1)STRUCTURE,LIFE CYCLE OF FLEAS 2)THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE OF HUMAN FLEAS презентация
Содержание
- 2. FLEAS:
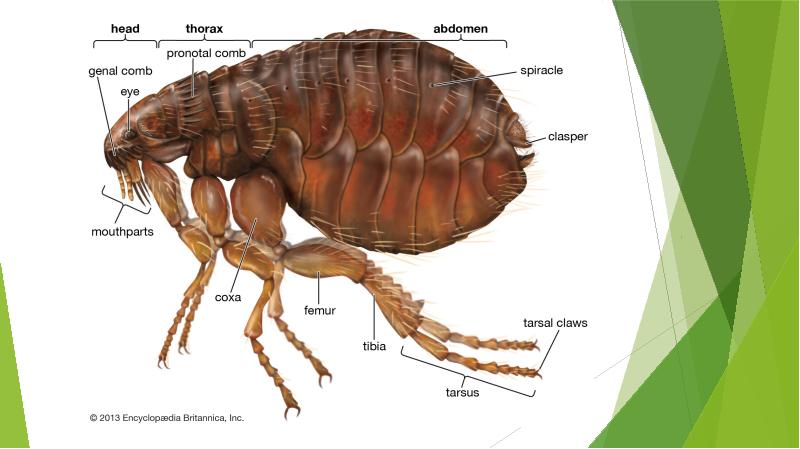
- 3. STRUCTURE OF FLEAS: Fleas are tiny, but anyone who has seen
- 5. To the naked eye, a flea's exoskeleton seems completely smooth, but it's really
- 7. A flea also has spines around its head and mouth –
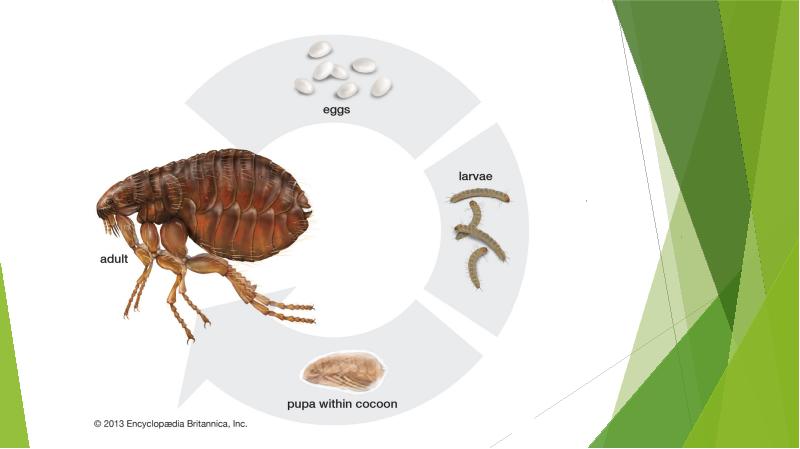
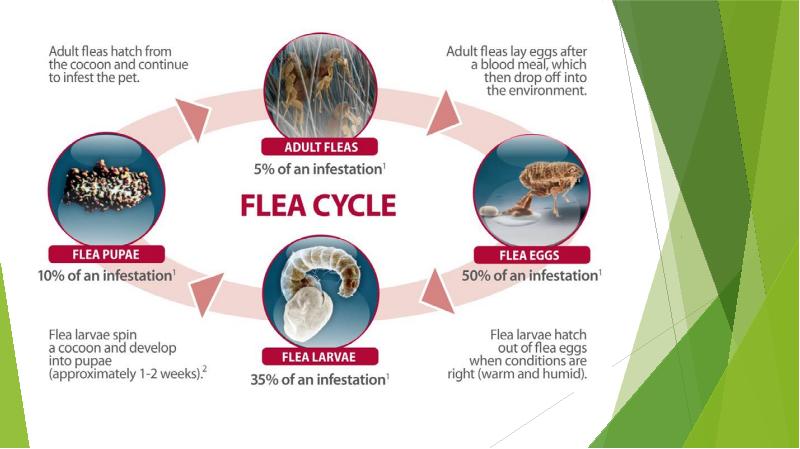
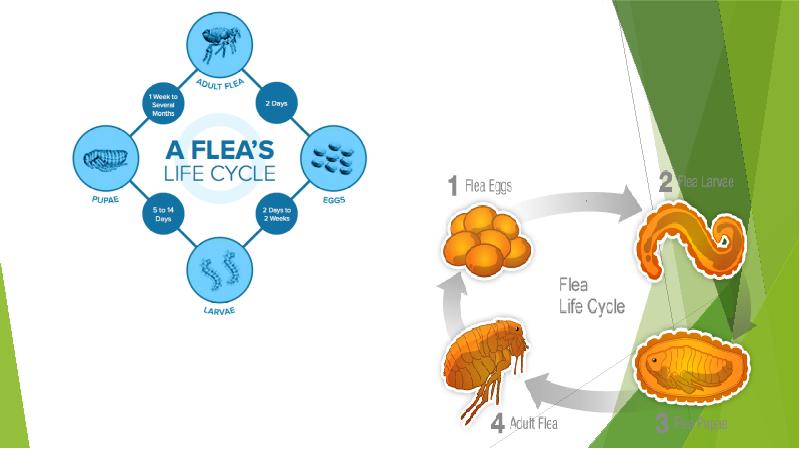
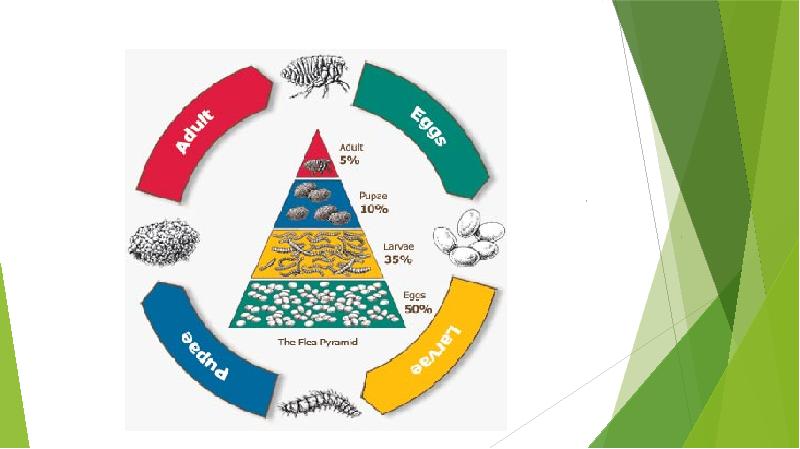
- 10. LIFE CYCLE OF FLEAS:
- 15. EPIDEMIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE OF HUMAN FLEAS
- 17. Some diseases by human fleas… Tungiansis Murine typhus Tularemia Bubonic plague
- 18. Flea associated allergies.. Flea saliva can cause skin dermatitis in
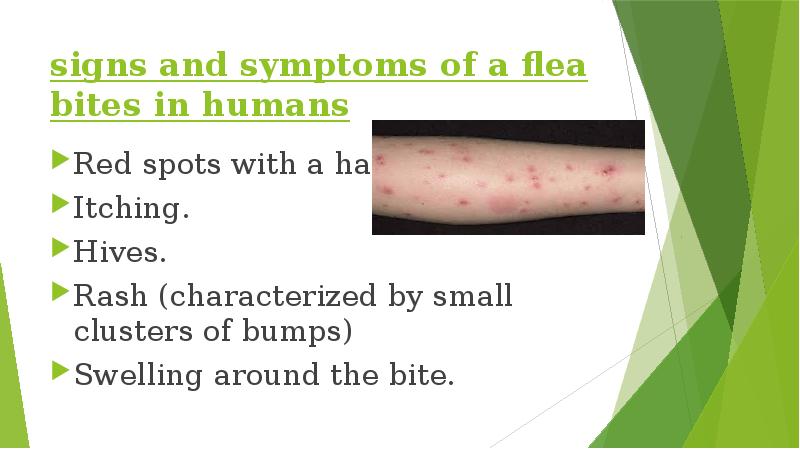
- 19. signs and symptoms of a flea bites in humans Red spots
- 20. Treatment for flea bites Resist the urge to scratch. Wash the
- 21. Diagnosis Identification of fleas is performed with the use of light
- 22. PREVENTION Clean animal bedding and the general surrounds thoroughly. Vacuum the
- 23. THANK YOU
- 24. Скачать презентацию

















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему 1)STRUCTURE,LIFE CYCLE OF FLEAS 2)THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE OF HUMAN FLEAS можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























