Antimicrobial drugs презентация
Содержание
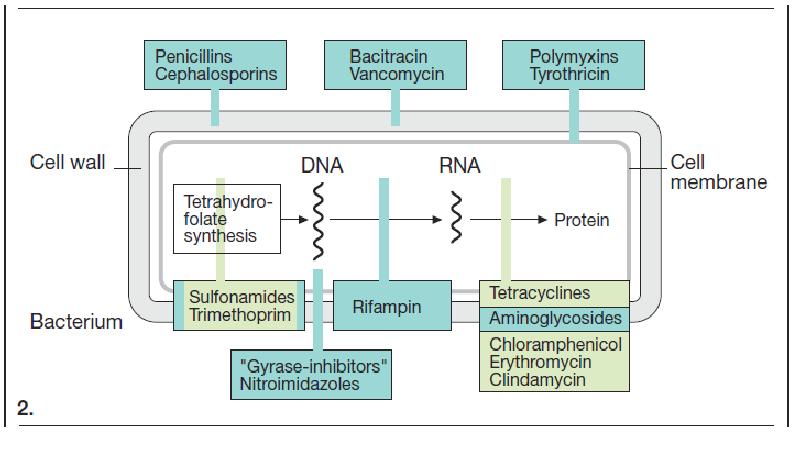
- 2. Antimicrobial drugs have antimicrobial properties. They are divided into 2 groups:
- 4. Disinfectants and Antiseptics Disinfectants and Antiseptics Disinfection denotes the inactivation or
- 5. Phenol was the first antiseptics. Phenol was the first antiseptics.
- 6. Antisepsis refers to the reduction by chemical agents of germ numbers
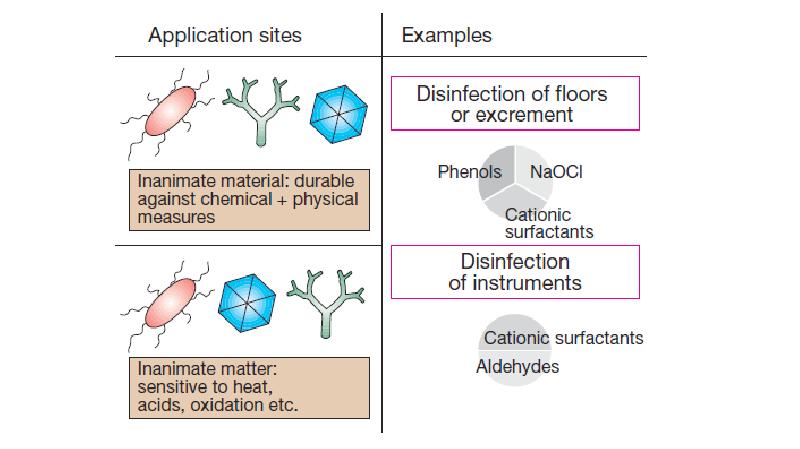
- 7. Disinfectants come from various chemical classes, including oxidants, halogens or halogen-releasing
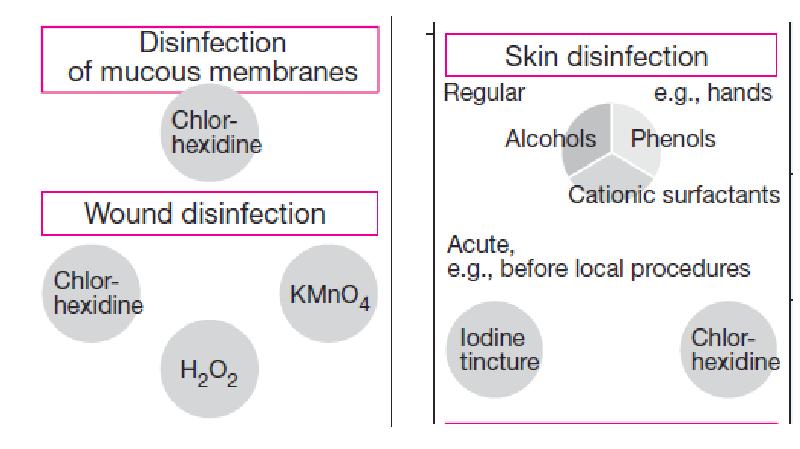
- 8. Applications Applications Skin “disinfection.” (Reduction of germs before injections or surgical
- 10. Wound disinfection can be achieved with hydrogen peroxide or with potassium
- 12. Disinfection of instruments: Instruments that cannot be heat- or steam sterilized
- 13. Chemotherapeutic drugs inhibit/kill the infecting organism and have no/minimal effect on
- 14. Basic principles of chemotherapy Basic principles of chemotherapy Early start of
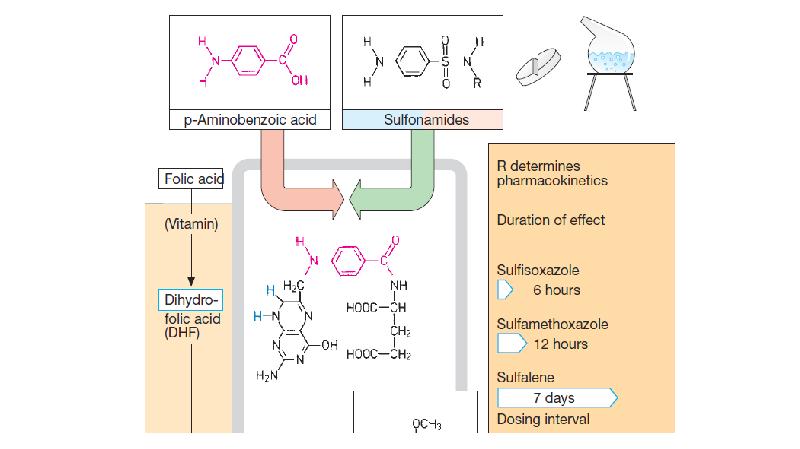
- 15. SULFONAMIDES Sulfonamides were the first antimicrobial agents (AMAs) effective against
- 17. Sulfonamides are primarily bacteriostatic against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. However,
- 18. 1. Preparations used for their systemic action: 1. Preparations used for
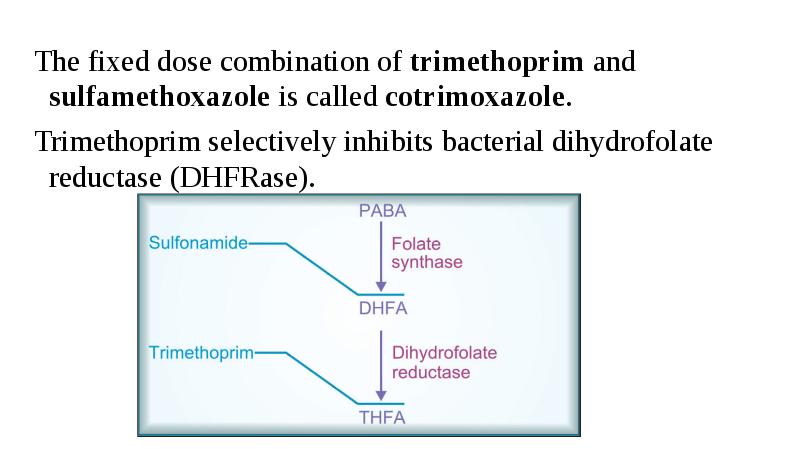
- 19. The mechanism is connected with their competitive antagonism with para-aminobenzoic acid
- 20. Sulfonamides are rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from G.I.T. Extent of
- 21. Sulfonamides are excreted mainly by the kidney through glomerular filtration. Both
- 22. Side effects: Side effects: Nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain. Crystalluria .
- 23. USES: USES: suppressive therapy of chronic urinary tract infection; ear, throat,
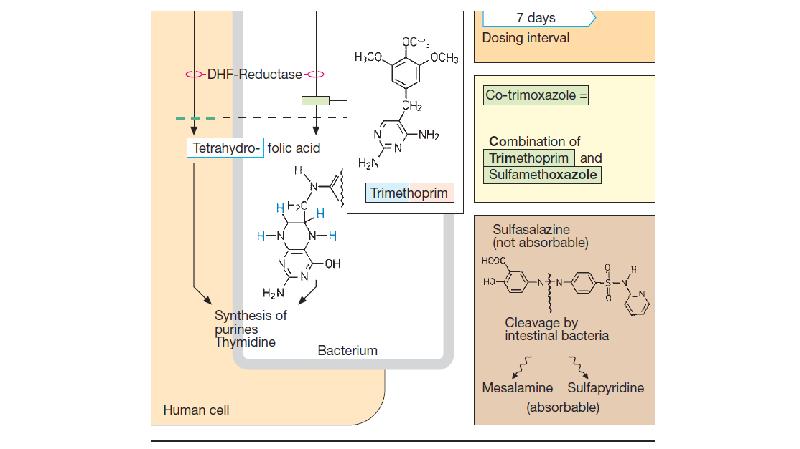
- 24. The fixed dose combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole is called cotrimoxazole.
- 26. Individually, both sulfonamide and trimethoprim are bacteriostatic, but the combination becomes
- 27. Uses Uses Urinary tract infections (acute cystitis, prostatitis); Respiratory
- 28. Side effects of cotrimoxazole Side effects of cotrimoxazole Nausea, vomiting, stomatitis,
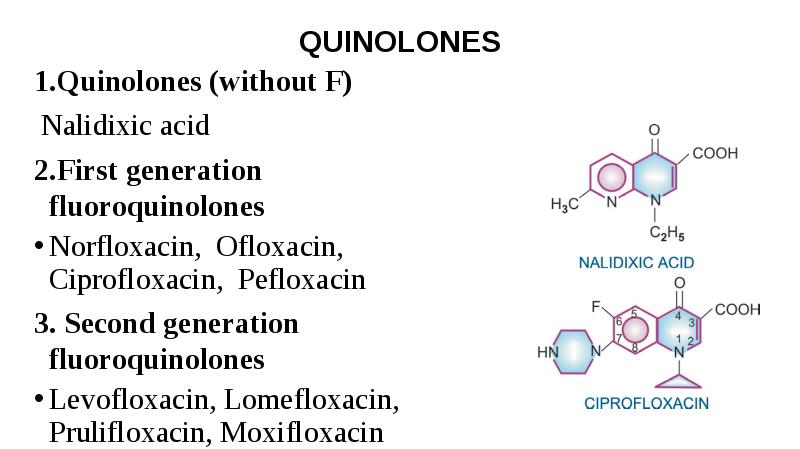
- 29. QUINOLONES 1.Quinolones (without F) Nalidixic acid 2.First generation fluoroquinolones Norfloxacin, Ofloxacin,
- 31. Nalidixic acid Nalidixic acid It is active against gram-negative bacteria (
- 32. Nalidixic acid is primarily used as a urinary antiseptic. It has
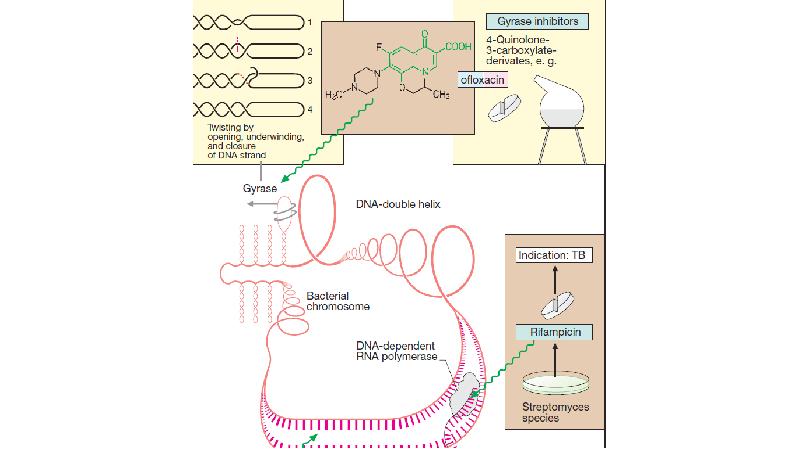
- 33. FLUOROQUINOLONES FLUOROQUINOLONES These preparations exhibit a bactericidal effect. Mechanism of action
- 34. The spectrum of action of First generation fluoroquinolones The spectrum of
- 35. The spectrum of action of 2 generation fluoroquinolones The spectrum of
- 36. Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacokinetics: Drugs are absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
- 37. Uses Uses Urinary tract infections; Gonorrhoea; Chancroid; Bacterial gastroenteritis: dysentery, salmonellosis,
- 38. Respiratory infections (2nd generation FQs is better); Respiratory infections (2nd generation
- 40. Side effects Side effects Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea); Allergic
- 41. Derivative of 8-hydroxyquinoline – Nitroxoline Derivative of 8-hydroxyquinoline – Nitroxoline Mechanism:
- 42. Pharmacokinetics. Pharmacokinetics. Nitroxoline is administered orally 4 times a
- 43. Nitrofuran derivatives Nitrofuran derivatives Nitrofural : antiseptic Furazolidon: intestinal infections, giardiasis,
- 44. Mechanism: Mechanism: The restoration of the nitro group to
- 45. Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics They are absorbed from the digestive tract
- 46. Side effects Side effects Dyspeptic disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; Cholestasis; disorders
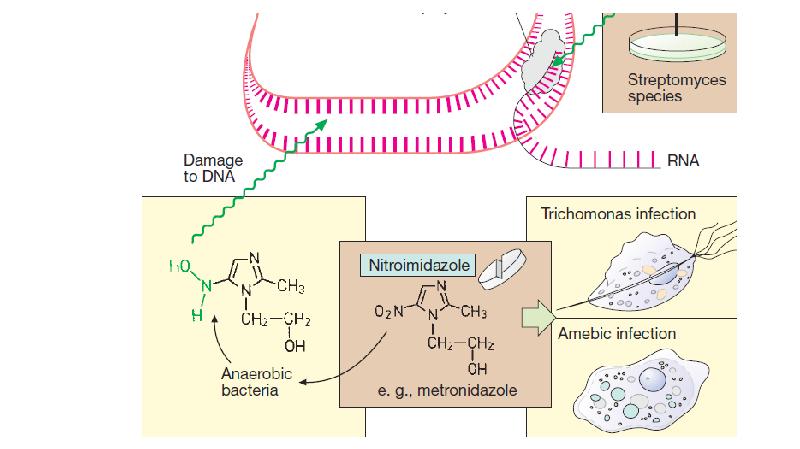
- 47. Nitroimidazoles Nitroimidazoles Metronidazole, Tinidazole, Ornidazole Spectrum: Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis,
- 49. Mechanism of action Mechanism of action Metronidazole is selectively toxic to
- 50. They are almost completely absorbed from the small intestines; little unabsorbed
- 51. Indications for uses Indications for uses Amoebiasis Giardiasis Trichomonas vaginitis Anaerobic
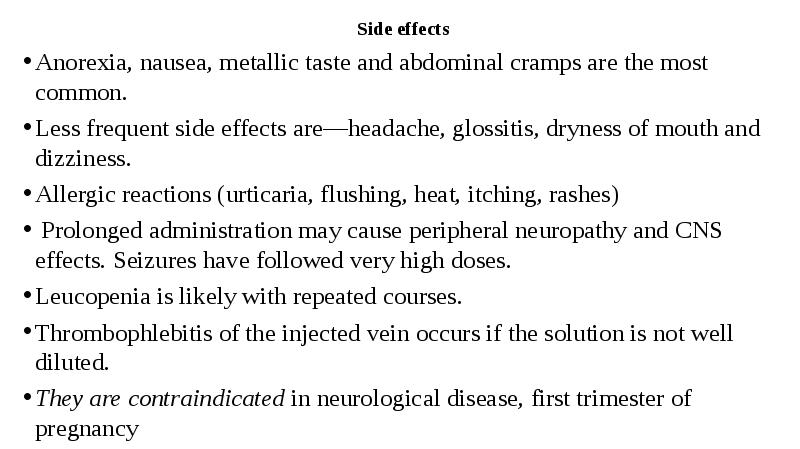
- 52. Side effects Side effects Anorexia, nausea, metallic taste and abdominal cramps
- 53. OXAZOLIDINONE - Linezolid OXAZOLIDINONE - Linezolid It is active against Staphylococcus
- 54. Linezolid inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by acting at an early step.
- 55. Quinoxaline derivatives – quinoxidine and dioxidine Quinoxaline derivatives – quinoxidine
- 56. Literature 1. Tripathi K.D. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. Eighth Edition. -2019.-
- 57. Скачать презентацию










































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























