The Design of power saving mechanisms in Ethernet Passive Optical Networks презентация
Содержание
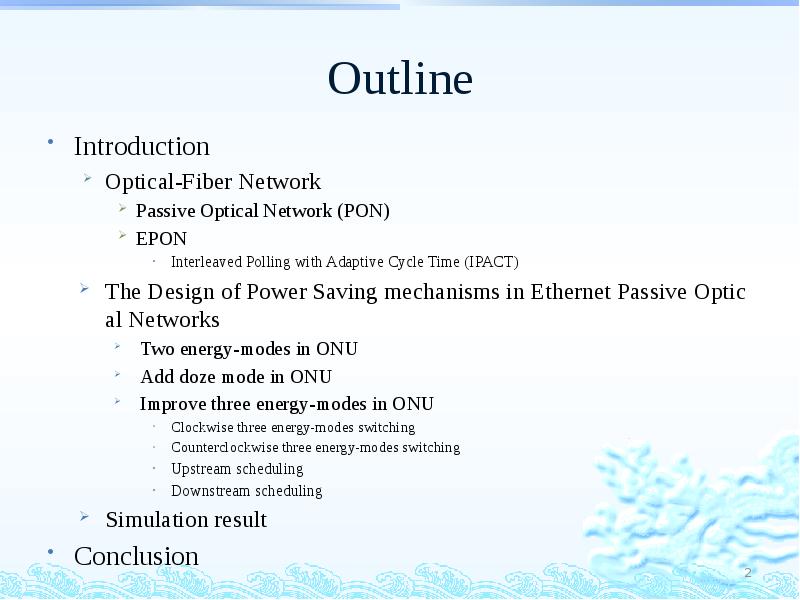
- 2. Outline Introduction Optical-Fiber Network Passive Optical Network (PON) EPON Interleaved Polling
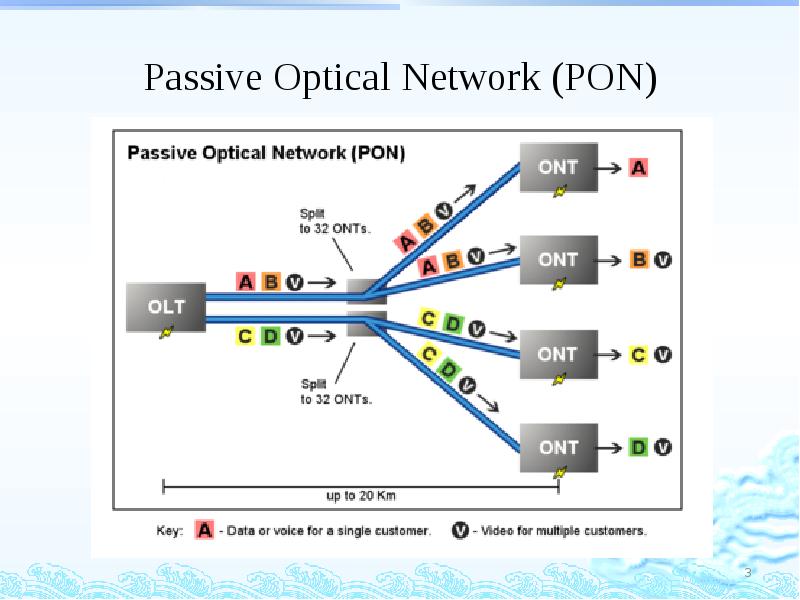
- 3. Passive Optical Network (PON)
- 4. Passive Optical Network (PON) Optical line terminal (OLT) Optical network units
- 5. EPON REPORT and GATE message REPORT ONU to report its bandwidth
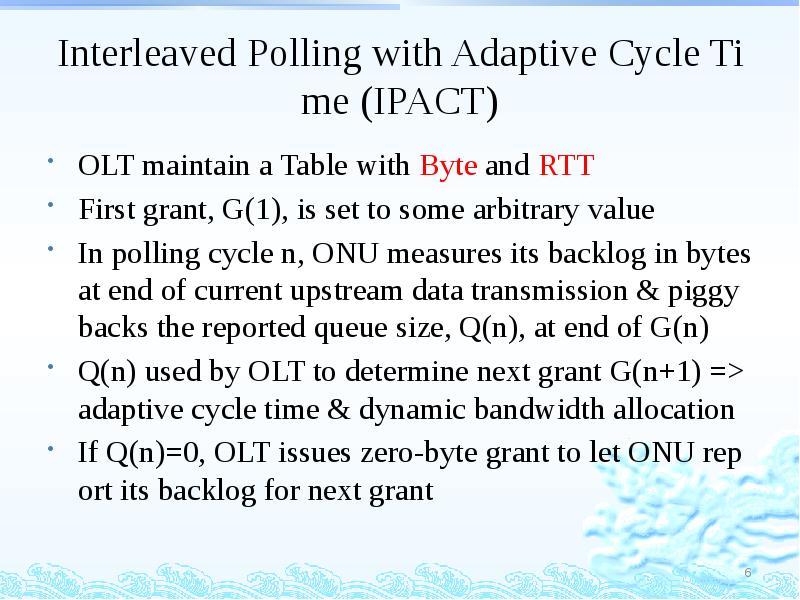
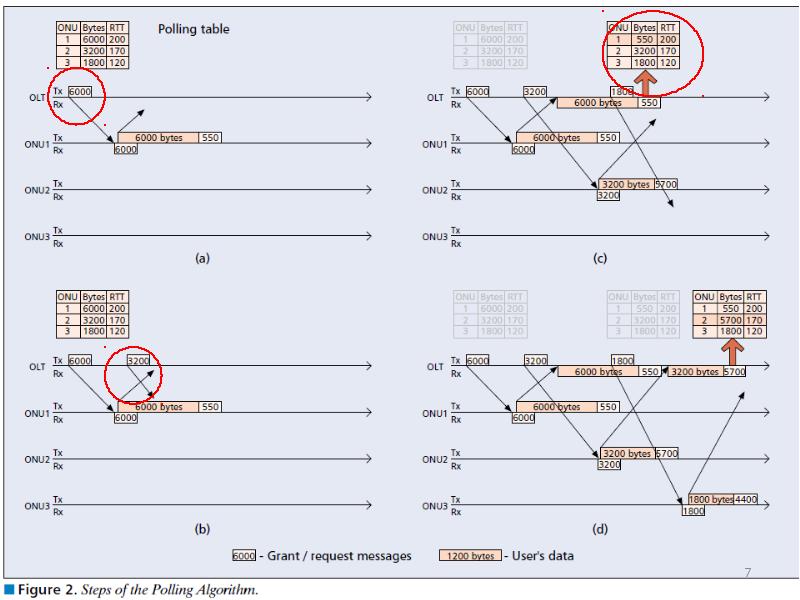
- 6. Interleaved Polling with Adaptive Cycle Time (IPACT) OLT maintain a Table
- 8. The Design of Power Saving mechanisms in Ethernet Passive Optical Networks
- 9. Two energy-modes in ONU In L. Shi, B. Mukherjee, and S.
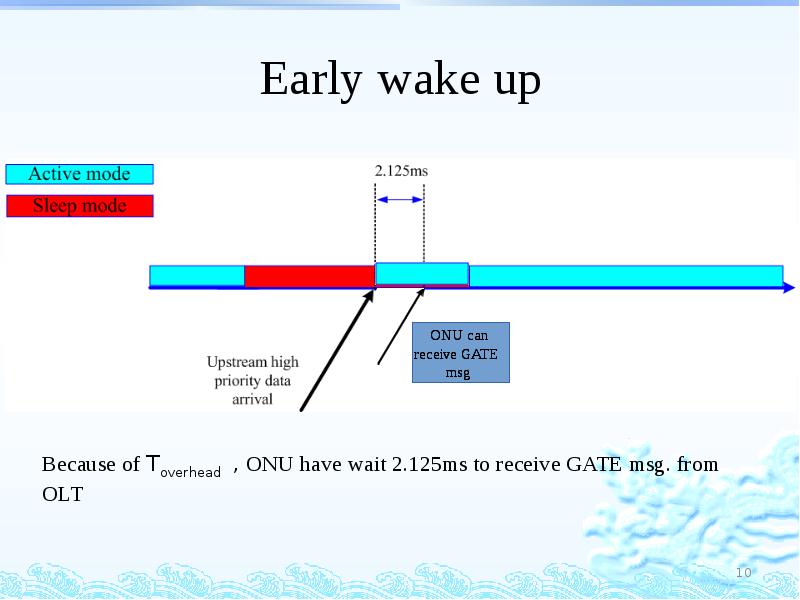
- 10. Early wake up
- 11. Lei Shi, Biswanath Mukherjee and Sang-Soo Lee’s research Didn’t consider downstream
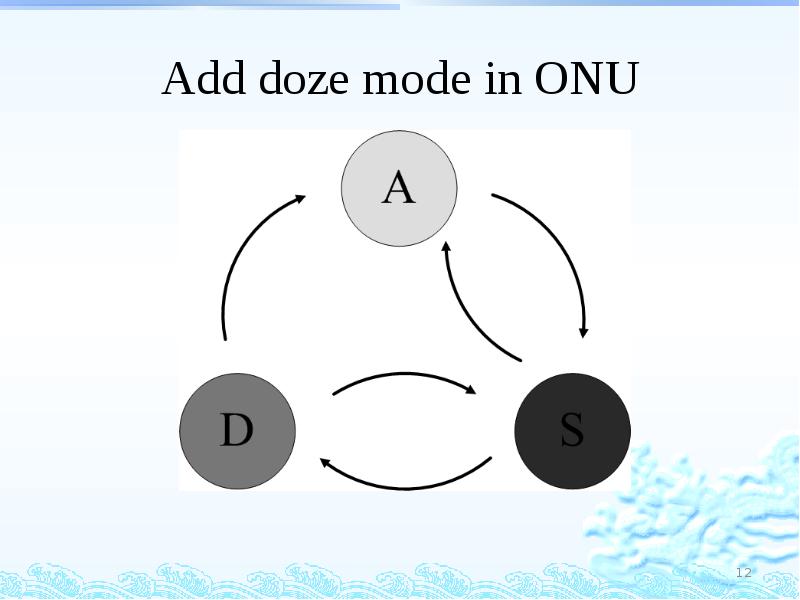
- 12. Add doze mode in ONU
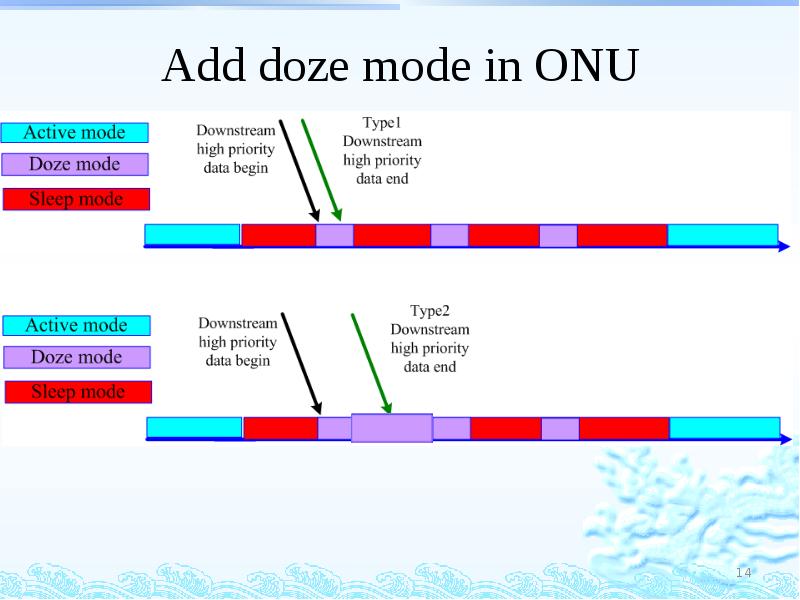
- 13. Add doze mode in ONU ONU Tx: off Rx:on Downstream high
- 14. Add doze mode in ONU
- 15. Add doze mode in ONU : Weak point Doze mode will
- 16. Improve three energy-modes in ONU Clockwise three energy-modes switching Counterclockwise three
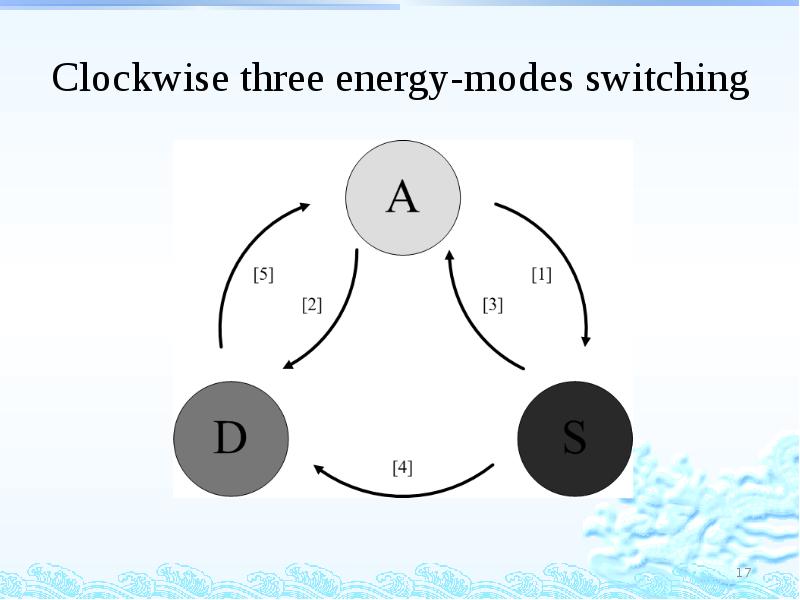
- 17. Clockwise three energy-modes switching
- 18. Clockwise three energy-modes switching Consider performance A -> S [1] No
- 19. Clockwise three energy-modes switching D -> A [5] Stay at doze
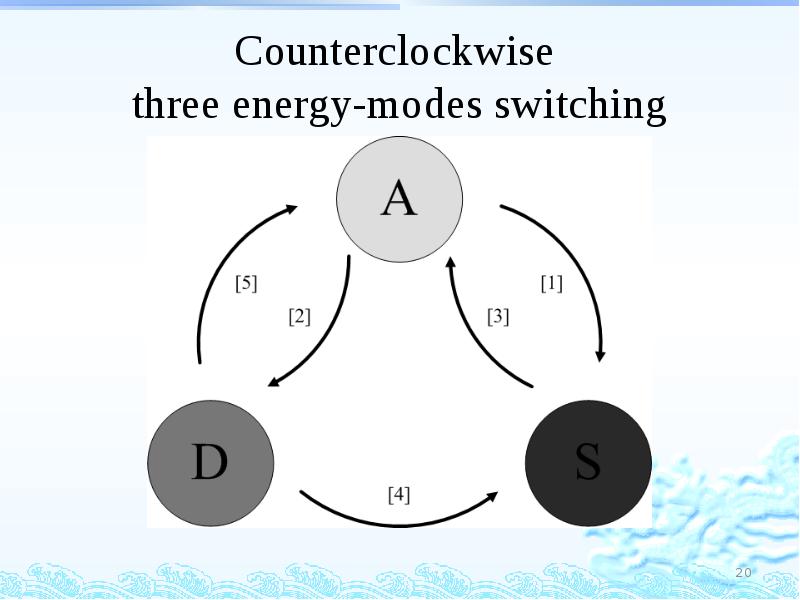
- 20. Counterclockwise three energy-modes switching
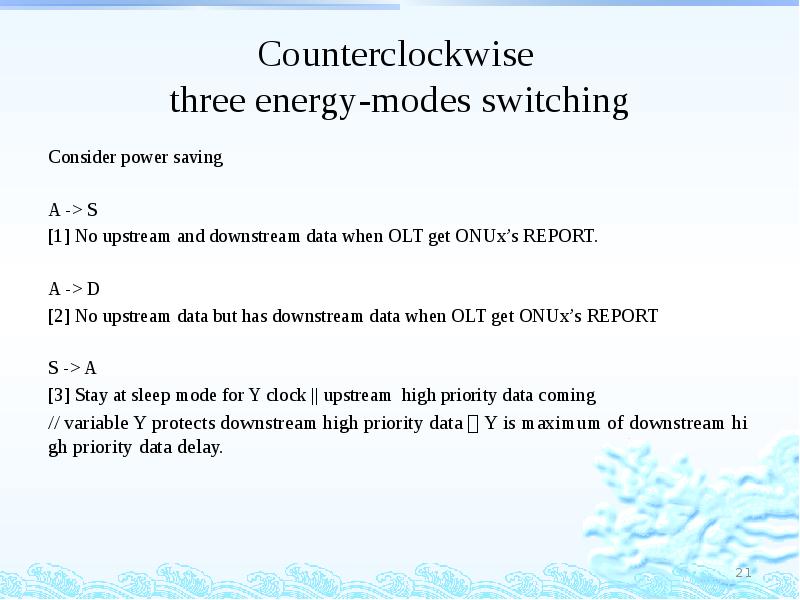
- 21. Counterclockwise three energy-modes switching Consider power saving A -> S [1]
- 22. Counterclockwise three energy-modes switching D -> S [4] Stay at doze
- 23. Upstream scheduling Using Limited service. Limited service : OLT grants requested
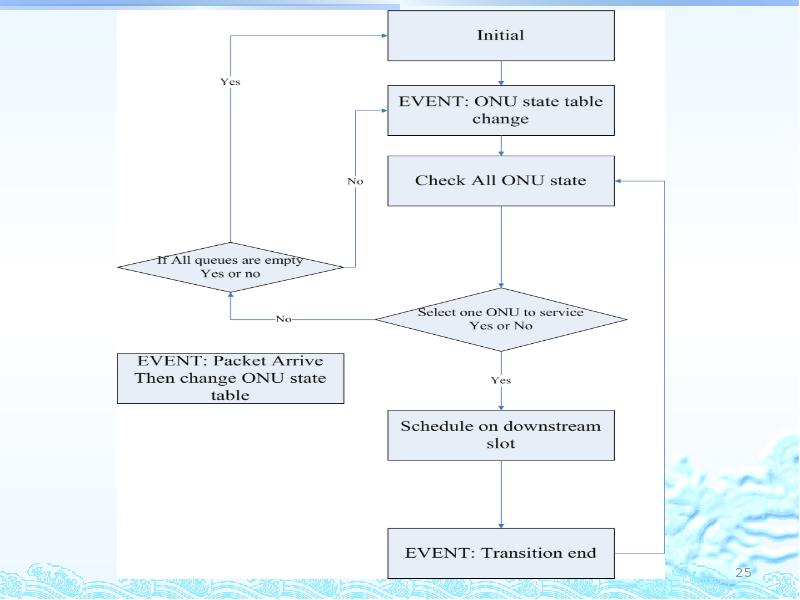
- 24. Downstream scheduling Although downstream slot and upstream slot are difference but
- 26. Simulation Result Clockwise three energy-modes switching ONU = 16
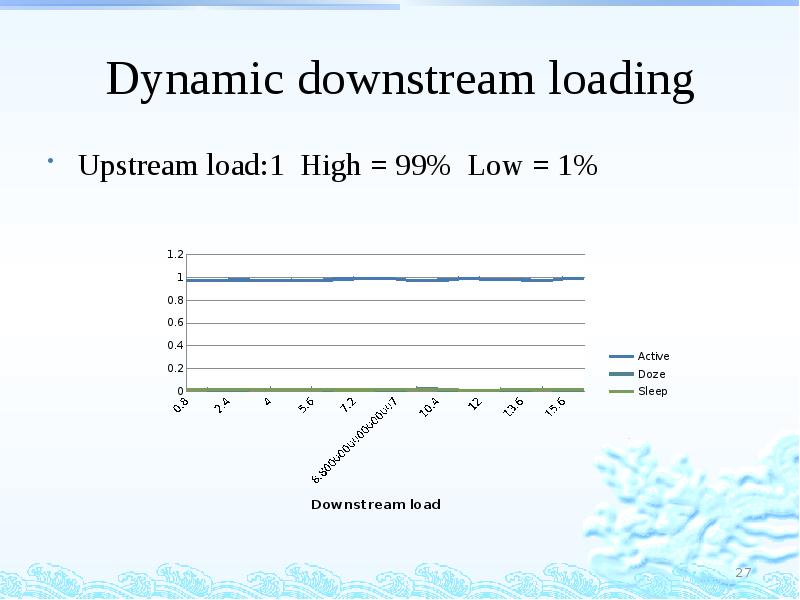
- 27. Dynamic downstream loading Upstream load:1 High = 99% Low = 1%
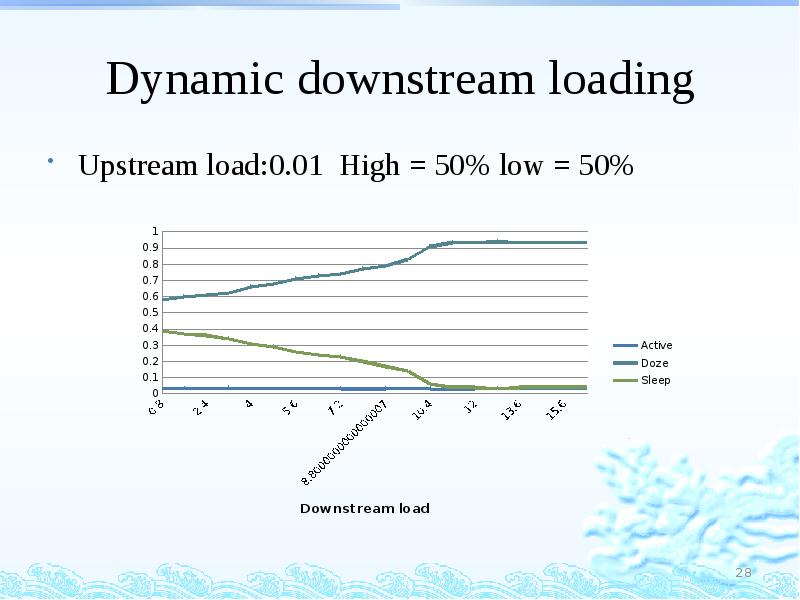
- 28. Dynamic downstream loading Upstream load:0.01 High = 50% low = 50%
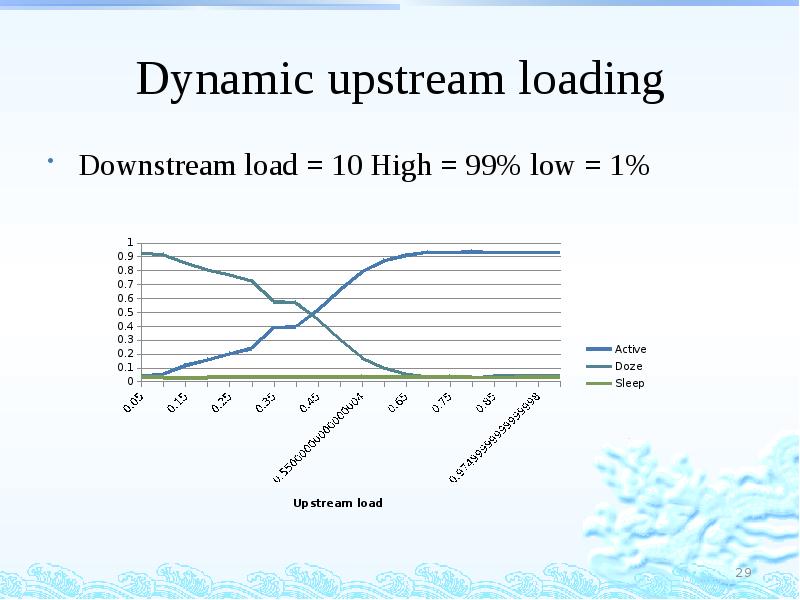
- 29. Dynamic upstream loading Downstream load = 10 High = 99% low
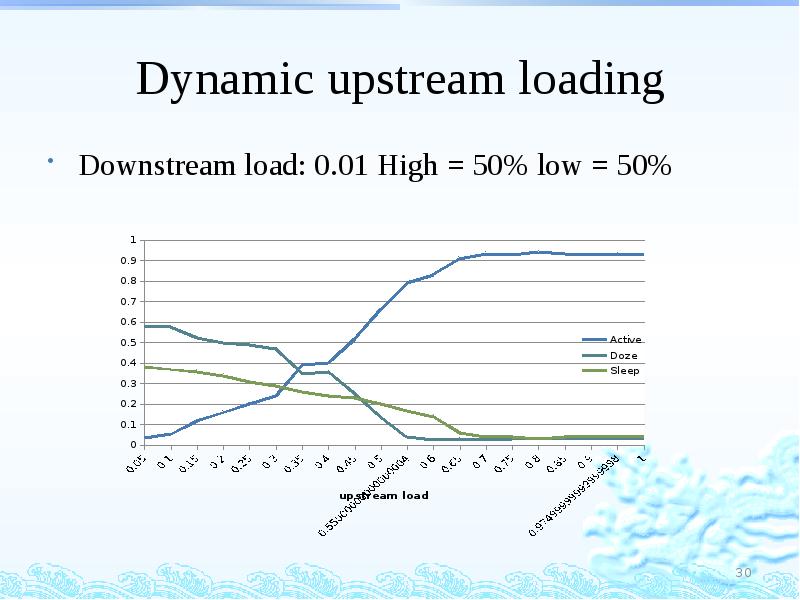
- 30. Dynamic upstream loading Downstream load: 0.01 High = 50% low =
- 31. Conclusion In this study, power saving mechanisms focus on reduce high
- 32. Reference [1] Glen Kramer and Biswanath Mukherjee “IPACT: A Dynamic Protocol
- 33. Thanks for your listening
- 34. Скачать презентацию








![Clockwise three energy-modes switching
Consider performance
A -> S
[1] No Clockwise three energy-modes switching
Consider performance
A -> S
[1] No](/documents_3/4c2c249bf3b5c541a2bc9f63d339fd77/img17.jpg)
![Clockwise three energy-modes switching
D -> A
[5] Stay at doze Clockwise three energy-modes switching
D -> A
[5] Stay at doze](/documents_3/4c2c249bf3b5c541a2bc9f63d339fd77/img18.jpg)
![Counterclockwise three energy-modes switching
D -> S
[4] Stay at Counterclockwise three energy-modes switching
D -> S
[4] Stay at](/documents_3/4c2c249bf3b5c541a2bc9f63d339fd77/img21.jpg)




![Reference
[1] Glen Kramer and Biswanath Mukherjee “IPACT: A Dynamic Protocol Reference
[1] Glen Kramer and Biswanath Mukherjee “IPACT: A Dynamic Protocol](/documents_3/4c2c249bf3b5c541a2bc9f63d339fd77/img31.jpg)

Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему The Design of power saving mechanisms in Ethernet Passive Optical Networks можно ниже:
Похожие презентации