Physiology of kidneys презентация
Содержание
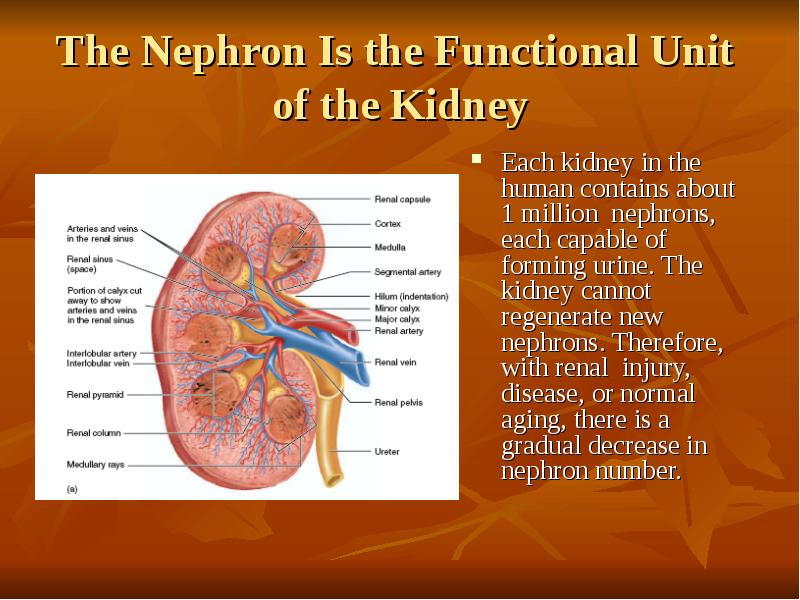
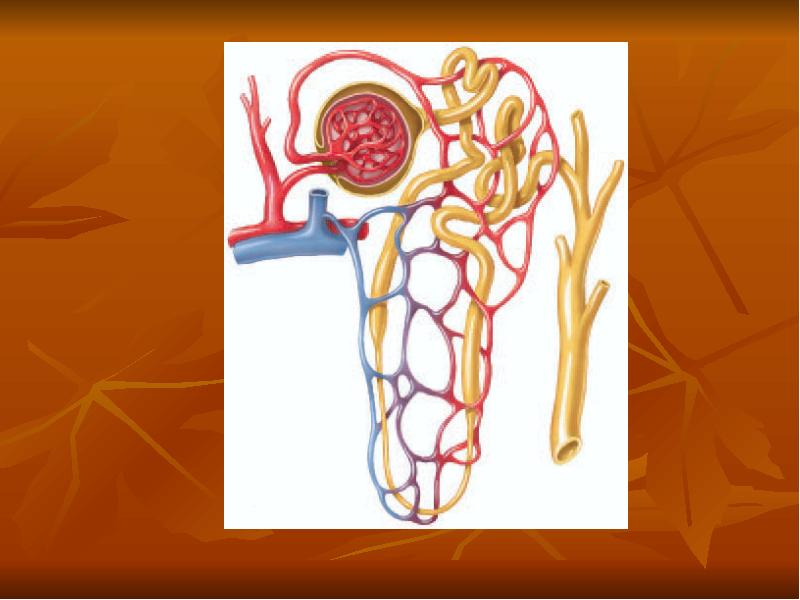
- 2. The Nephron Is the Functional Unit of the Kidney Each kidney
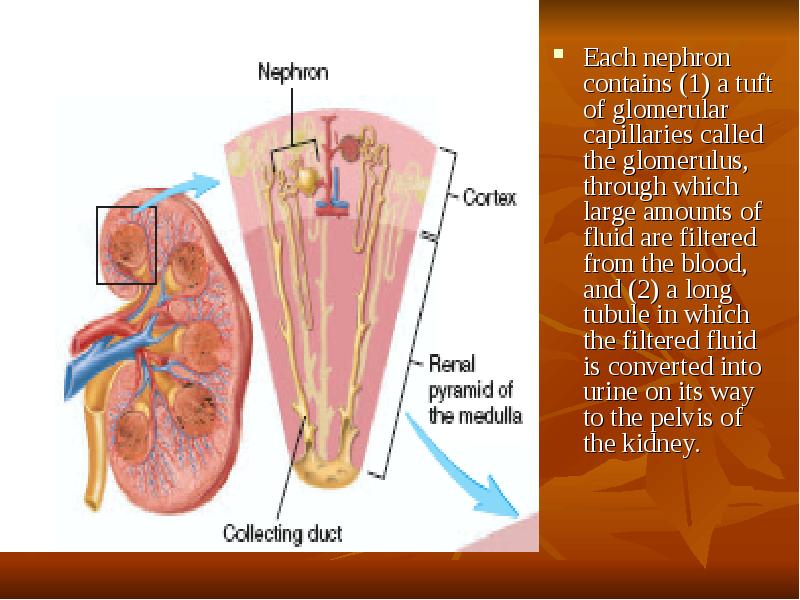
- 3. Each nephron contains (1) a tuft of glomerular capillaries called the
- 5. The macula densa plays an important role in controlling nephron function.
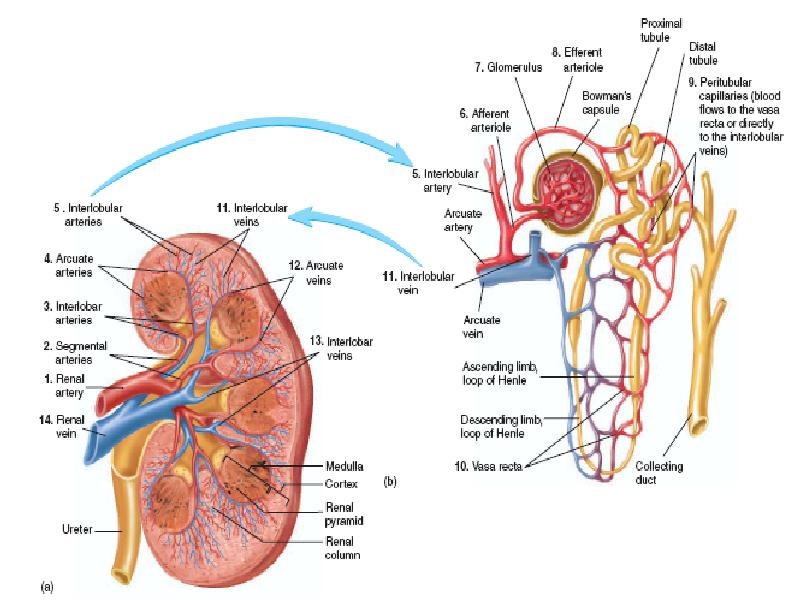
- 6. Renal Blood Supply Blood flow to the two kidneys is normally
- 8. PHYSIOLOGIC CONTROL OF GLOMERULAR FILTRATION AND RENAL BLOOD FLOW The determinants
- 9. Sympathetic Nervous System Activation Decreases GFR Strong activation of the renal
- 10. Hormonal and Autacoid Control of Renal Circulation Norepinephrine, Epinephrine, and Endothelin
- 11. Angiotensin II Constricts Efferent Arterioles A powerful renal vasoconstrictor, angiotensin II,
- 13. Endothelial-Derived Nitric Oxide Decreases Renal Vascular Resistance and Increases GFR A
- 14. Prostaglandins and Bradykinin Tend to Increase GFR Hormones and autacoids that
- 15. Function of nephrone Video
- 16. AUTOREGULATION OF GFR AND RENAL BLOOD FLOW Feedback mechanisms intrinsic to
- 17. Myogenic Autoregulation of Renal Blood Flow and GFR A second mechanism
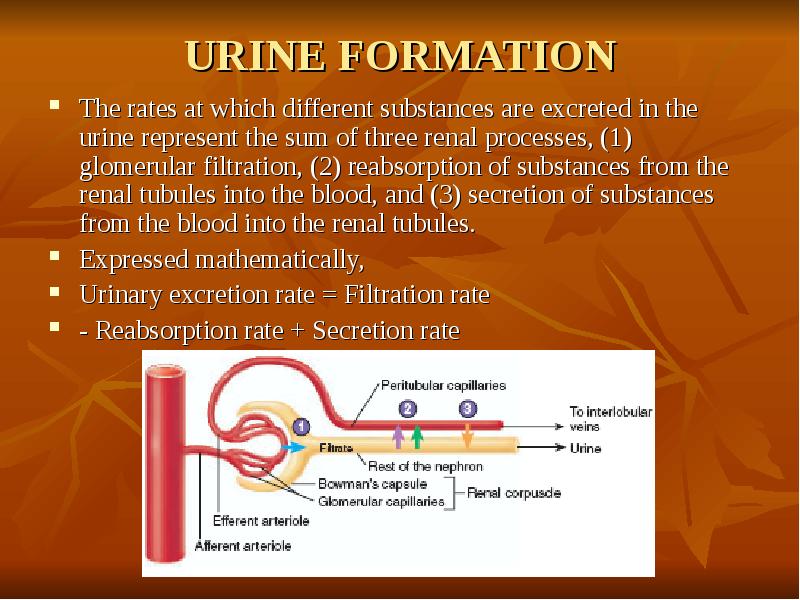
- 18. URINE FORMATION The rates at which different substances are excreted in
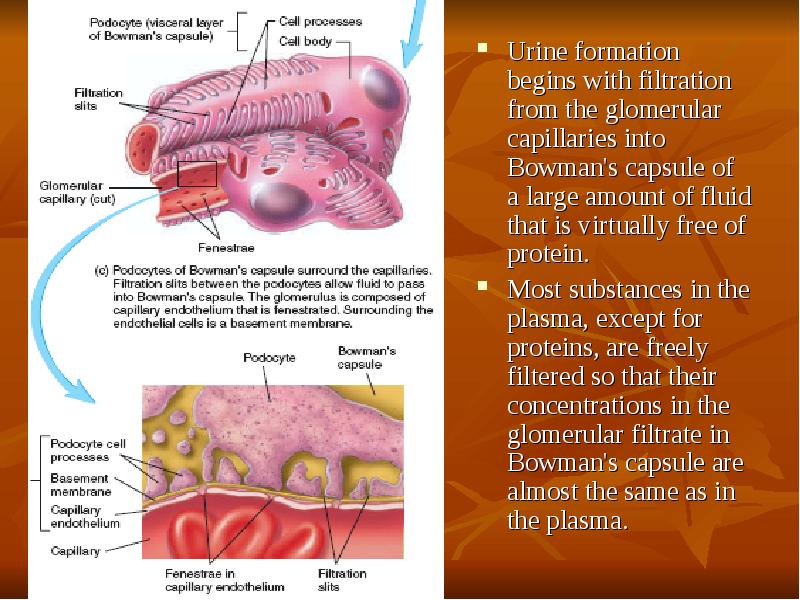
- 19. Urine formation begins with filtration from the glomerular capillaries into Bowman's
- 20. Why Are Large Amounts of Solutes Filtered and Then Reabsorbed by
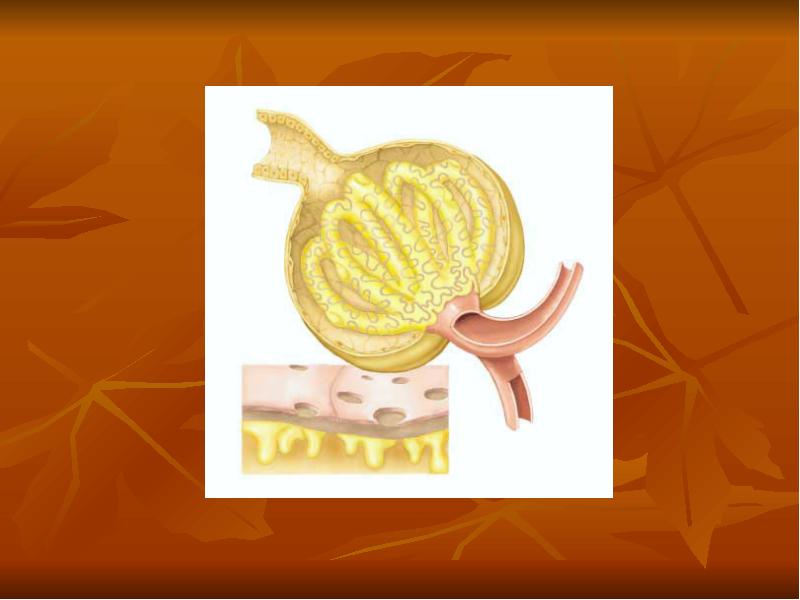
- 21. Glomerular Capillary Membrane The glomerular capillary membrane is similar to that
- 22. Glomerular Capillary Membrane Although the fenestrations are relatively large, endothelial cells
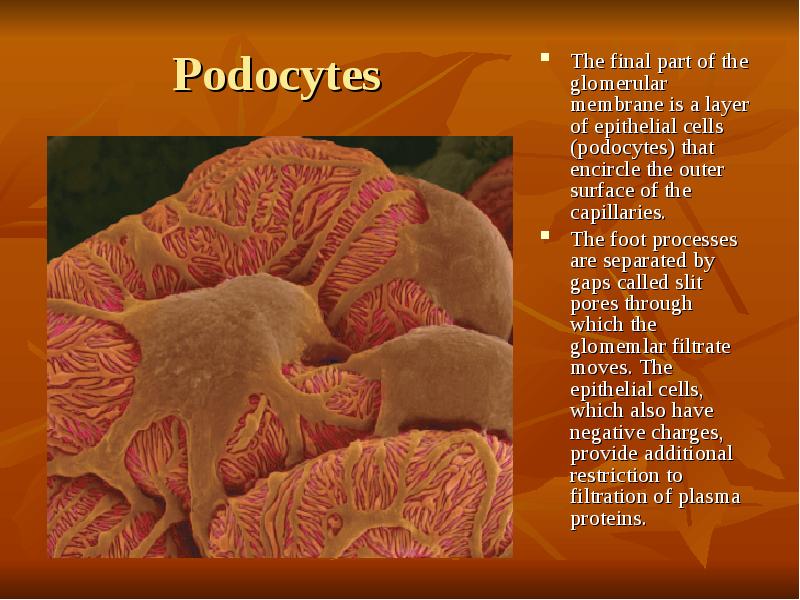
- 23. Podocytes The final part of the glomerular membrane is a layer
- 25. Three basic renal processes The substance is freely filtered but is
- 26. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion of Different Substances In general, tubular, reabsorption
- 28. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion of Different Substances Nutritional substances, such as
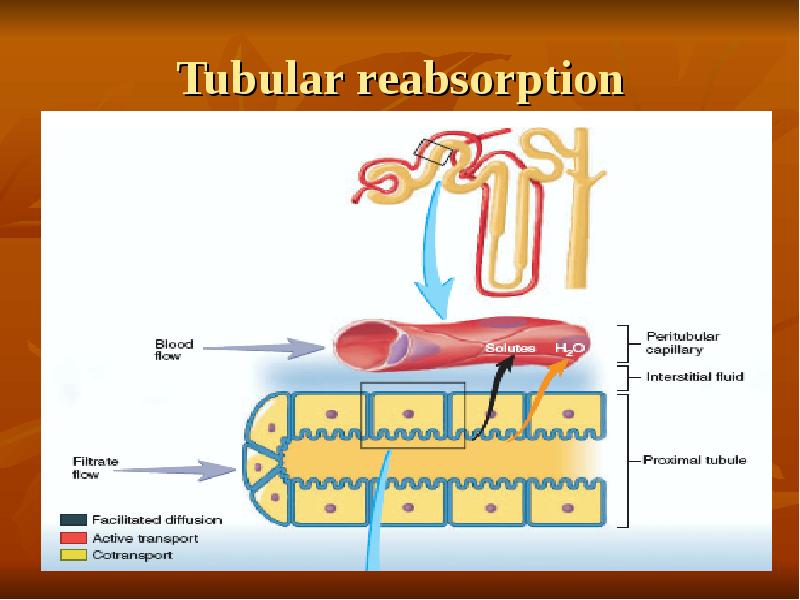
- 29. Tubular reabsorption
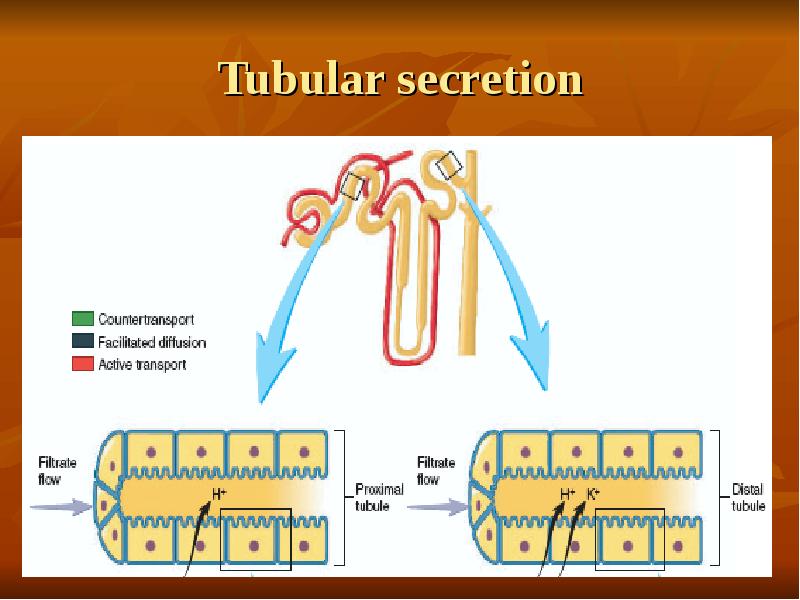
- 30. Tubular secretion
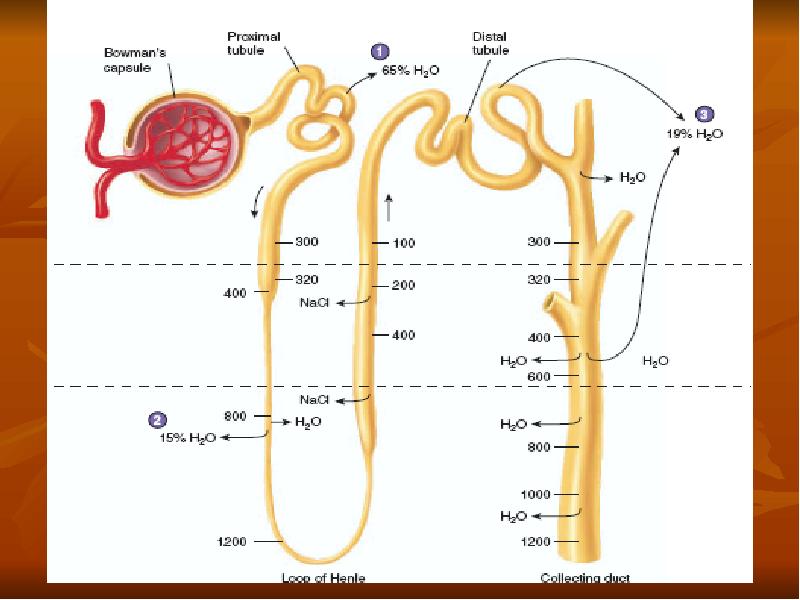
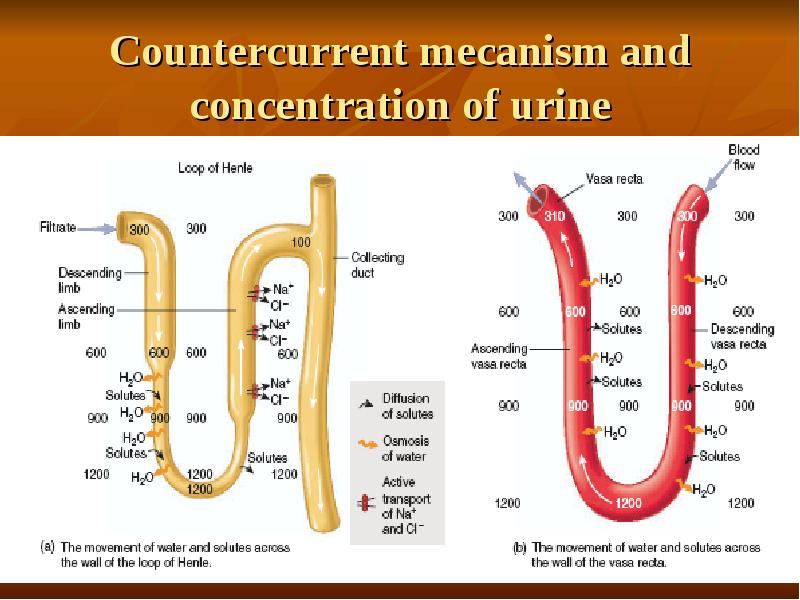
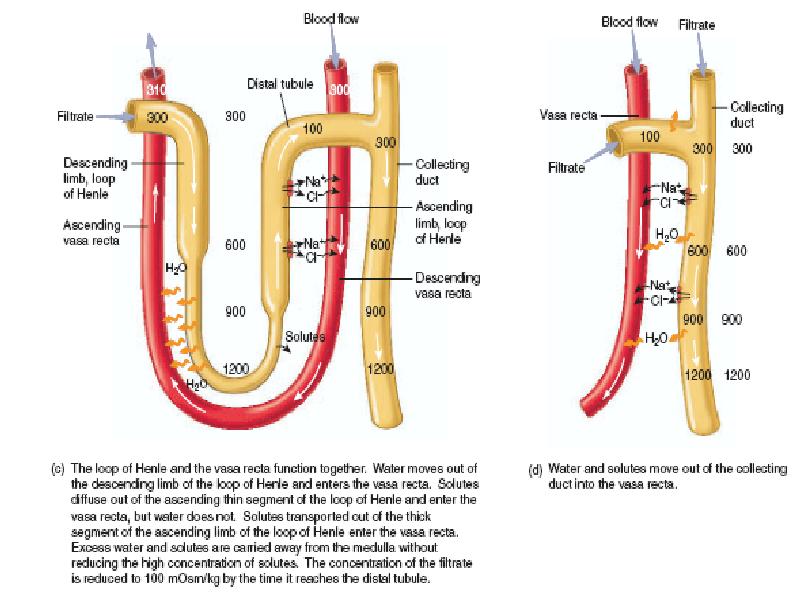
- 31. Countercurrent mecanism and concentration of urine
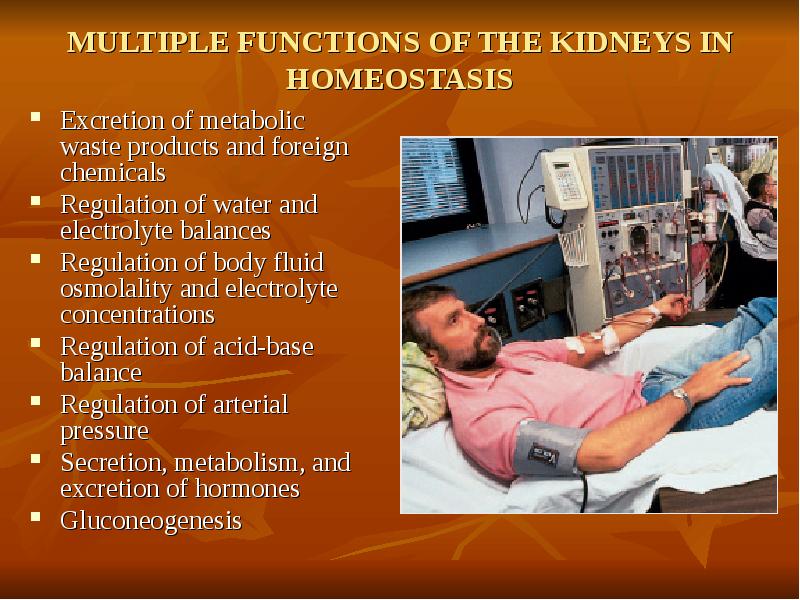
- 34. MULTIPLE FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEYS IN HOMEOSTASIS Excretion of metabolic waste
- 35. Excretion of Metabolic Waste Products, Foreign Chemicals, Drugs, and Hormone Metabolites
- 36. Regulation of Water and Electrolyte Balances For maintenance of homeostasis, excretion
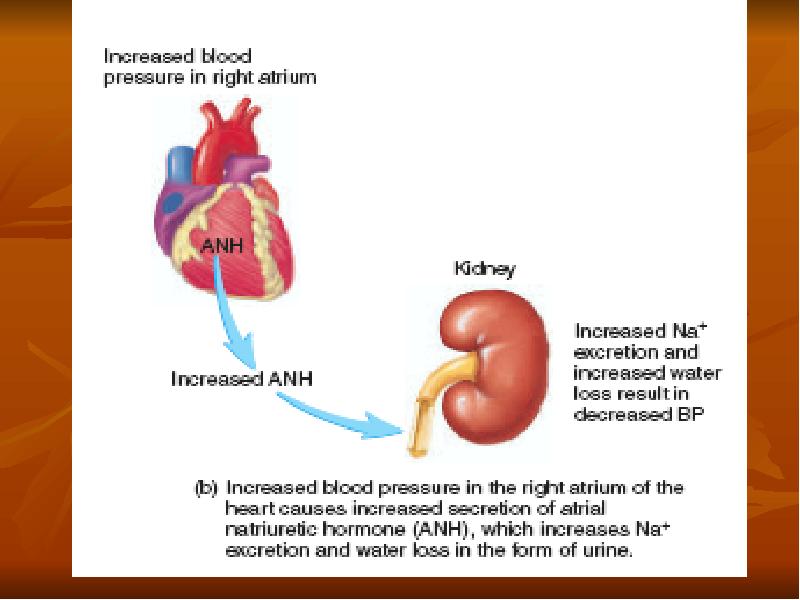
- 37. Regulation of Arterial Pressure In addition, the kidneys contribute to short-term
- 39. Regulation of Acid-Base Balance The kidneys contribute to acid-base regulation, along
- 40. Regulation of 1,25-Dihydroxy Vitamin D 3 Production The kidneys produce the
- 41. Glucose Synthesis The kidneys synthesize glucose from amino acids and other
- 42. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF OSMOSIS AND OSMOTIC PRESSURE Osmosis is' the net
- 43. Isosmotic, Hyperosmotic, and Hypo-osmotic Fluids Solutions with an osmolarity the same
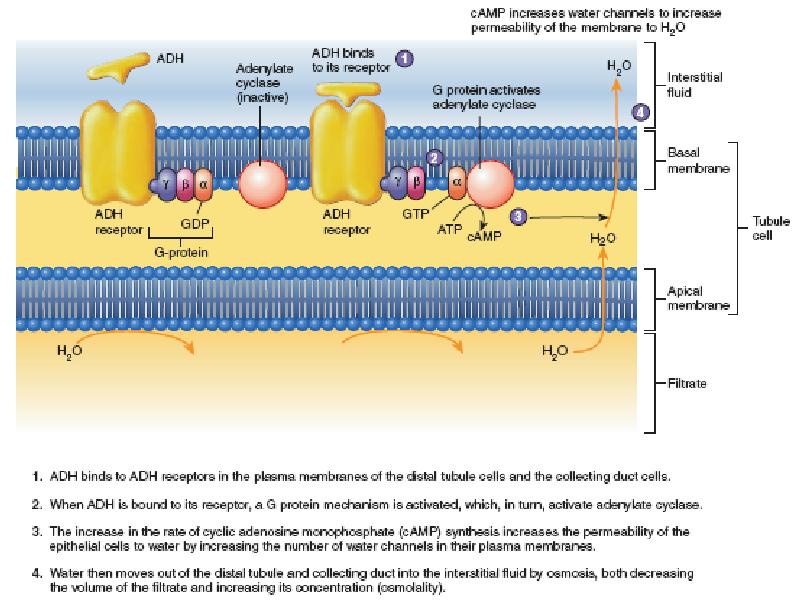
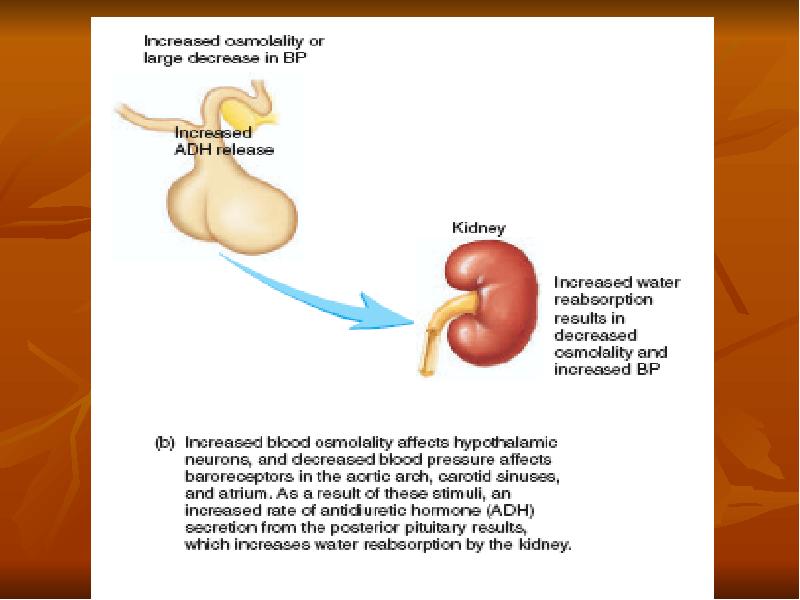
- 44. OSMORECEPTOR-ADH FEEDBACK SYSTEM 1. An increase in extracellular fluid osmolarity causes
- 46. ADH Synthesis in Supraoptic and Paraventricular Nuclei of the Hypothalamus and
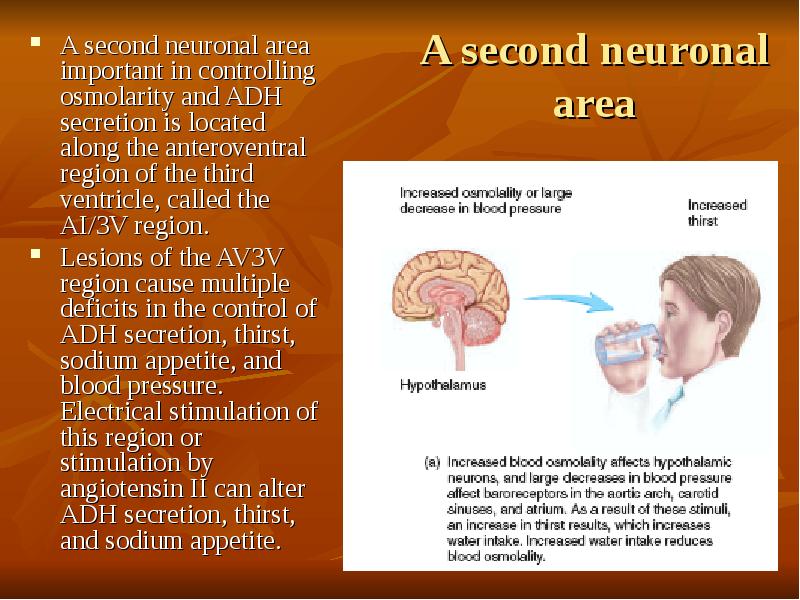
- 47. A second neuronal area A second neuronal area important in controlling
- 48. ROLE OF THIRST IN CONTROLLING EXTRACELLULAR FLUID OSMOLARITY AND SODIUM CONCENTRATION
- 49. Central Nervous System Centers for Thirst Located anterolaterally in the preoptic
- 50. Stimuli for Thirst One of the most important is increased extracellular
- 51. Stimuli for Thirst These regions are outside the blood-brain barrier, and
- 52. Threshold for Osmolar Stimulus of Drinking The kidneys must continually excrete
- 53. Cardiovascular Reflex Stimulation of ADH Release by Decreased Arterial Pressure and/or
- 55. Role of Angiotensin II and Aldosterone in Controlling Extracellular Fluid Osmolarity
- 57. SALT-APPETITE MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING EXTRACELLULAR FLUID SODIUM CONCENTRATION AND VOLUME Maintenance
- 59. Скачать презентацию

































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации