Chapter 42 презентация
Содержание
- 2. Overview: Trading Places Every organism must exchange materials with its environment.
- 3. For most cells making up multicellular organisms, direct exchange with the
- 5. Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body In
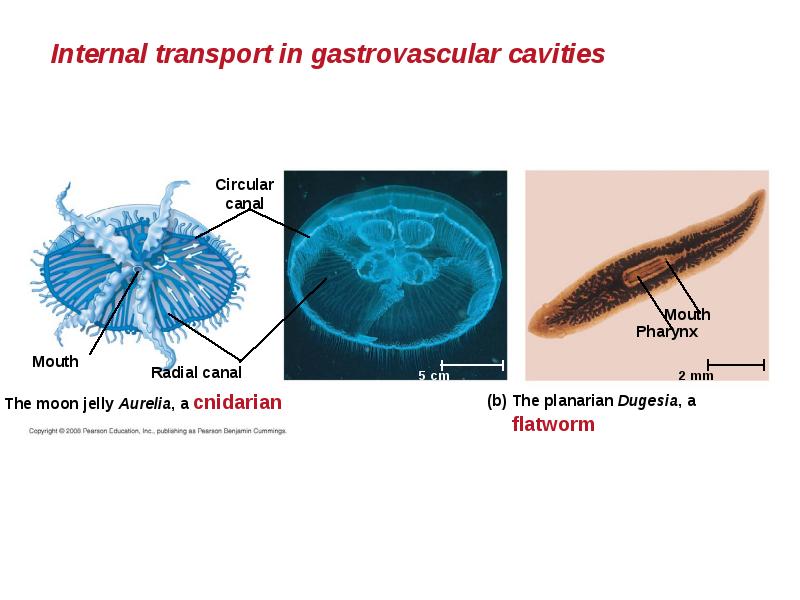
- 6. Gastrovascular Cavities Simple animals, such as cnidarians, have a body wall
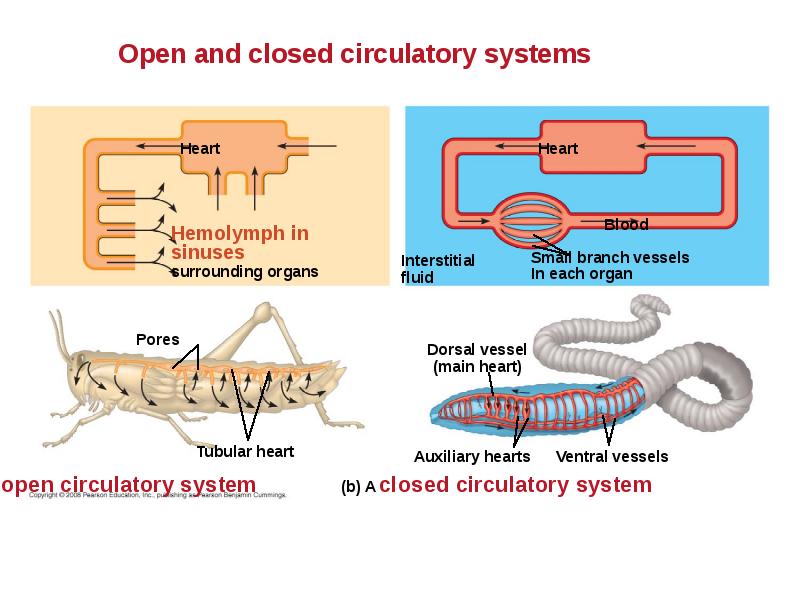
- 8. Open and Closed Circulatory Systems More complex animals have either open
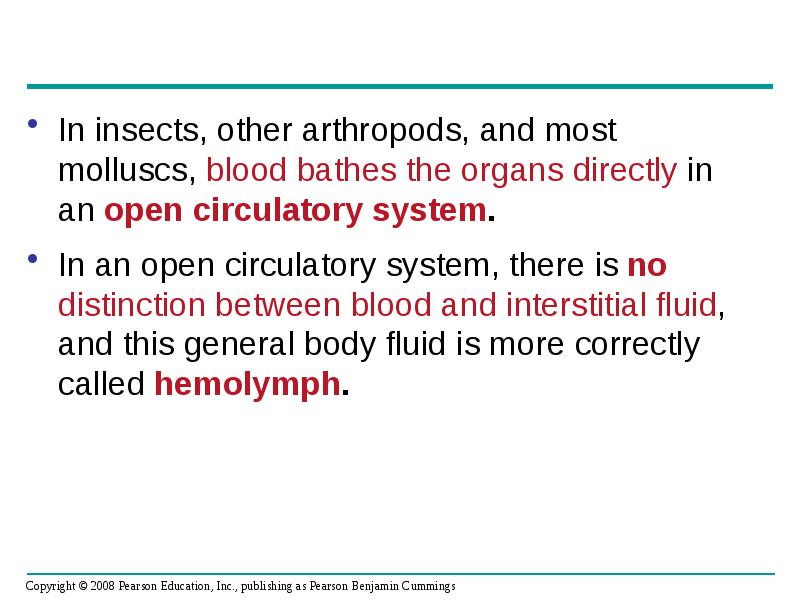
- 9. In insects, other arthropods, and most molluscs, blood bathes the organs
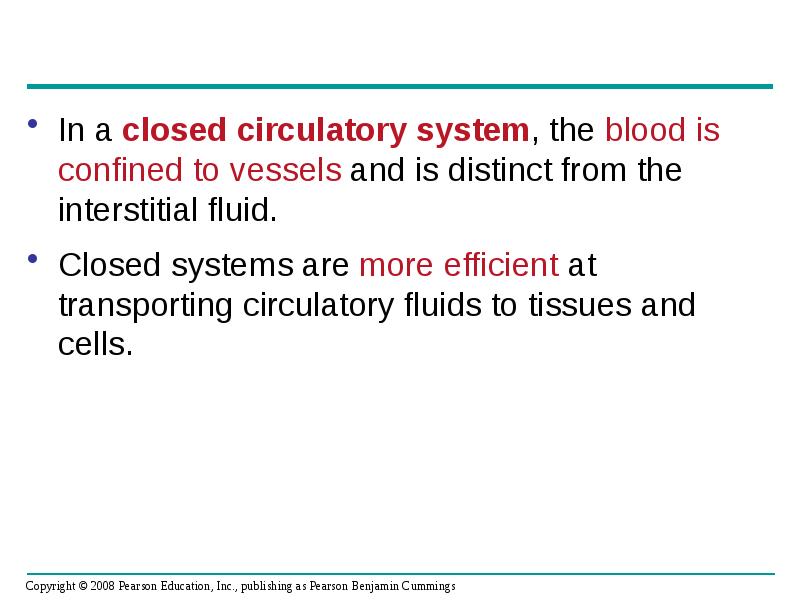
- 10. In a closed circulatory system, the blood is confined to vessels
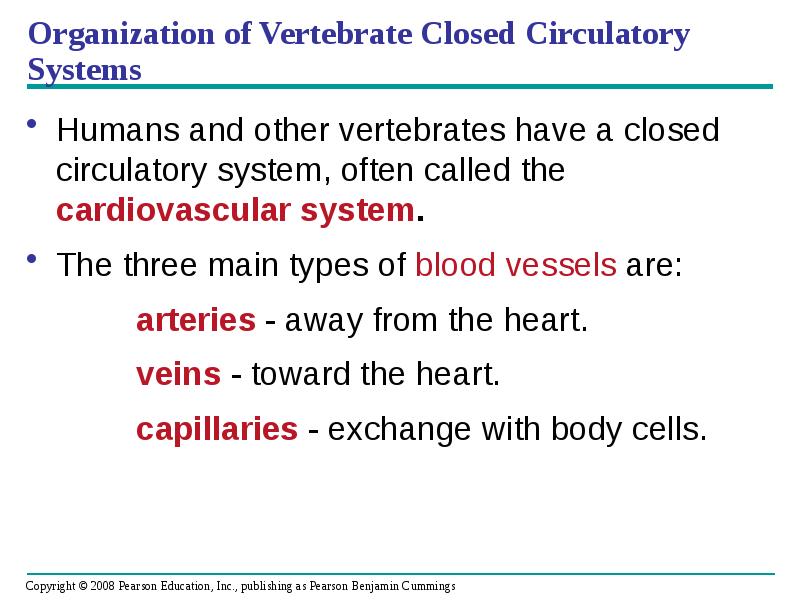
- 12. Organization of Vertebrate Closed Circulatory Systems Humans and other vertebrates have
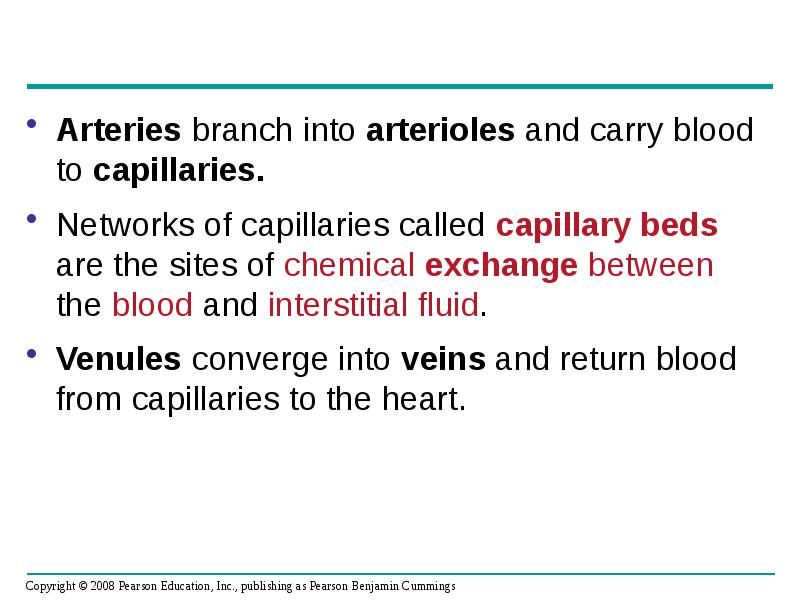
- 13. Arteries branch into arterioles and carry blood to capillaries. Arteries
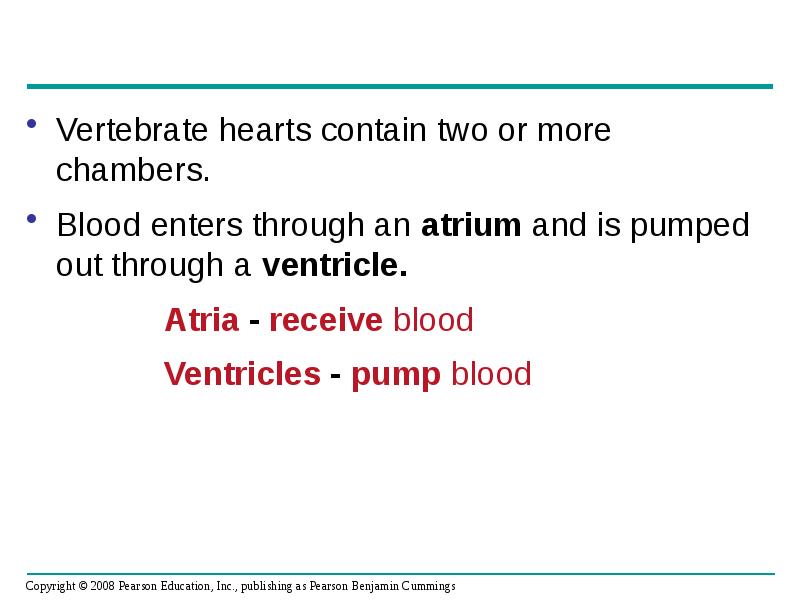
- 14. Vertebrate hearts contain two or more chambers. Vertebrate hearts contain two
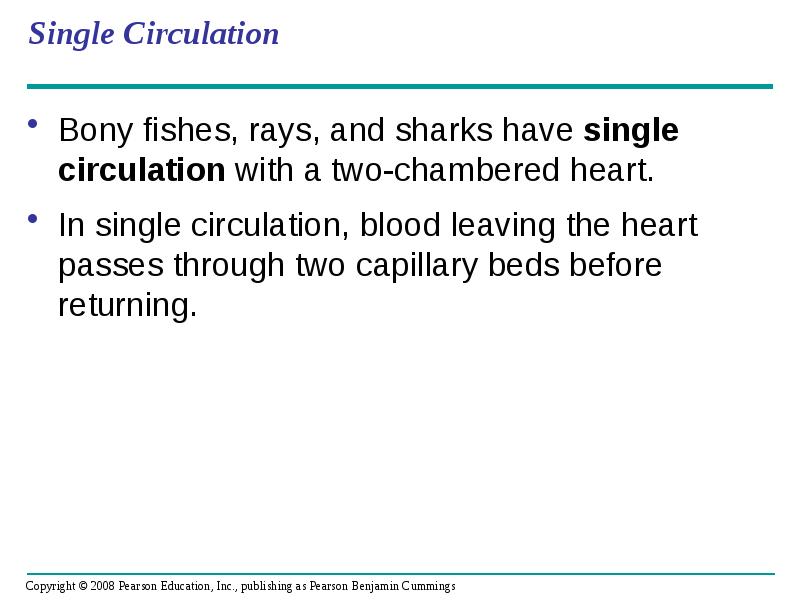
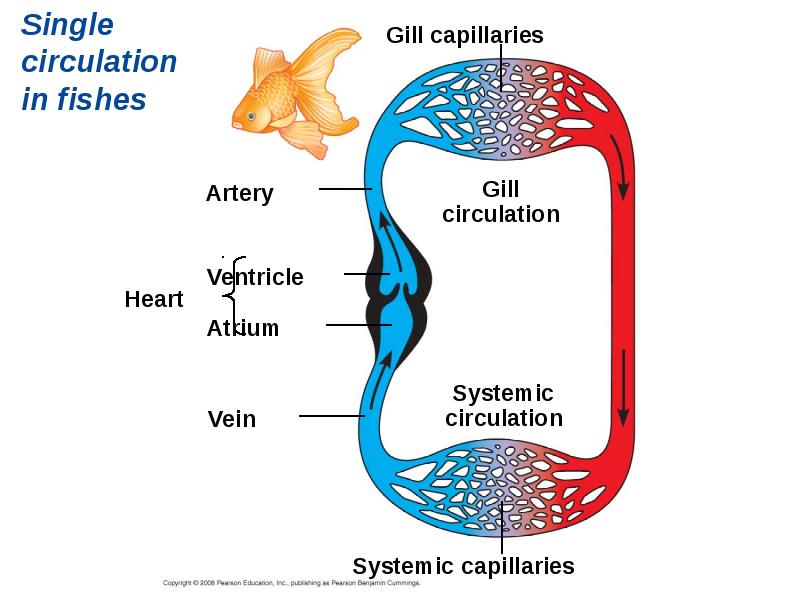
- 15. Single Circulation Bony fishes, rays, and sharks have single circulation with
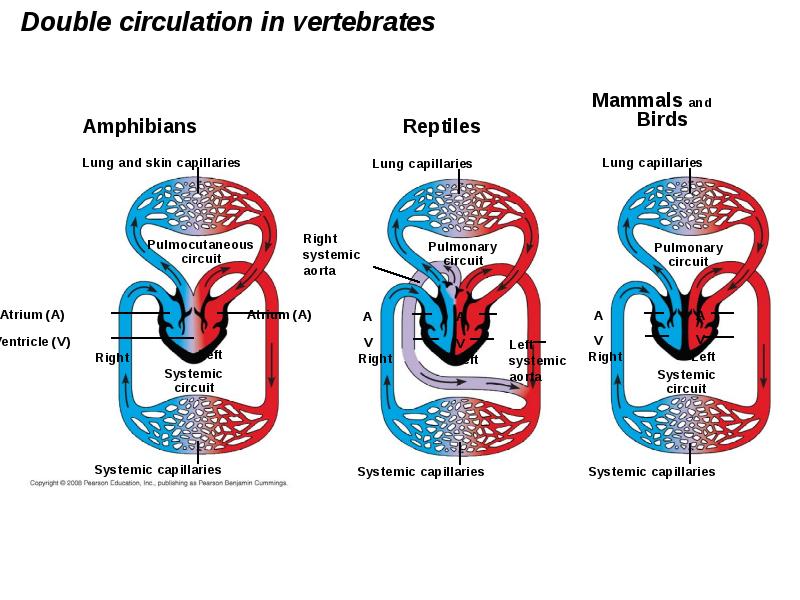
- 17. Double Circulation Amphibian, reptiles, and mammals have double circulation. Oxygen-poor and
- 19. In reptiles and mammals, oxygen-poor blood flows through the pulmonary circuit
- 20. Adaptations of Double Circulatory Systems Amphibians: Frogs / amphibians have a
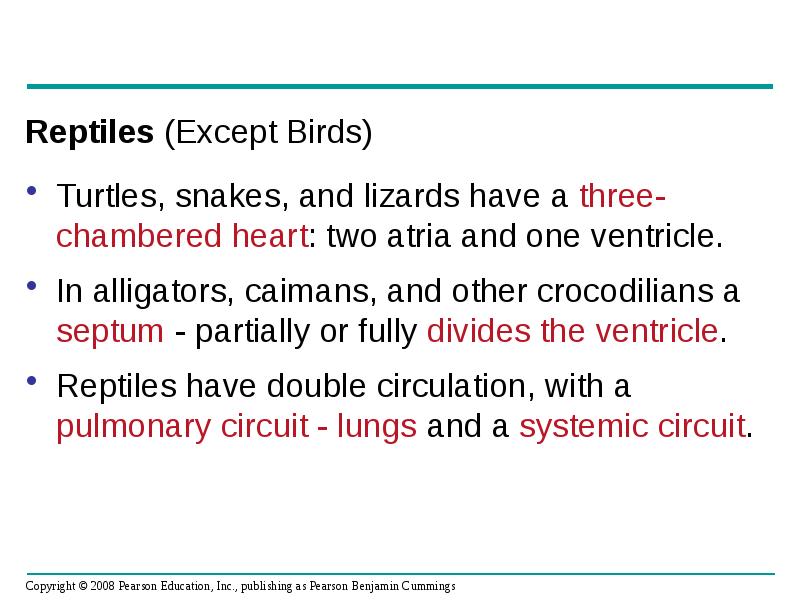
- 21. Reptiles (Except Birds) Turtles, snakes, and lizards have a three-chambered heart:
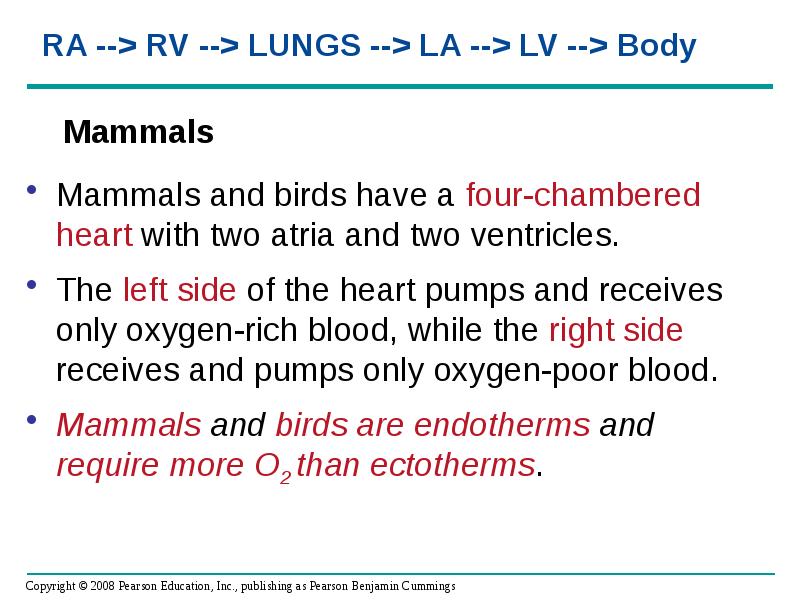
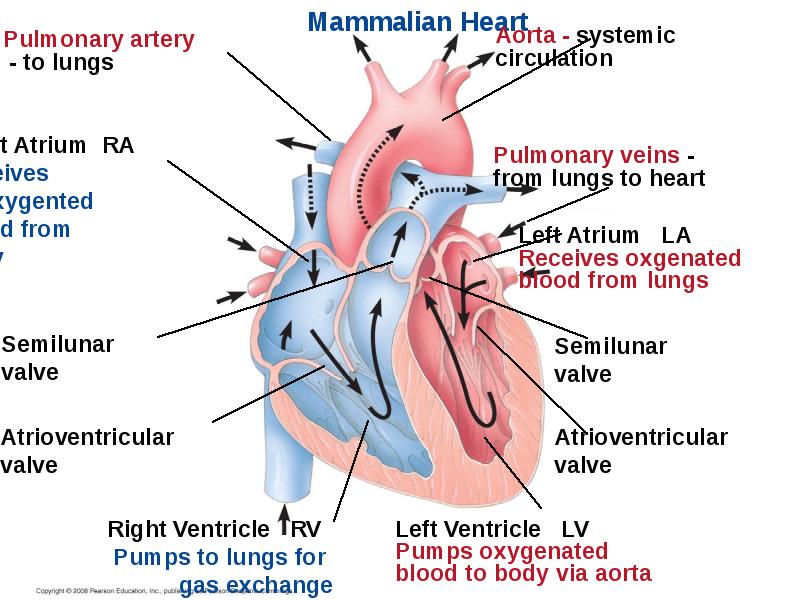
- 22. Mammals Mammals and birds have a four-chambered heart with two atria
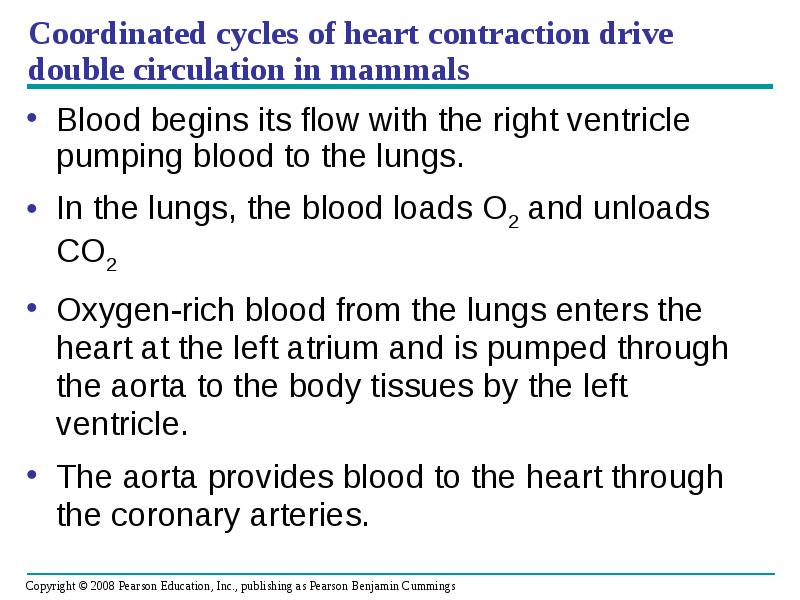
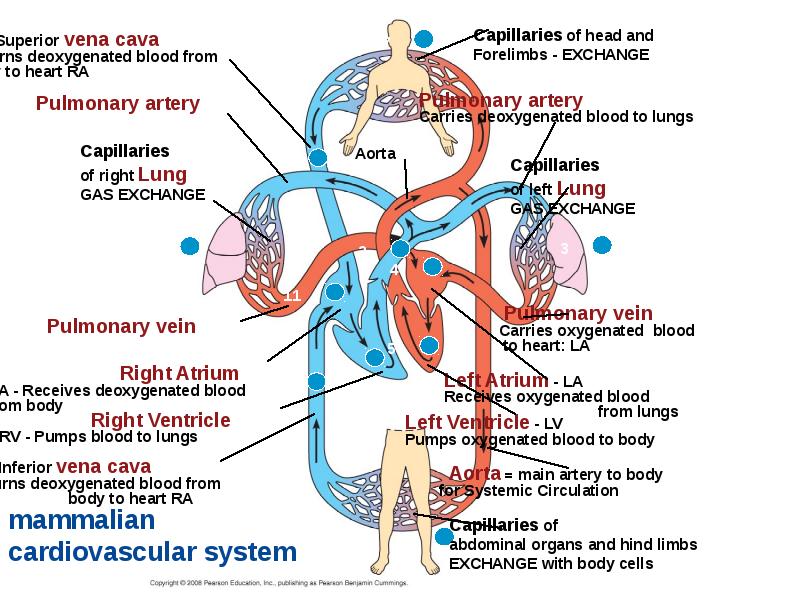
- 23. Coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive double circulation in mammals Blood
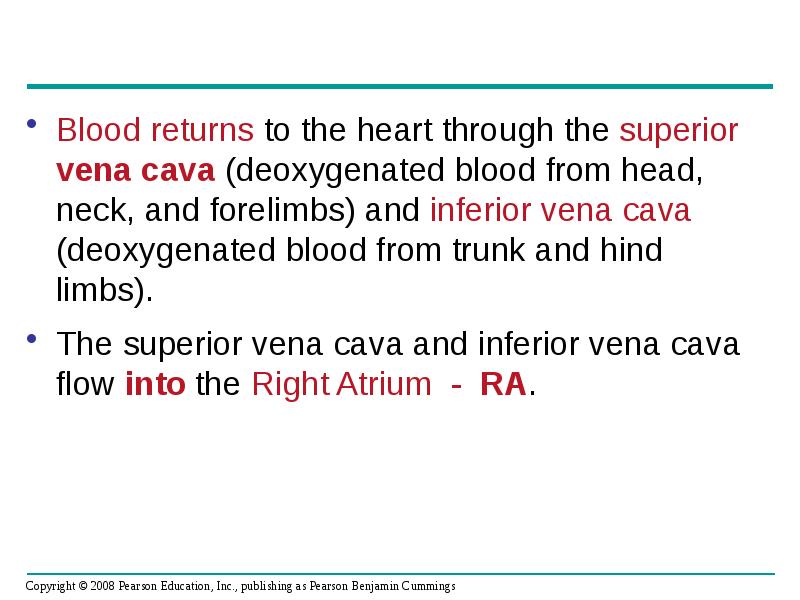
- 24. Blood returns to the heart through the superior vena cava (deoxygenated
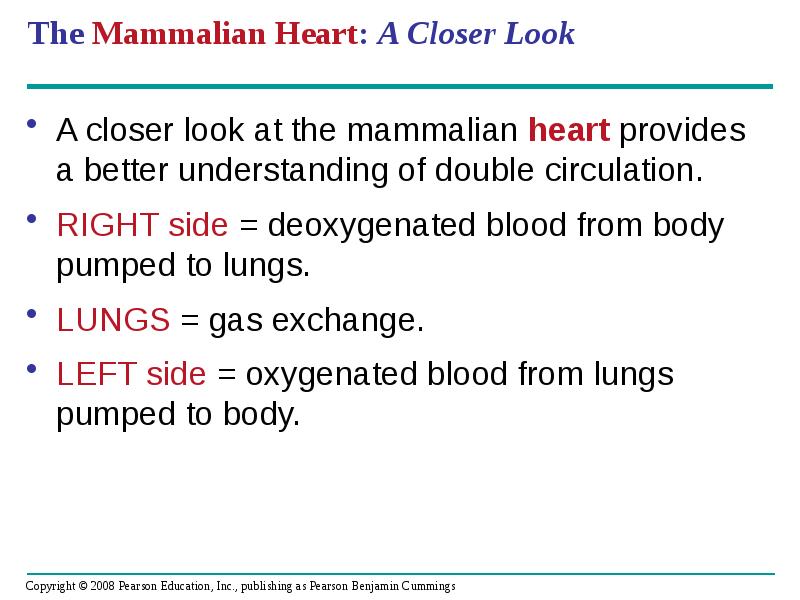
- 26. The Mammalian Heart: A Closer Look A closer look at the
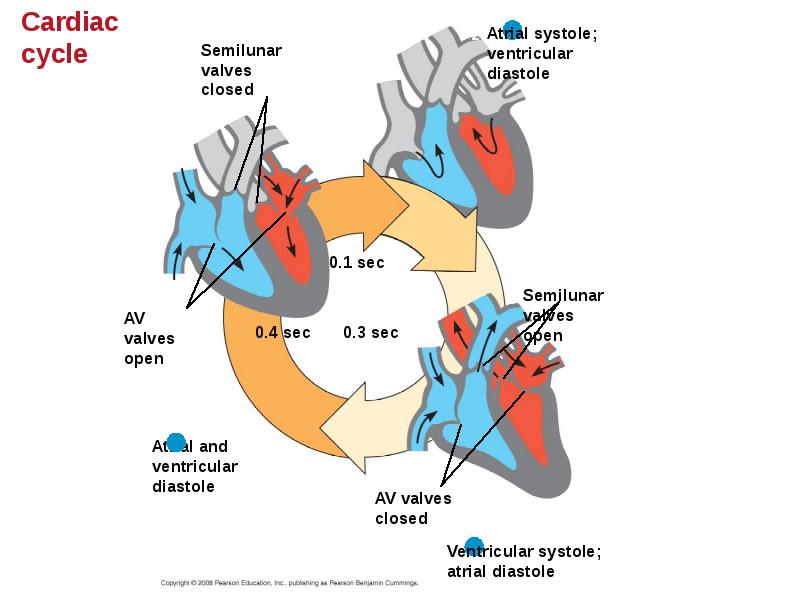
- 28. The heart contracts and relaxes in a rhythmic cycle called the
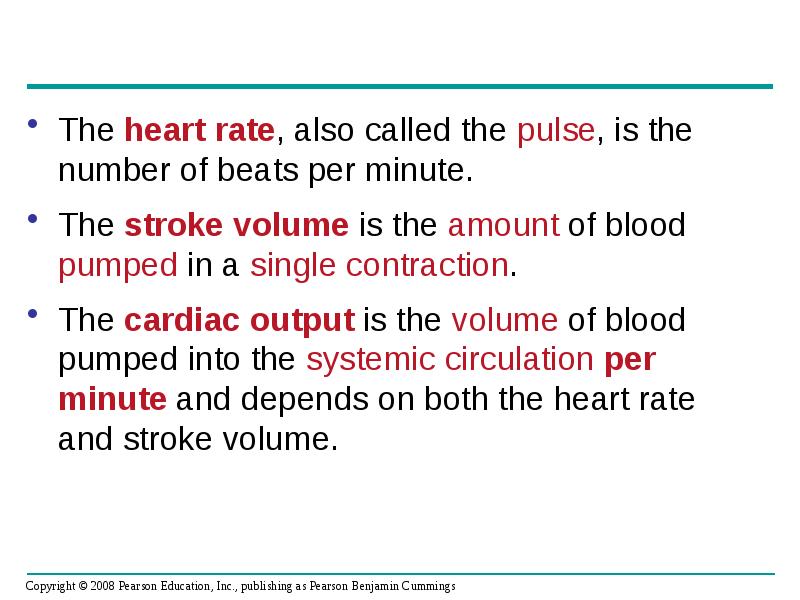
- 30. The heart rate, also called the pulse, is the number of
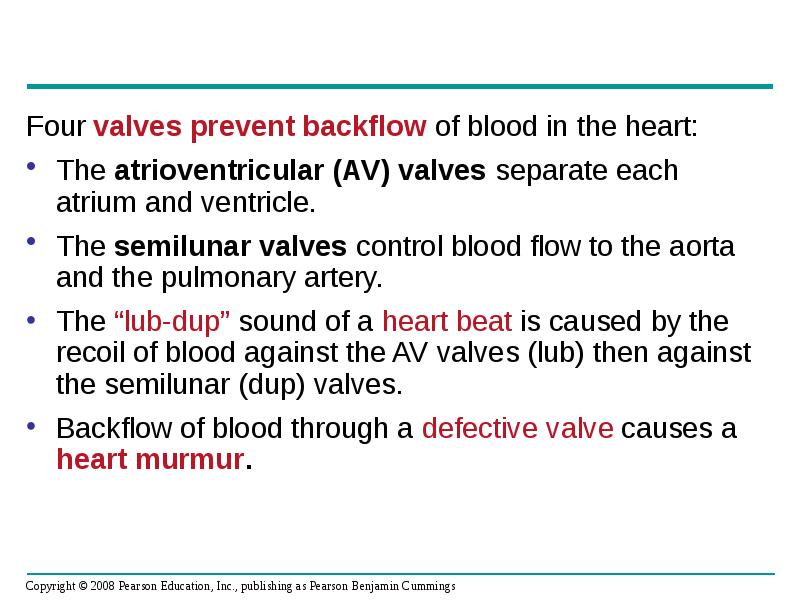
- 31. Four valves prevent backflow of blood in the heart: Four valves
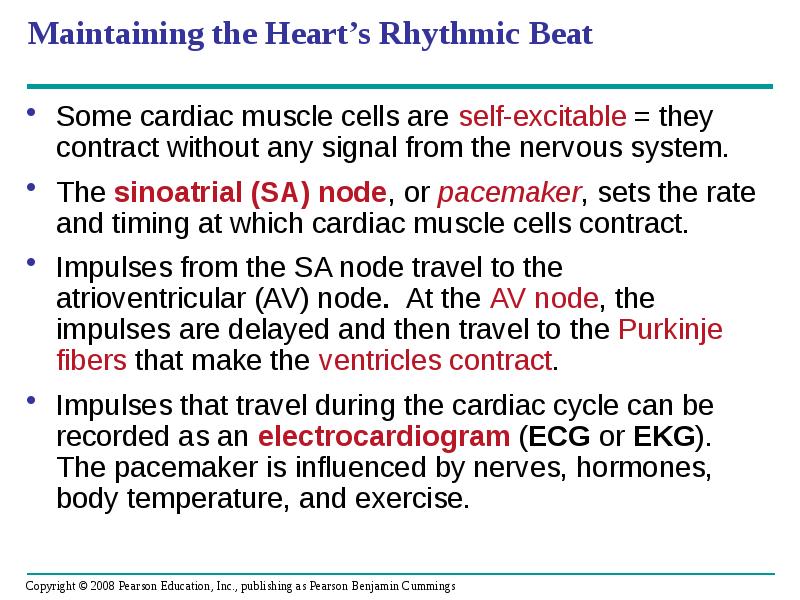
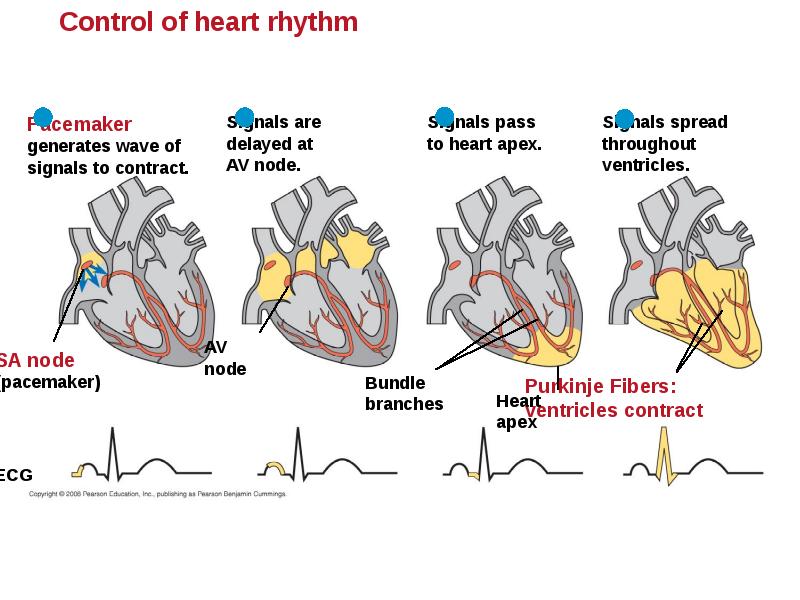
- 32. Maintaining the Heart’s Rhythmic Beat Some cardiac muscle cells are self-excitable
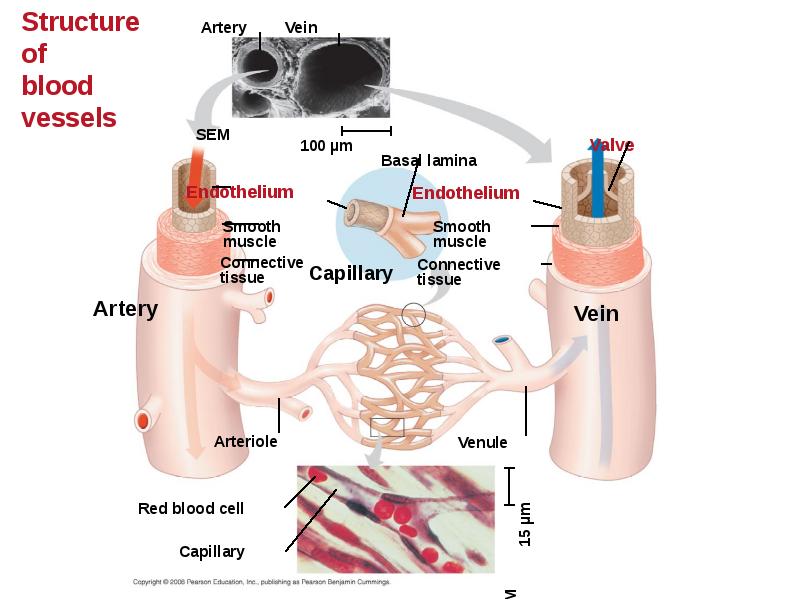
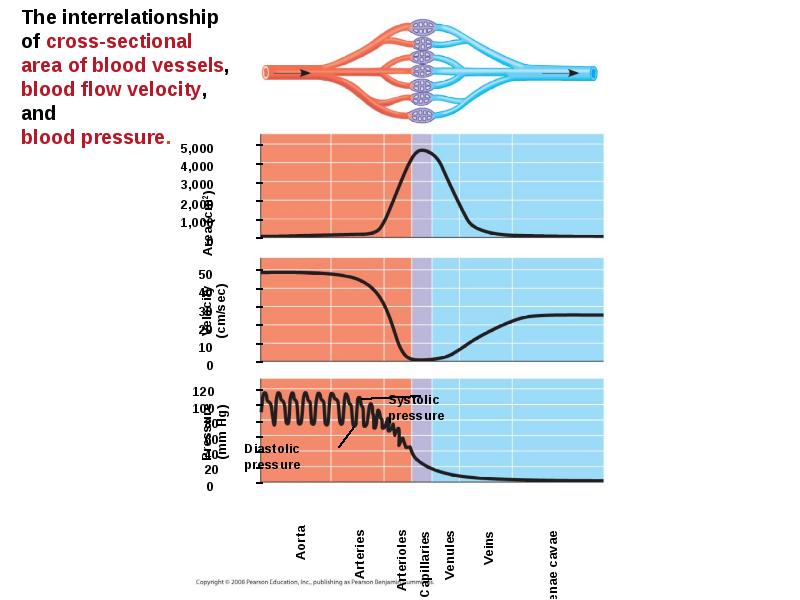
- 34. Patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect the structure and arrangement
- 36. Capillaries have thin walls, the endothelium plus its basement membrane, to
- 37. Blood Flow Velocity Physical laws governing movement of fluids through pipes
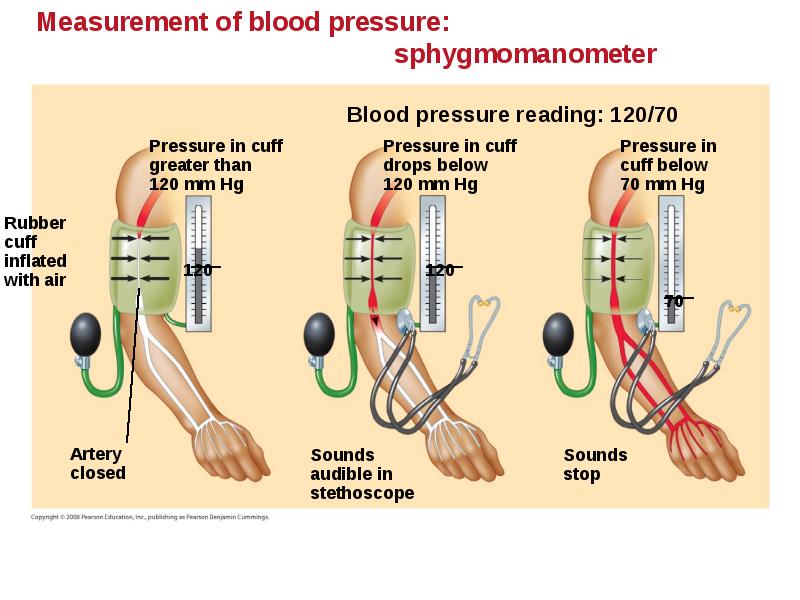
- 39. Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the hydrostatic pressure that blood exerts
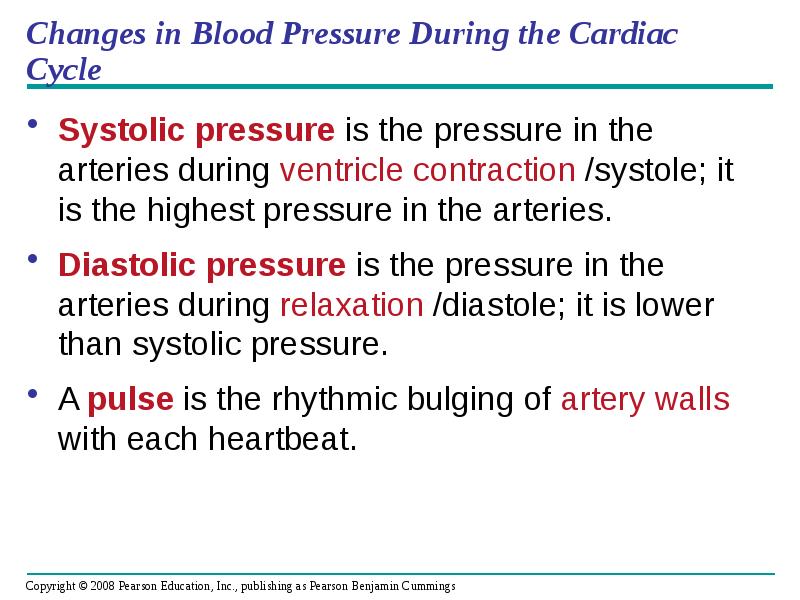
- 40. Changes in Blood Pressure During the Cardiac Cycle Systolic pressure is
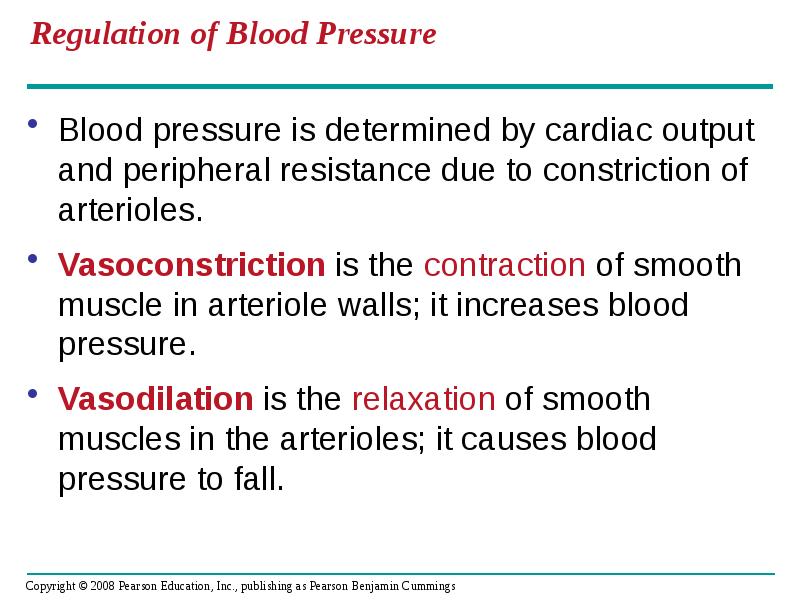
- 41. Regulation of Blood Pressure Blood pressure is determined by cardiac output
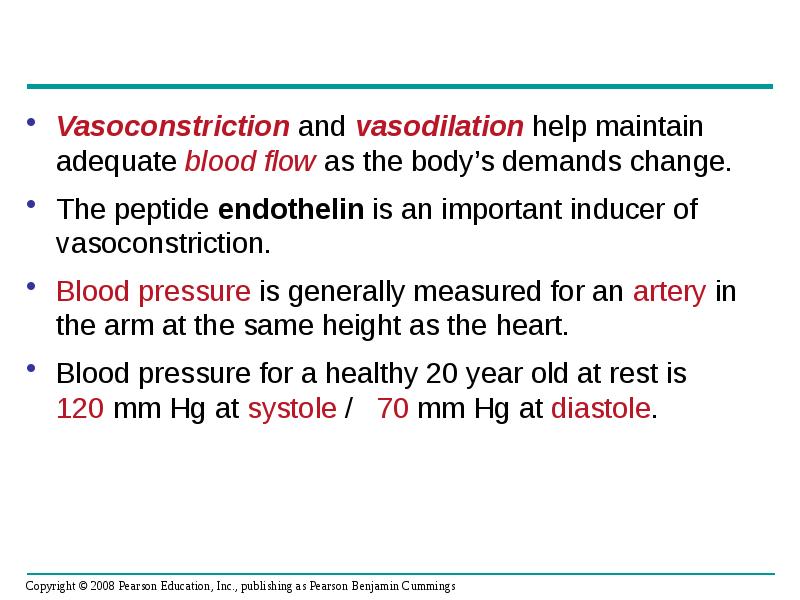
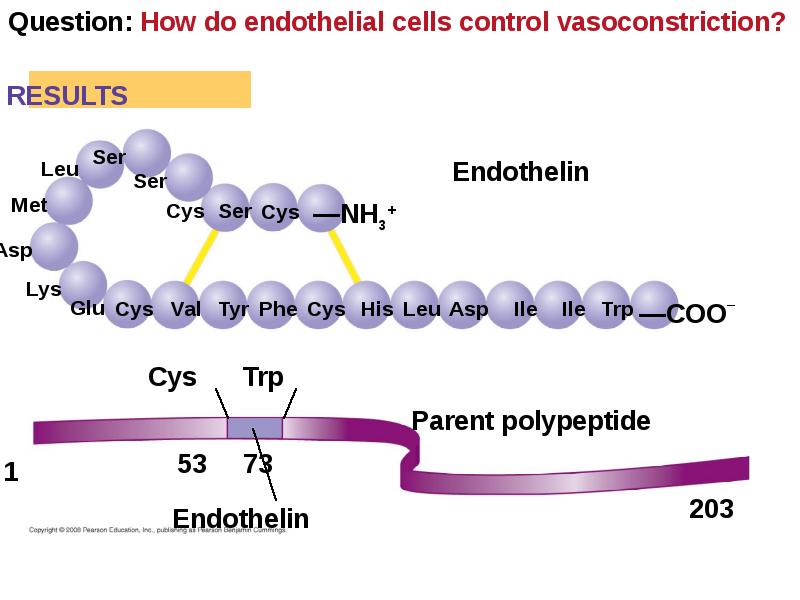
- 42. Vasoconstriction and vasodilation help maintain adequate blood flow as the body’s
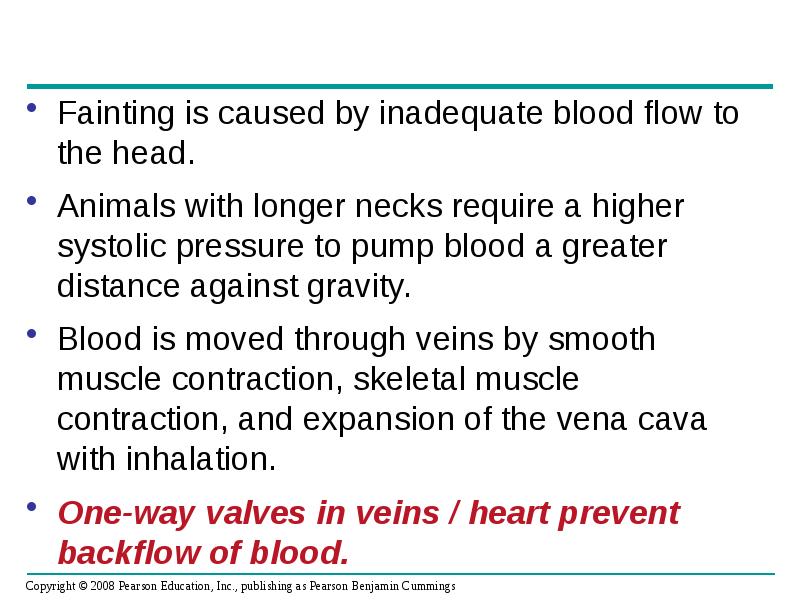
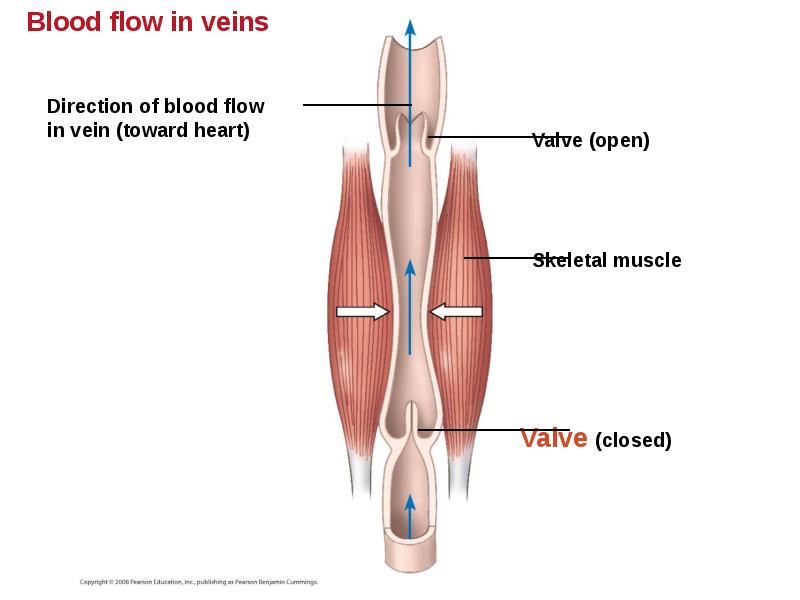
- 45. Fainting is caused by inadequate blood flow to the head. Fainting
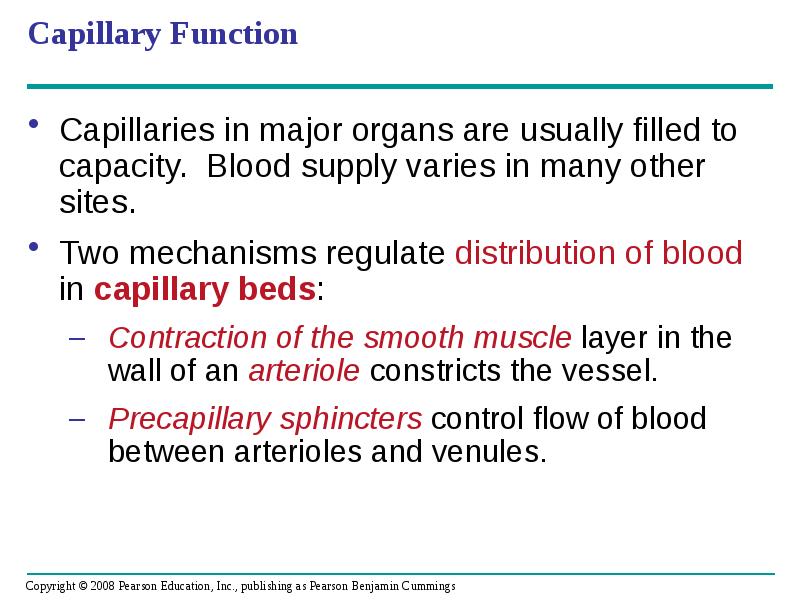
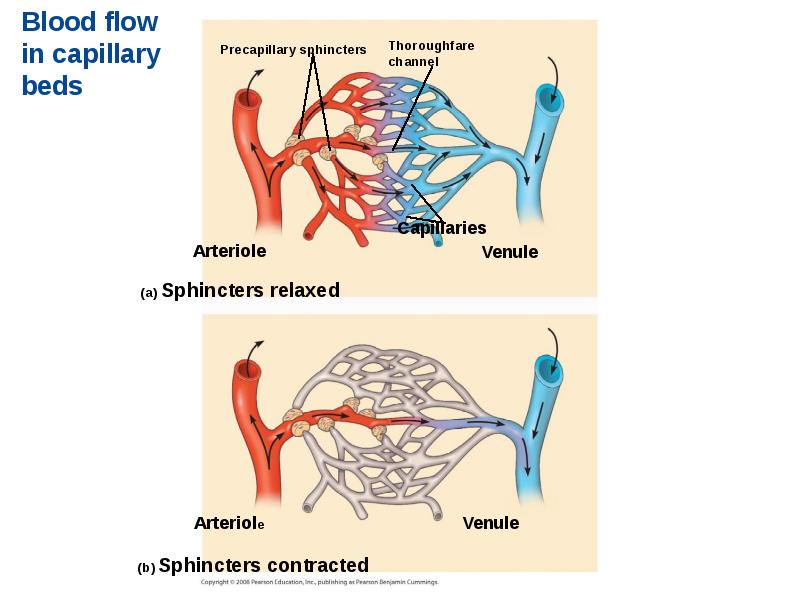
- 47. Capillary Function Capillaries in major organs are usually filled to capacity.
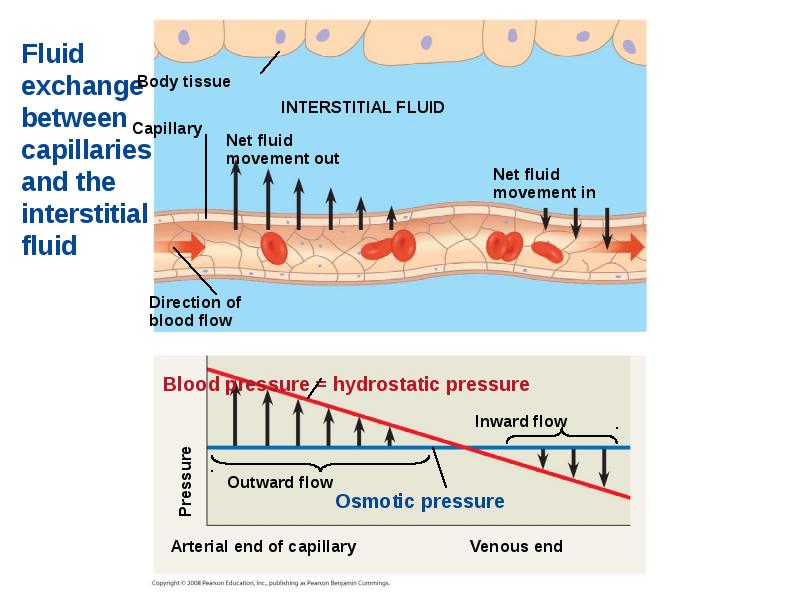
- 49. The critical exchange of substances between the blood and interstitial fluid
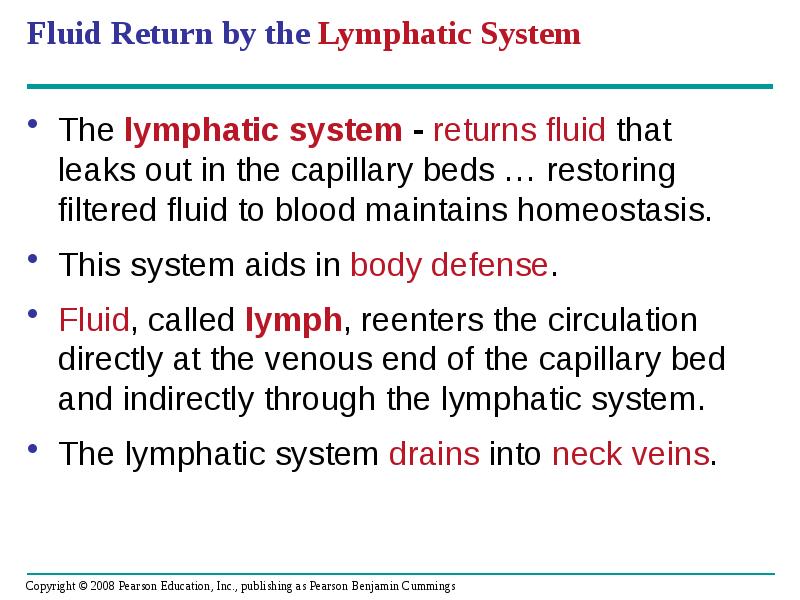
- 51. Fluid Return by the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system - returns
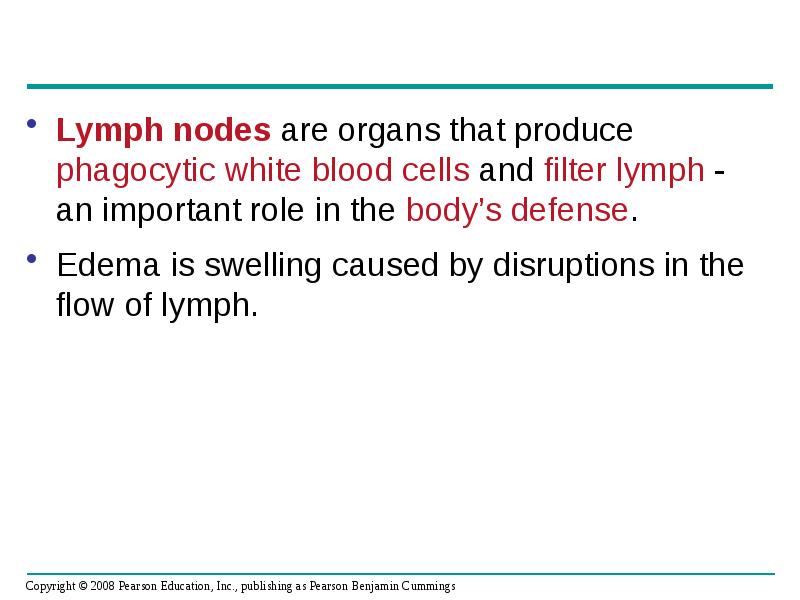
- 52. Lymph nodes are organs that produce phagocytic white blood cells and
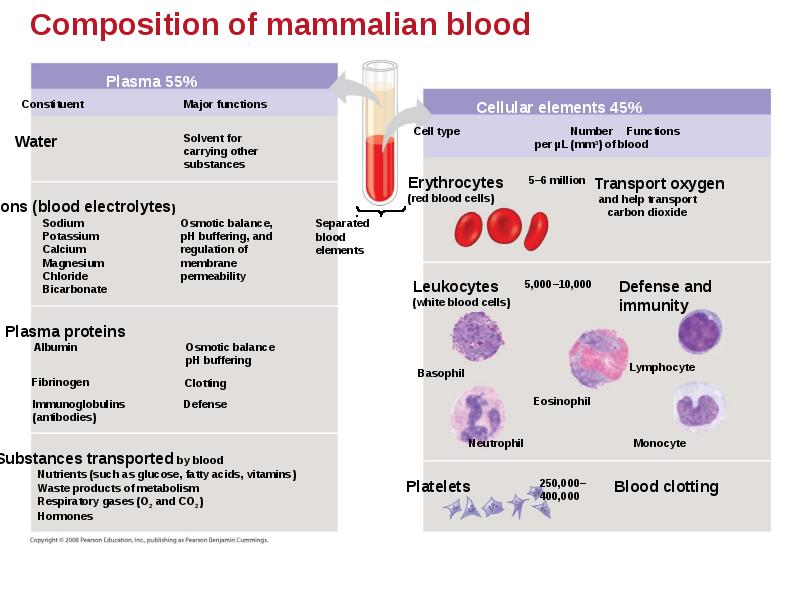
- 53. Blood Composition and Function Blood consists of several kinds of blood
- 55. Plasma Blood plasma is about 90% water. Among its solutes are
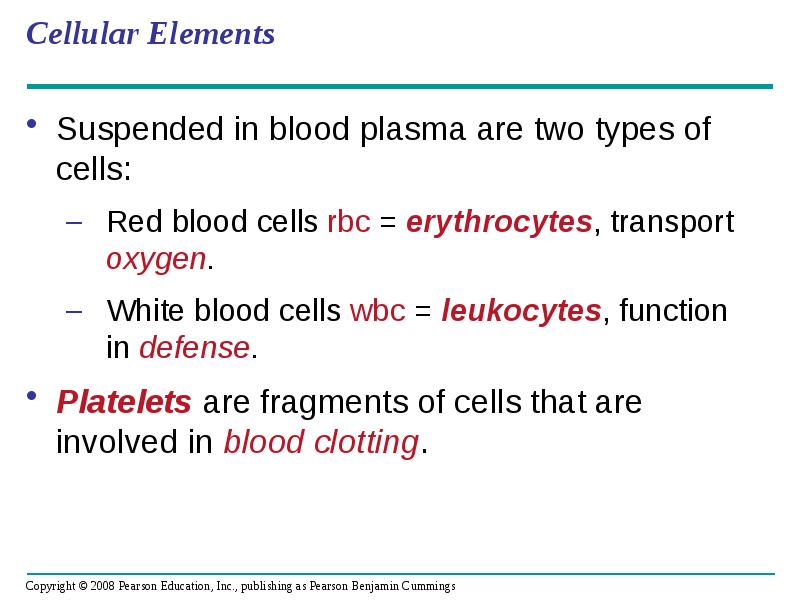
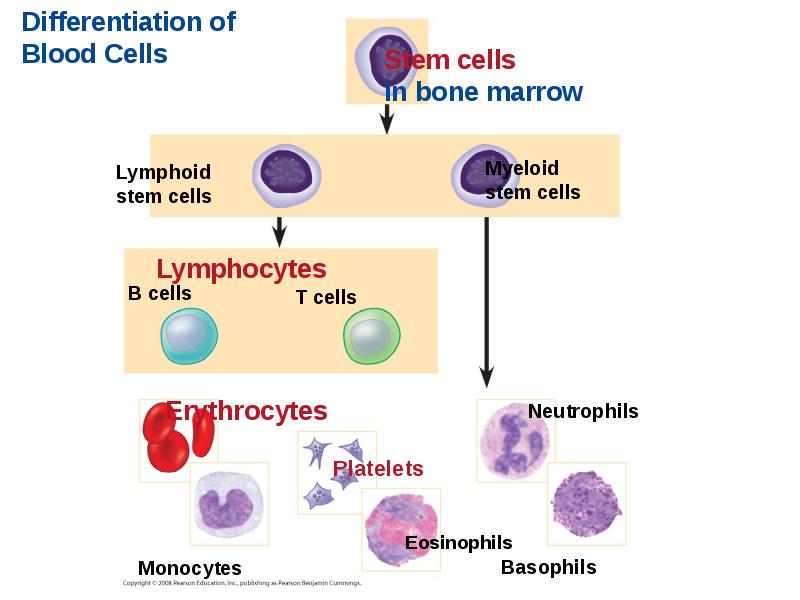
- 56. Cellular Elements Suspended in blood plasma are two types of cells:
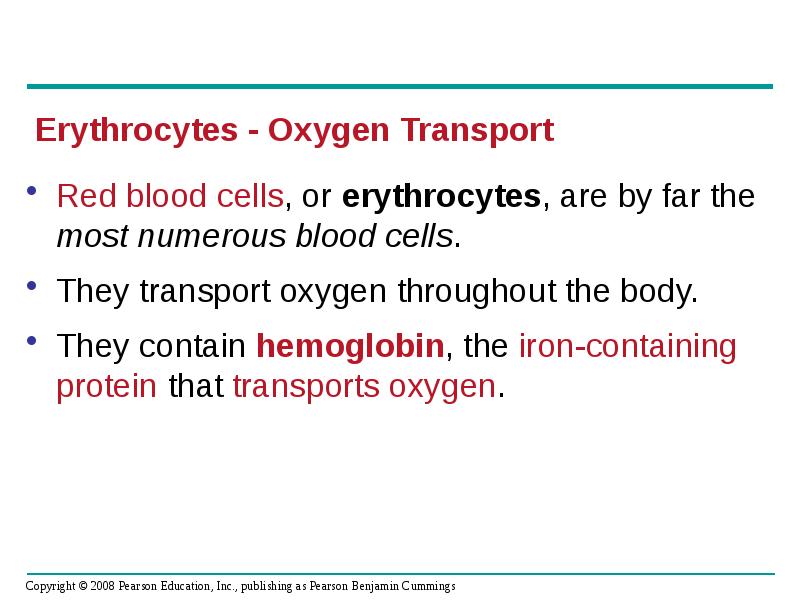
- 57. Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are by far the most numerous
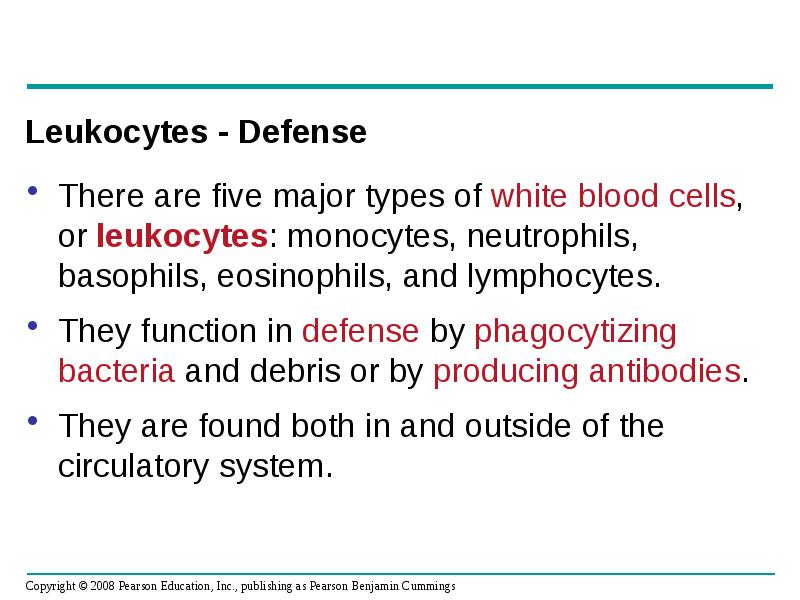
- 58. Leukocytes - Defense There are five major types of white blood
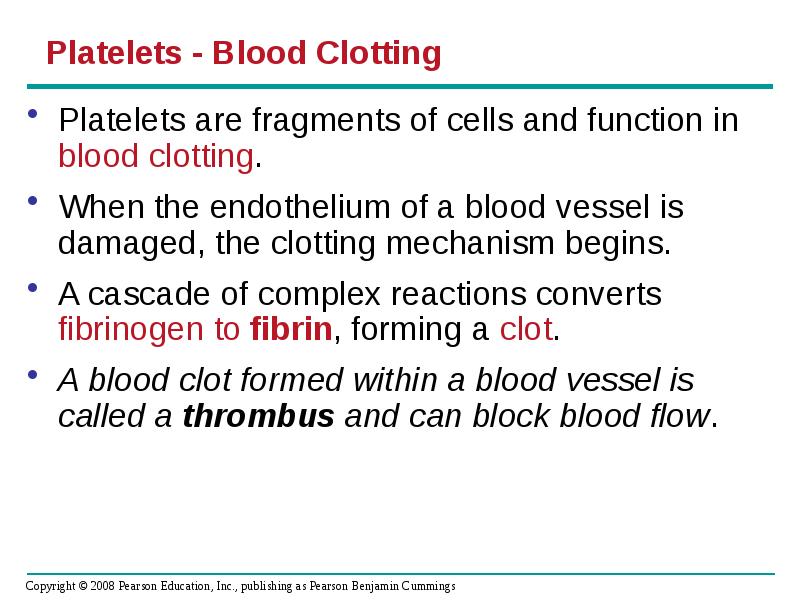
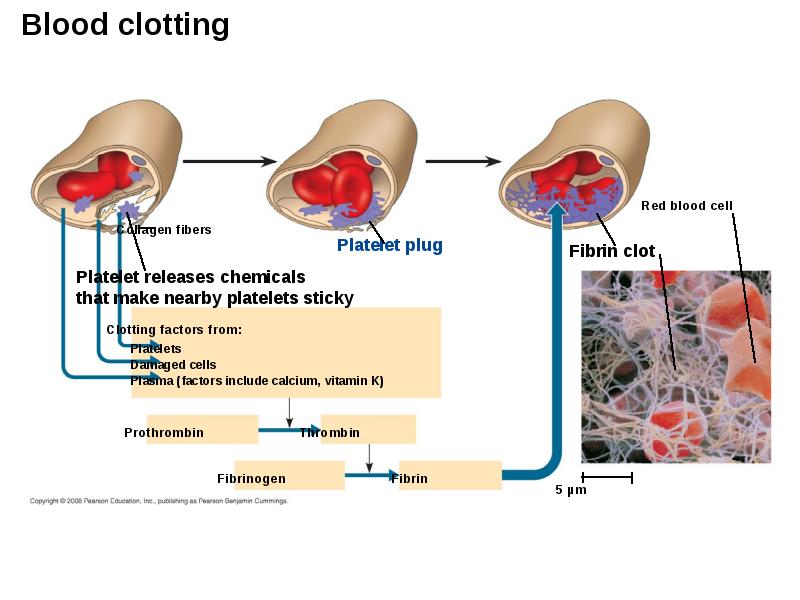
- 59. Platelets - Blood Clotting Platelets are fragments of cells and function
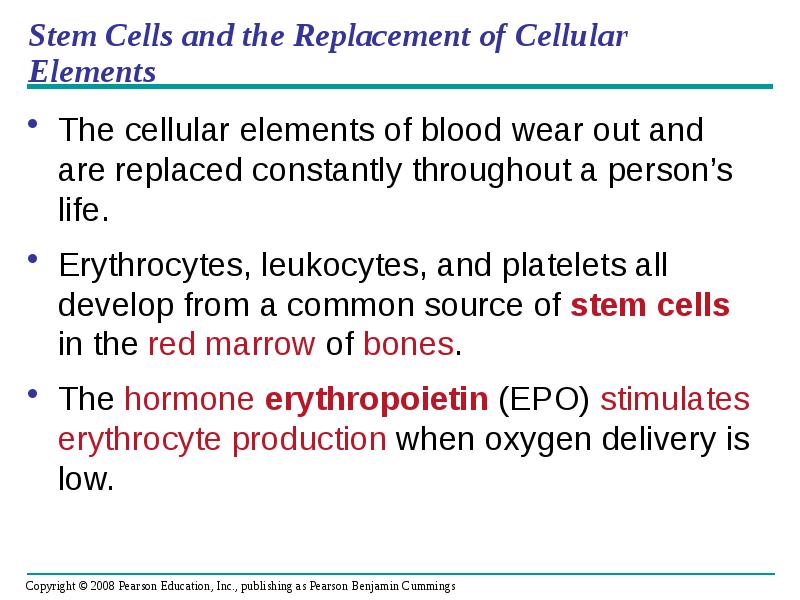
- 61. Stem Cells and the Replacement of Cellular Elements The cellular elements
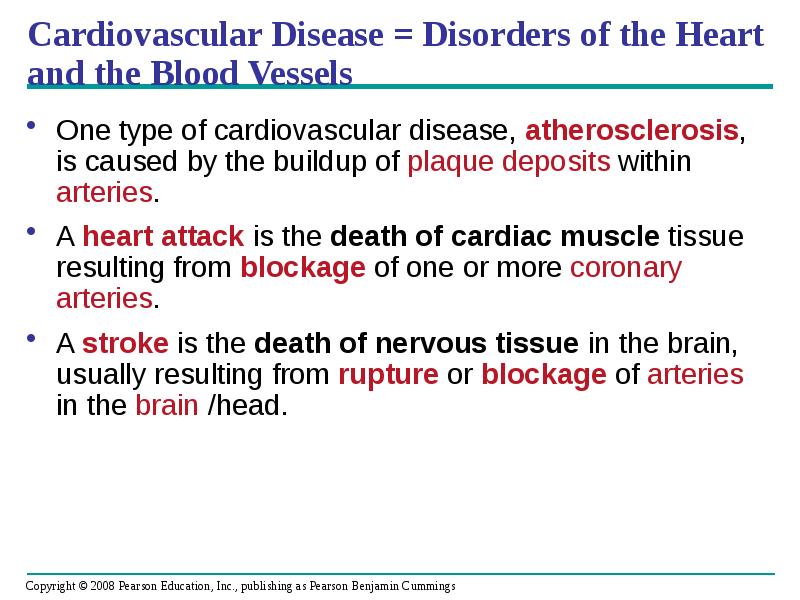
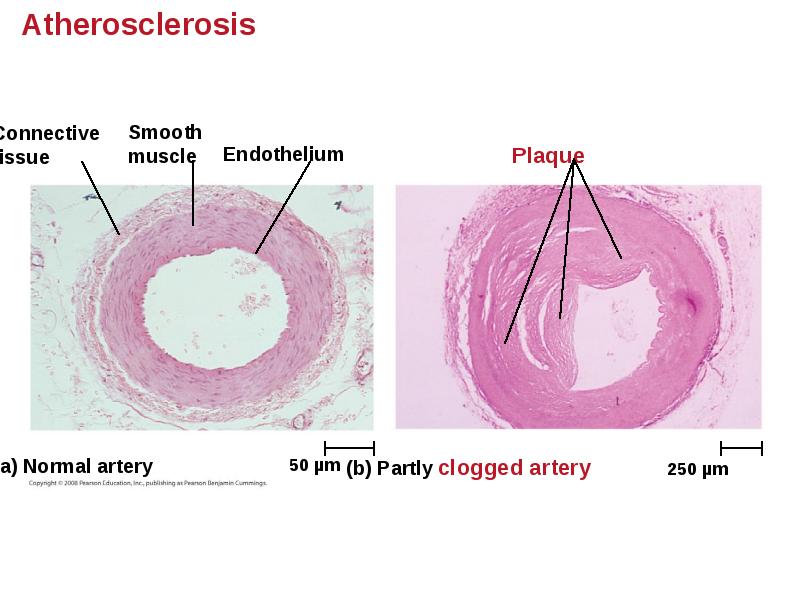
- 63. Cardiovascular Disease = Disorders of the Heart and the Blood Vessels
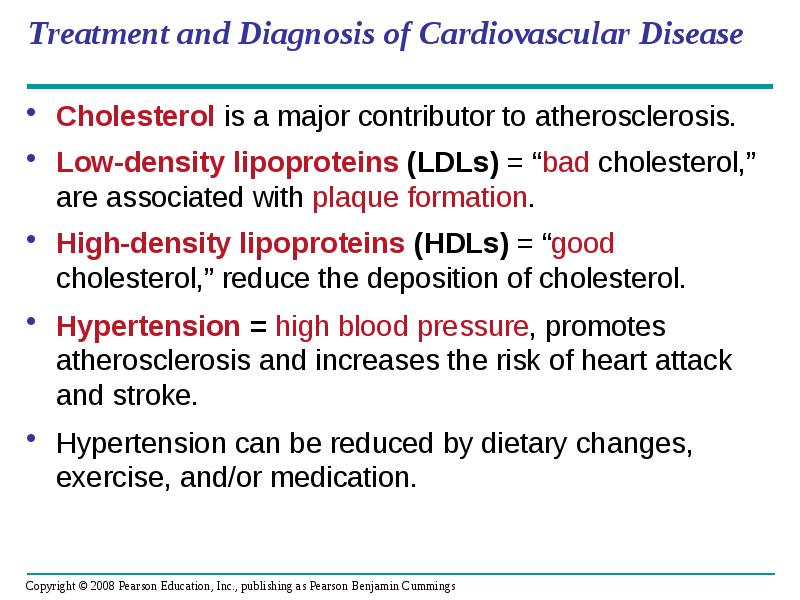
- 65. Treatment and Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease Cholesterol is a major contributor
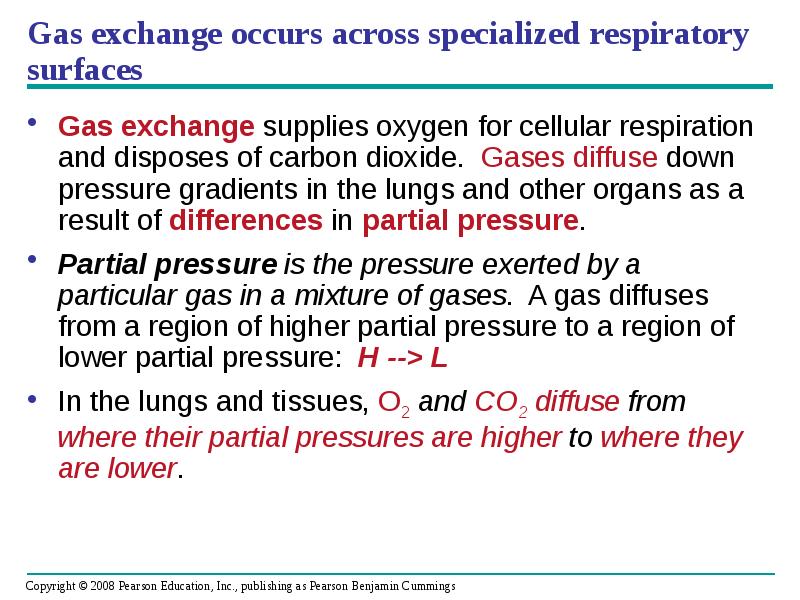
- 66. Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces Gas exchange supplies oxygen
- 67. Respiratory Media Animals can use air or water as a source
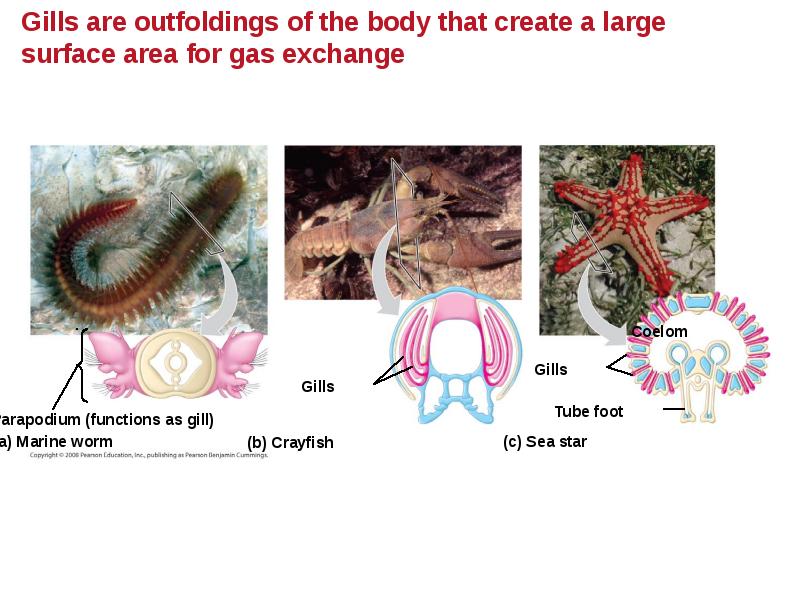
- 68. Respiratory Surfaces Animals require large, moist respiratory surfaces for exchange of
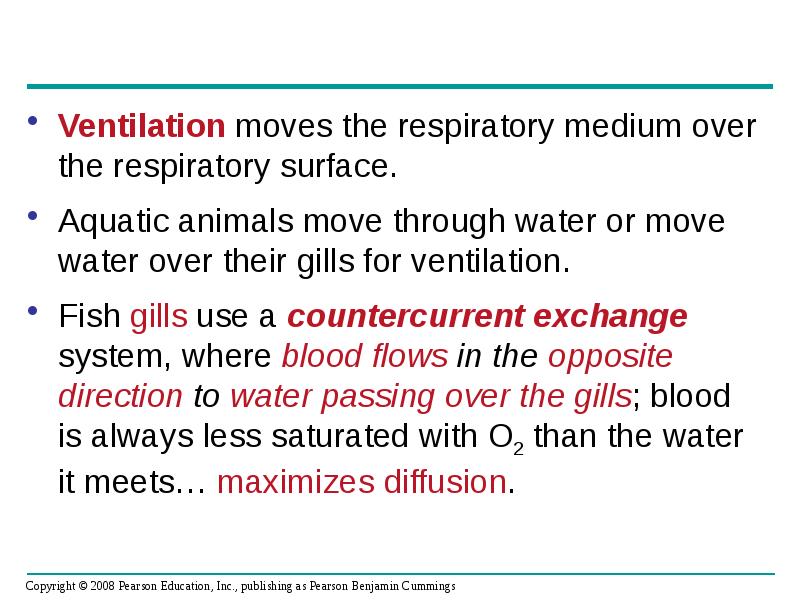
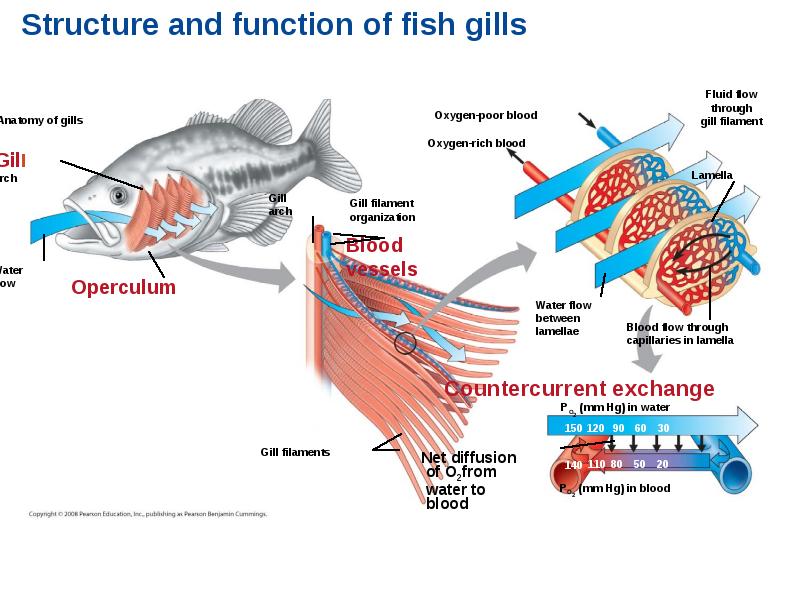
- 70. Ventilation moves the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface. Ventilation moves
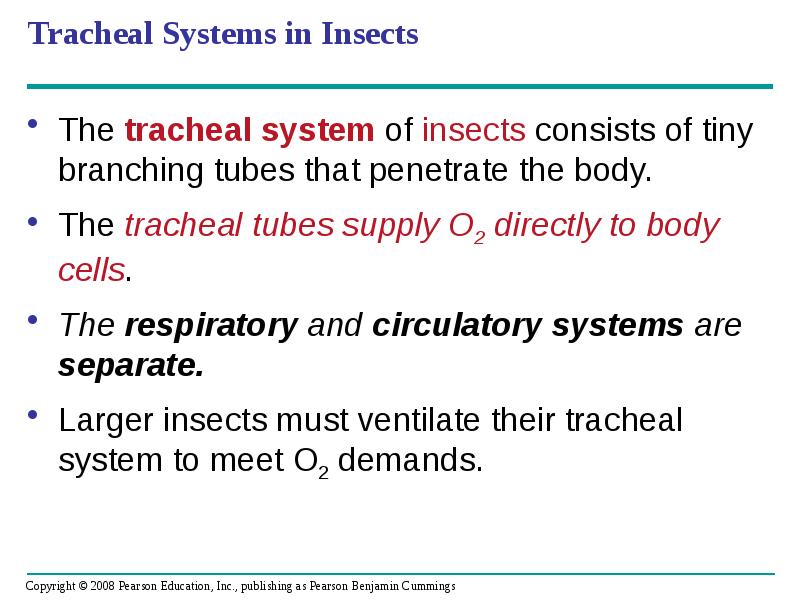
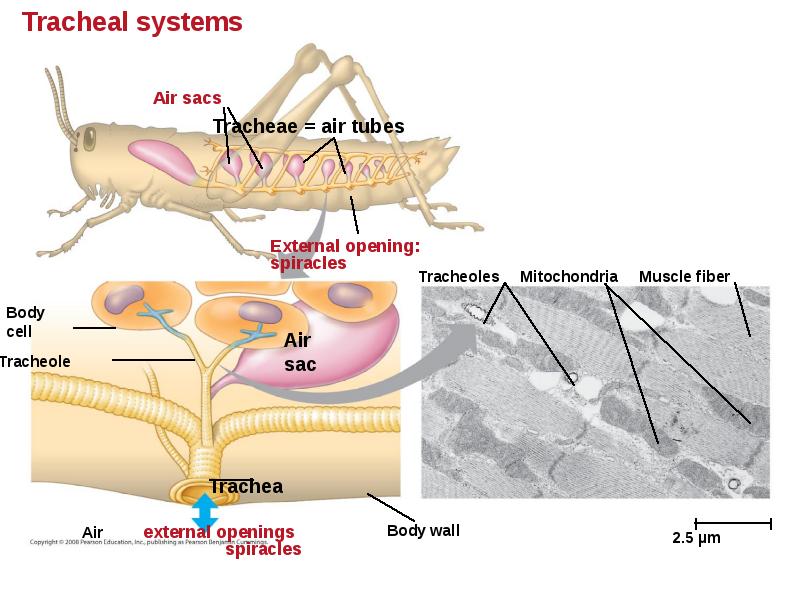
- 72. Tracheal Systems in Insects The tracheal system of insects consists of
- 74. Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface The circulatory system
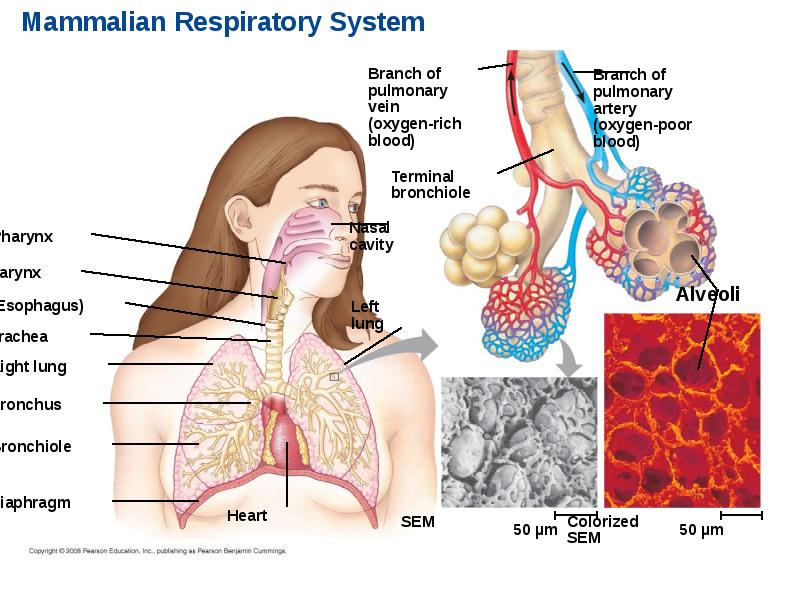
- 75. Mammalian Respiratory Systems: A Closer Look A system of branching ducts
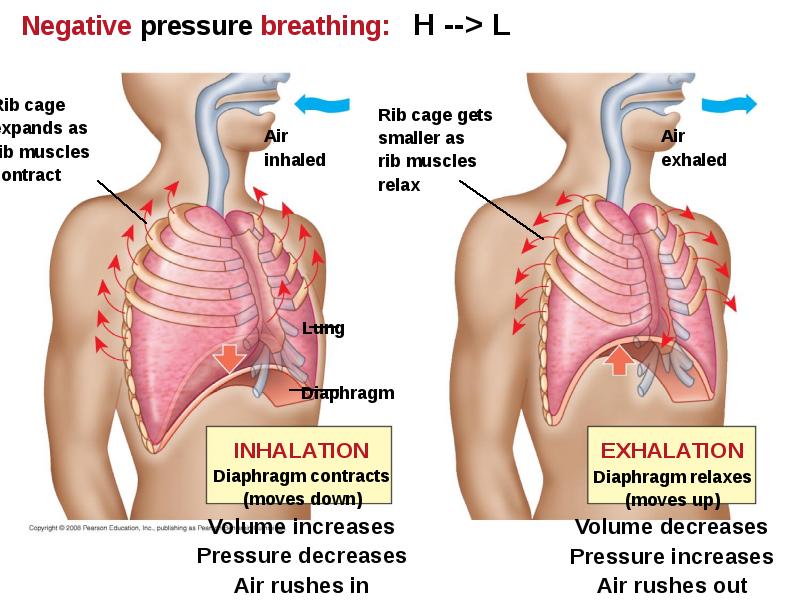
- 77. Breathing Ventilates the Lungs by Inhalation and Exhalation of Air
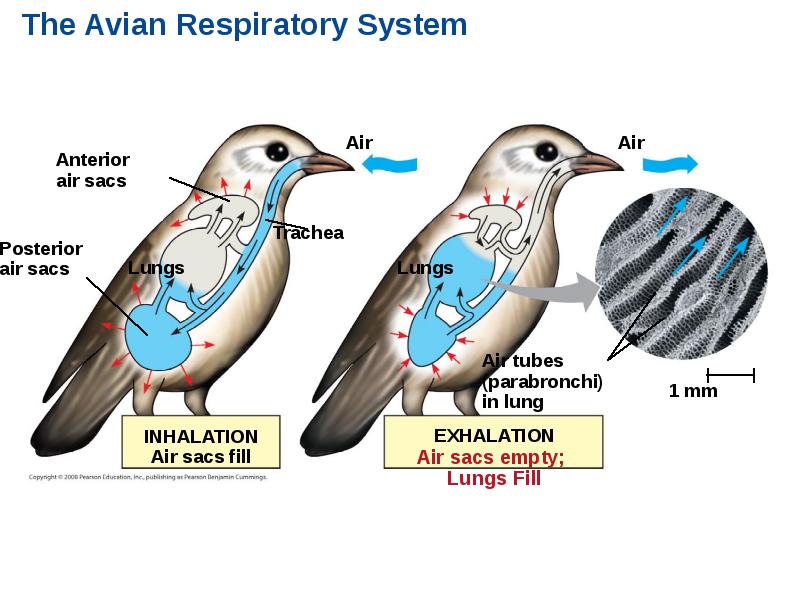
- 79. How a Bird Breathes Birds have eight or nine air sacs
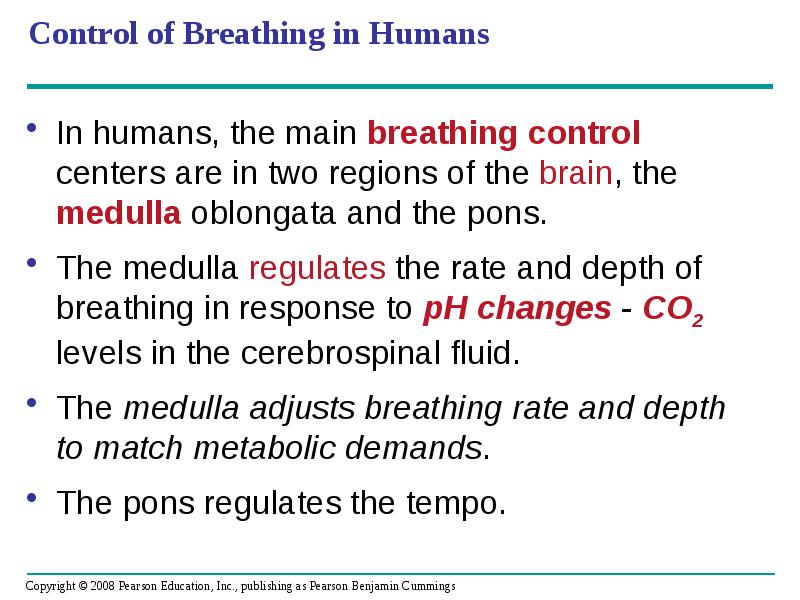
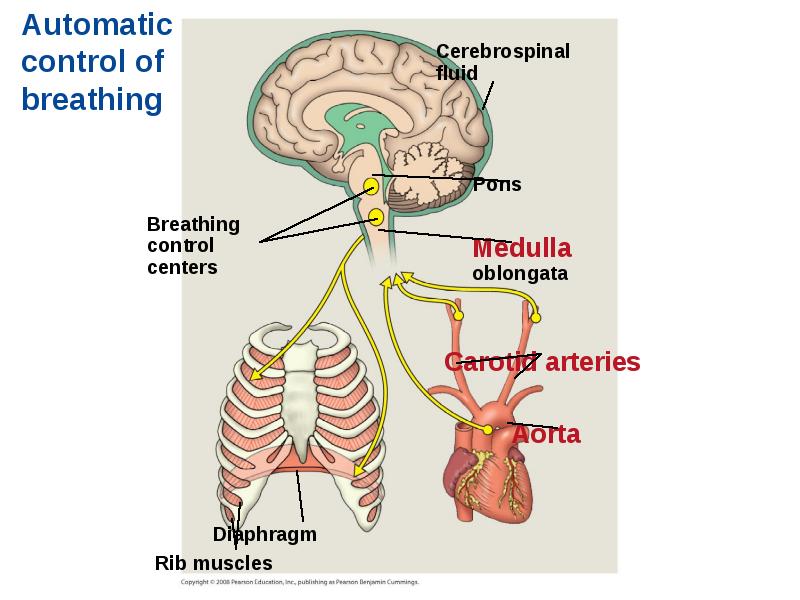
- 81. Control of Breathing in Humans In humans, the main breathing control
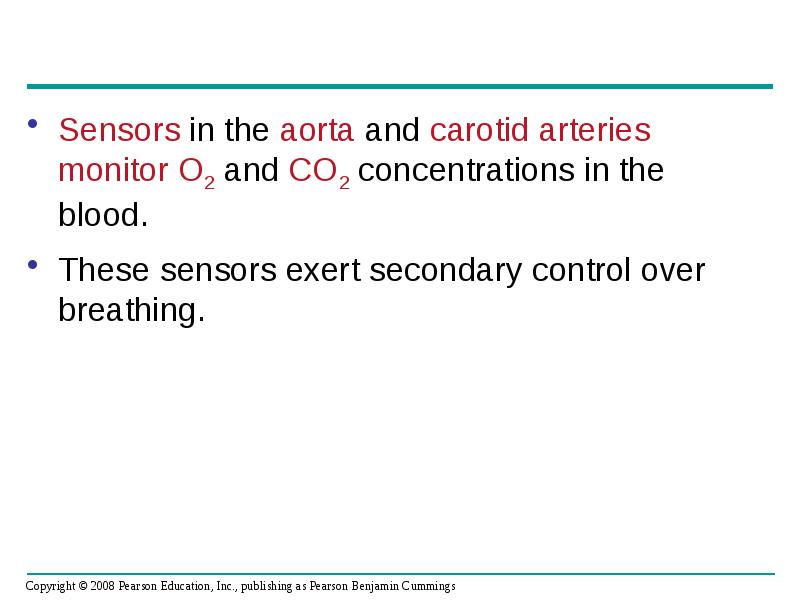
- 82. Sensors in the aorta and carotid arteries monitor O2 and CO2
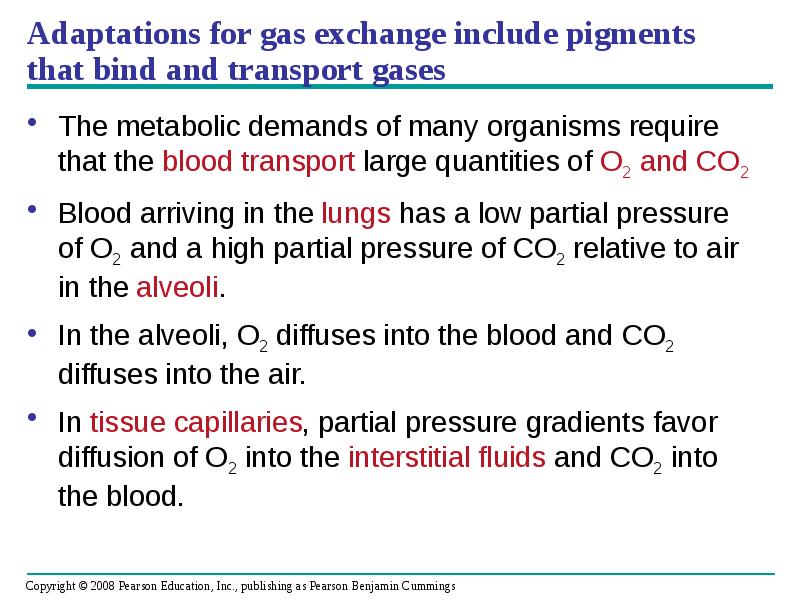
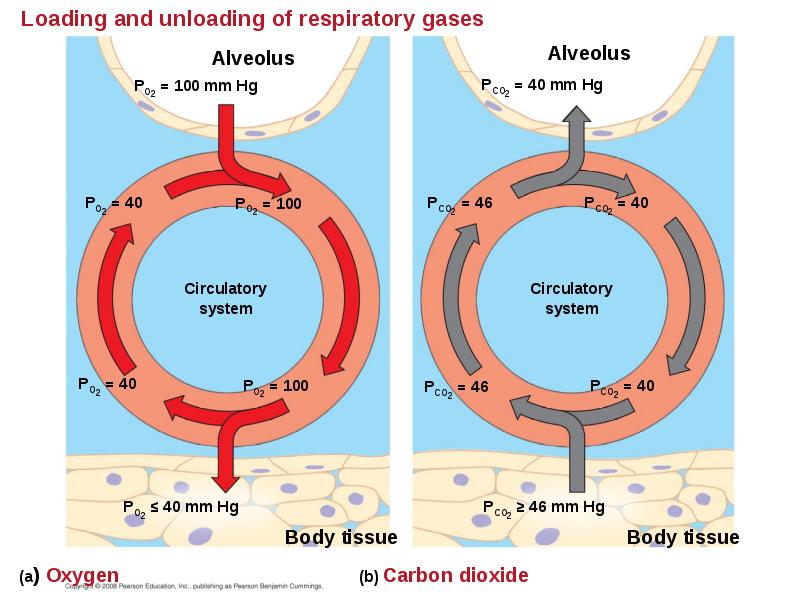
- 84. Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
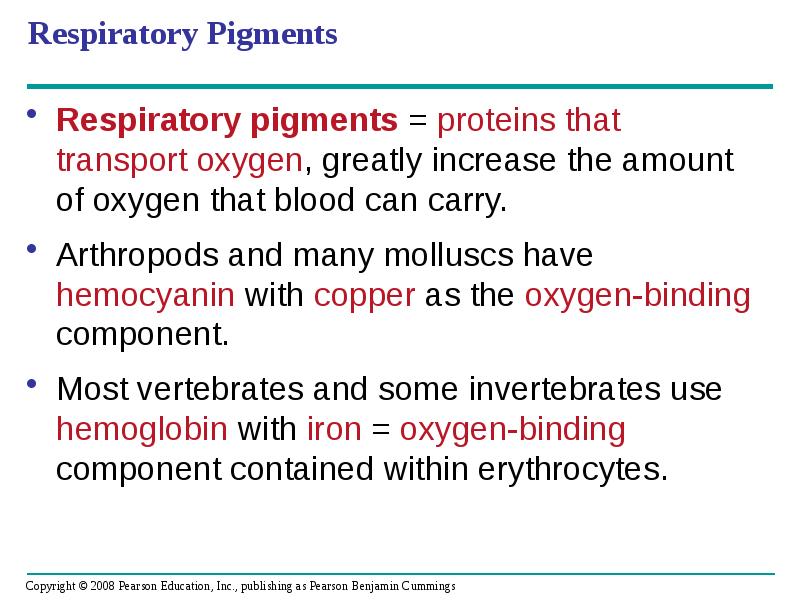
- 86. Respiratory Pigments Respiratory pigments = proteins that transport oxygen, greatly increase
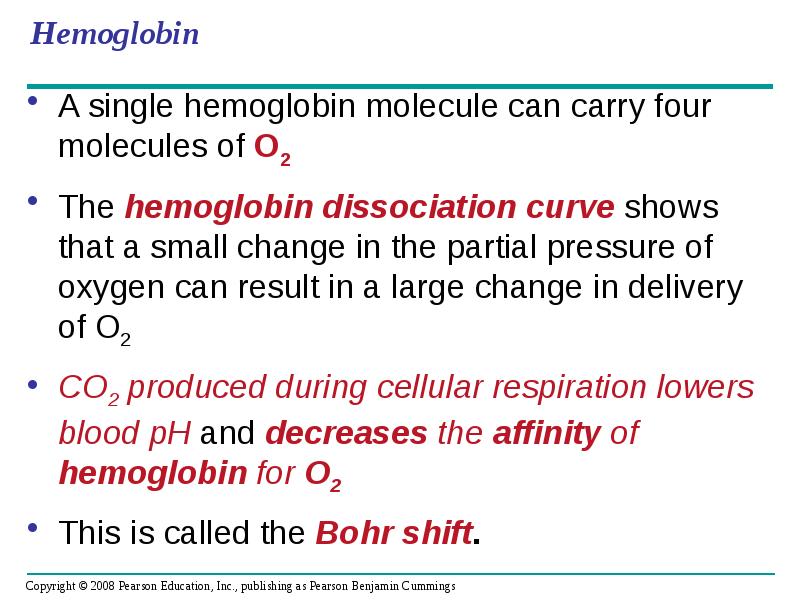
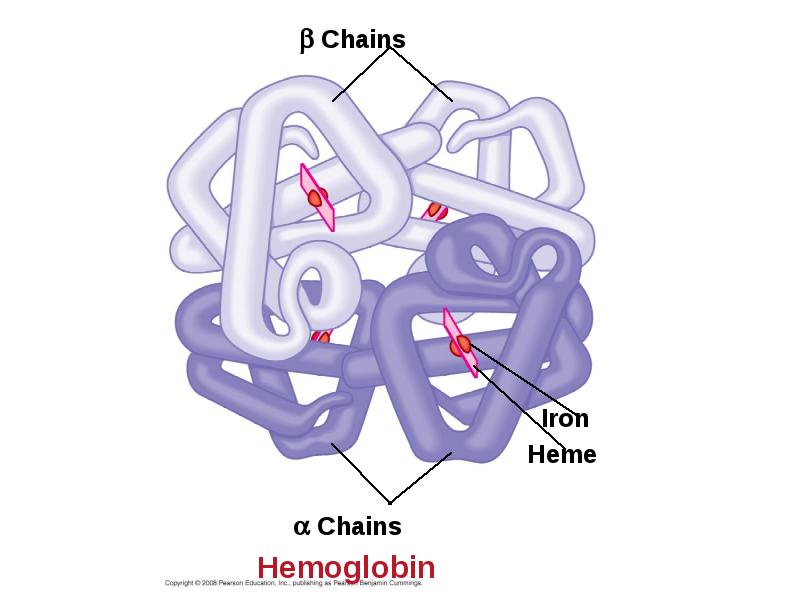
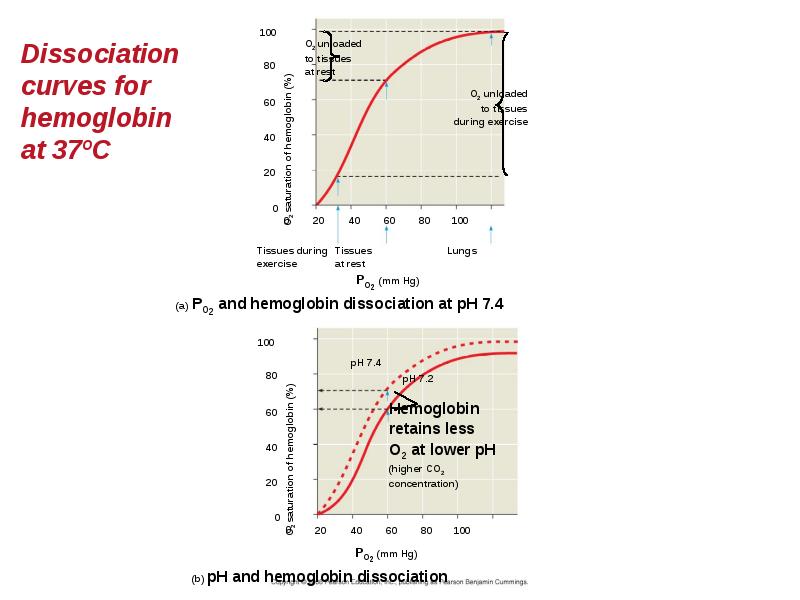
- 87. Hemoglobin A single hemoglobin molecule can carry four molecules of O2
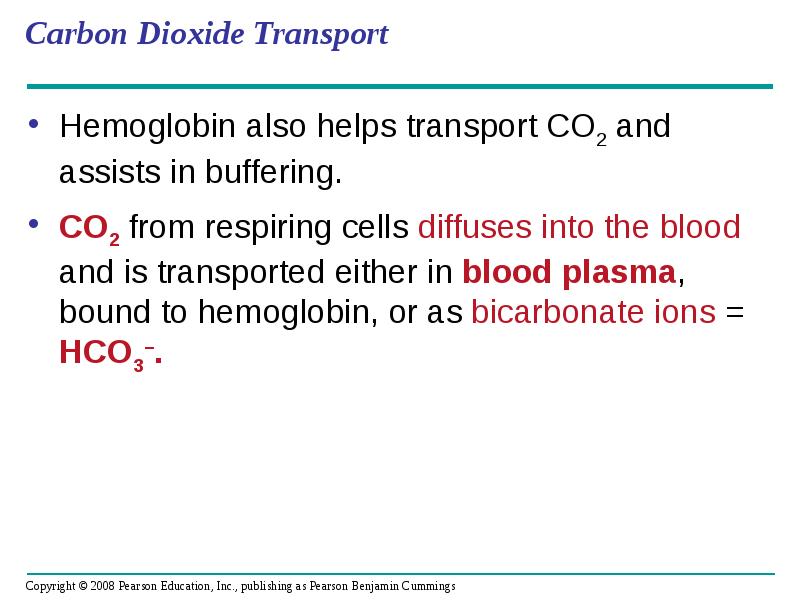
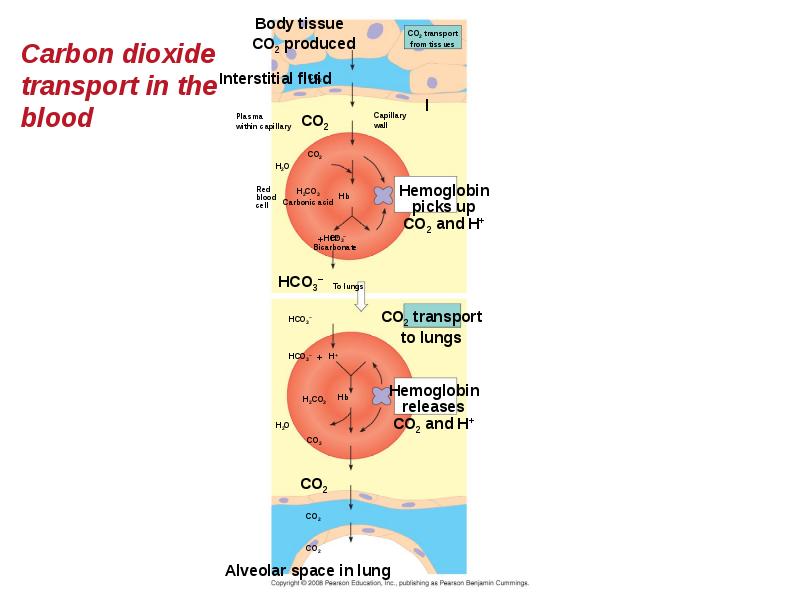
- 90. Carbon Dioxide Transport Hemoglobin also helps transport CO2 and assists in
- 92. Elite Animal Athletes Migratory and diving mammals have evolutionary adaptations that
- 94. You should now be able to: Compare and contrast open and
- 95. Define cardiac cycle and explain the role of the sinoatrial node.
- 96. Describe the role played by the lymphatic system in relation to
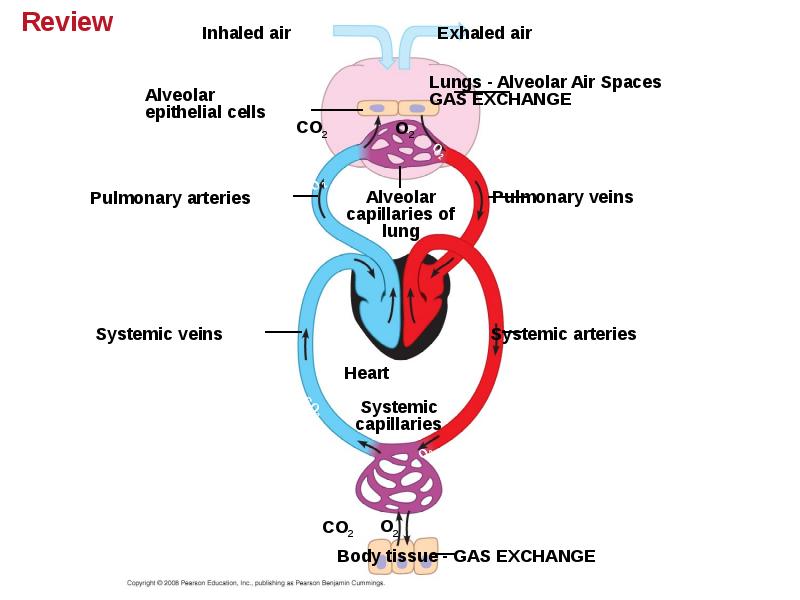
- 97. For humans, describe the exchange of gases in the lungs and
- 98. Скачать презентацию

















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























