Theoretical grammar. (Lecture 1) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Grammar: the origin of the term The term grammar is derived
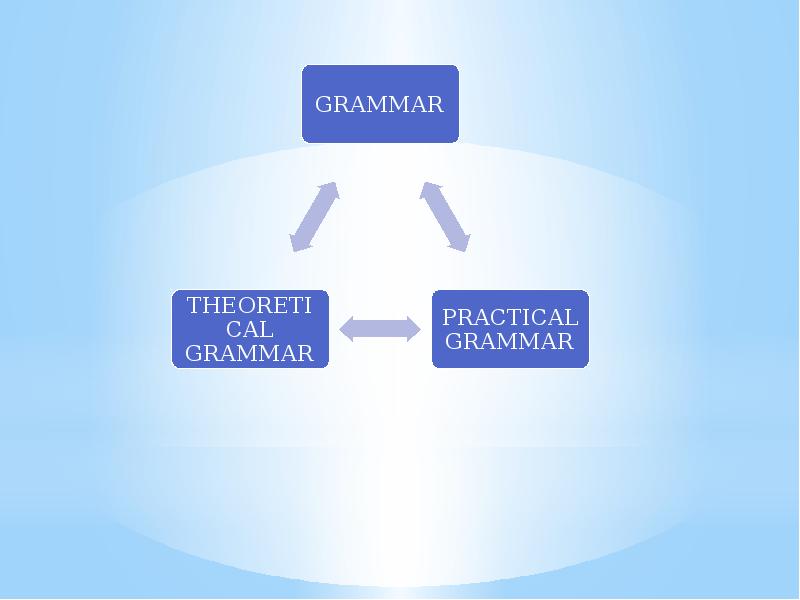
- 4. Theoretical and Practical Grammar Practical grammar gives practical rules of the
- 5. THE AIM OF THEORETICAL GRAMMAR Any course of theoretical grammar today
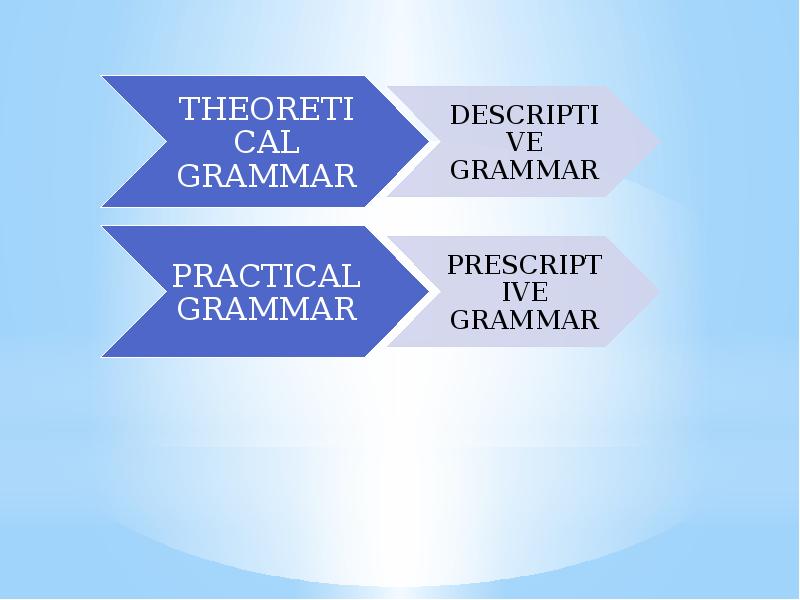
- 7. Prescriptive and Descriptive Grammar Practical grammar prescribes certain rules of usage
- 8. Historical Types of Grammars
- 9. Pāṇini (4th century BCE) is known for his Sanskrit grammar, particularly
- 10. A 17th century birch bark manuscript of Panini’s grammar treatise from
- 11. In ancient Greece and ancient Rome the term ‘grammar’ denoted the
- 12. Traditional Grammar in Ancient Greece Traditional grammar has its origins
- 13. Thrax’s Grammar Thrax distinguishes two basic units of description – the
- 15. Traditional Grammar in Ancient Rome The first Latin grammar was
- 16. From Antiquity to the Present Day The Latin grammars of
- 17. In the middle ages, grammar was the study of Latin.
- 18. Latin Grammars in English Schools Until the end of the sixteenth
- 19. One of the earliest and most popular Latin grammars written in
- 20. Early English Grammars The Renaissance widened linguistic horizons. Scholars turned their
- 21. The First English Grammar The first grammars of English were
- 22. English described through Latin The aim of this grammar was “to
- 23. The Features of Prescriptive Grammar To sum up, early prescriptive
- 24. Descriptive (non-structural) grammar
- 25. Non-Structural Descriptive Grammar Henry Sweet (1845–1912), “New English Grammar,
- 26. Non-Structural Descriptive Grammar in Summary Unlike prescriptivists, descriptivists focus their attention
- 27. Otto Jespersen (1860–1943), a Danish linguist, developed the theory of grammar
- 28. The Emergence of Structuralism
- 30. As a reaction to the atomistic approach to language a new
- 31. The first linguists to speak of language as a system or
- 32. The American Descriptive School
- 33. Frantz Boas, linguist and anthropologist (1858-1942) is usually mentioned as the
- 34. Leonard Bloomfield: ”The study of language can be conducted...only so long
- 35. The American Descriptive School
- 37. The chief contribution of the American Descriptive School to modern linguistics
- 38. The Descriptivist Methods The main methods are (1) the Distributional
- 39. The Distributional Analysis is a method of linguistic research in
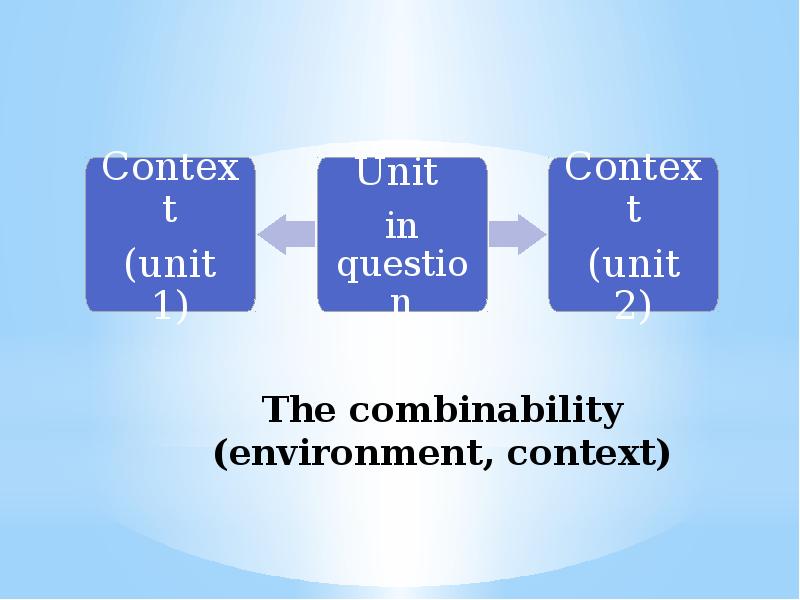
- 40. The combinability (environment, context)
- 41. Distributional hypothesis Linguistic units with similar distributions have similar meanings.
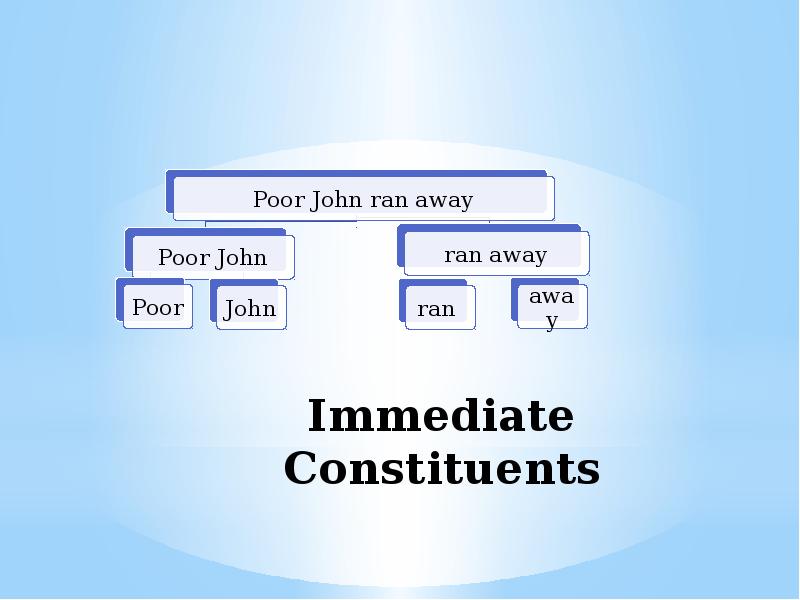
- 42. 2. The Method of Immediate Constituents The term immediate constituents (IC)
- 43. Immediate Constituents
- 44. 2. The Method of Immediate Constituents This method is based on
- 45. DEFINITIONS for the Method of Immediate Constituents
- 46. Definition 1 An immediate constituent is a word or a group
- 47. Definition 2 The ultimate constituents are the smallest meaningful units which
- 48. Definition 3 The linguistics procedure which divides sentences into their component
- 49. Definition 4 The segmentation of the sentence into its immediate constituents
- 50. TRANSFORMATIONAL AGRAMMAR
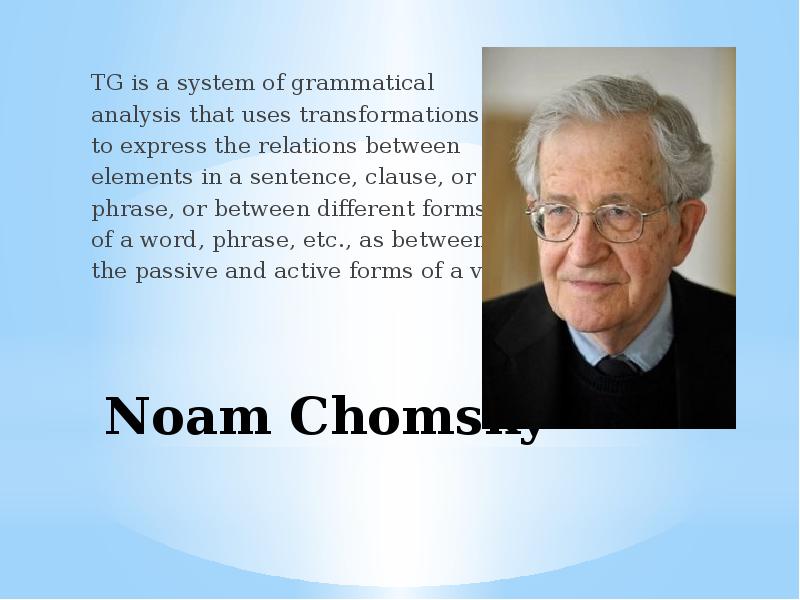
- 51. The idea of the Transformational Grammar (TG) was first suggested by
- 52. Noam Chomsky TG is a system of grammatical analysis that uses
- 53. TG refers to syntax and presupposes the recognition (identification) of such
- 54. According to Chomsky, the central goal of linguistic theory is to
- 55. Кnowing a language involves having the ability to produce and understand
- 56. А GM is a system of explicit rules that may apply
- 58. In generative linguistics 'grammar' refers to the implicit, totally unarticulated knowledge
- 59. In generative linguistics the term 'grammar' covers not only morphology and
- 60. Chomsky has shifted the focus of linguistic theory from the study
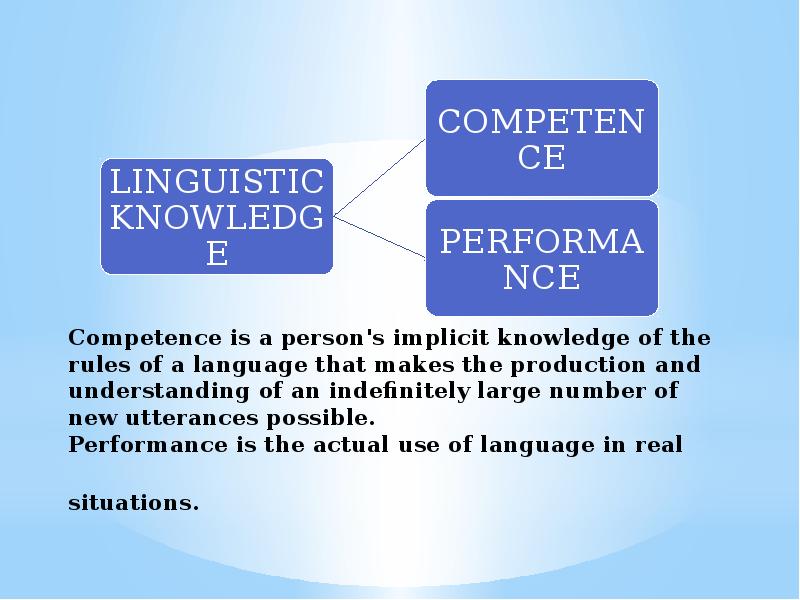
- 61. Chomsky characterises linguistic knowledge using the concepts of competence and performance.
- 62. Competence is a person's implicit knowledge of the rules of a
- 63. Chomsky proposes that competence, rather than performance, is the primary object
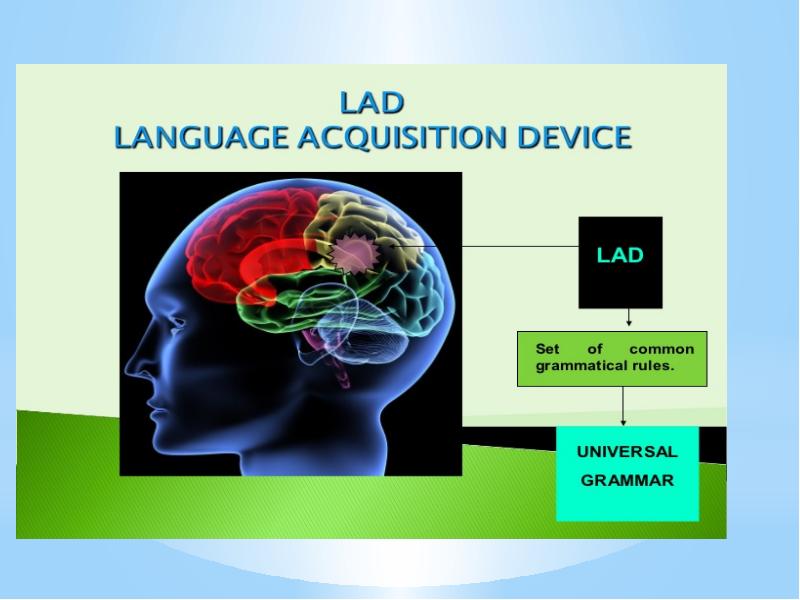
- 64. Chomsky contends that the linguistic capacity of humans is innate. The
- 66. According to Chomsky, Universal Grammar is the faculty of the mind
- 68. The properties that lie behind the competence of speakers of various
- 70. This explains the striking similarity between languages in their essential structural
- 72. TEST 1 1. The method based on the binary principle, which
- 73. 3-5. Add one word into each gap. The first letter is
- 74. 6. Show the chronological order in which the four great grammarians
- 75. 7. Choose as many possible correct answers as necessary: In the
- 76. 8. According to Chomsky, the central goal of linguistic theory is
- 77. 9. According to Chomsky, the linguistic capacity of humans is
- 78. Скачать презентацию




































































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации