Complex numbers презентация
Содержание
- 2. Key words: Definition, equality, ordering, conjugate, addition and subtraction, multiplication, divison,
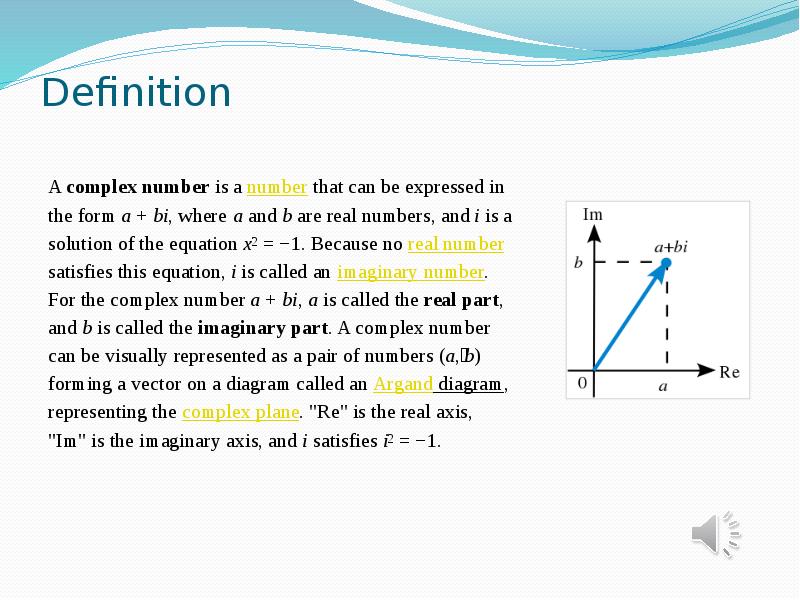
- 3. Definition A complex number is a number that can be expressed in the
- 4. For example, the equation has no real solution, since the square
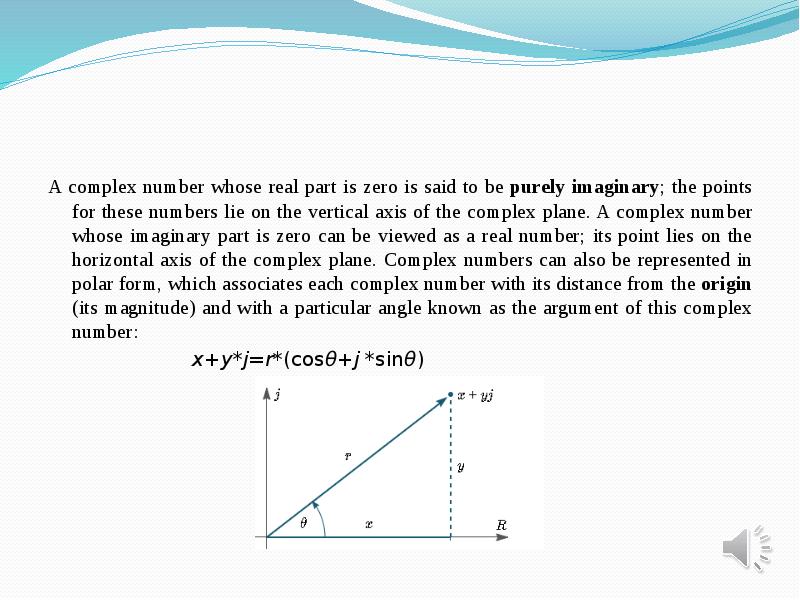
- 5. A complex number whose real part is zero is said to
- 6. Some relations and operations Equality. Two complex numbers are equal if
- 7. Ordering. Since complex numbers are naturally thought of as existing on
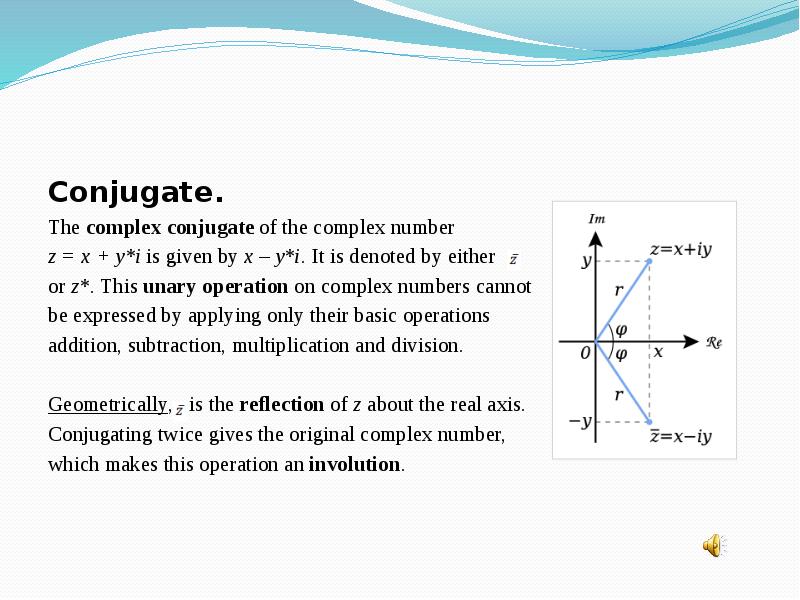
- 8. Conjugate. The complex conjugate of the complex number z = x + y*i is given by x – y*i.
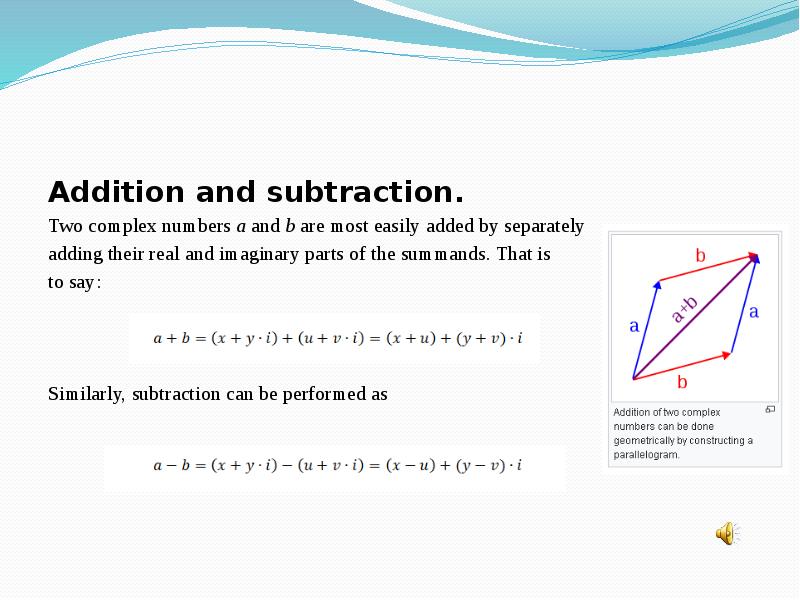
- 9. Addition and subtraction. Two complex numbers a and b are most easily added by separately
- 10. Multiplication. Since the real part, the imaginary part, and the indeterminate i in
- 11. Divison. Using the conjugation, the reciprocal of a nonzero complex number z = x + y*i can
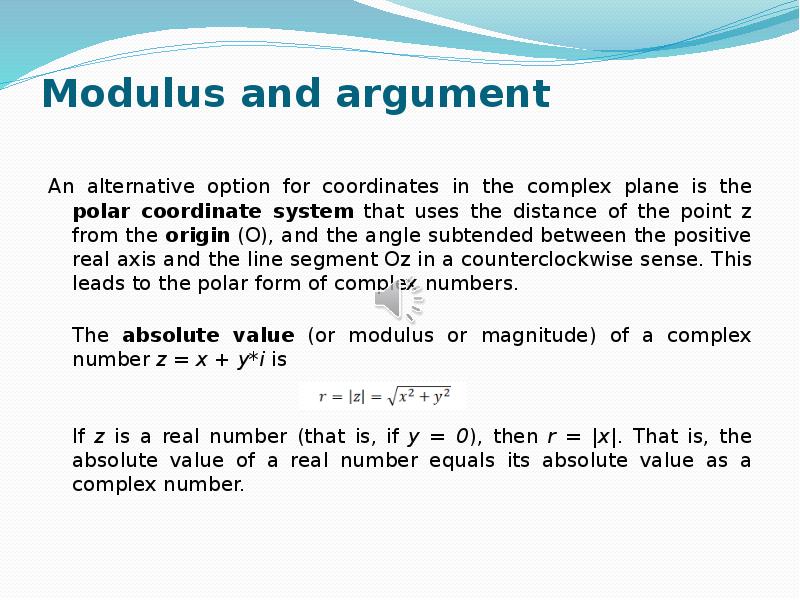
- 12. Modulus and argument An alternative option for coordinates in the
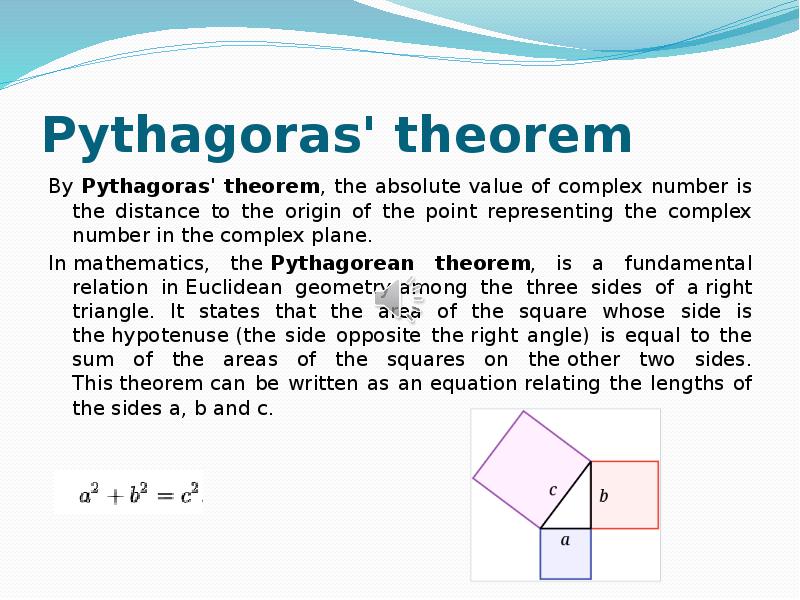
- 13. Pythagoras' theorem By Pythagoras' theorem, the absolute value of complex number
- 14. The argument of z (in many applications referred to as the
- 15. Normally, as given above, the principal value in the interval (−π,
- 16. Together, r and φ give another way of representing complex numbers,
- 17. Thanks for watching
- 18. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























