Subjects: forces in mechanics. Dynamics. Newton’s laws презентация
Содержание
- 2. Lecture 2 SUBJECTS: Forces in mechanics Dynamics Newton’s laws
- 3. Dynamics Dynamics studies the cause of changes in motion. Forces act
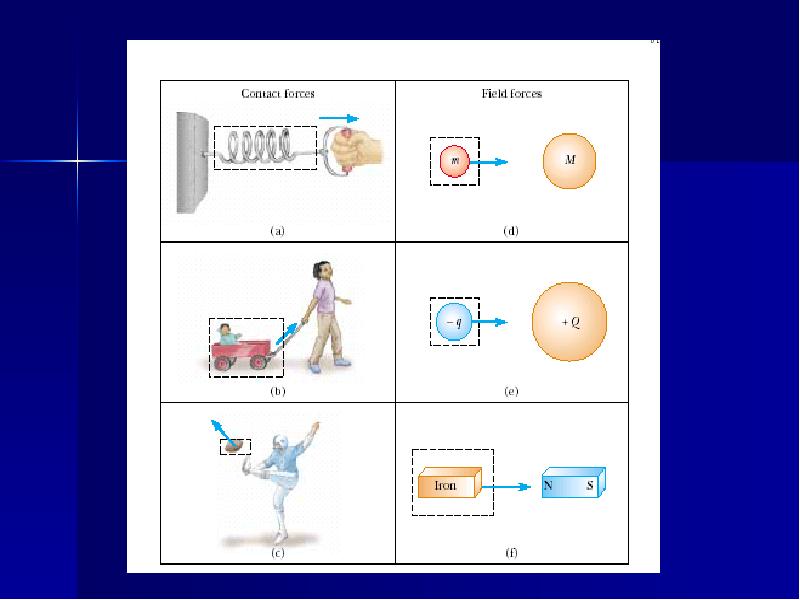
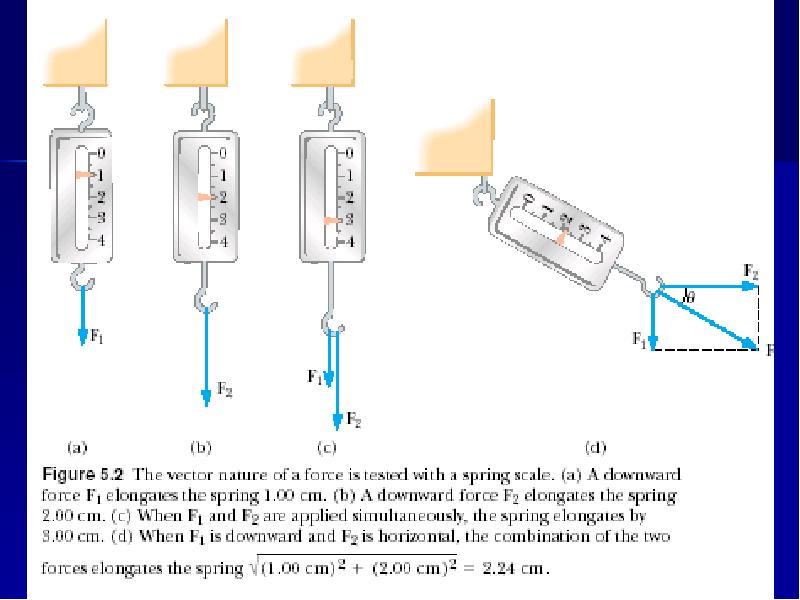
- 4. Force A force is a vector, so that it has: a
- 7. Three fundamental forces Gravitational force. Electroweak force: a united force of
- 8. Newton’s first law of motion two equivalent variants: 1. When there
- 9. Such a reference frame is called an inertial frame of reference.
- 10. Newton’s second law of motion When viewed from an inertial reference
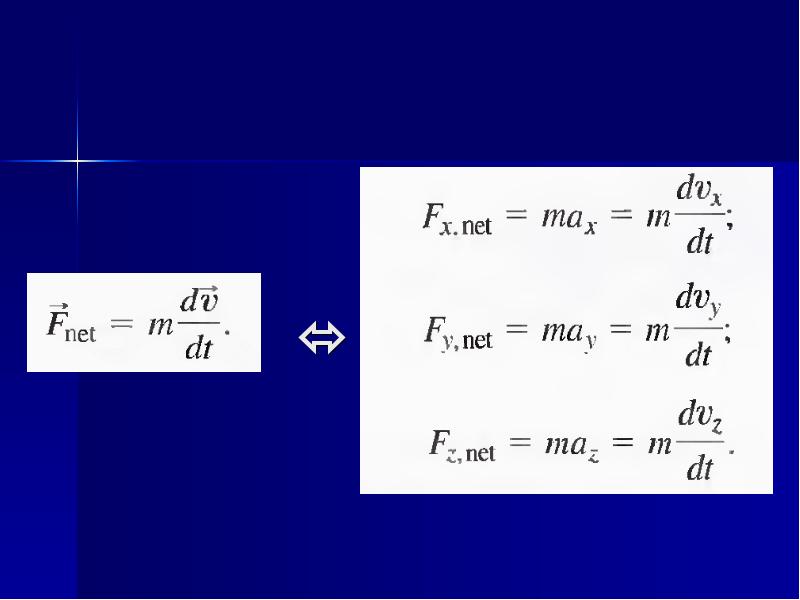
- 11.
- 12. Newton’s third law of motion When a force due to object
- 13. Mass and Weight Mass is that property of an object that
- 14. The attractive force exerted by the Earth on an object is
- 15. Mass and weight are two different quantities The weight of an
- 16. Action – Reaction forces Forces always occur in pairs, or that
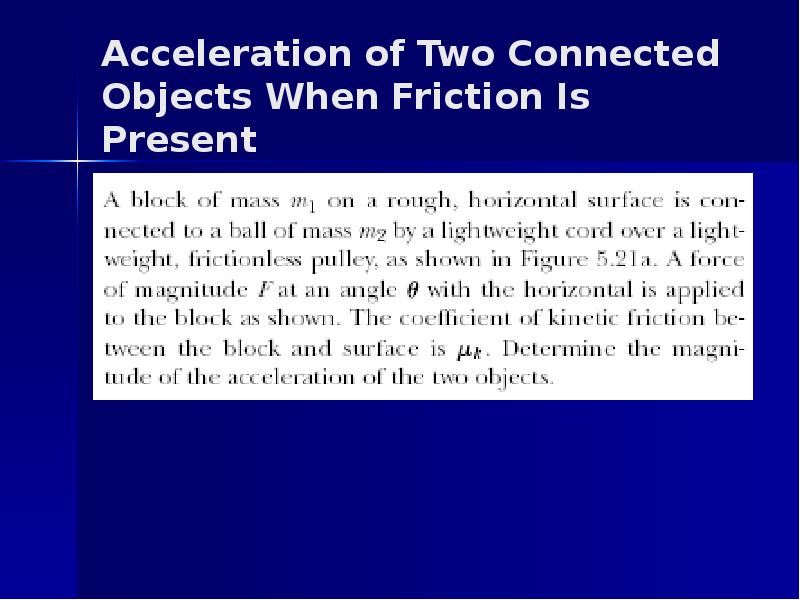
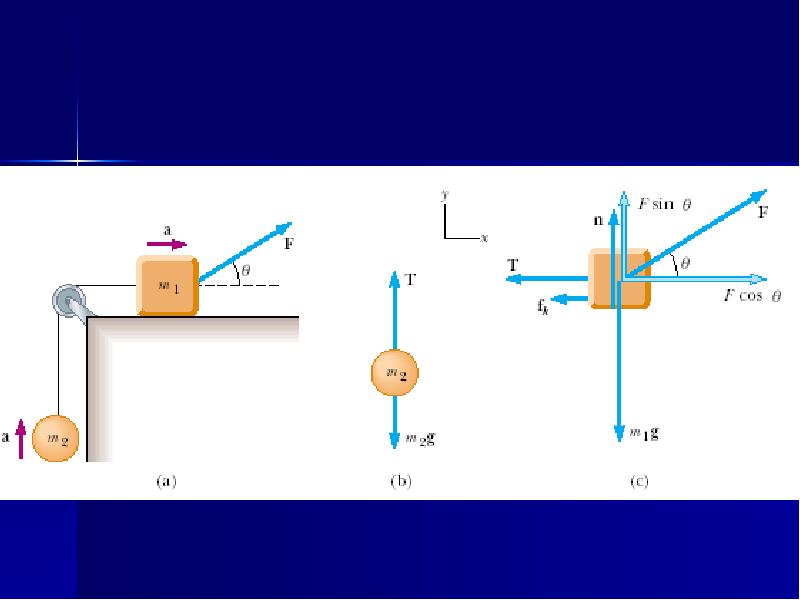
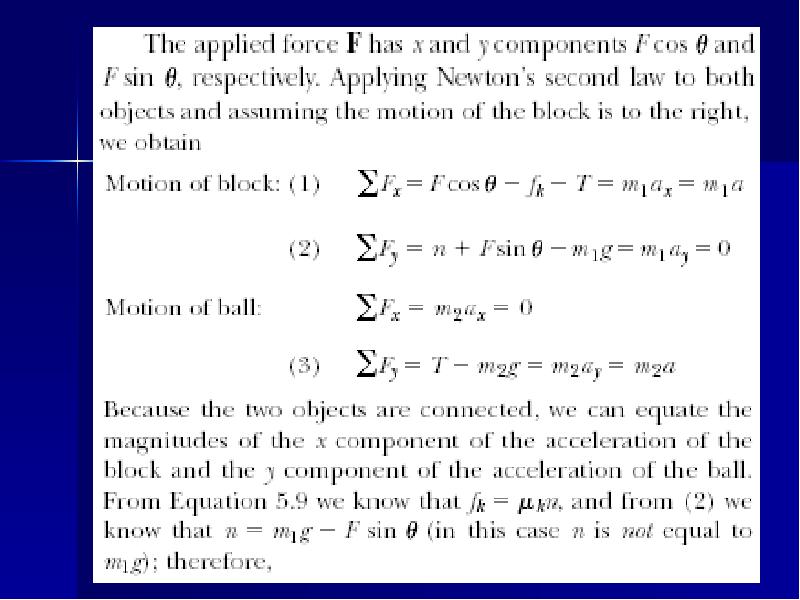
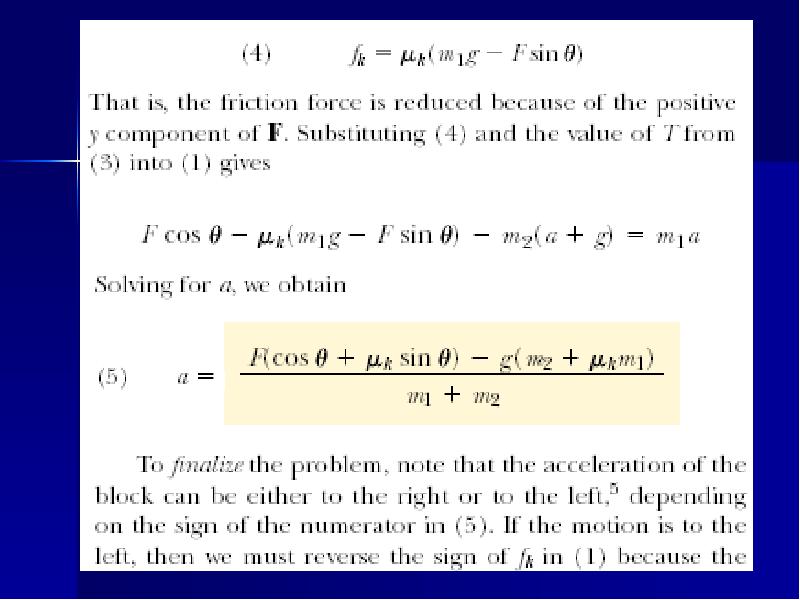
- 17. Acceleration of Two Connected Objects When Friction Is Present
- 23. Units in SI Force F N=kg*m/s2 Acceleration a,g m/s2
- 24. Скачать презентацию
















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Subjects: forces in mechanics. Dynamics. Newton’s laws можно ниже:
Похожие презентации