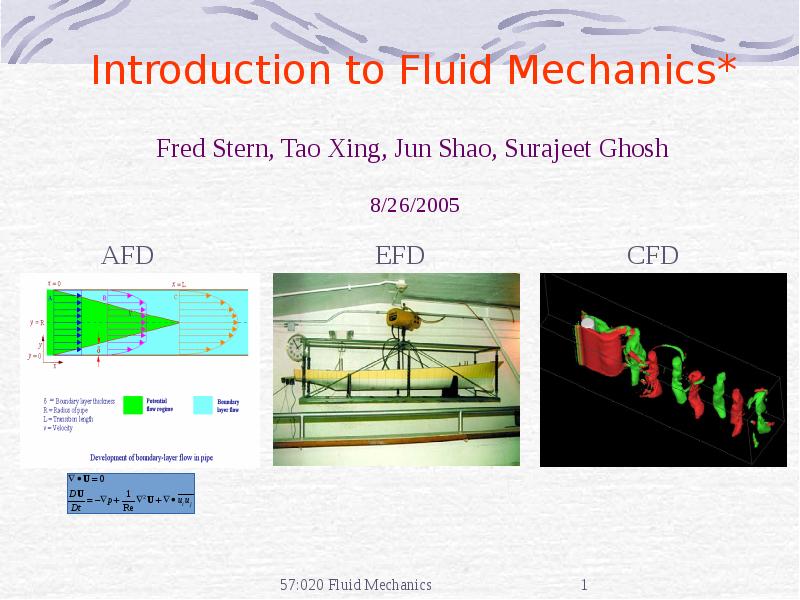
57:020 Fluid Mechanics 1 Introduction to Fluid Mechanics* CFD EFD AFD Fred презентация
Содержание
- 2. Fluid Mechanics Fluids essential to life Human body 65% water Earth’s
- 3. History
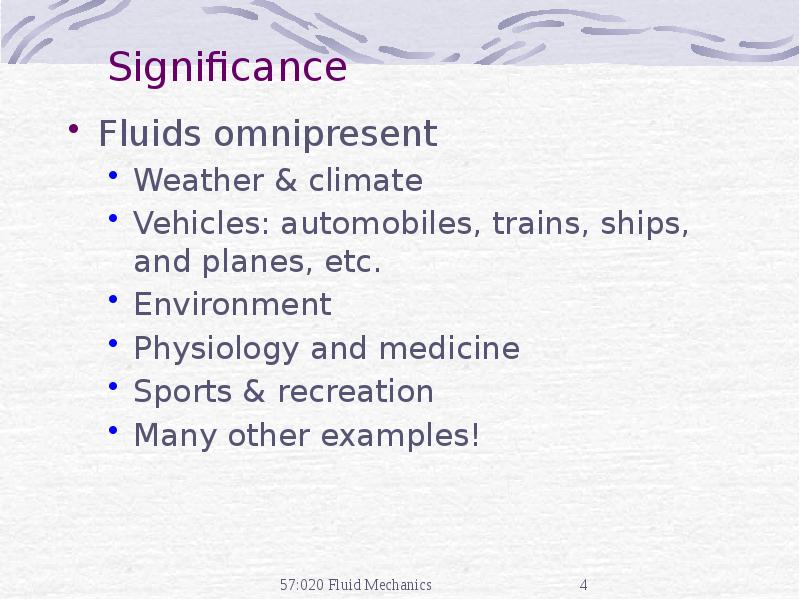
- 4. Significance Fluids omnipresent Weather & climate Vehicles: automobiles, trains, ships, and
- 5. Weather & Climate
- 6. Vehicles
- 7. Environment
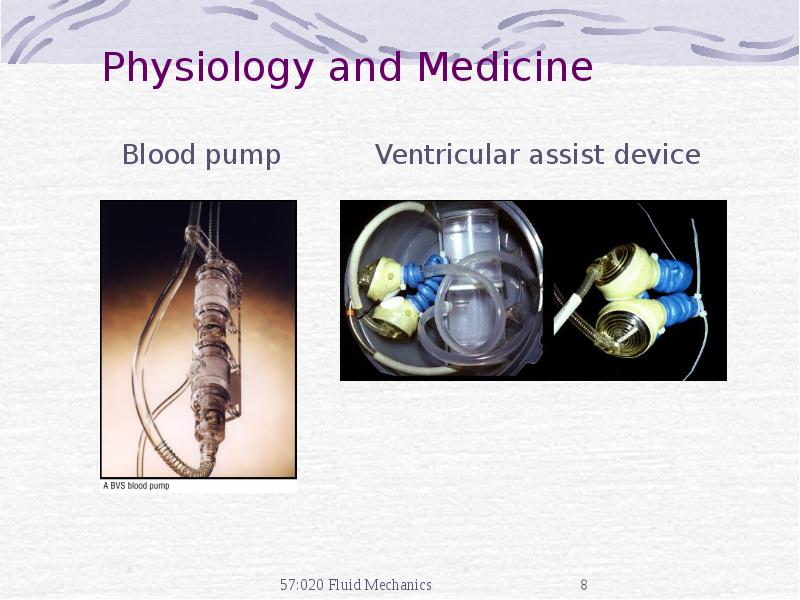
- 8. Physiology and Medicine
- 9. Sports & Recreation
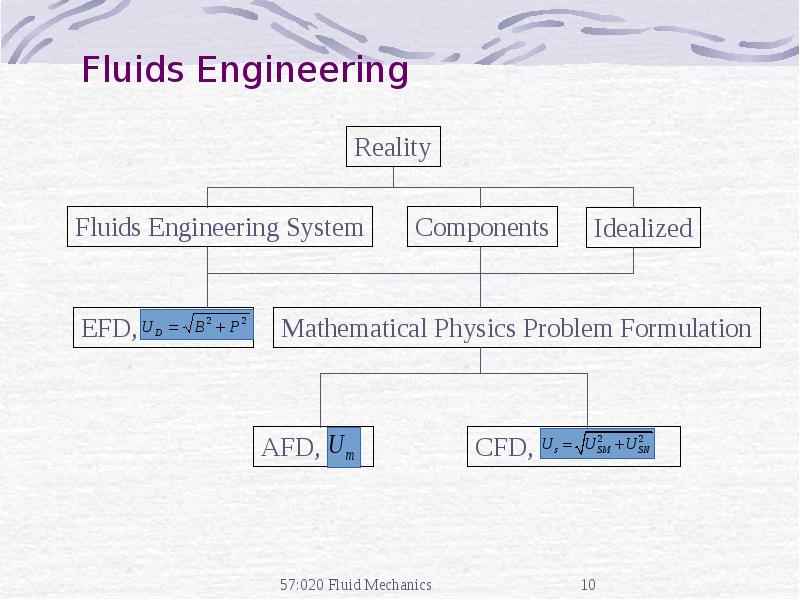
- 10. Fluids Engineering
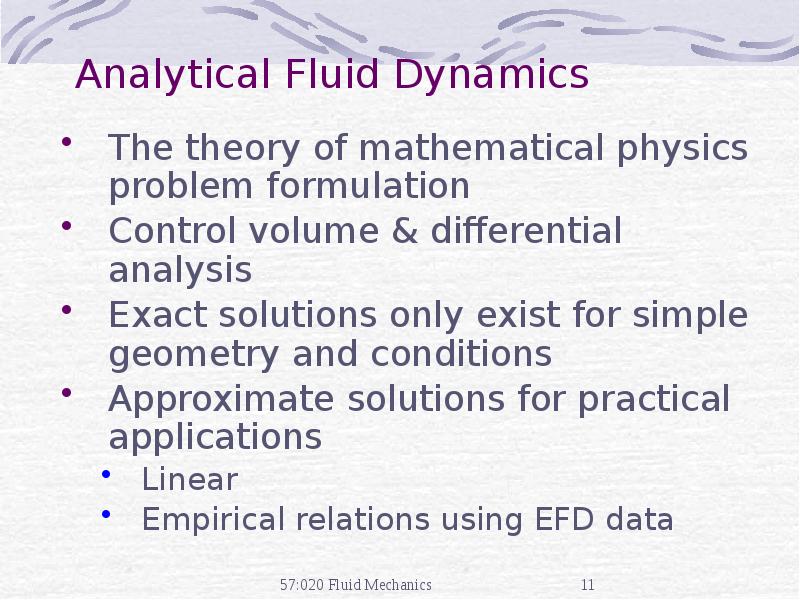
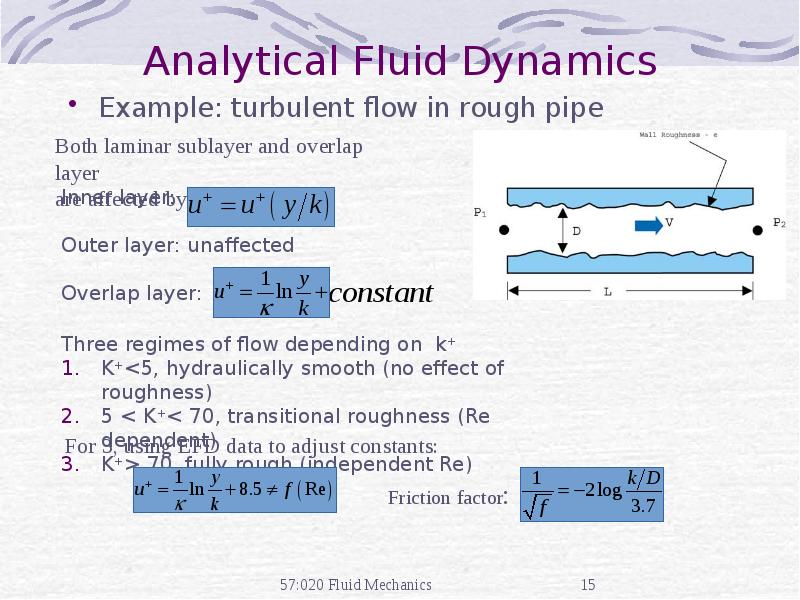
- 11. Analytical Fluid Dynamics The theory of mathematical physics problem formulation Control
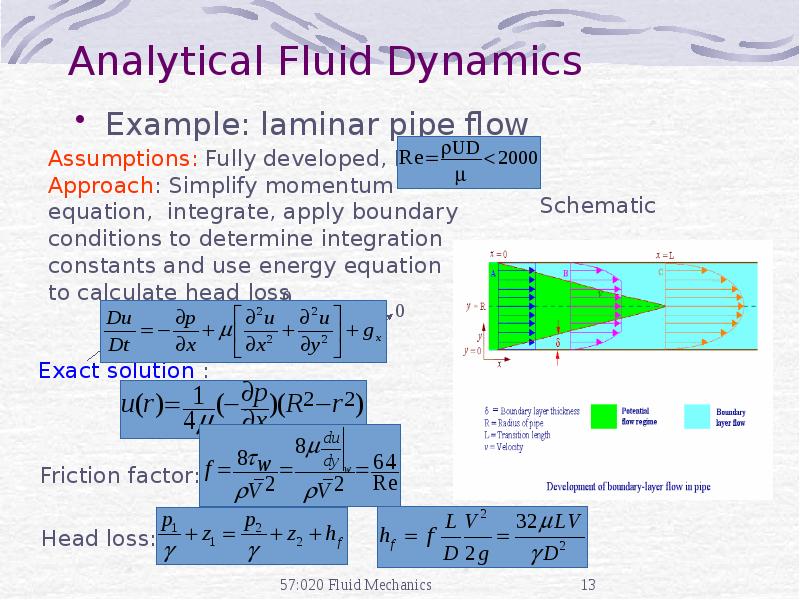
- 13. Analytical Fluid Dynamics Example: laminar pipe flow
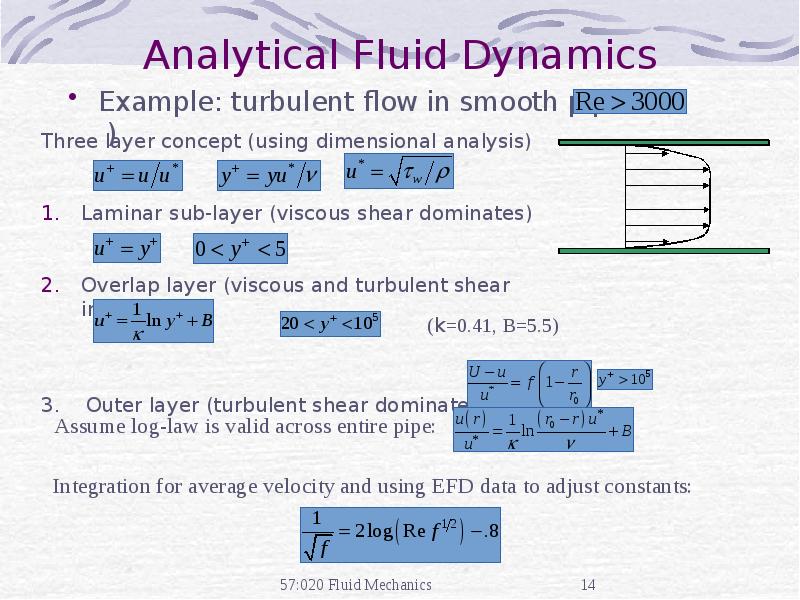
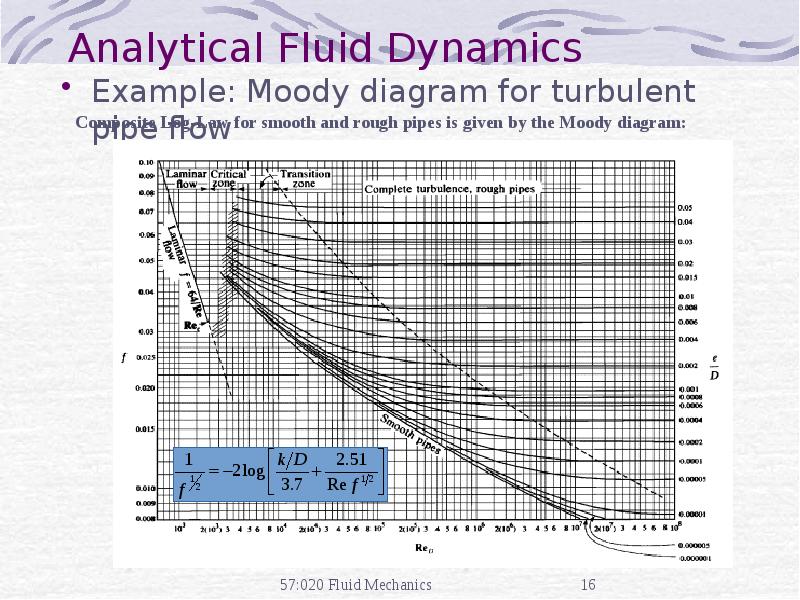
- 16. Analytical Fluid Dynamics Example: Moody diagram for turbulent pipe flow
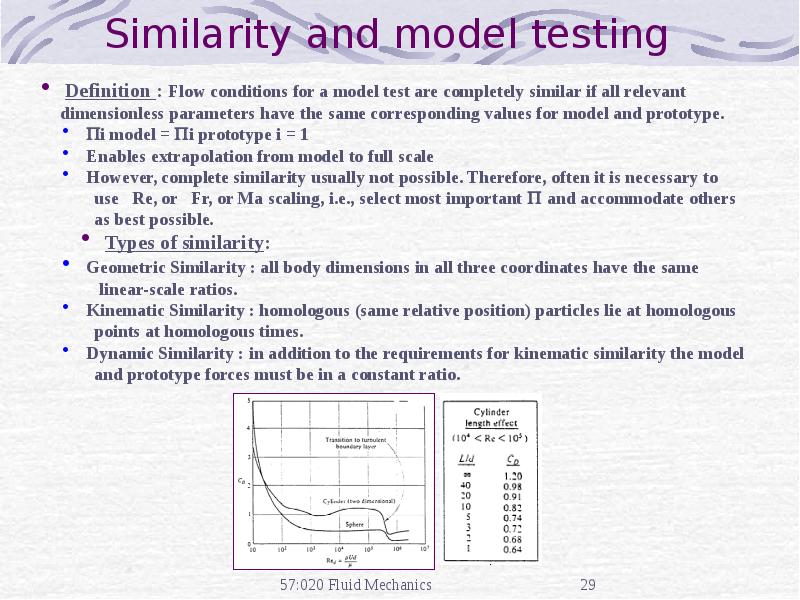
- 17. Experimental Fluid Dynamics (EFD) Definition: Use of experimental methodology and
- 18. Purpose
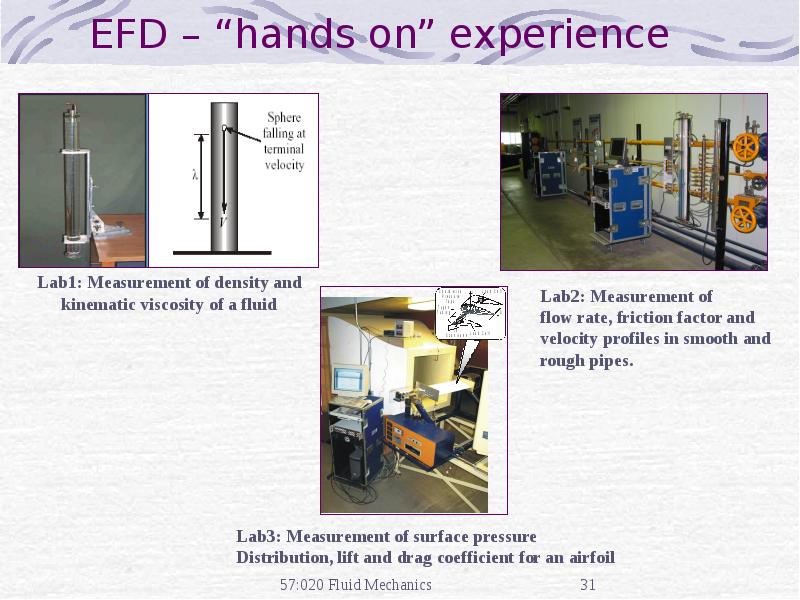
- 19. Applications of EFD
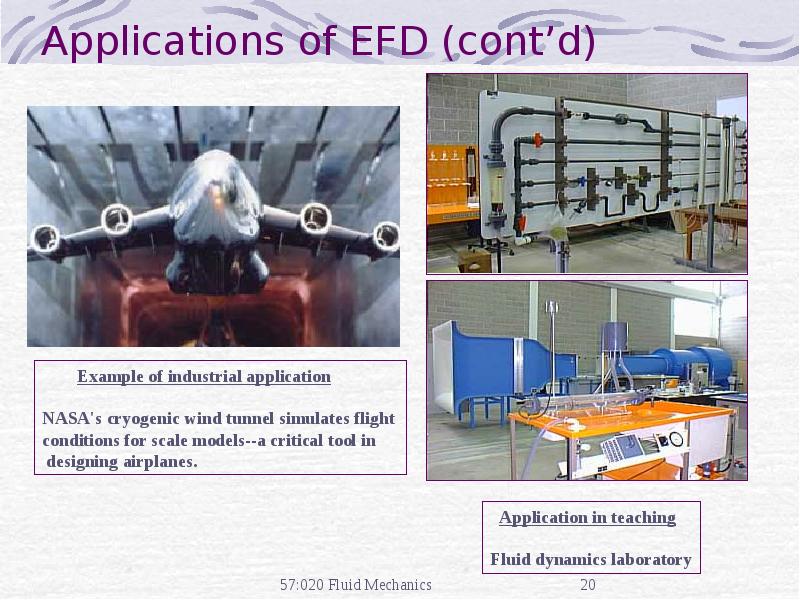
- 20. Applications of EFD (cont’d)
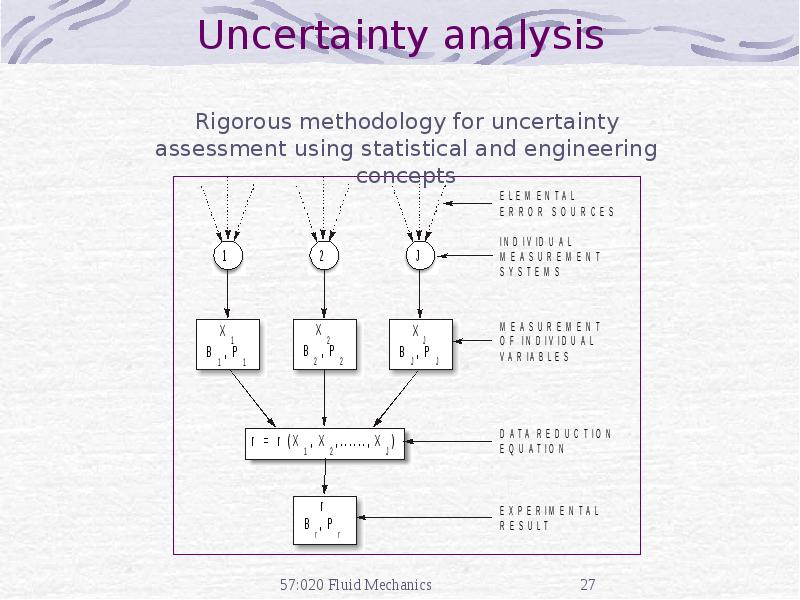
- 30. EFD process
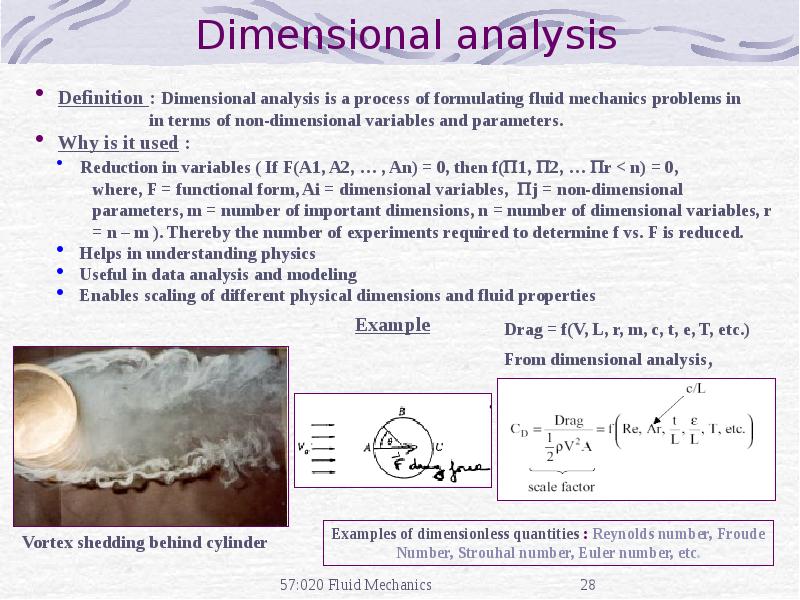
- 32. Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD is use of computational methods for solving
- 33. Purpose The objective of CFD is to model the continuous fluids
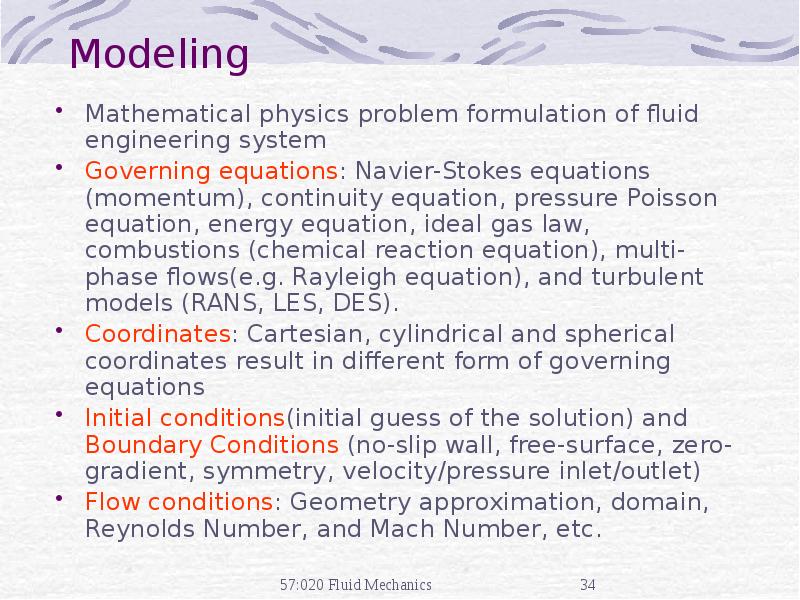
- 34. Modeling Mathematical physics problem formulation of fluid engineering system Governing equations:
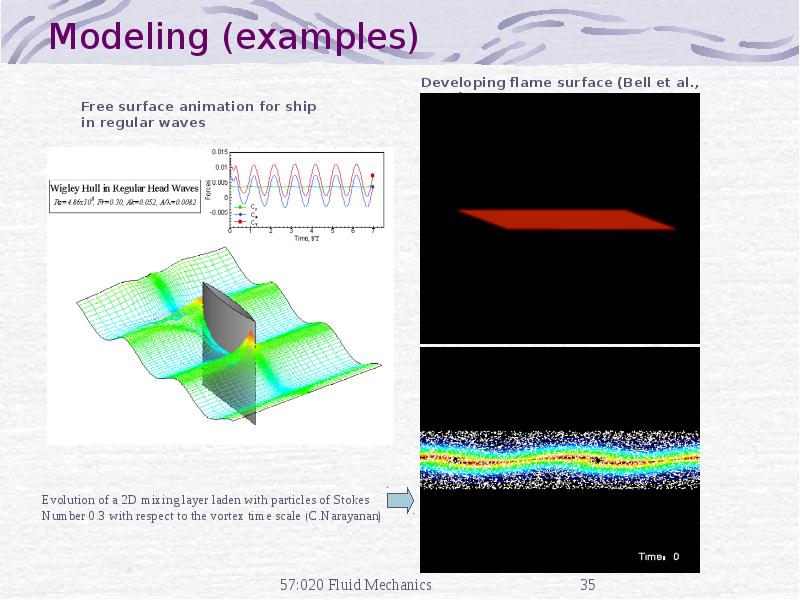
- 35. Modeling (examples)
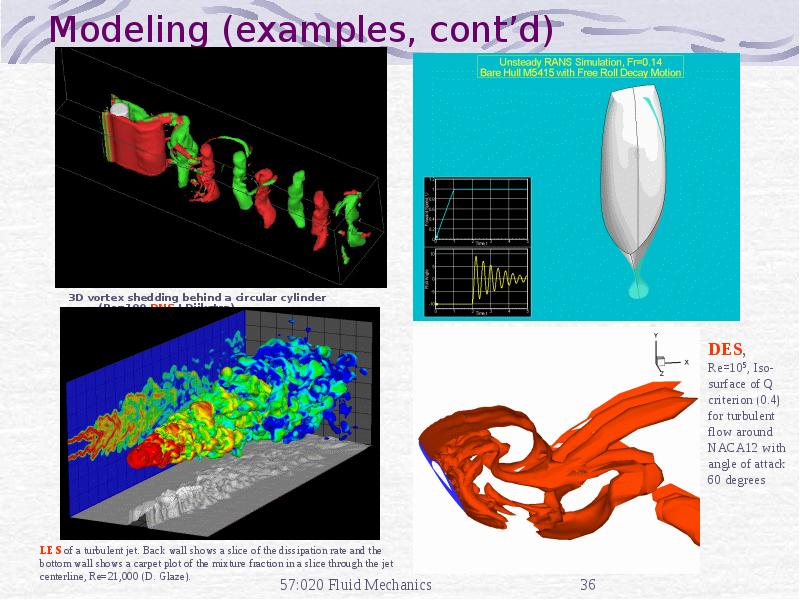
- 36. Modeling (examples, cont’d) 3D vortex shedding behind a circular cylinder (Re=100,DNS,J.Dijkstra)
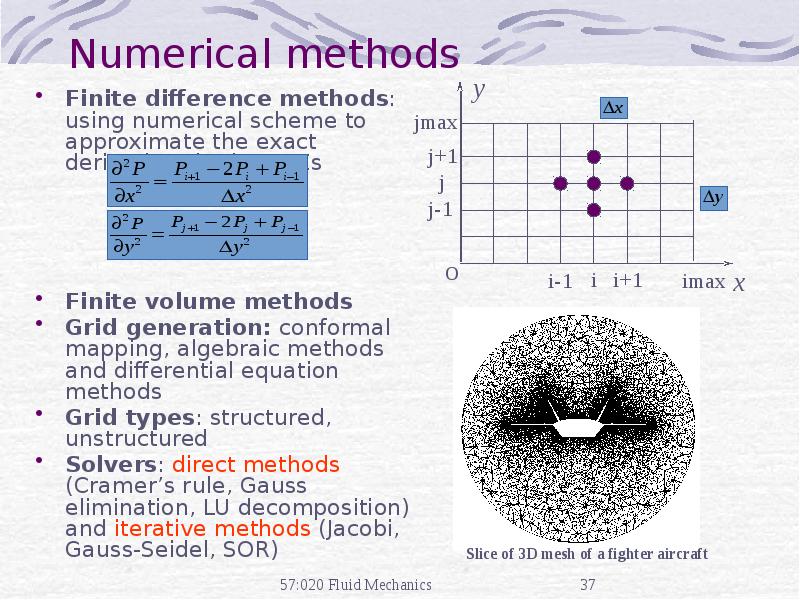
- 37. Numerical methods Finite difference methods: using numerical scheme to approximate the
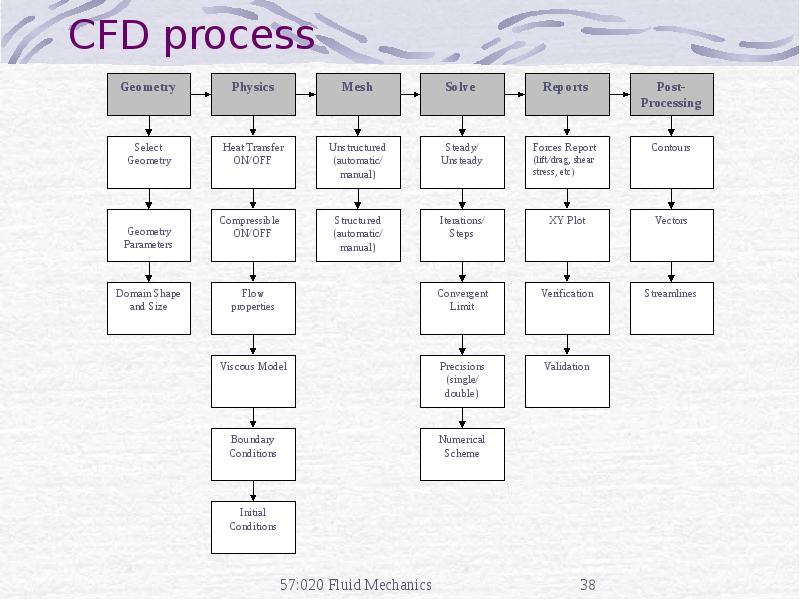
- 38. CFD process
- 39. Commercial software CFD software 1. FLUENT: http://www.fluent.com 2.
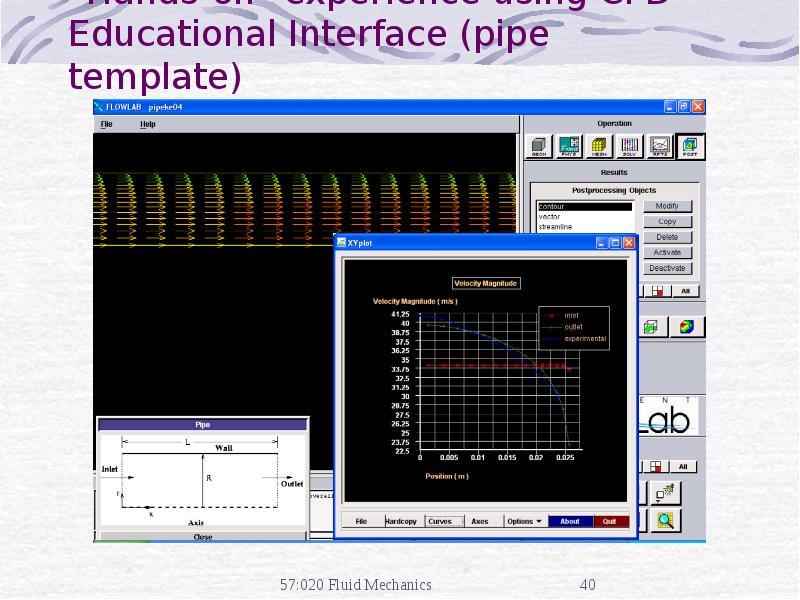
- 40. “Hands-on” experience using CFD Educational Interface (pipe template)
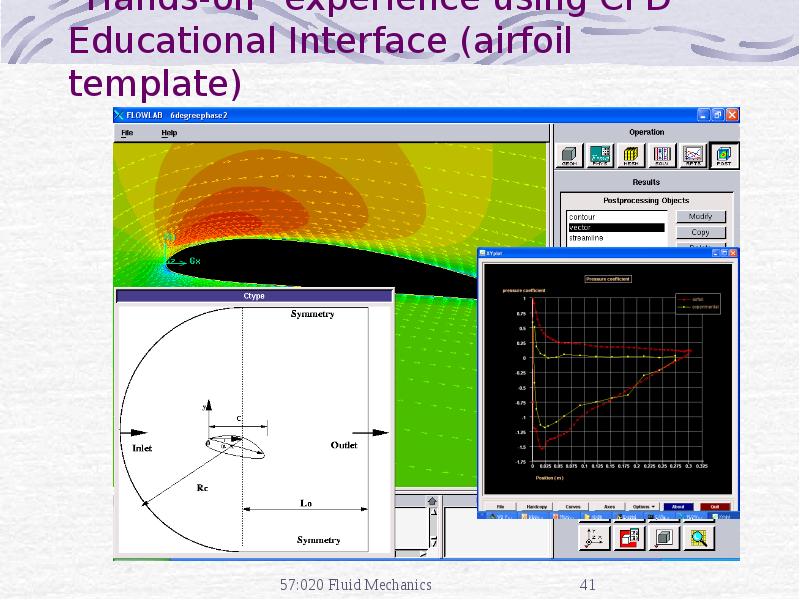
- 41. “Hands-on” experience using CFD Educational Interface (airfoil template)
- 42. 57:020 Fluid Mechanics Lectures cover basic concepts in fluid statics,
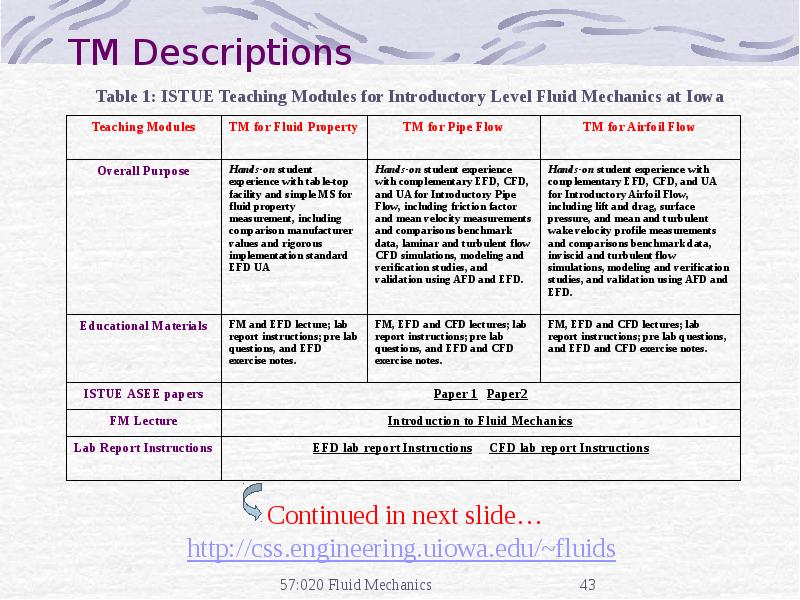
- 43. TM Descriptions
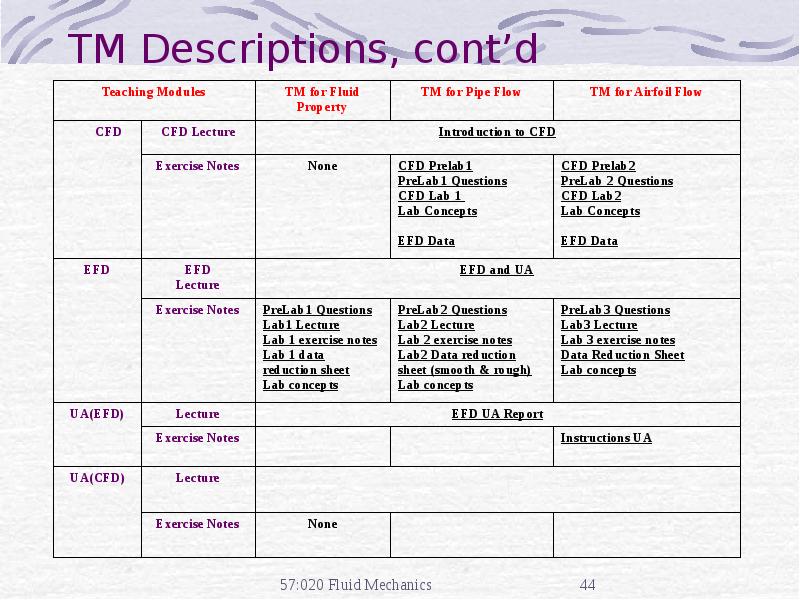
- 44. TM Descriptions, cont’d
- 45. Скачать презентацию















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему 57:020 Fluid Mechanics
1
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics*
CFD
EFD
AFD
Fred можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























