10 Metrics Dividend Investors Need to Know презентация
Содержание
- 2. There are hundreds of possible metrics you can use to evaluate
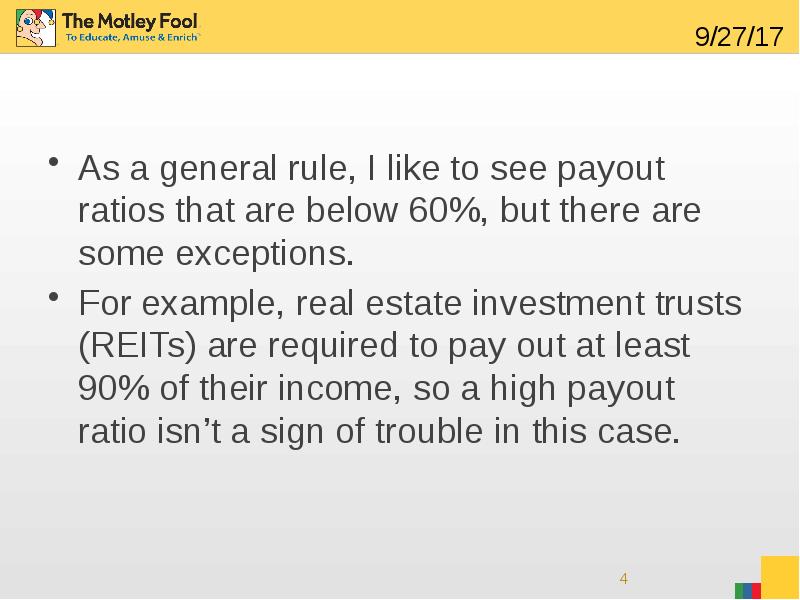
- 3. 1. Payout ratio A stock’s payout ratio is a measurement of
- 4. As a general rule, I like to see payout ratios that
- 5. 2. Dividend yield Surprisingly, dividend yield is possibly the least important
- 6. It’s also worth noting that, because dividend yield depends on the
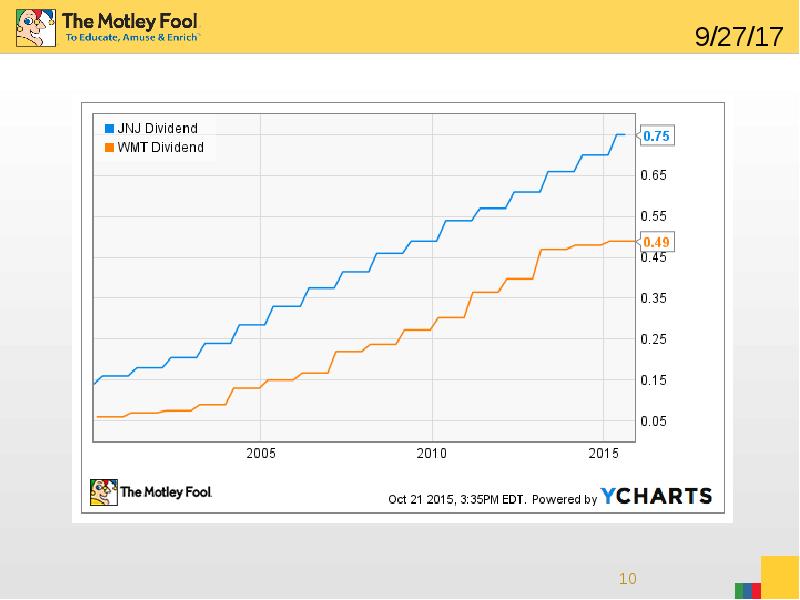
- 7. 3. Dividend history and growth One of the most important factors
- 8. Two examples Let’s look at two of my favorite dividend stocks
- 9. Two examples Wal-Mart has a dividend yield of 3.33%, and a
- 11. 4. Interest coverage Also known as “debt coverage,” this metric tells
- 12. Interest coverage tells us whether a company will be able to
- 13. 5. Total return A stock’s dividend is only one part of
- 14. Wal-Mart and Johnson & Johnson have produced average annual total returns
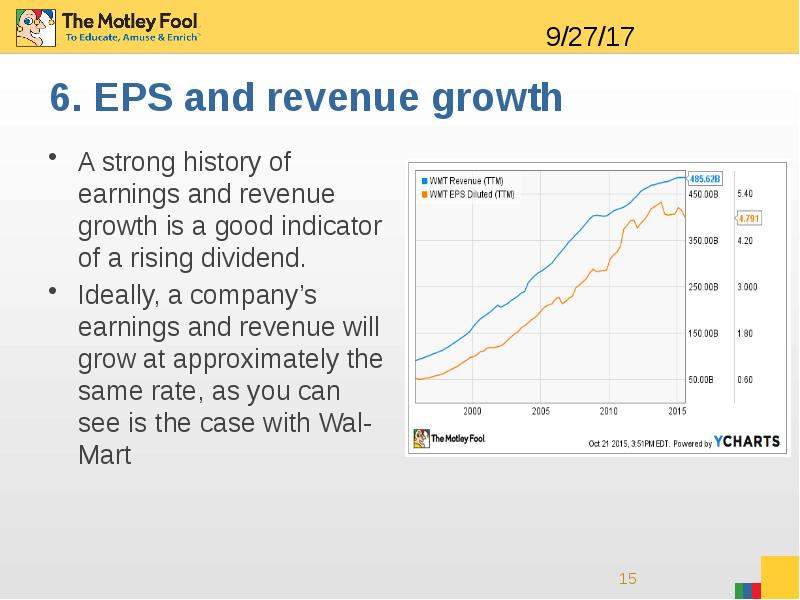
- 15. 6. EPS and revenue growth A strong history of earnings and
- 16. 7. P/E ratio Perhaps the most widely used valuation metric, a
- 17. 8. Share buybacks There are two main ways a company can
- 18. Many investors actually prefer share buybacks to dividends. Dividends paid to
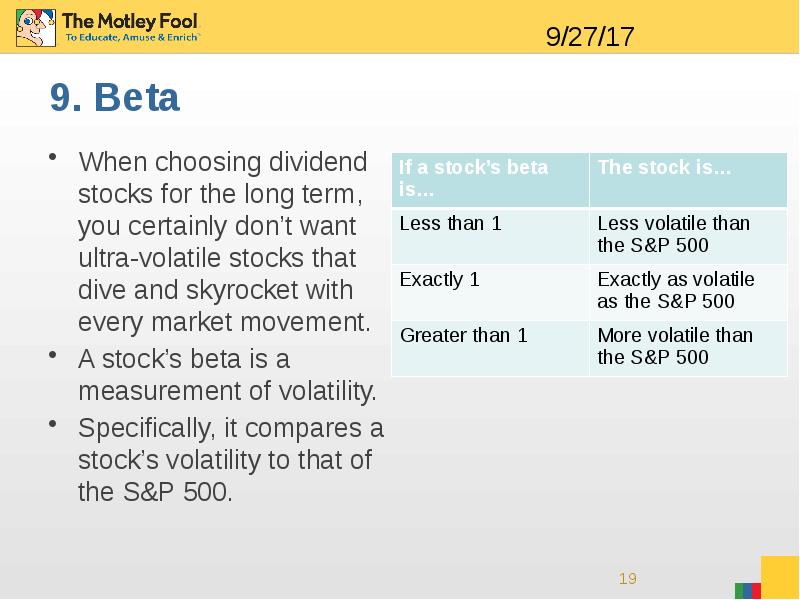
- 19. 9. Beta When choosing dividend stocks for the long term, you
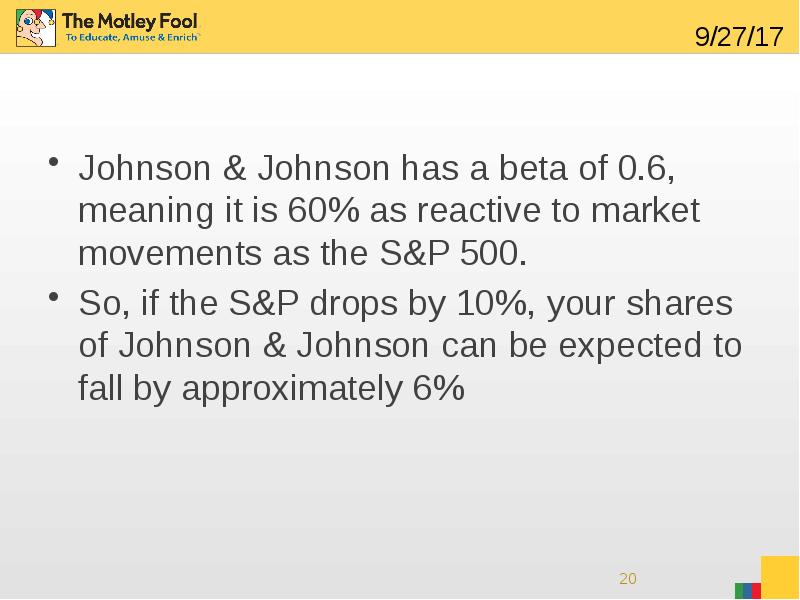
- 20. Johnson & Johnson has a beta of 0.6, meaning it is
- 21. 10. Return on equity (ROE) Return on equity, or ROE, is
- 22. Wal-Mart has a ROE (TTM) of 19.78%, superior to its industry’s
- 23. The simple trick that can add $15,978 to your Social SecurityCLICK
- 24. Скачать презентацию















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему 10 Metrics Dividend Investors Need to Know можно ниже:
Похожие презентации