Chapter 43 презентация
Содержание
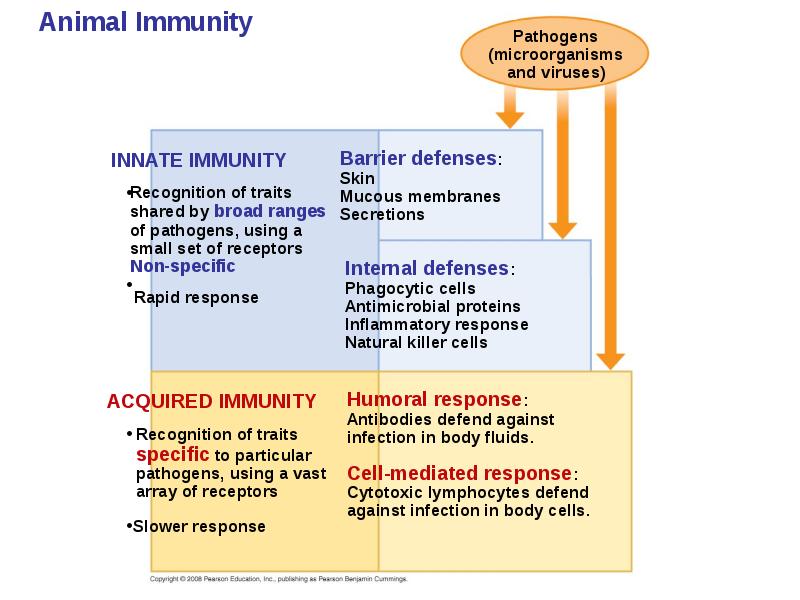
- 2. Overview: Reconnaissance, Recognition, and Response Barriers help an animal to defend
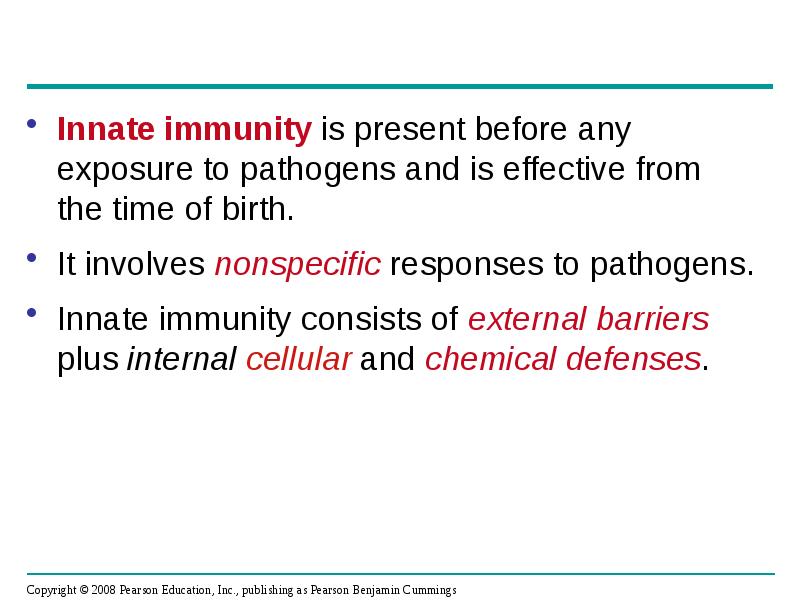
- 4. Innate immunity is present before any exposure to pathogens and is
- 5. Acquired immunity = adaptive immunity, develops after exposure to agents such
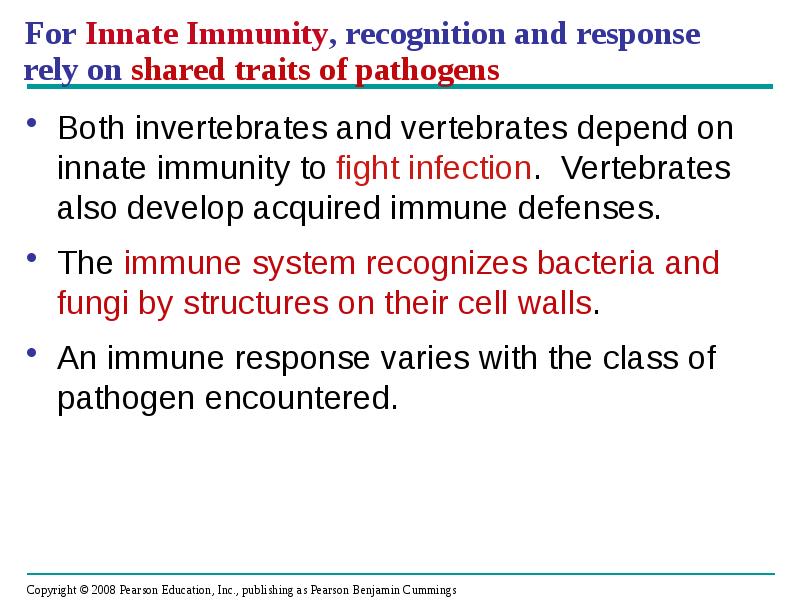
- 7. For Innate Immunity, recognition and response rely on shared traits of
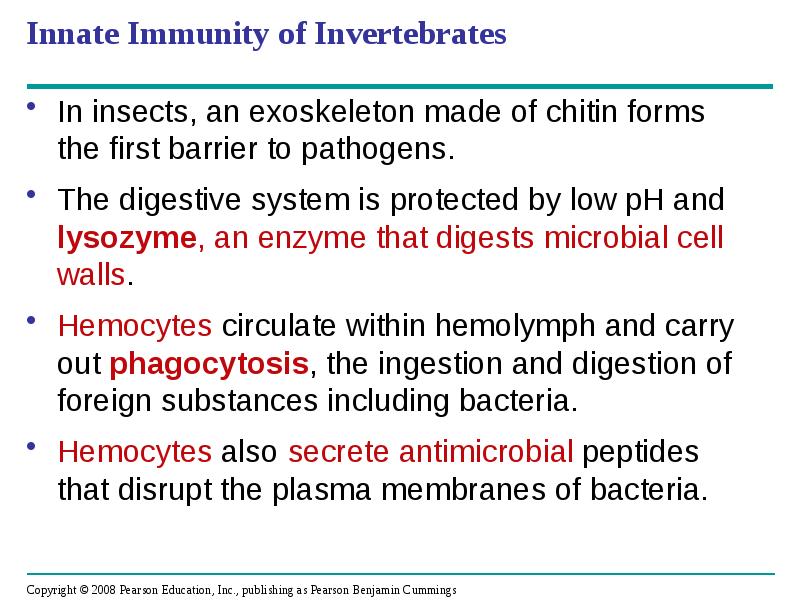
- 8. Innate Immunity of Invertebrates In insects, an exoskeleton made of chitin
- 10. Innate Immunity Defenses of Vertebrates The immune system of mammals is
- 11. Barrier Defenses Barrier defenses include the skin and mucous membranes of
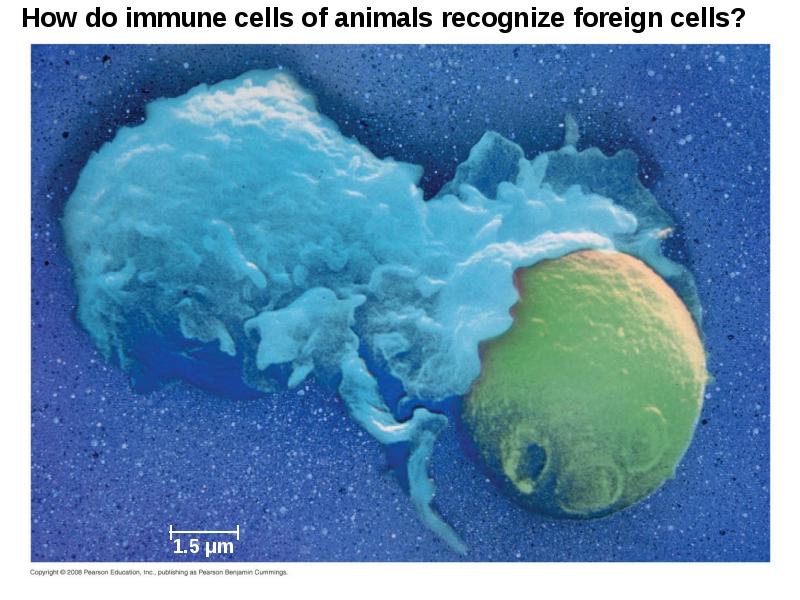
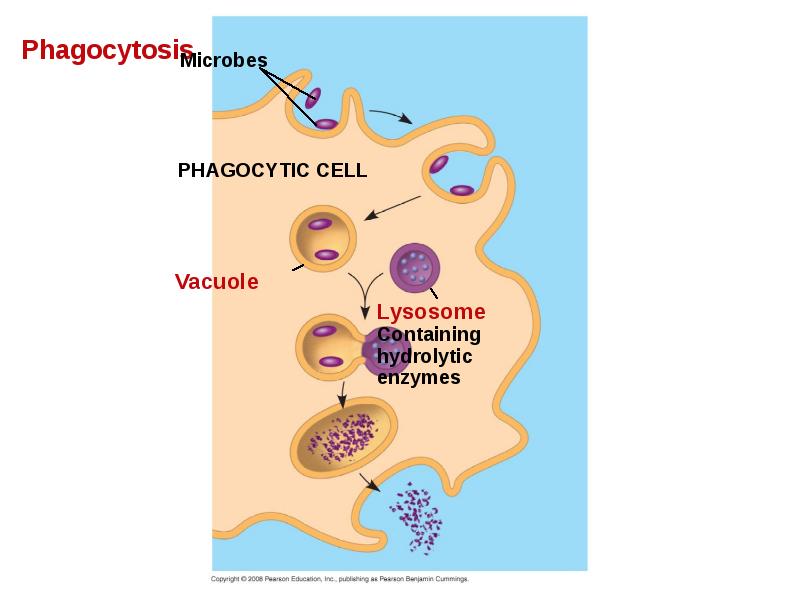
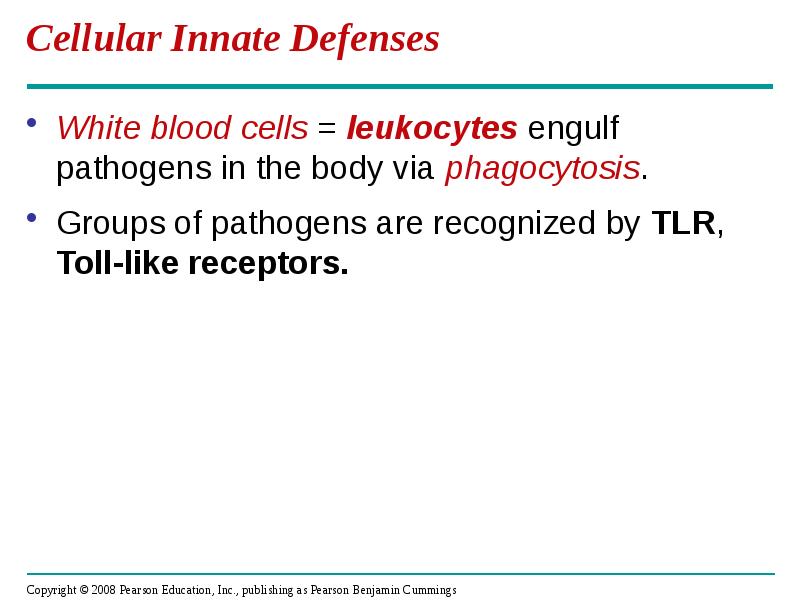
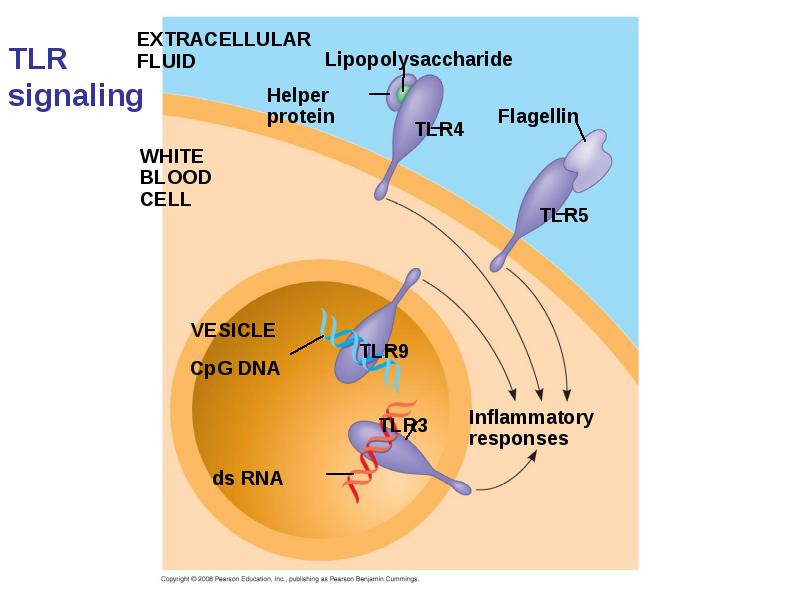
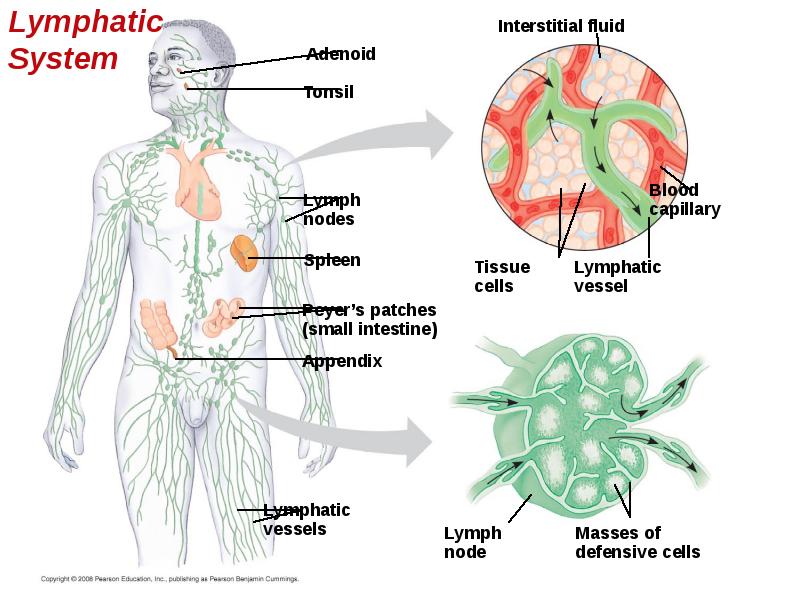
- 12. Cellular Innate Defenses White blood cells = leukocytes engulf pathogens in
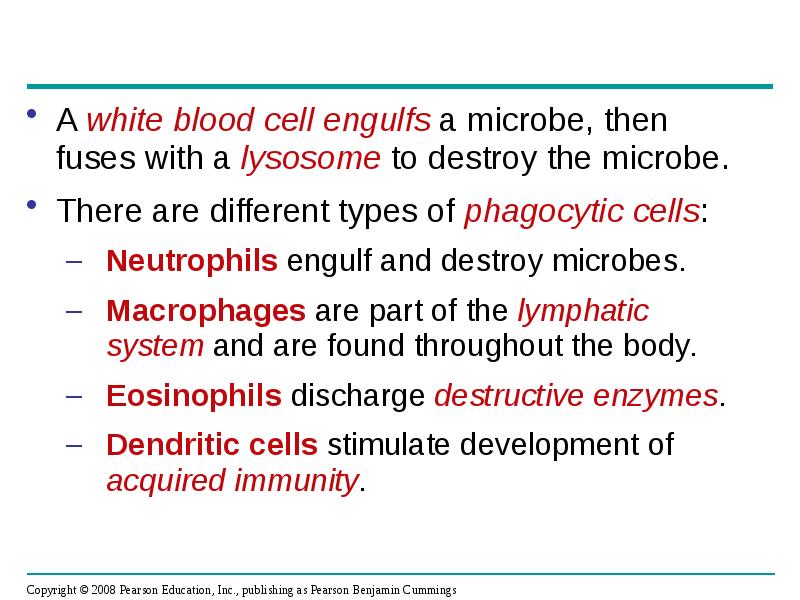
- 14. A white blood cell engulfs a microbe, then fuses with a
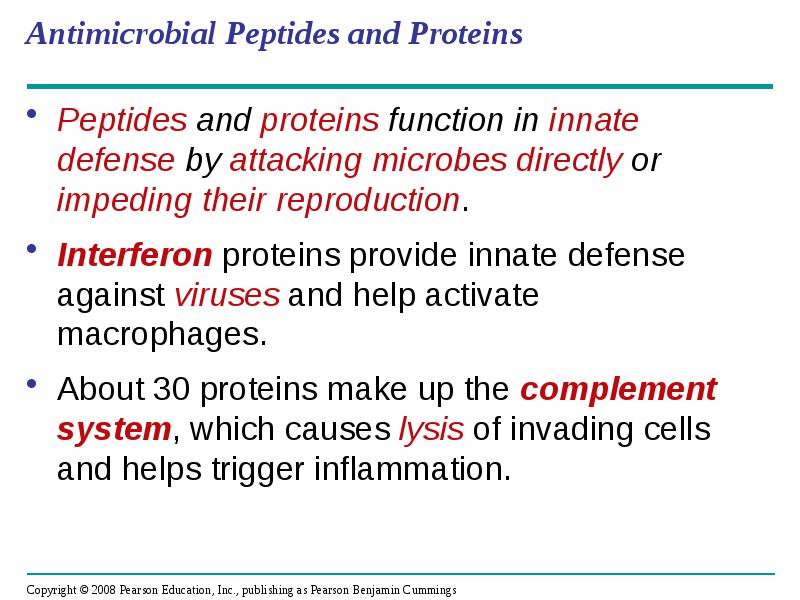
- 16. Antimicrobial Peptides and Proteins Peptides and proteins function in innate defense
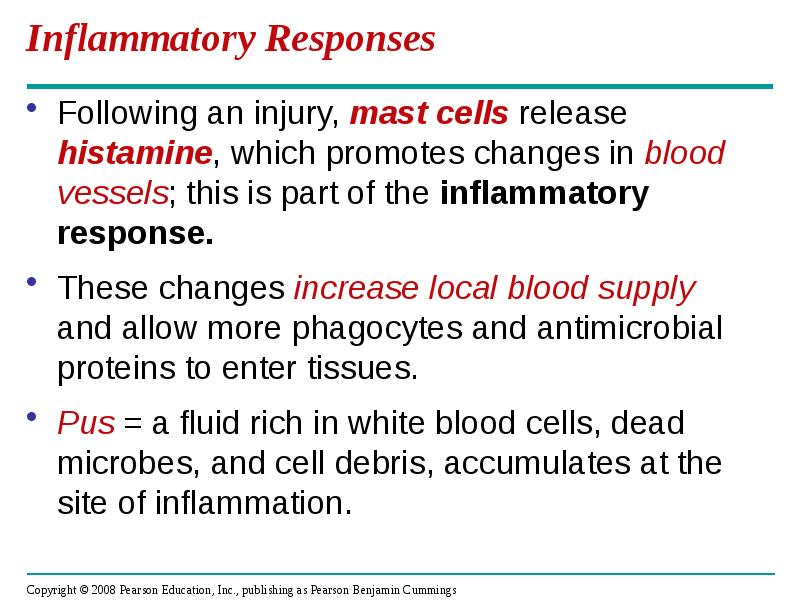
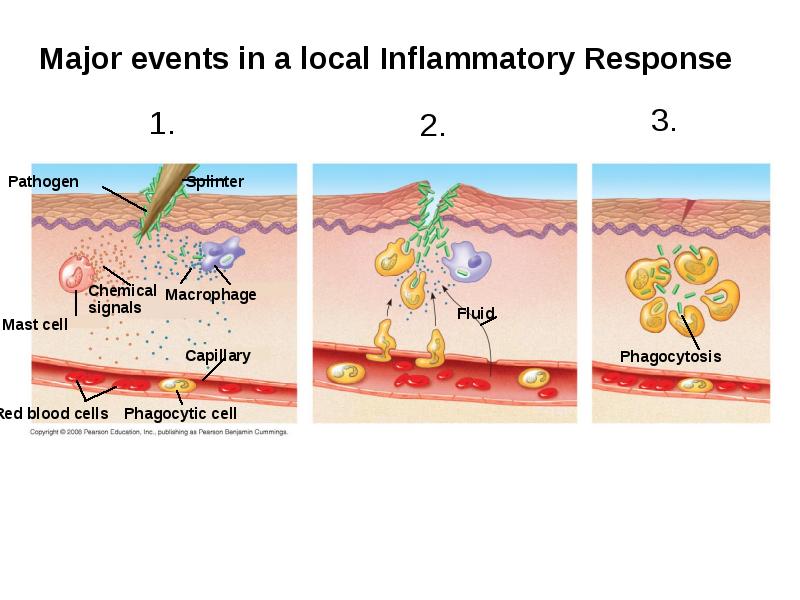
- 17. Inflammatory Responses Following an injury, mast cells release histamine, which promotes
- 19. Inflammation can be either local or systemic (throughout the body). Inflammation
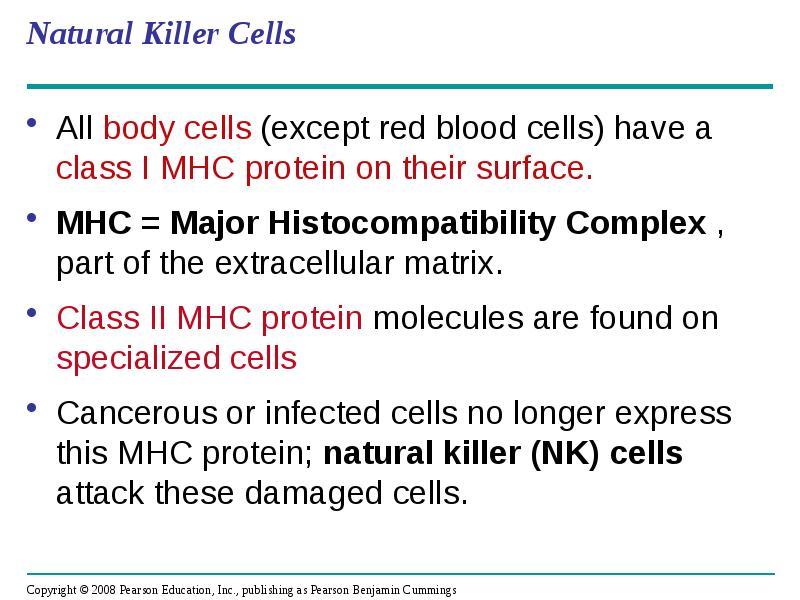
- 20. Natural Killer Cells All body cells (except red blood cells) have
- 21. Innate Immune System Evasion by Pathogens Some pathogens avoid destruction by
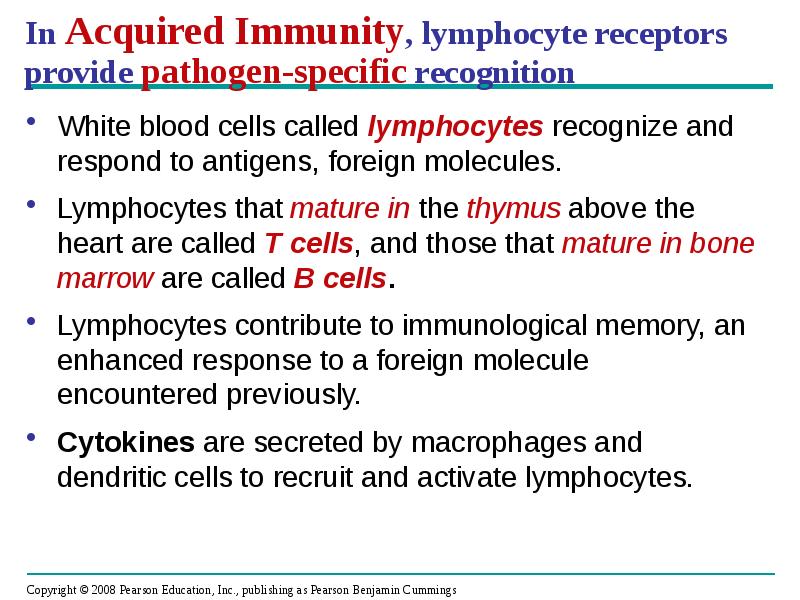
- 22. In Acquired Immunity, lymphocyte receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition White blood cells
- 23. Acquired Immunity = Active Immunity: Specific B cells and T cells
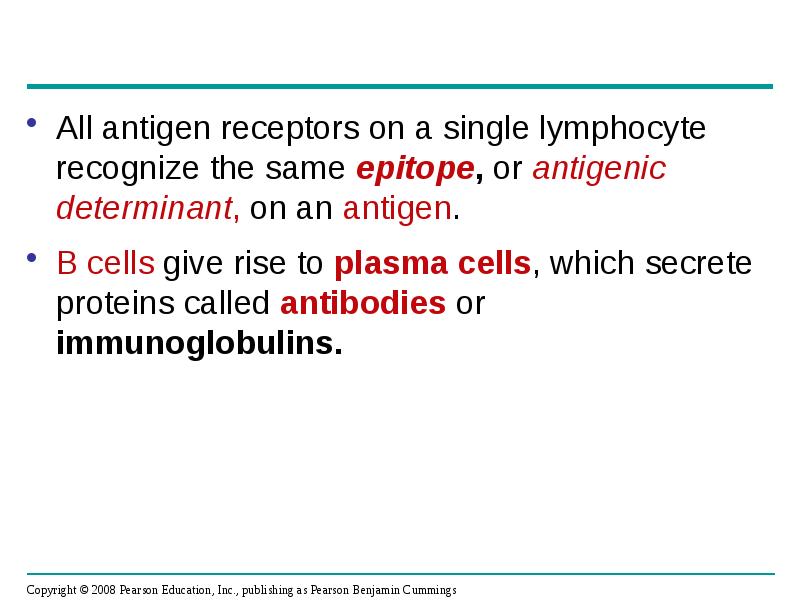
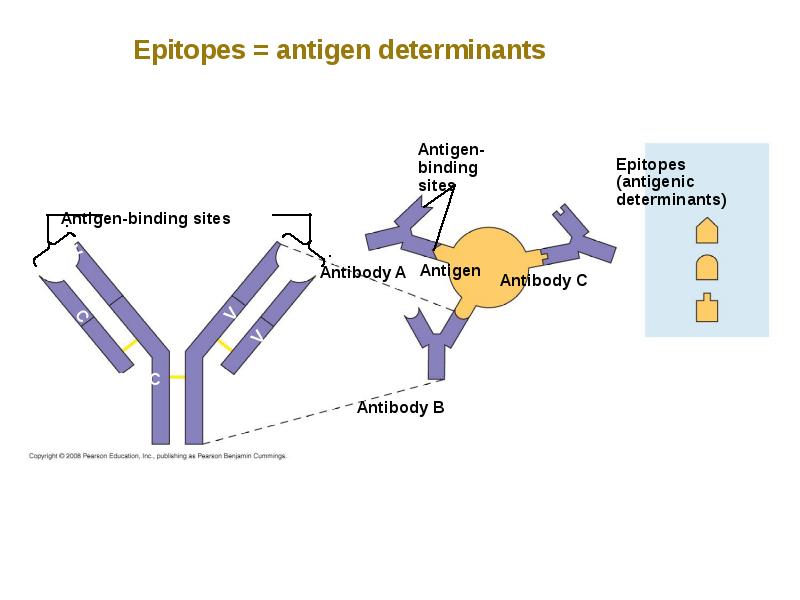
- 25. All antigen receptors on a single lymphocyte recognize the same epitope,
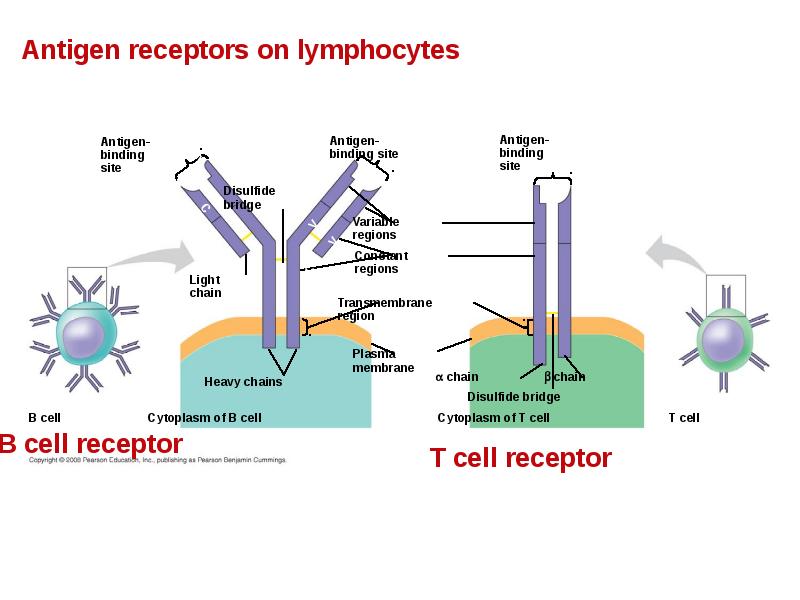
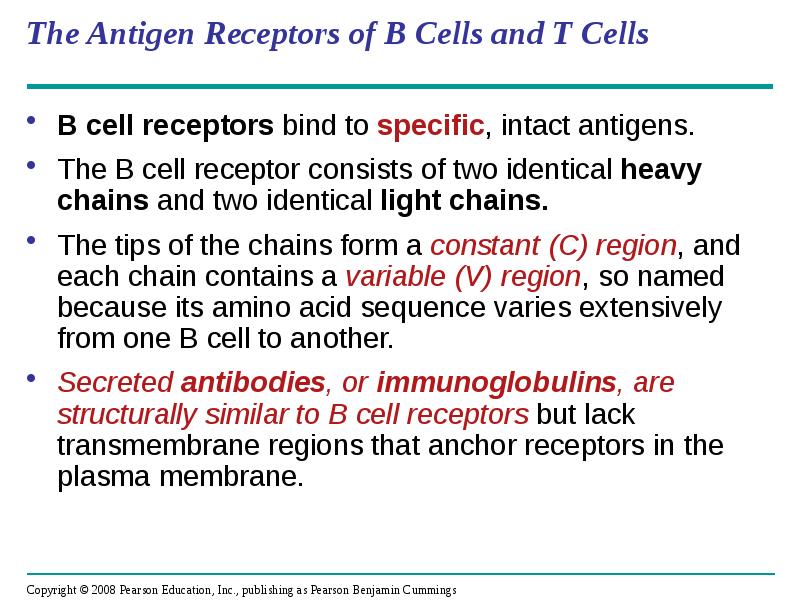
- 27. The Antigen Receptors of B Cells and T Cells B cell
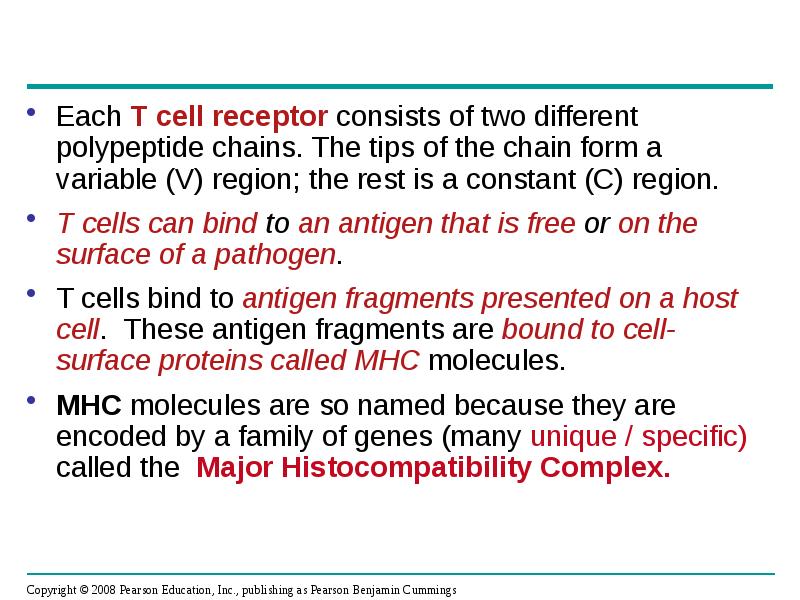
- 28. Each T cell receptor consists of two different polypeptide chains. The
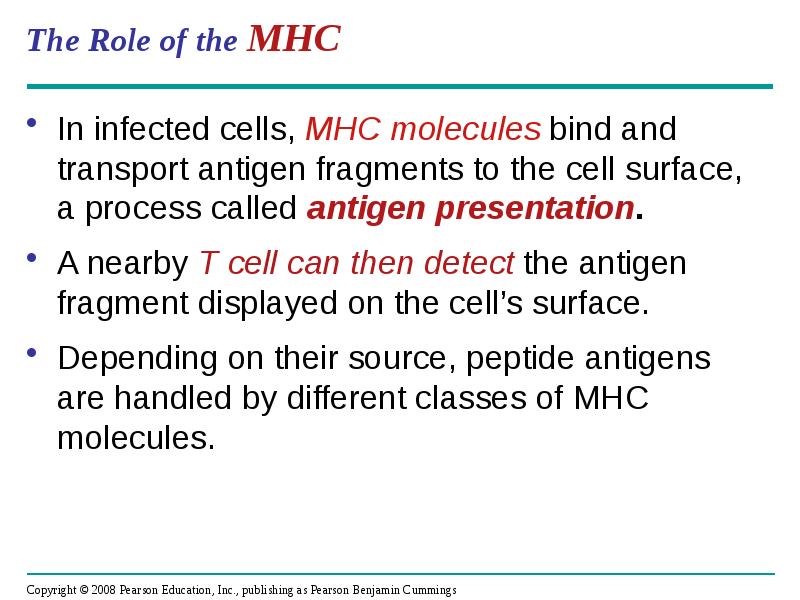
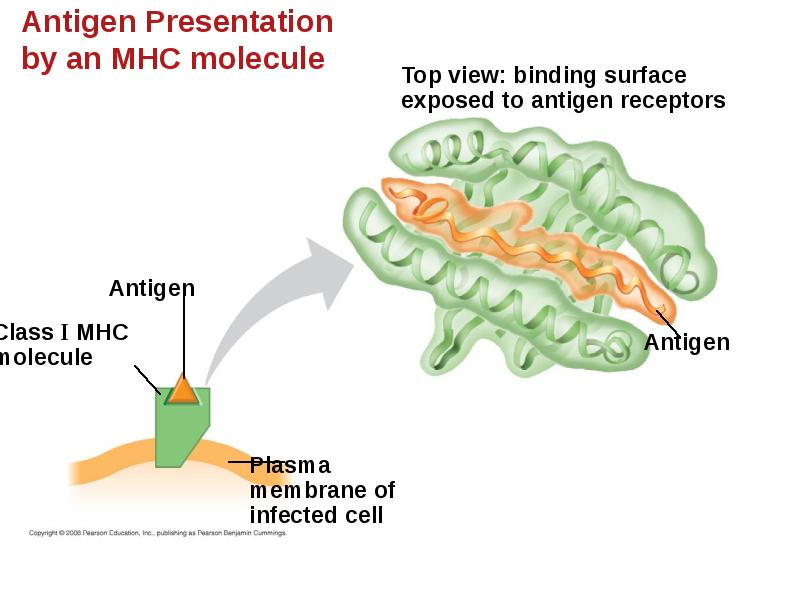
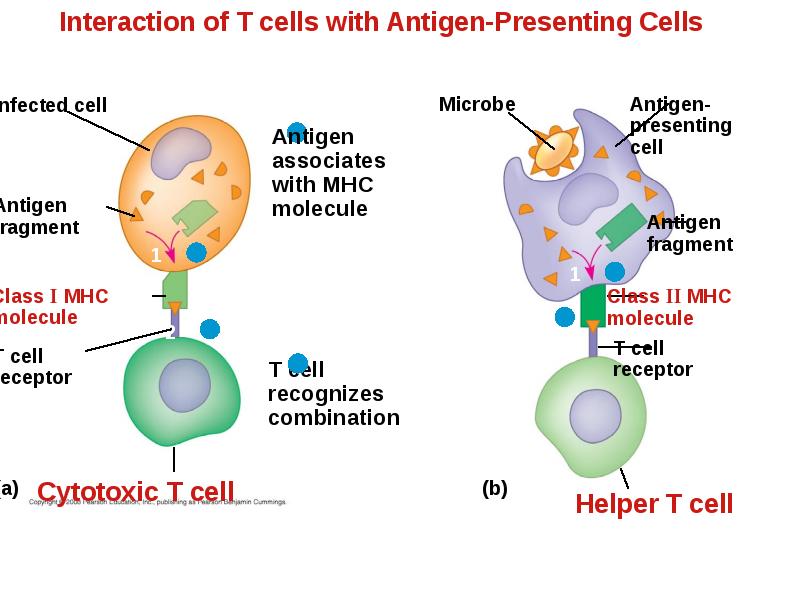
- 29. The Role of the MHC In infected cells, MHC molecules bind
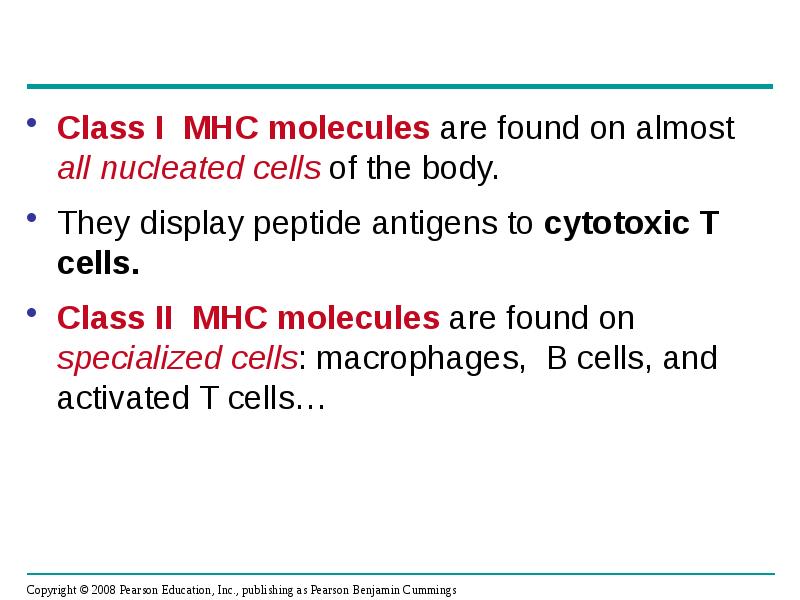
- 31. Class I MHC molecules are found on almost all nucleated cells
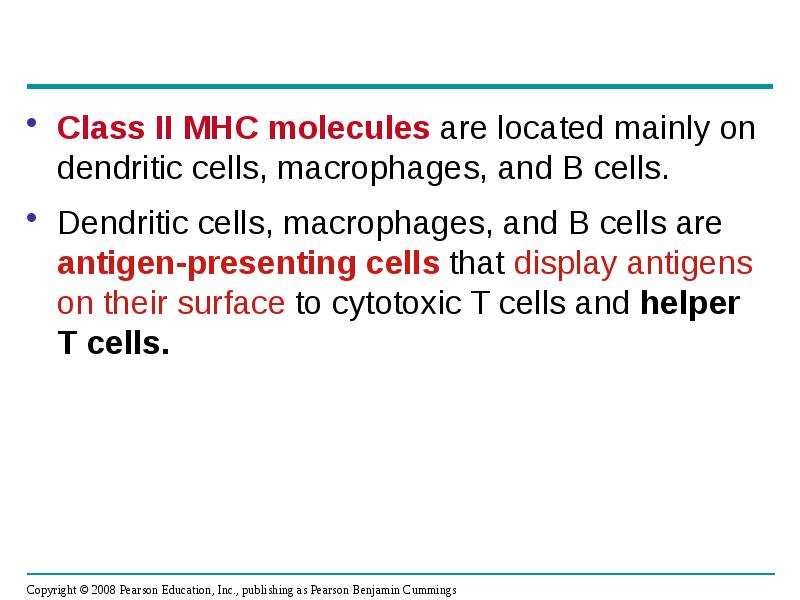
- 33. Class II MHC molecules are located mainly on dendritic cells, macrophages,
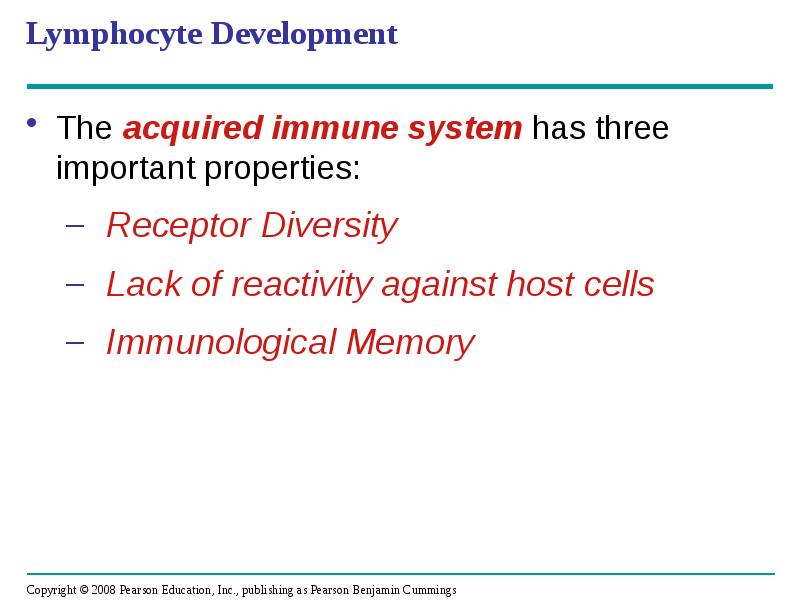
- 34. Lymphocyte Development The acquired immune system has three important properties: Receptor
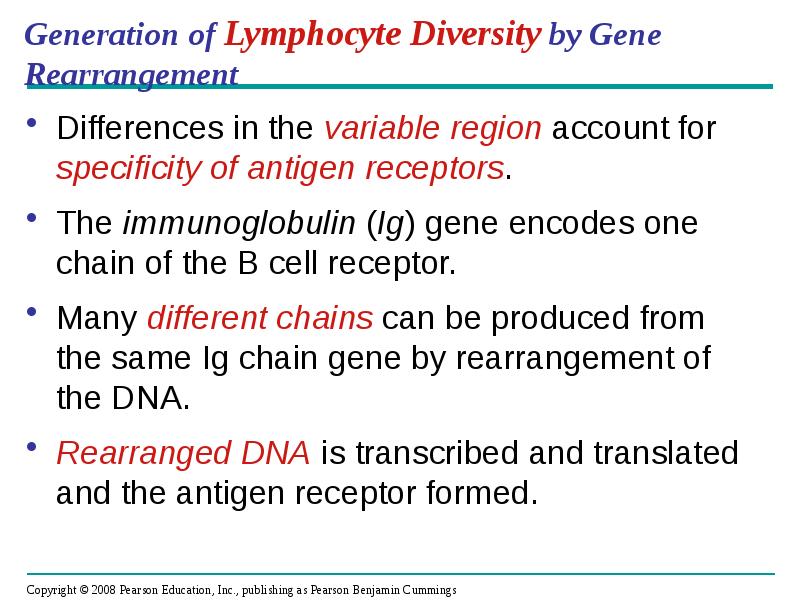
- 35. Generation of Lymphocyte Diversity by Gene Rearrangement Differences in the variable
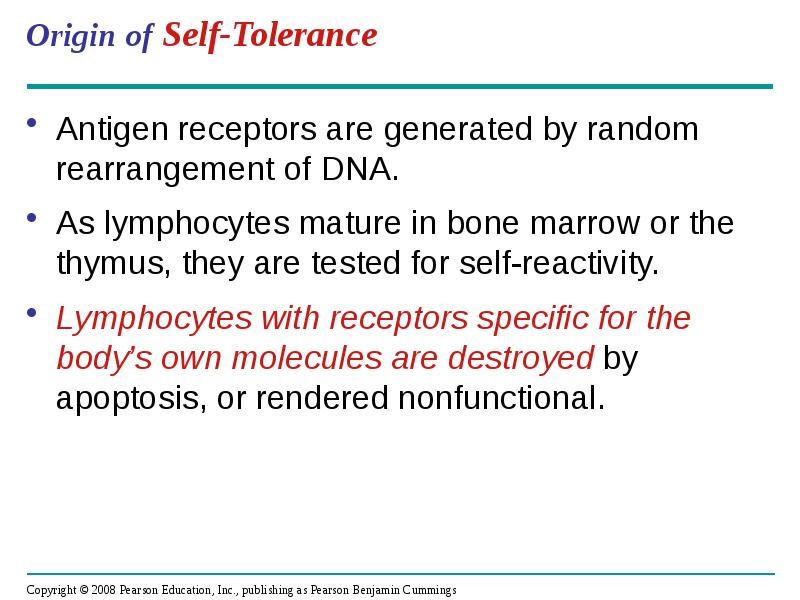
- 36. Origin of Self-Tolerance Antigen receptors are generated by random rearrangement of
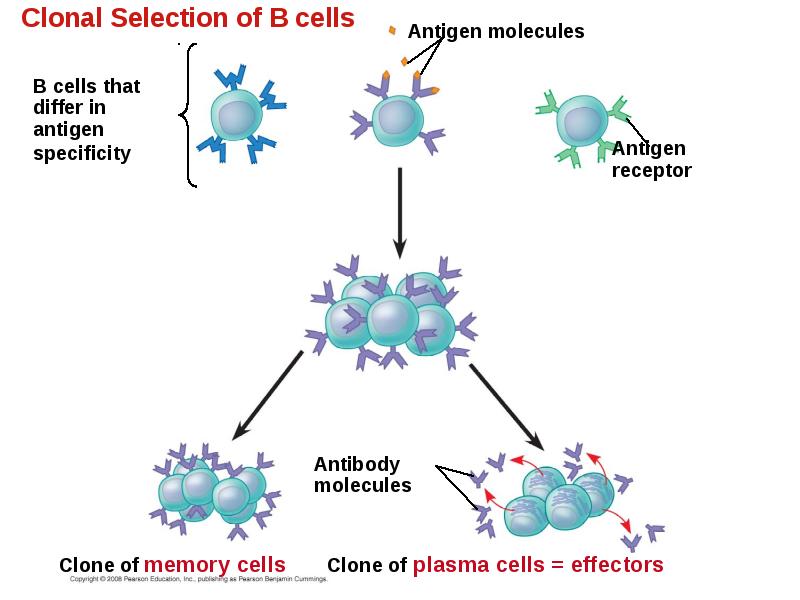
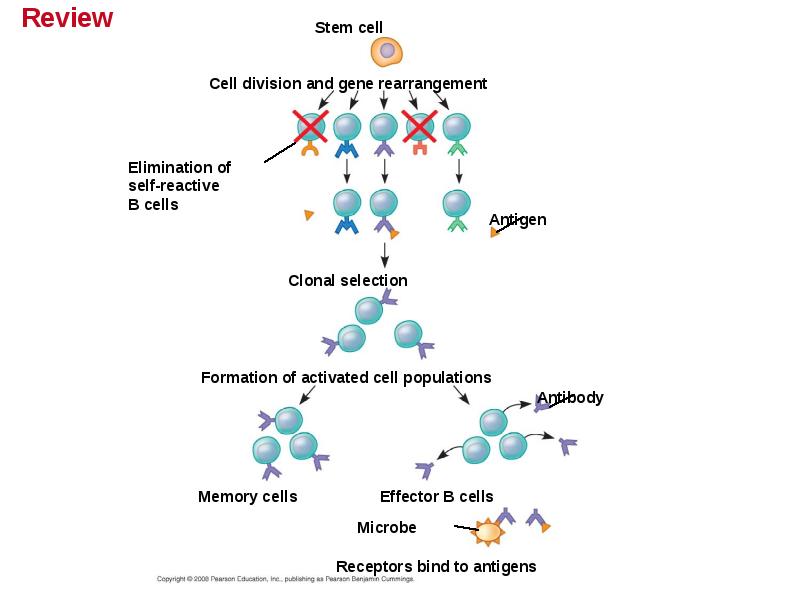
- 37. Amplifying Lymphocytes by Clonal Selection In the body there are few
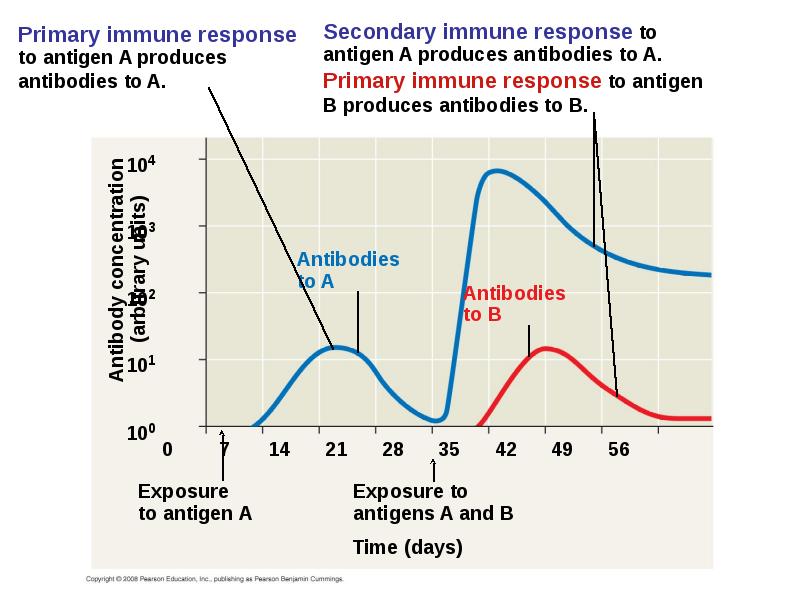
- 39. The first exposure to a specific antigen represents the primary immune
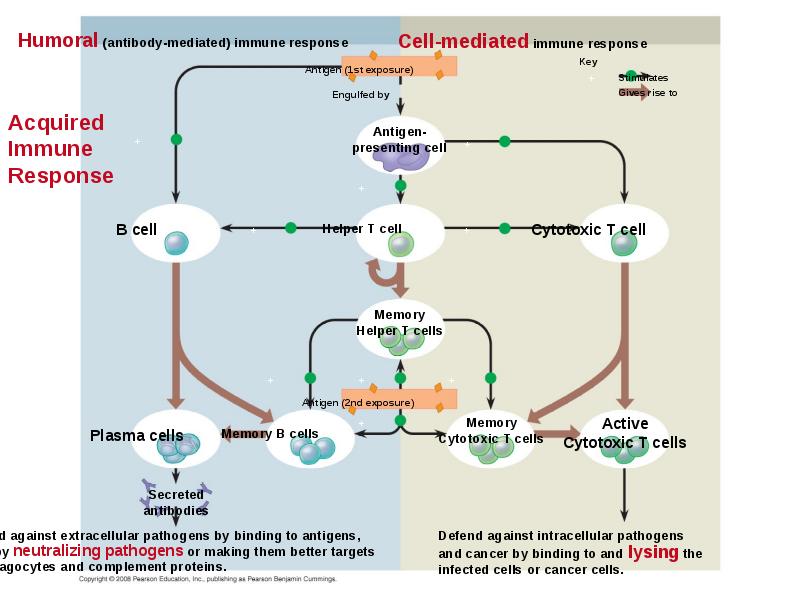
- 41. Acquired immunity defends against infection of body cells and fluids Acquired
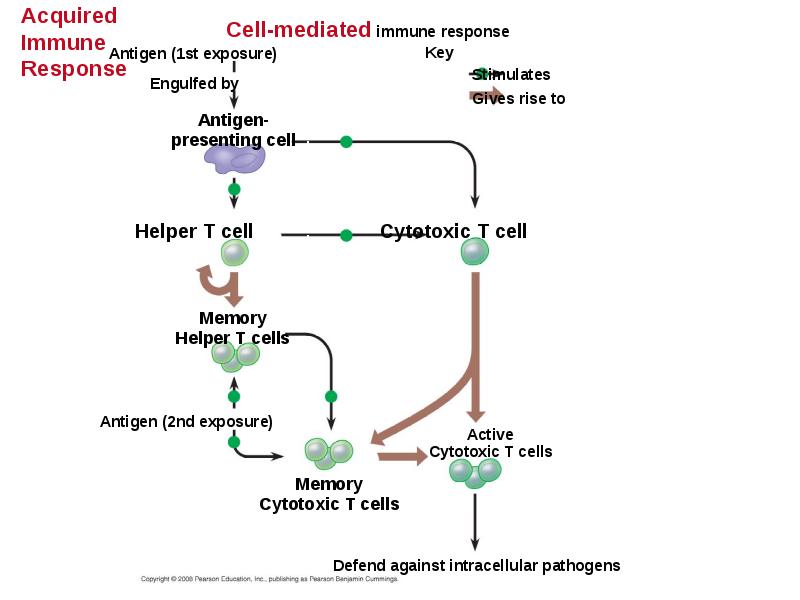
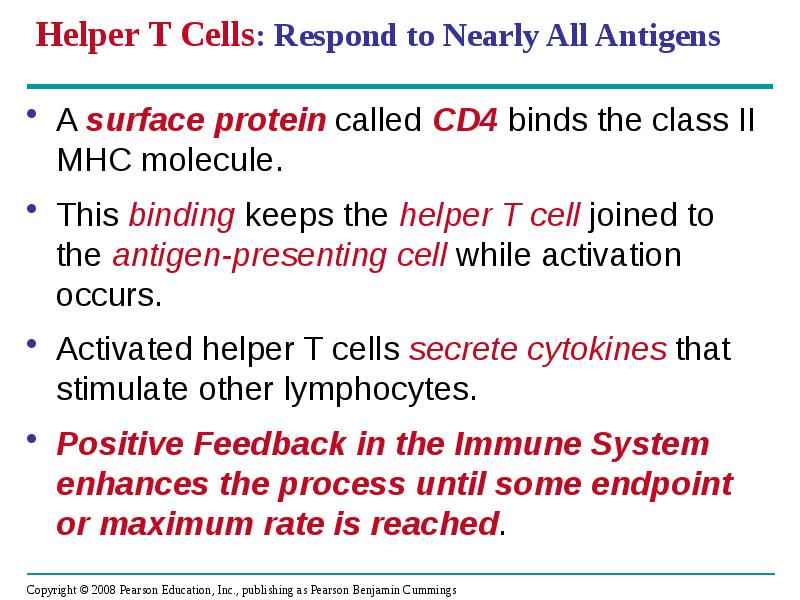
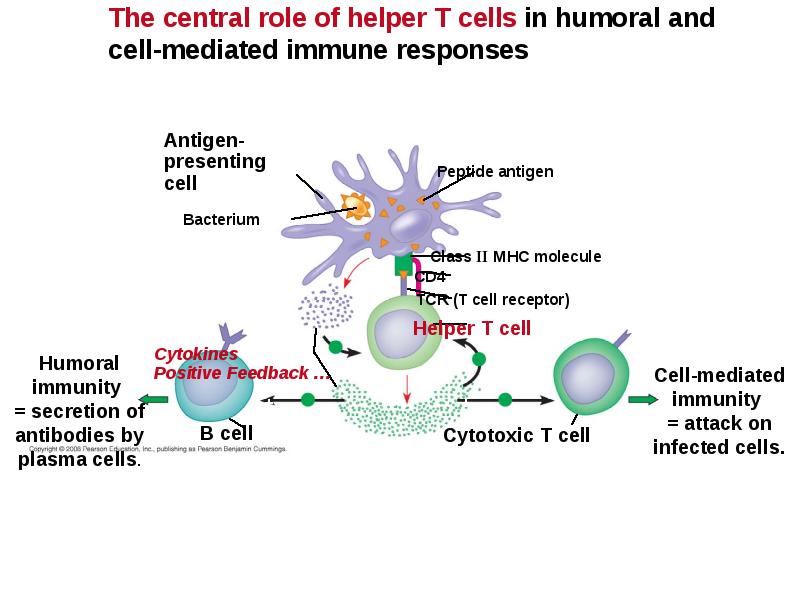
- 45. Helper T Cells: Respond to Nearly All Antigens A surface protein
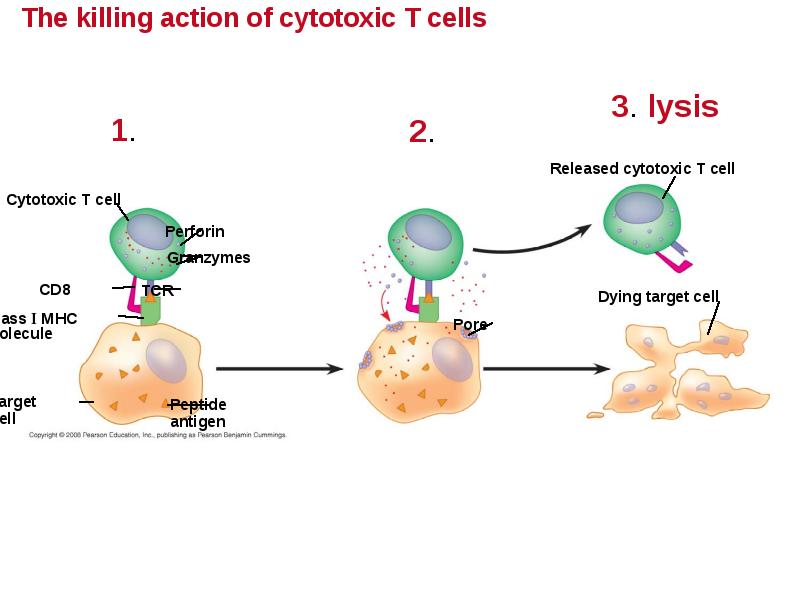
- 47. Cytotoxic T Cells: A Response to Infected Cells Cytotoxic T cells
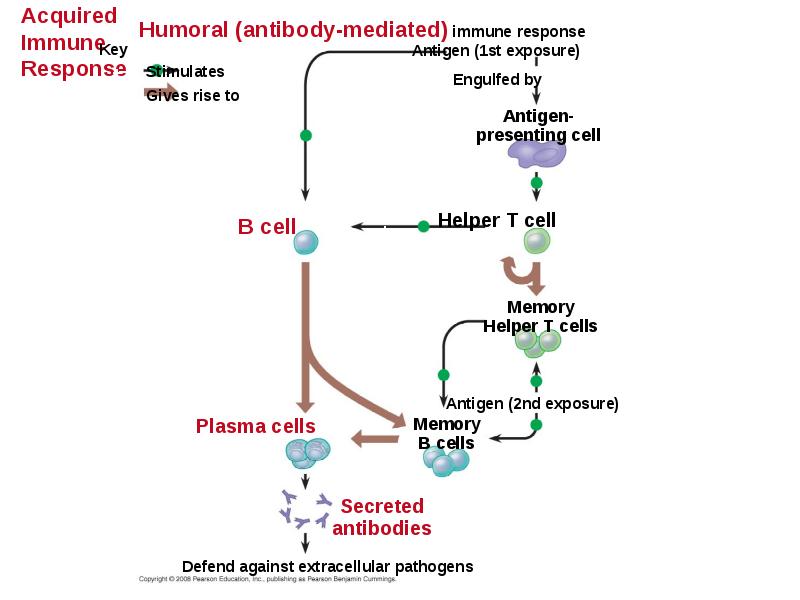
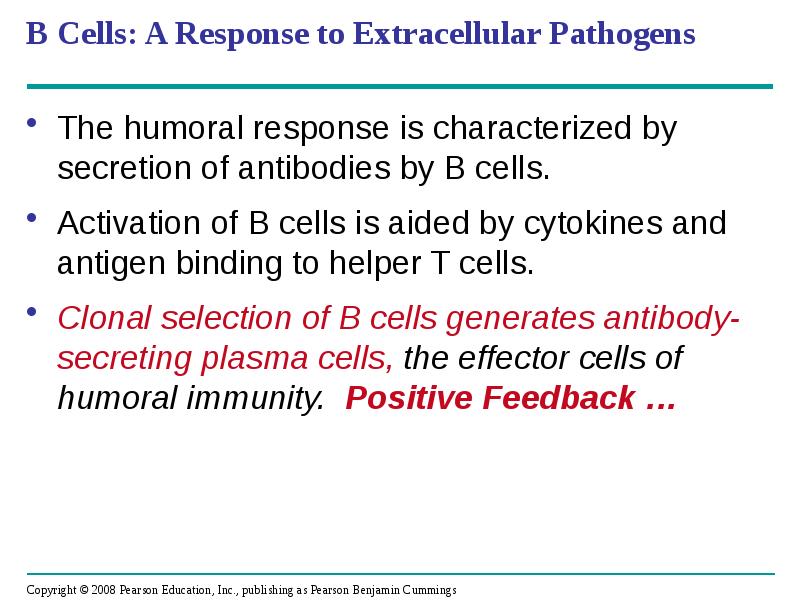
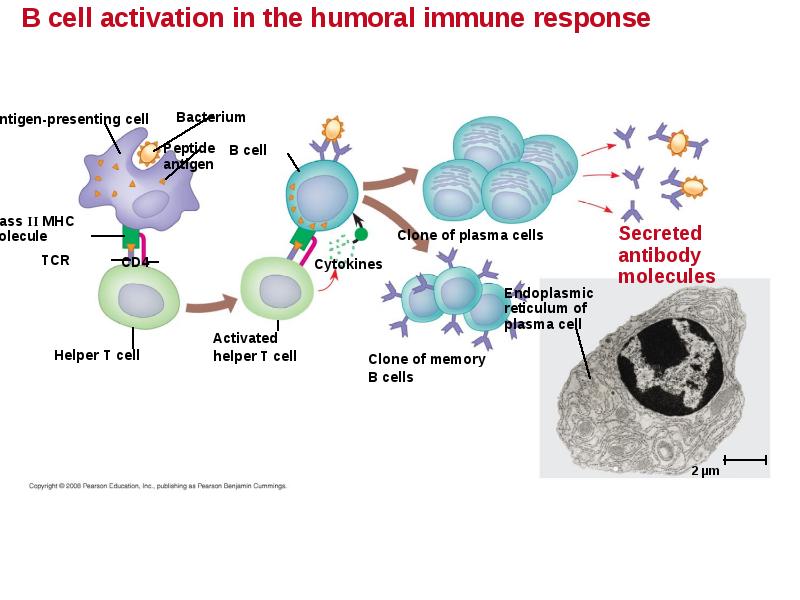
- 49. B Cells: A Response to Extracellular Pathogens The humoral response is
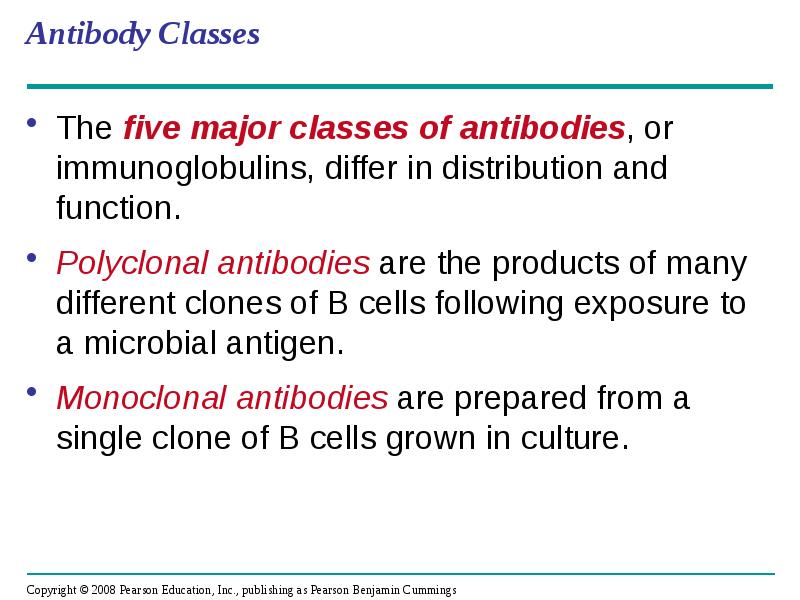
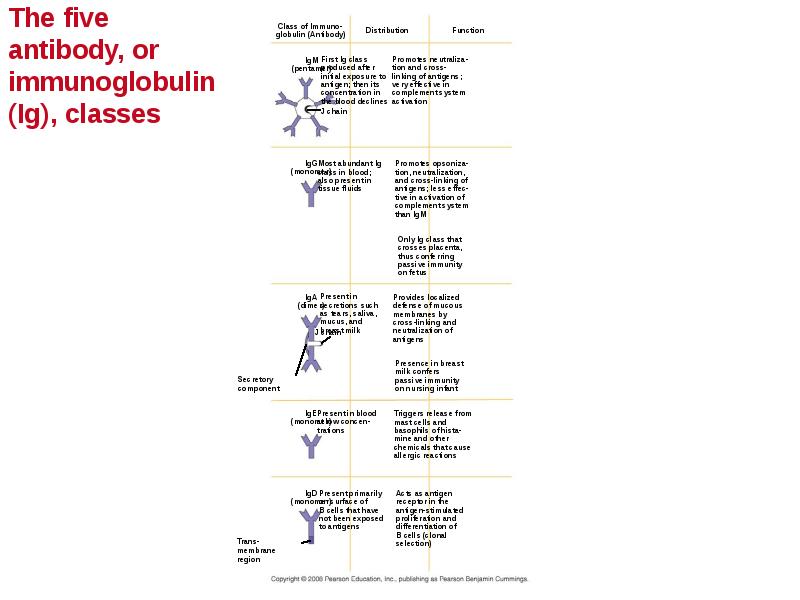
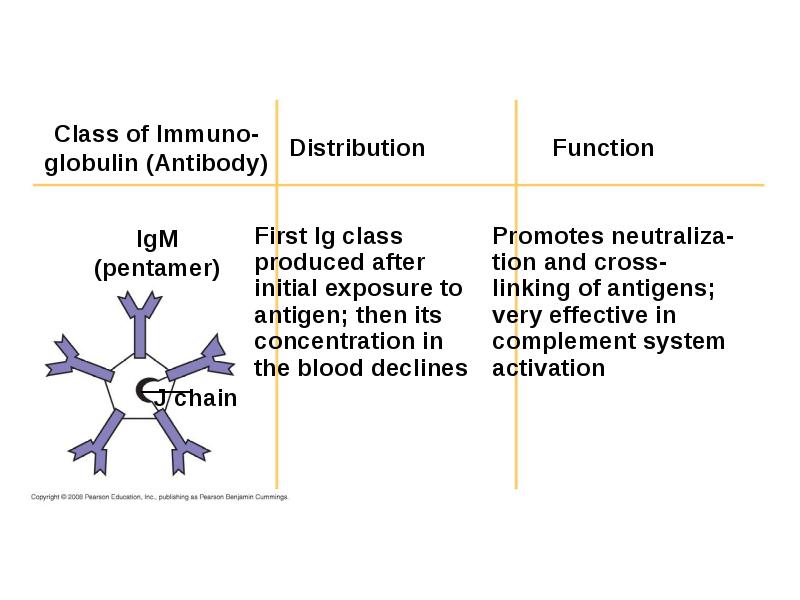
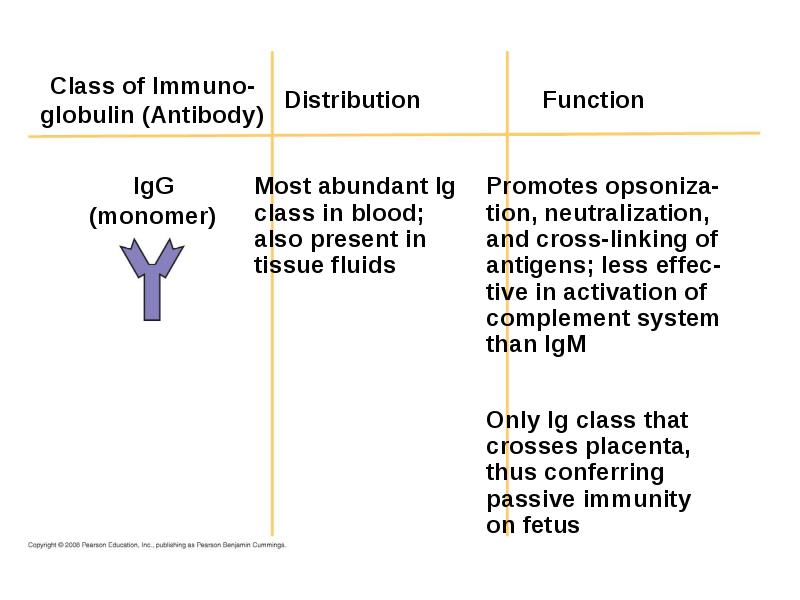
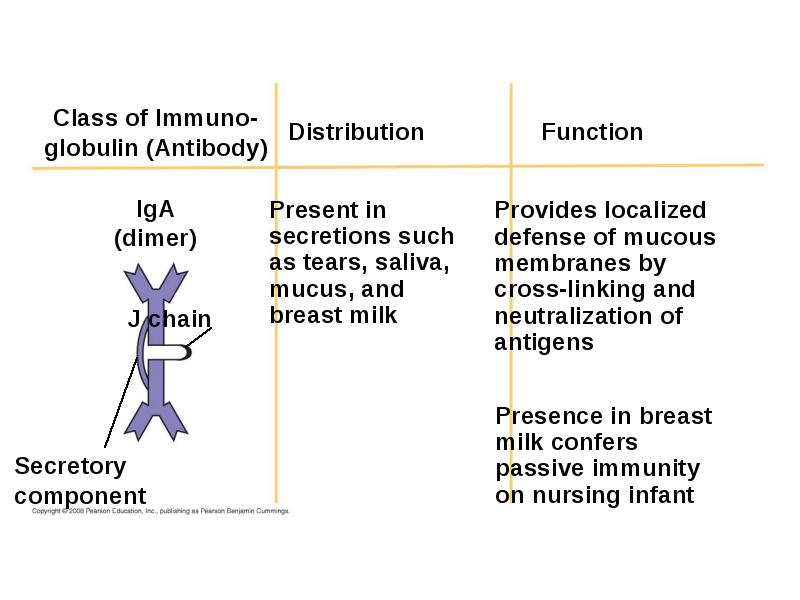
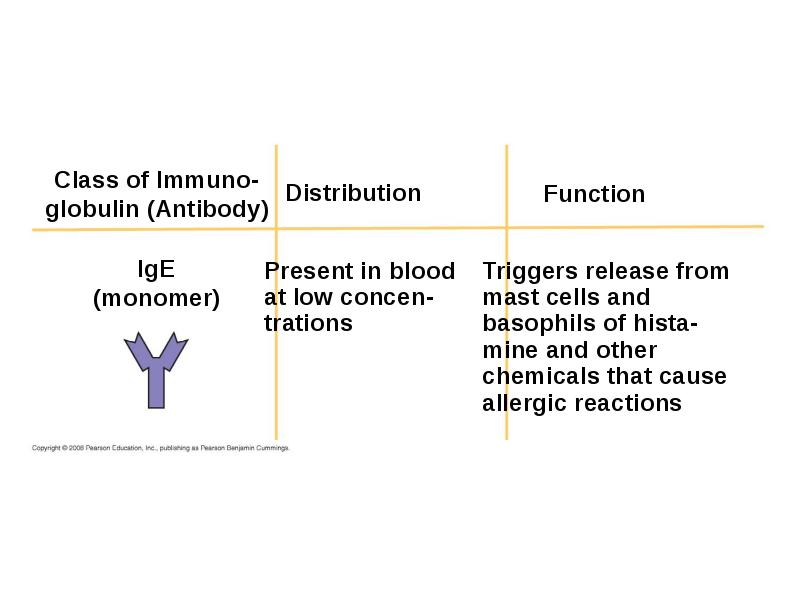
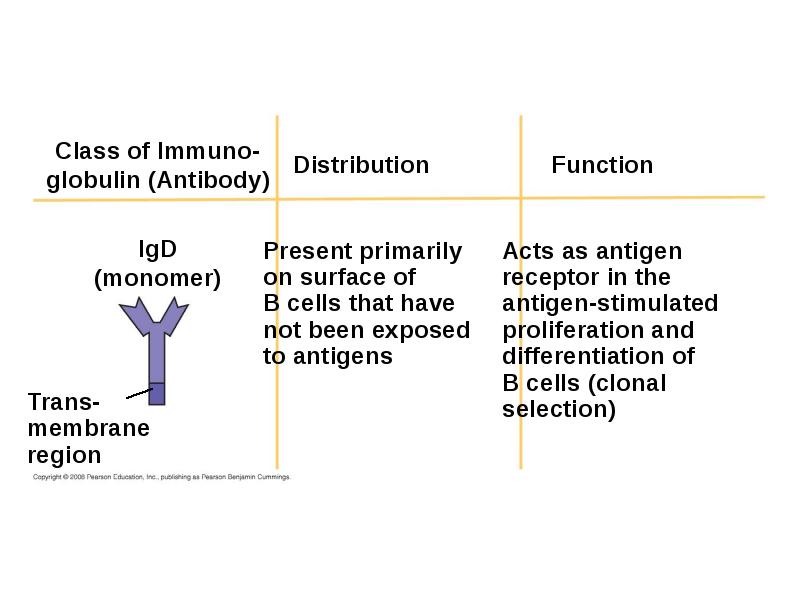
- 51. Antibody Classes The five major classes of antibodies, or immunoglobulins, differ
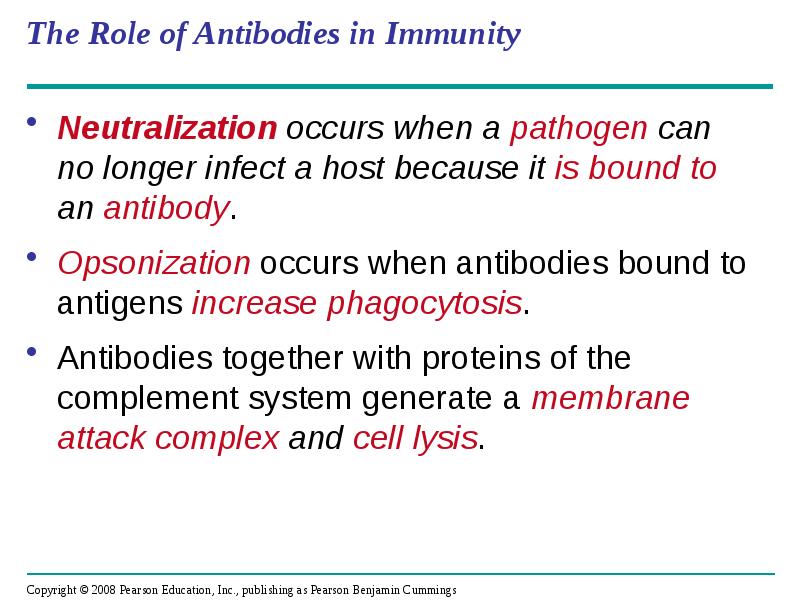
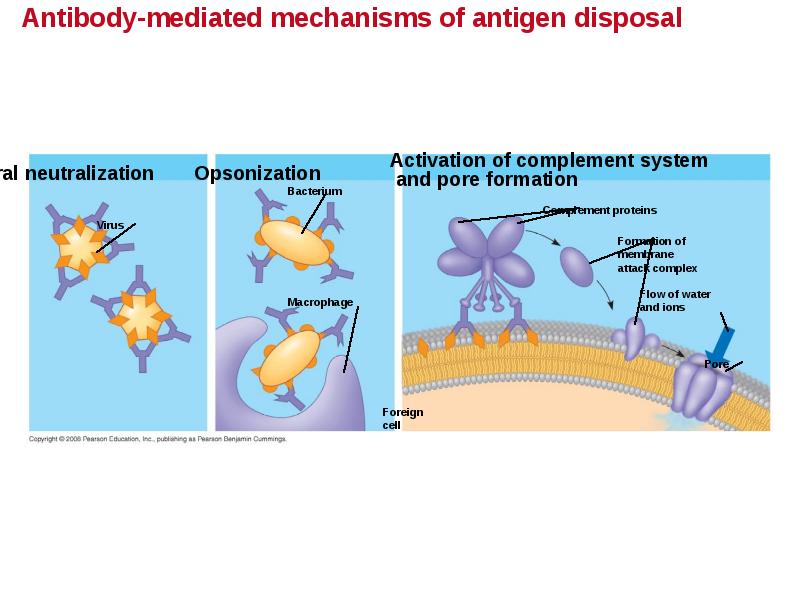
- 58. The Role of Antibodies in Immunity Neutralization occurs when a pathogen
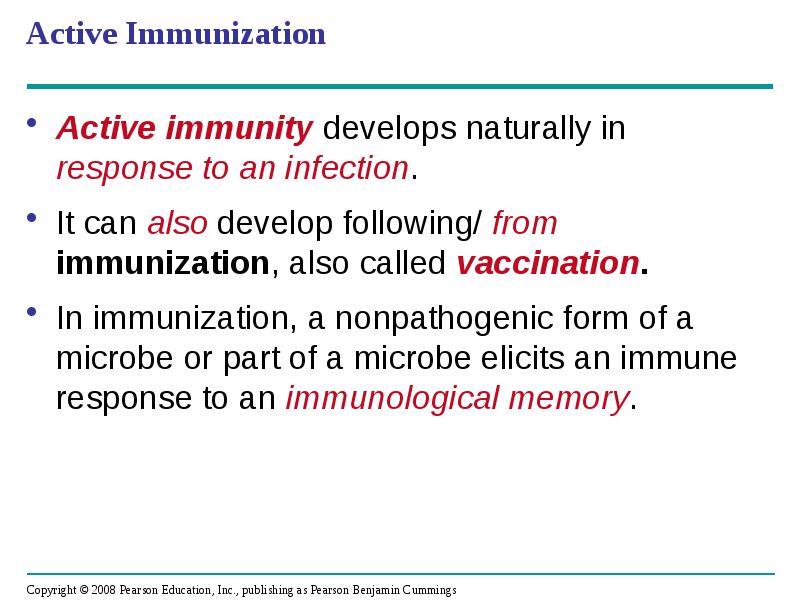
- 60. Active Immunization Active immunity develops naturally in response to an infection.
- 61. Passive immunity provides immediate, short-term protection. Passive immunity provides immediate, short-term
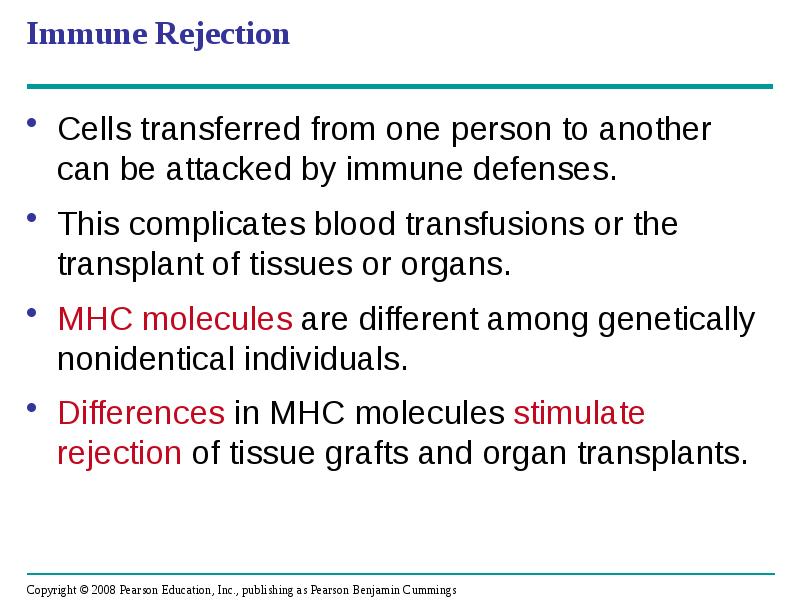
- 63. Immune Rejection Cells transferred from one person to another can be
- 64. Chances of successful transplantation increase if donor and recipient MHC tissue
- 65. Blood Groups Antigens on red blood cells surface determine whether a
- 66. Disruption in immune system function can elicit or exacerbate disease Some
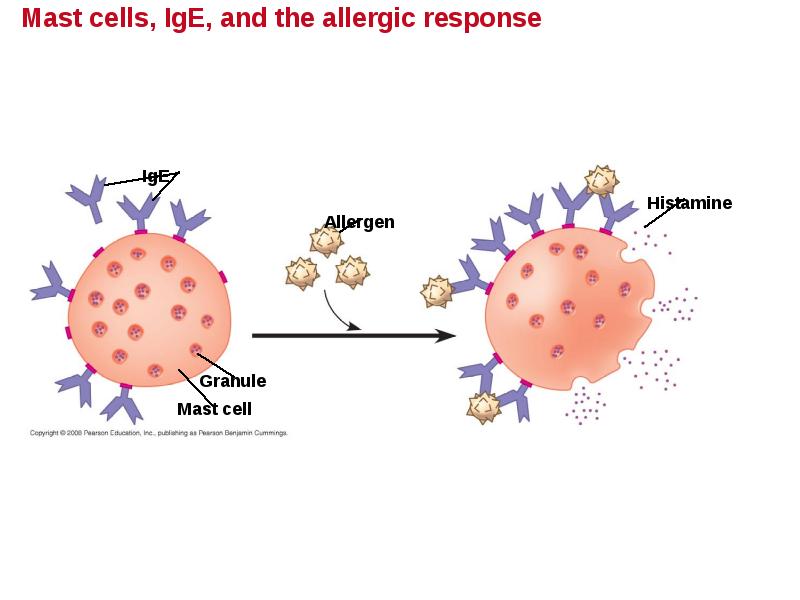
- 67. Allergies Allergies are exaggerated (hypersensitive) responses to antigens called allergens. In
- 69. The next time the allergen enters the body, it binds to
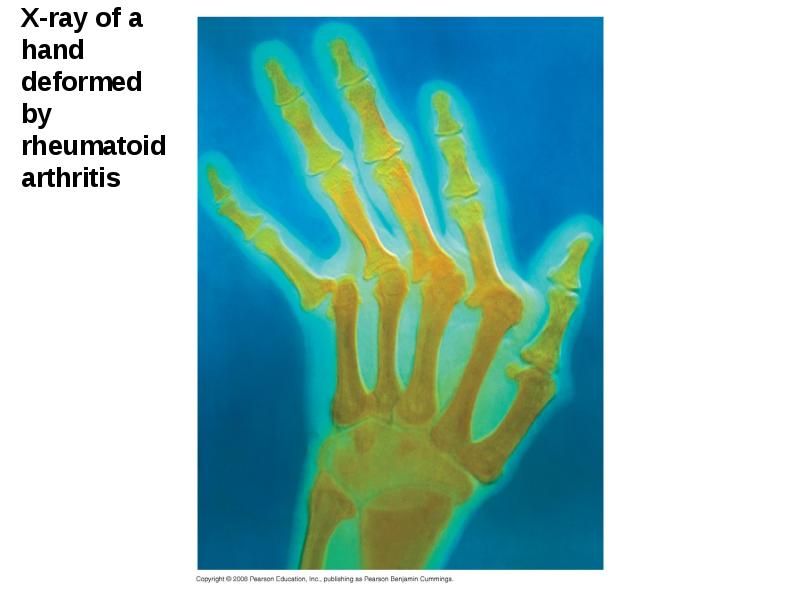
- 70. Autoimmune Diseases In individuals with autoimmune diseases, the immune system loses
- 72. Exertion, Stress, and the Immune System Moderate exercise improves immune system
- 73. Immunodeficiency Diseases Inborn immunodeficiency results from hereditary or developmental defects that
- 74. Acquired Immune System Evasion by Pathogens Pathogens have evolved mechanisms to
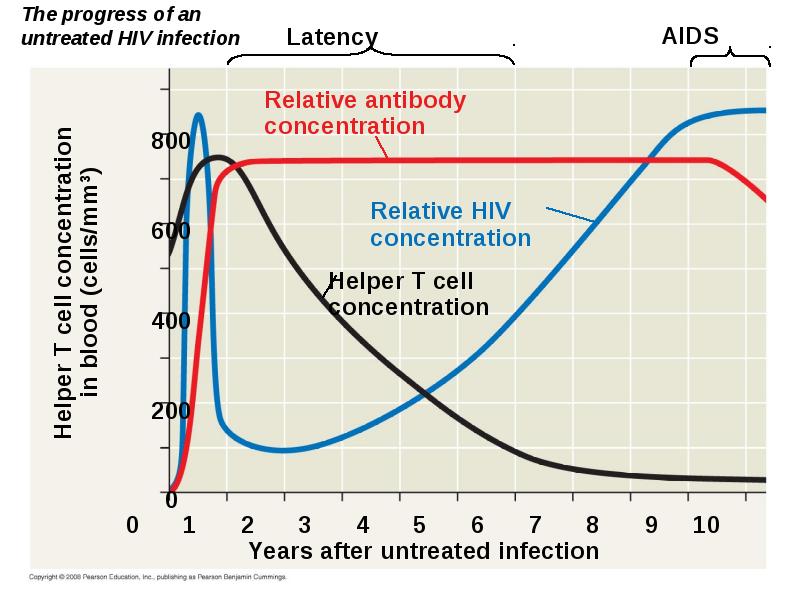
- 75. Latency Some viruses may remain in a host in an inactive
- 76. Attack on the Immune System: HIV Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects
- 78. People with AIDS are highly susceptible to opportunistic infections and cancers
- 79. Cancer and Immunity The frequency of certain cancers increases when the
- 81. You should now be able to: Distinguish between innate and acquired
- 82. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: antigens and antibodies; antigen
- 83. Describe clonal selection and distinguish between effector cells and memory cells.
- 84. Describe the role of MHC in the rejection of tissue transplants.
- 85. Скачать презентацию





















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























