AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM презентация
Содержание
- 2. Metabolism, Energy, and Life 1. The chemistry of life is organized into
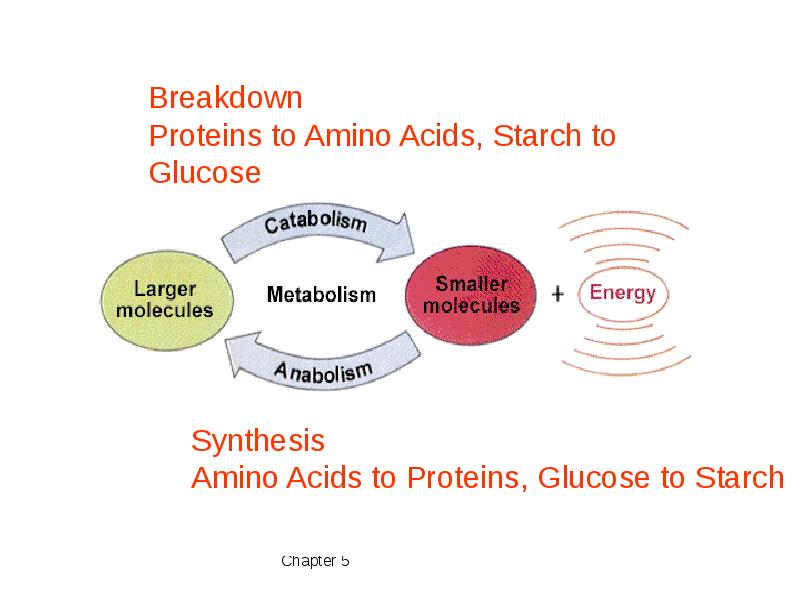
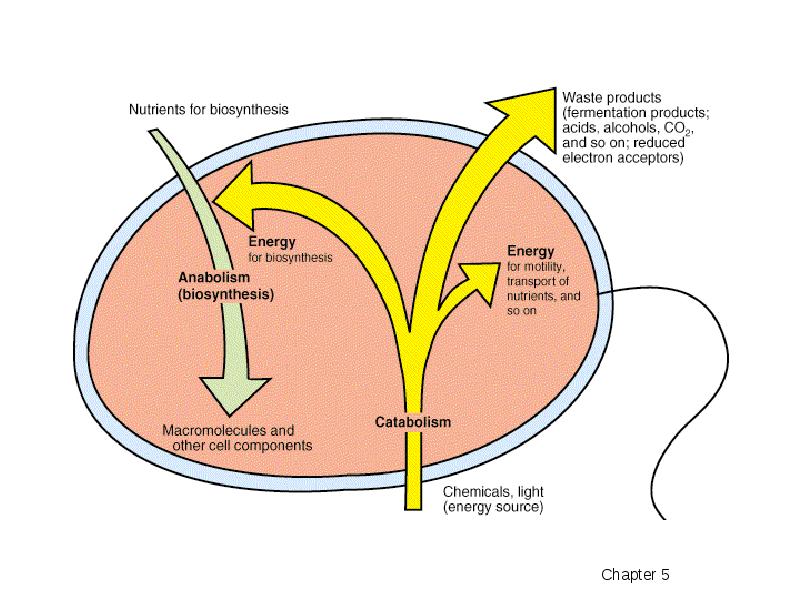
- 4. Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler
- 6. Organisms transform energy Energy is the capacity to do work -
- 7. Organisms live at the expense of free energy Spontaneous processes can
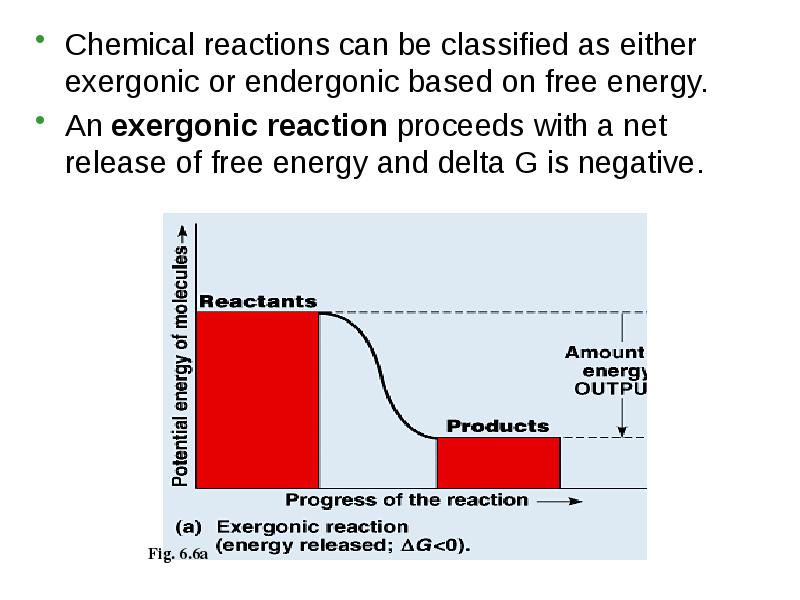
- 8. Chemical reactions can be classified as either exergonic or endergonic based
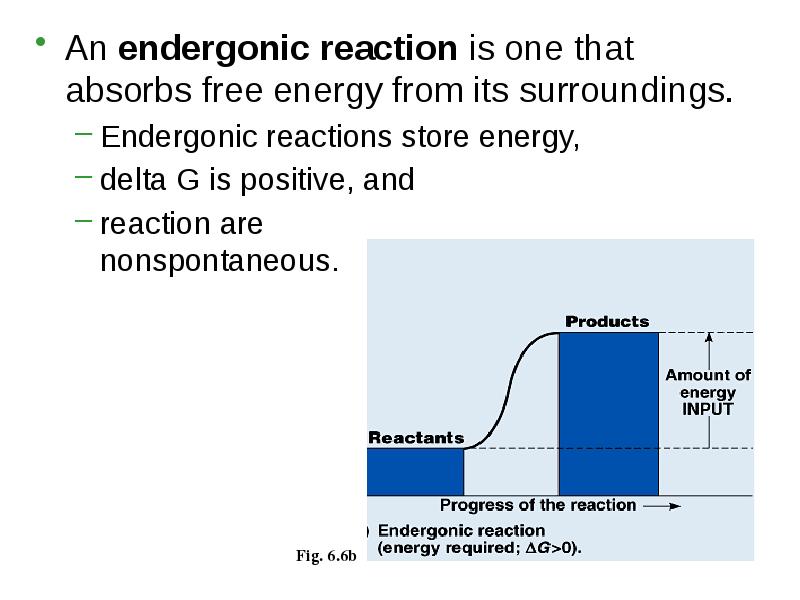
- 9. An endergonic reaction is one that absorbs free energy from its
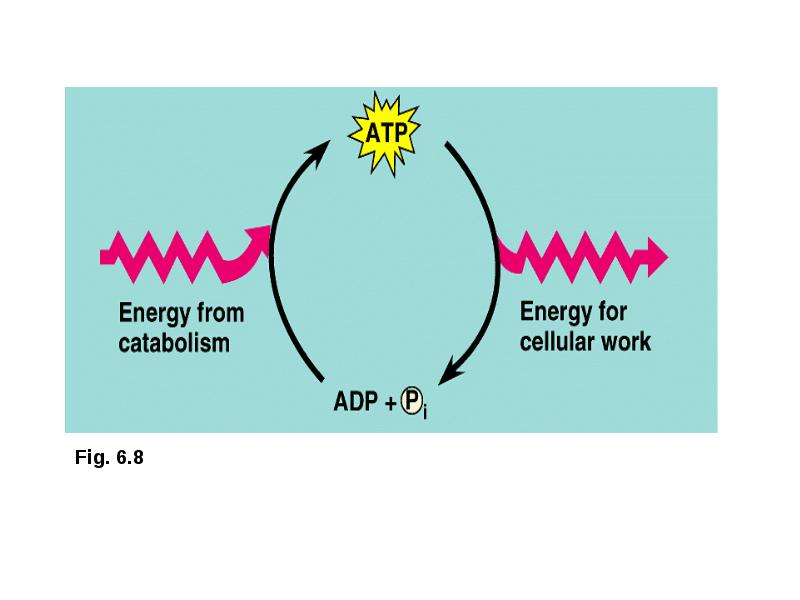
- 10. ATP ATP powers cellular work A cell does three main kinds
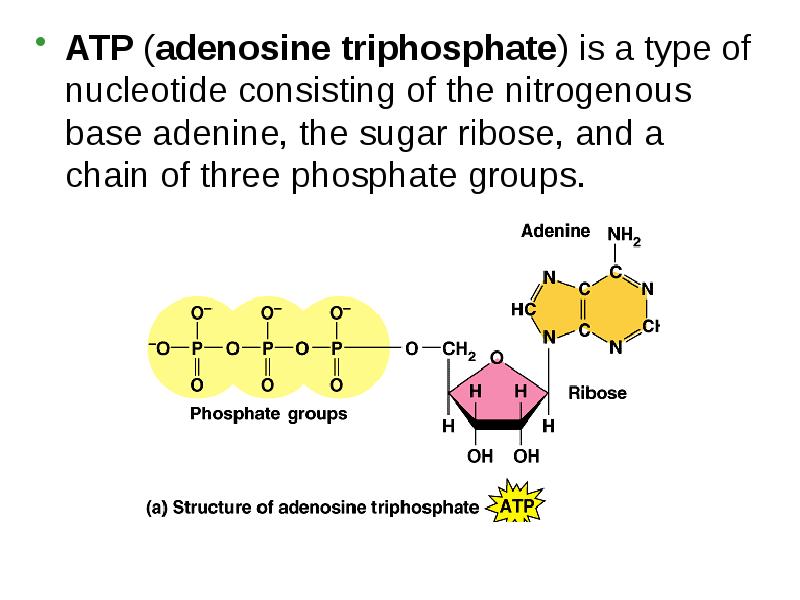
- 11. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a type of nucleotide consisting of the
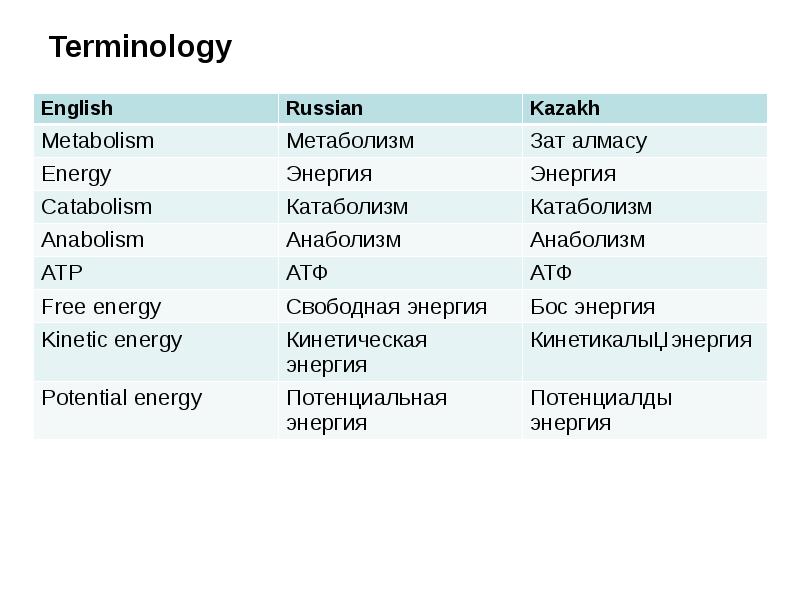
- 13. Terminology
- 14. Скачать презентацию






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























