ solution
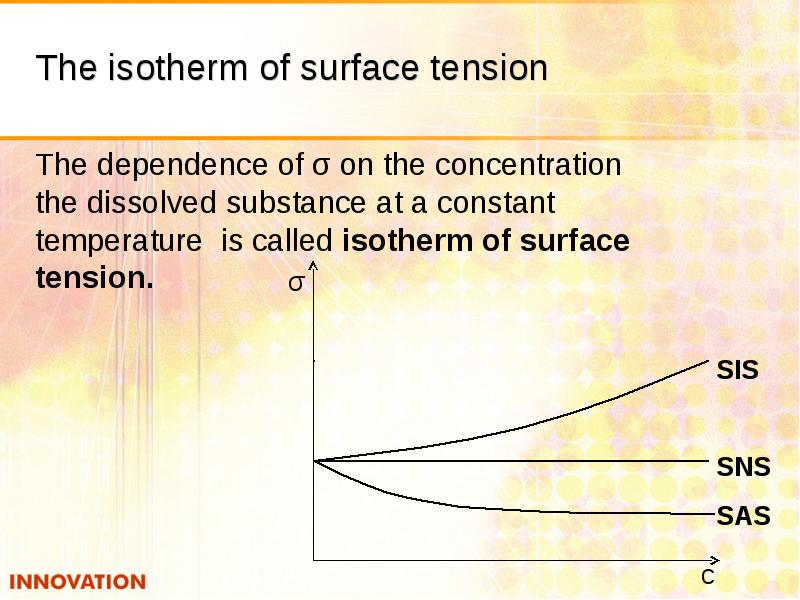
- 15. The isotherm of surface tension The dependence of σ on the
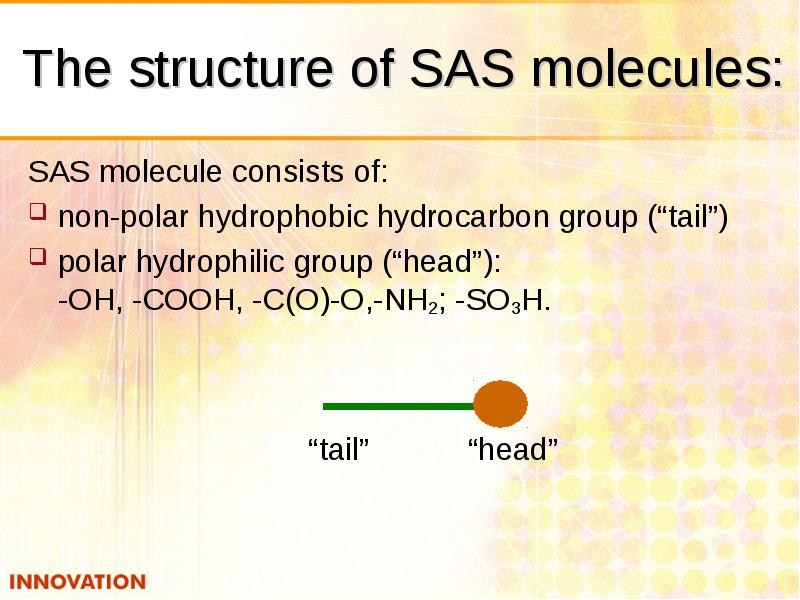
- 16. The structure of SAS molecules: SAS molecule consists of: non-polar hydrophobic
- 17. ADSORPTION ON THE SOLUTION-GAS ADSORPTION ON THE SOLUTION-GAS BORDER
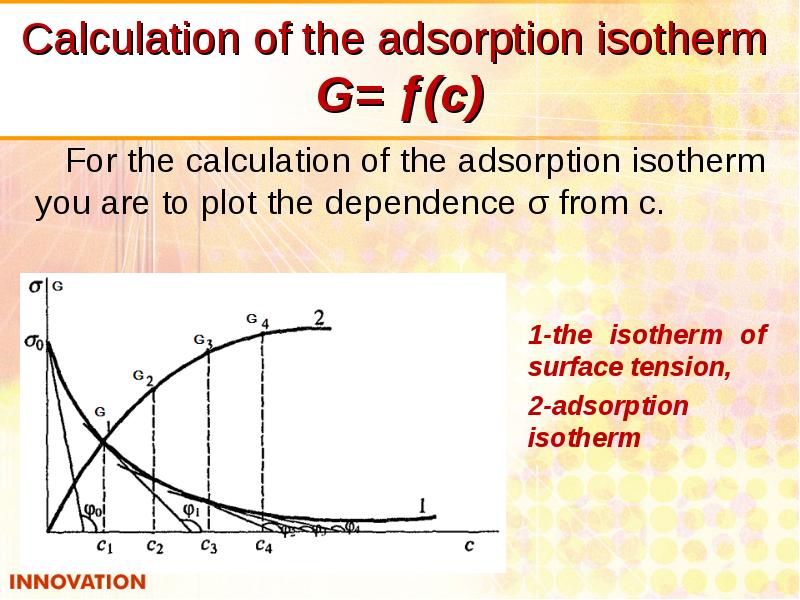
- 18. Calculation of the adsorption isotherm G= ƒ(с) For the calculation of
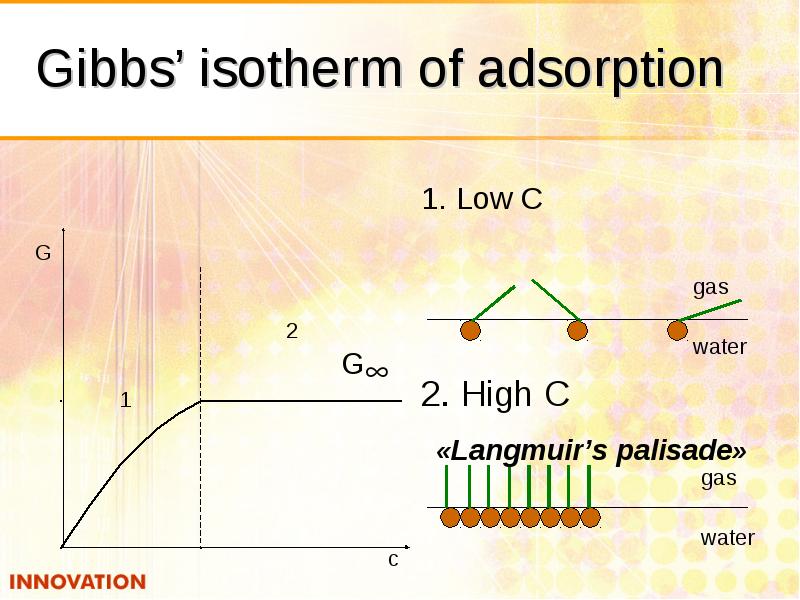
- 19. Gibbs’ isotherm of adsorption 1. Low С
- 20. ADSORPTION ON THE SOLID-GAS ADSORPTION ON THE SOLID-GAS BORDER
- 21. Adsorption by solids The adsorption value depends on: 1. The size
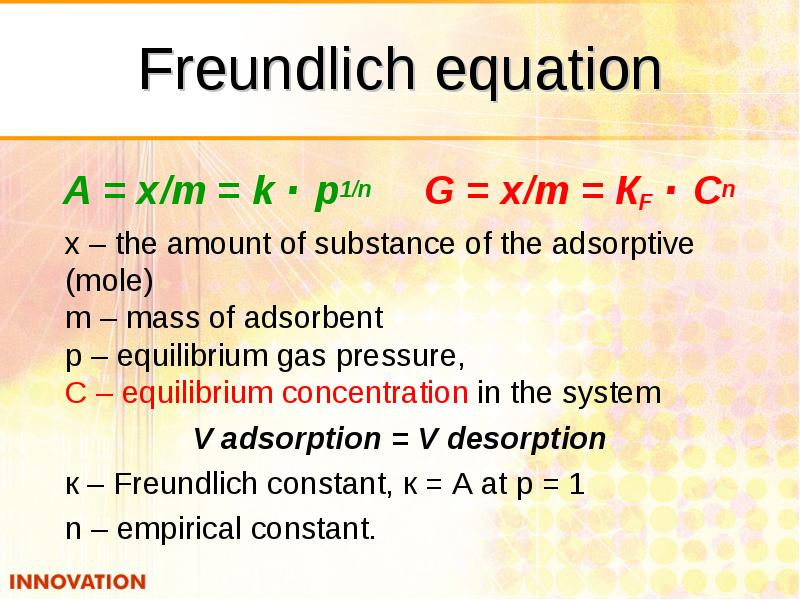
- 22. Freundlich equation А = x/m = k · p1/n G
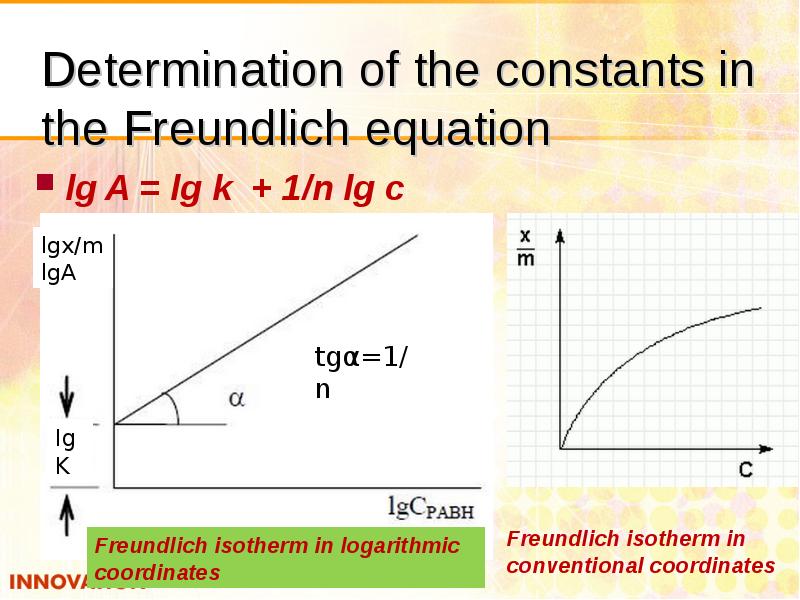
- 23. Determination of the constants in the Freundlich equation lg A =
- 24. The theory of Langmuir 1) On each absorption place on the
- 25. The theory of Langmuir According to this theory localization adsorption can
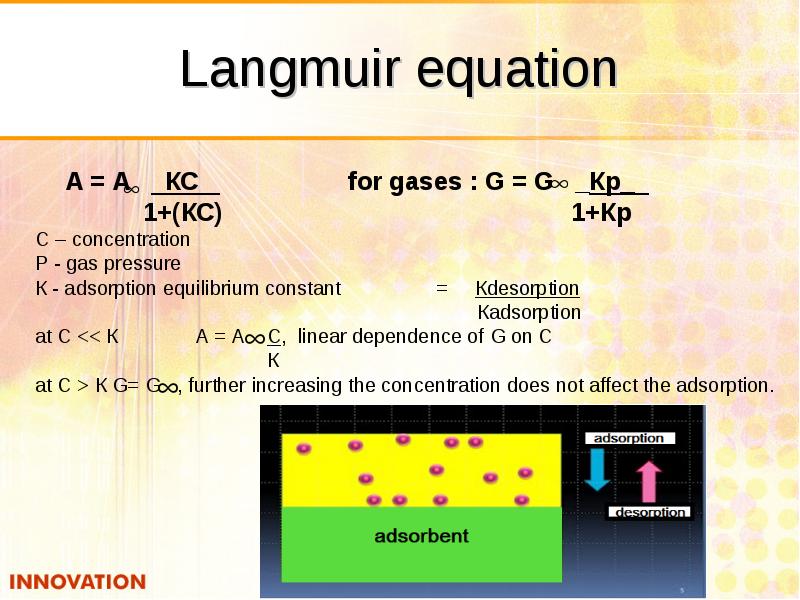
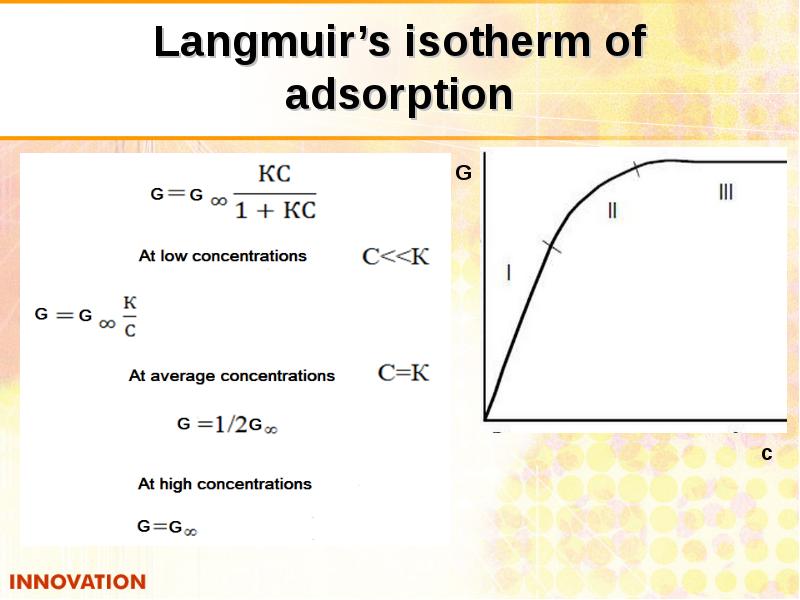
- 26. Langmuir equation А = А КС
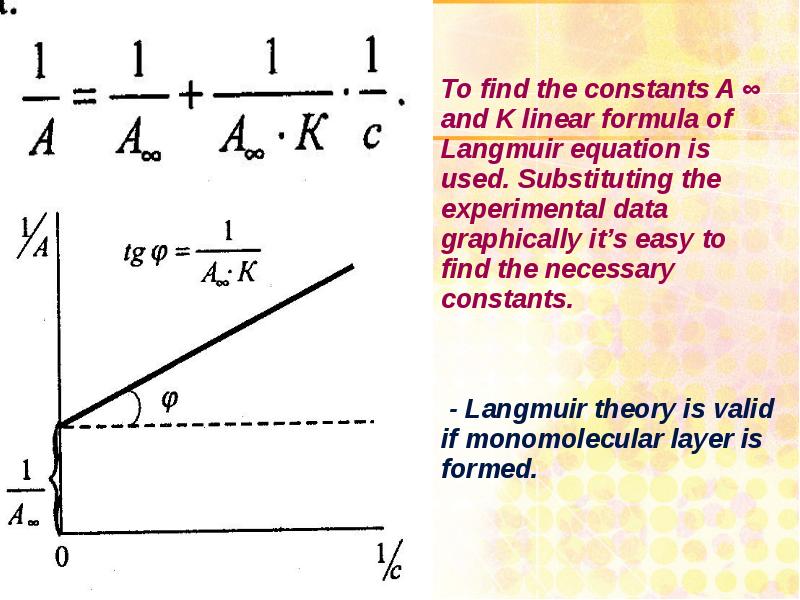
- 28. Langmuir’s isotherm of adsorption
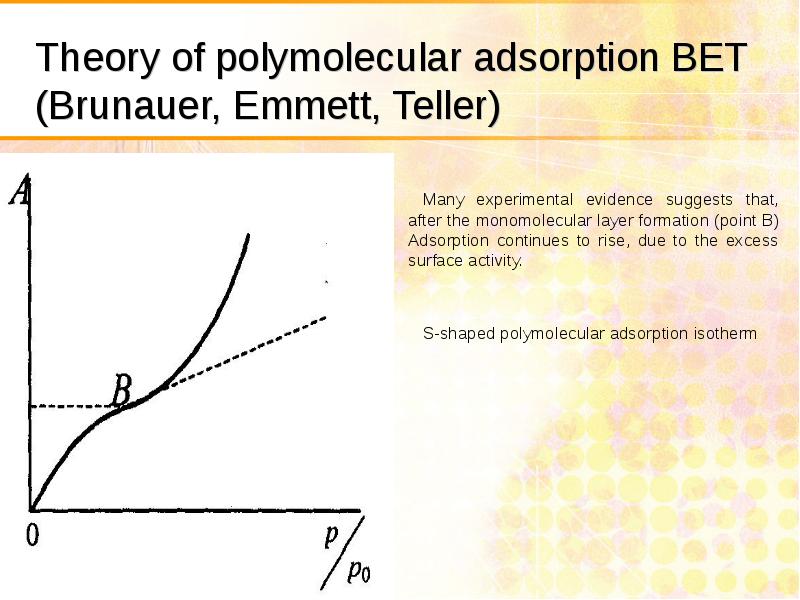
- 29. Theory of polymolecular adsorption BET (Brunauer, Emmett, Teller)
- 30. ADSORPTION ON THE BORDER OF ADSORPTION ON THE BORDER OF
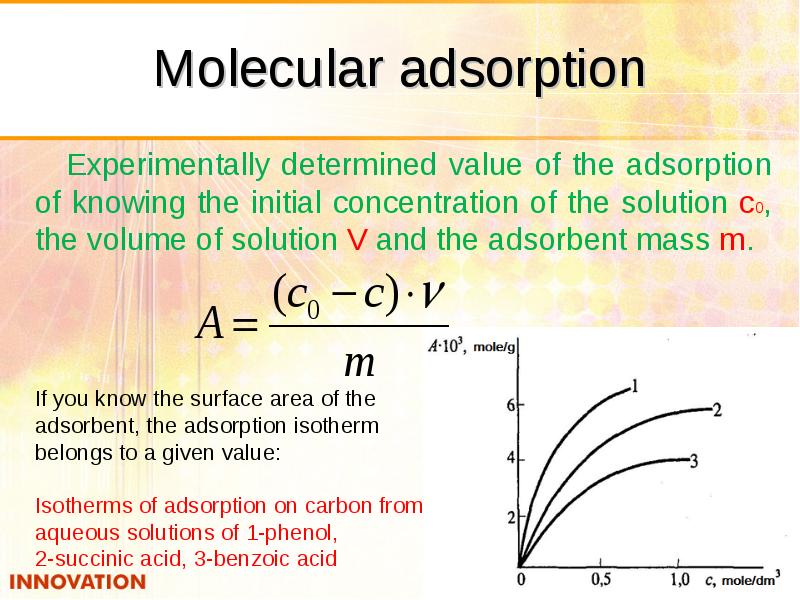
- 31. Molecular adsorption Experimentally determined value of the adsorption of knowing the
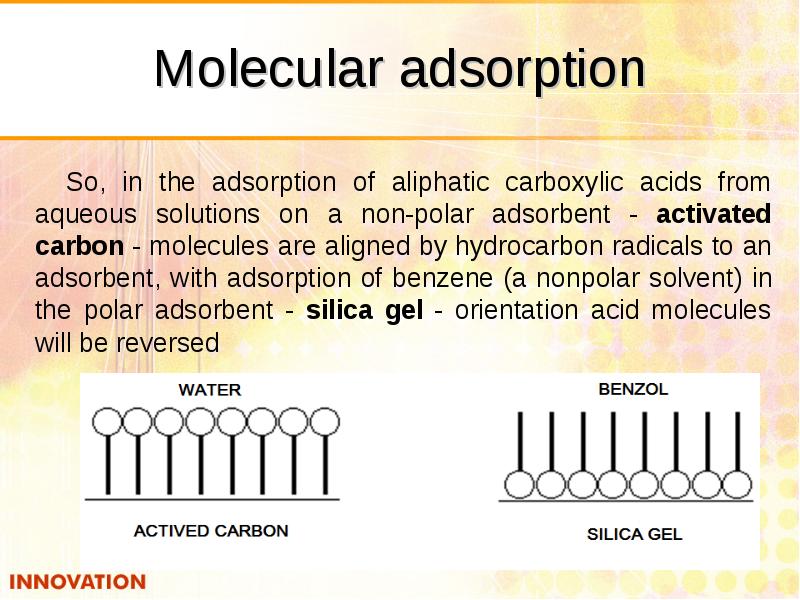
- 32. Molecular adsorption So, in the adsorption of aliphatic carboxylic acids from
- 33. Conclusion From the above that is confirmed, that: For adsorption
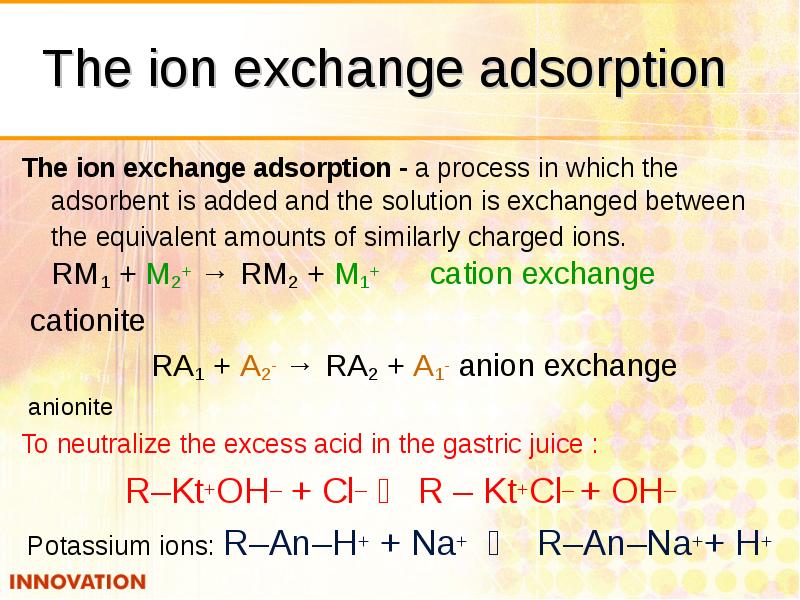
- 34. The ion exchange adsorption The ion exchange adsorption - a process
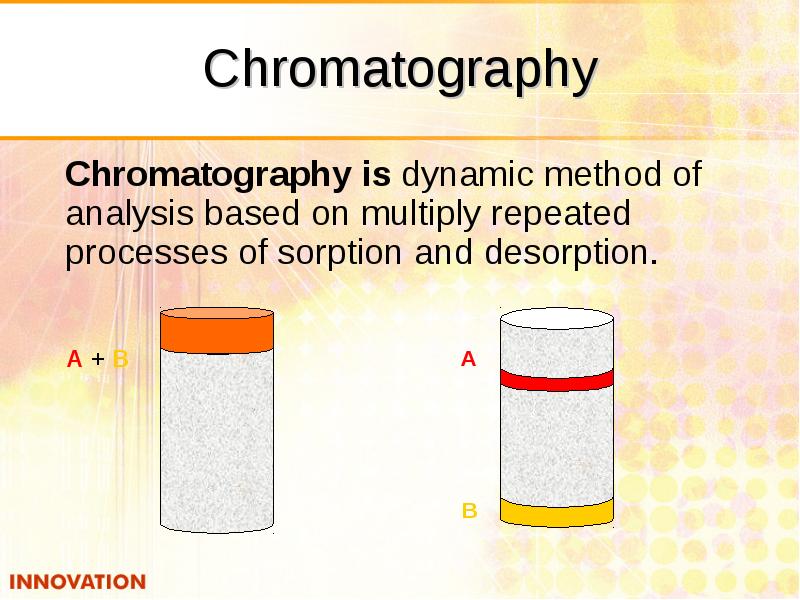
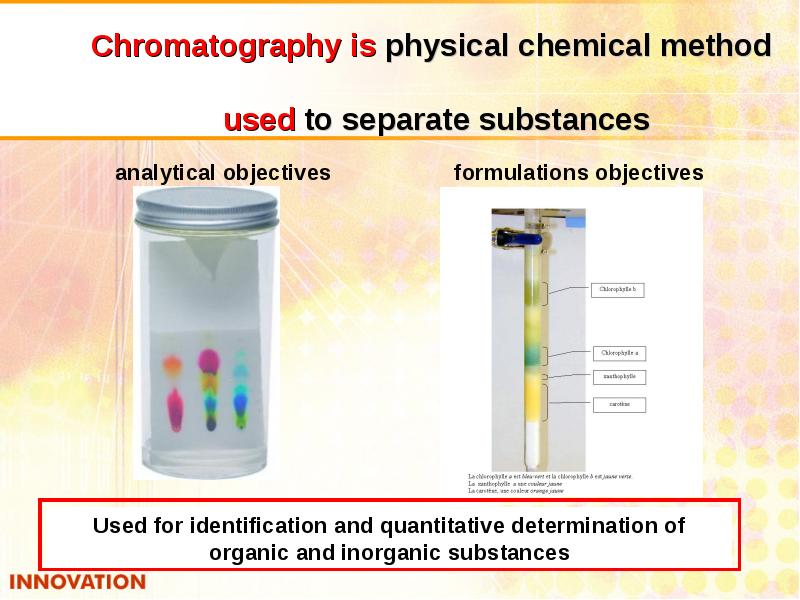
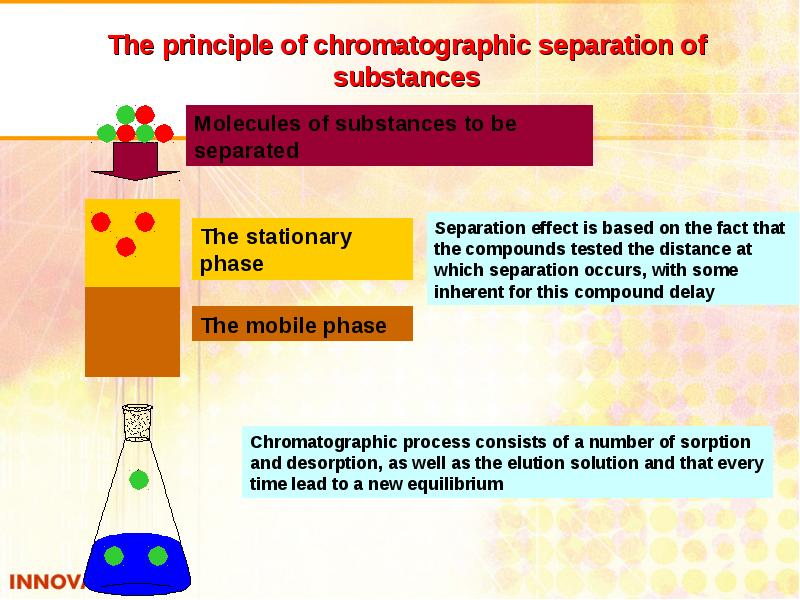
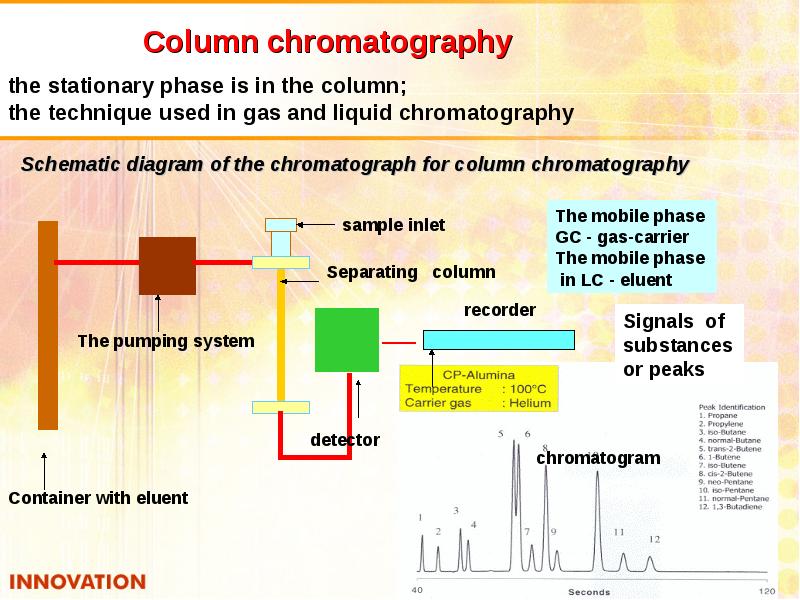
- 35. Chromatography Chromatography is dynamic method of analysis based on multiply repeated
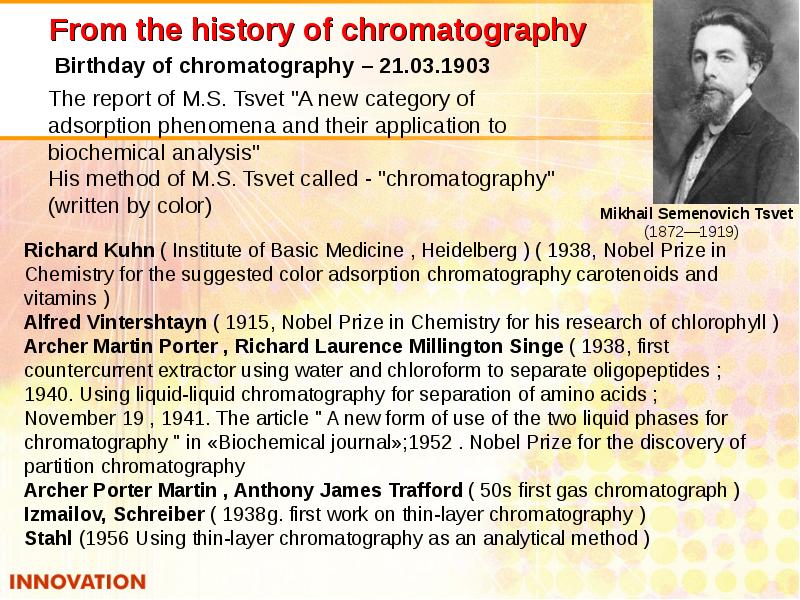
- 37. From the history of chromatography
- 42. HPLC Agilent Technologies
- 43. HPLC Milichrom
- 44. HPLC HP
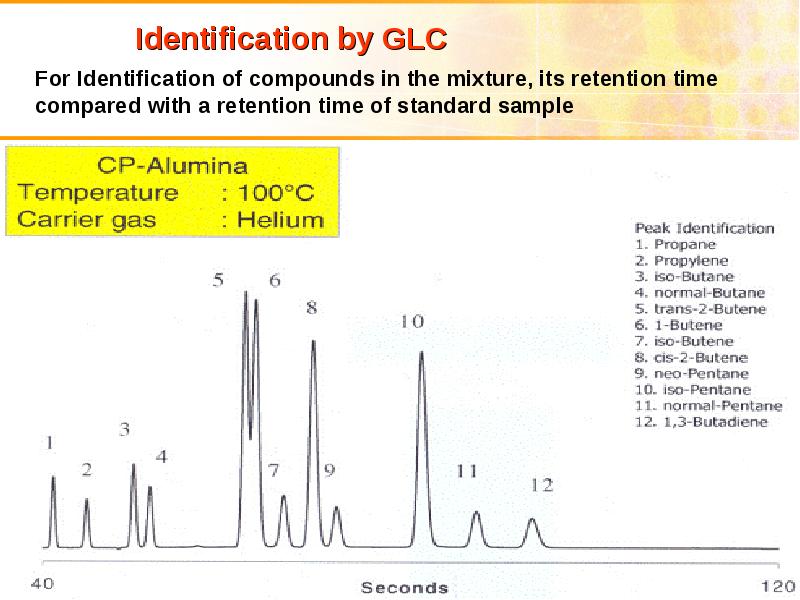
- 45. GLC “Agilent Technologies”
- 46. Enterosorption It is method of treatment of various diseases, based on
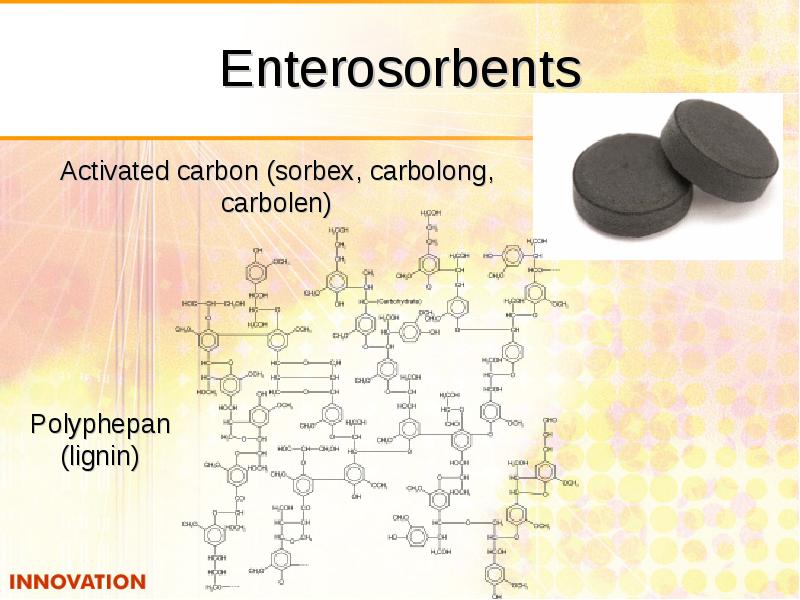
- 47. Enterosorbents
- 48. Enterosorbents Smecta
- 49. Enterosorption Enterosorption is part of efferent therapy (from the Latin word
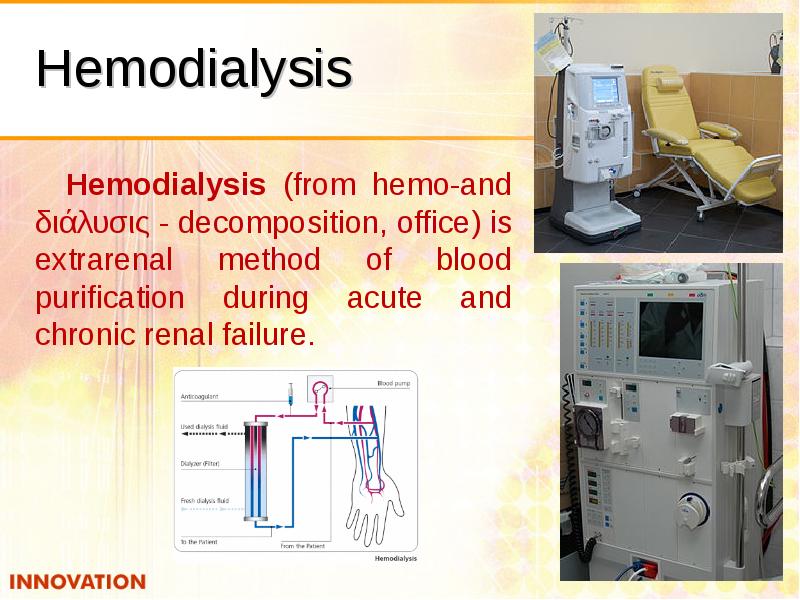
- 50. Hemodialysis Hemodialysis (from hemo-and διάλυσις - decomposition, office) is extrarenal method
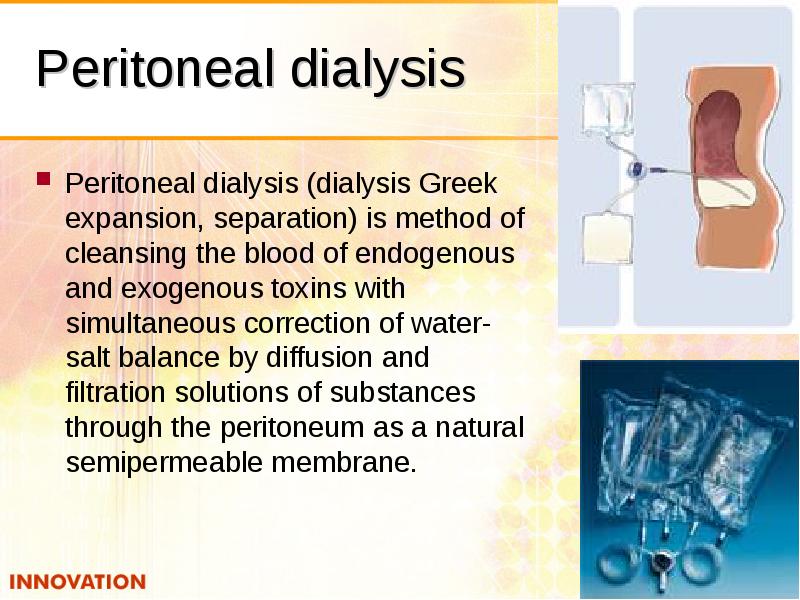
- 51. Peritoneal dialysis Peritoneal dialysis (dialysis Greek expansion, separation) is method of
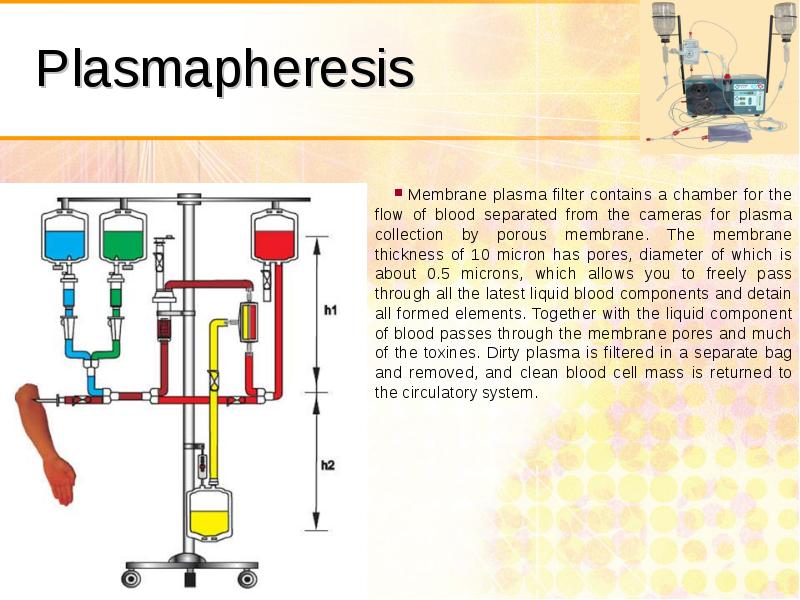
- 52. Plasmapheresis Membrane plasma filter contains a chamber for the flow of
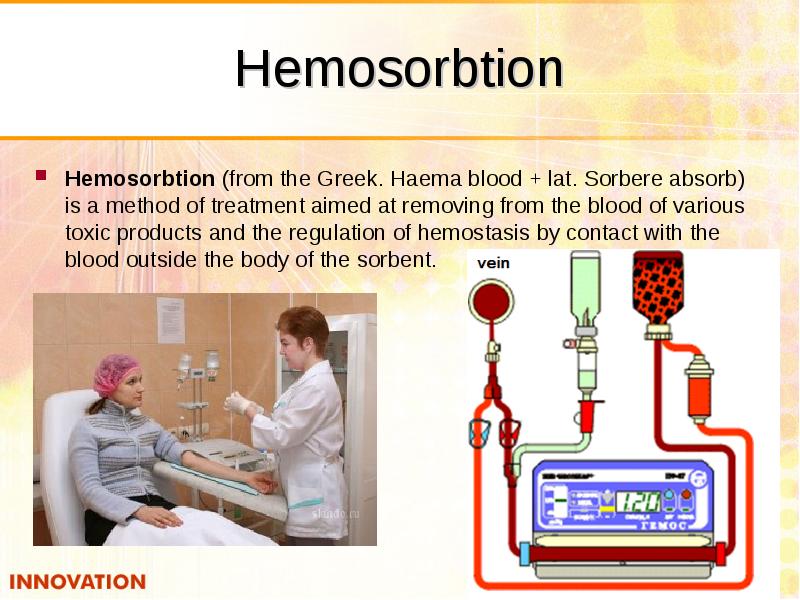
- 53. Hemosorbtion Hemosorbtion (from the Greek. Haema blood + lat. Sorbere absorb)
- 54. Скачать презентацию





















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Physical chemistry of surface phenomena. Basics of adsorptive therapy можно ниже:
Похожие презентации