Constituent Structure of the Sentence. Syntactic Processes презентация
Содержание
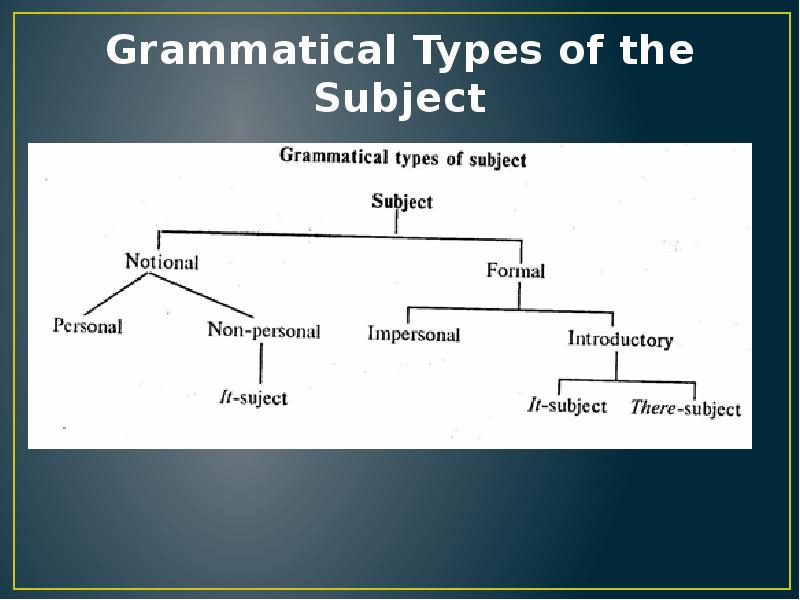
- 2. 2. The Subject The subject is one of the two main
- 3. Grammatical Types of the Subject
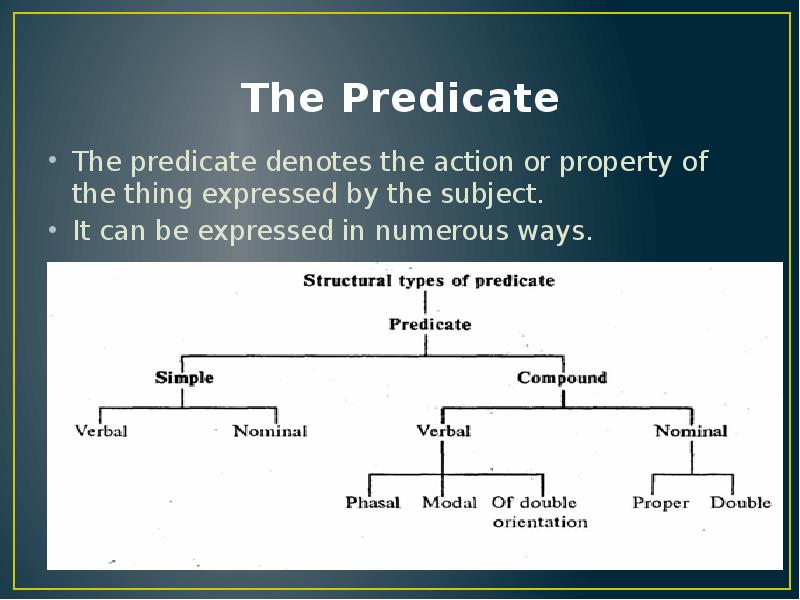
- 4. The Predicate The predicate denotes the action or property of the
- 5. Sentences for Analysis John runs quickly. Did you have a sleep?
- 6. 3. The Secondary Sentence Parts The Object 1. Objects are divided
- 7. The Adverbial Modifier It is a secondary part of the sentence
- 9. The Attribute Attribute is a dependent element of a nominative phrase
- 10. The Apposition Apposition has been often regarded as a special kind
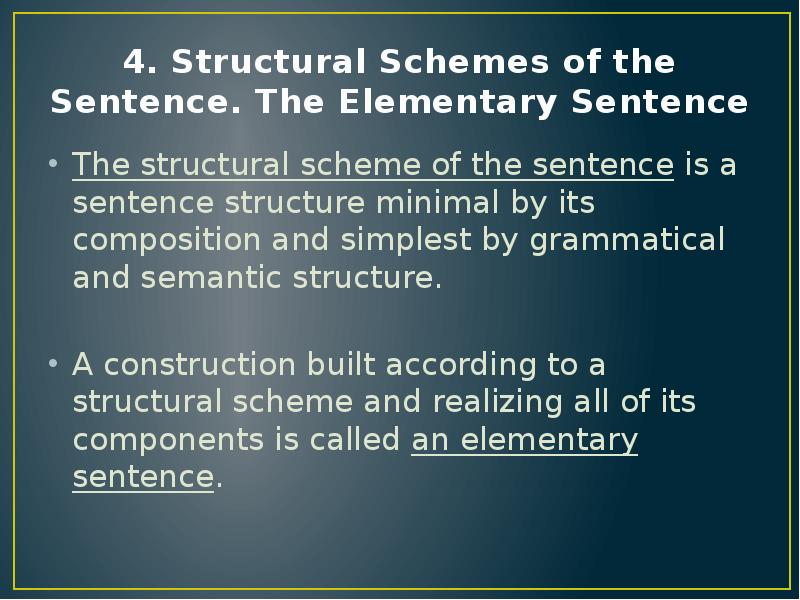
- 11. 4. Structural Schemes of the Sentence. The Elementary Sentence The structural
- 12. Prof. Pocheptsov lists some structural schemes for verbal sentences and examples
- 13. Subject – predicate expressed by a verb of spatial directivity (Active
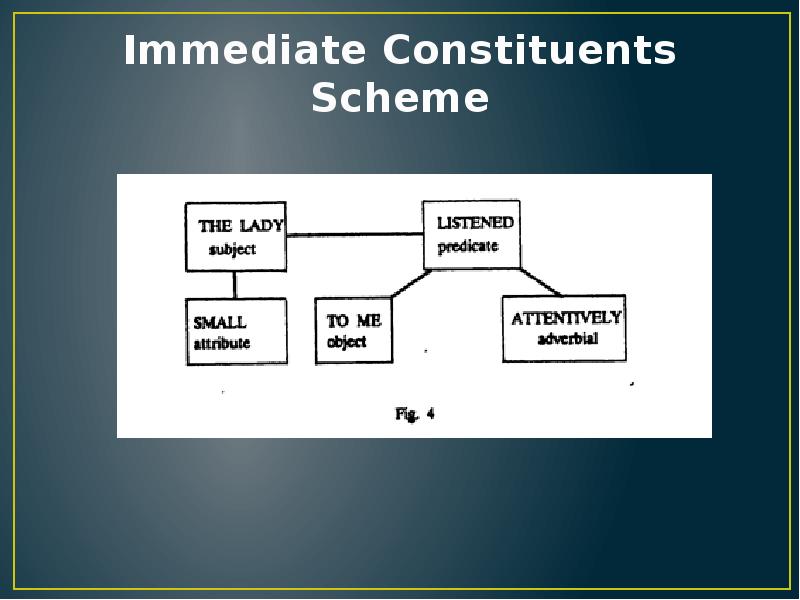
- 14. Immediate Constituents Scheme
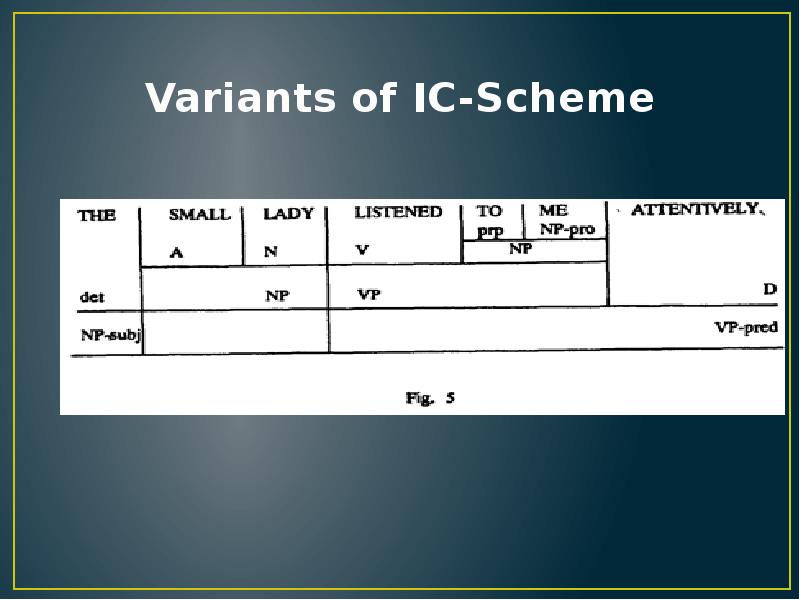
- 15. Variants of IC-Scheme
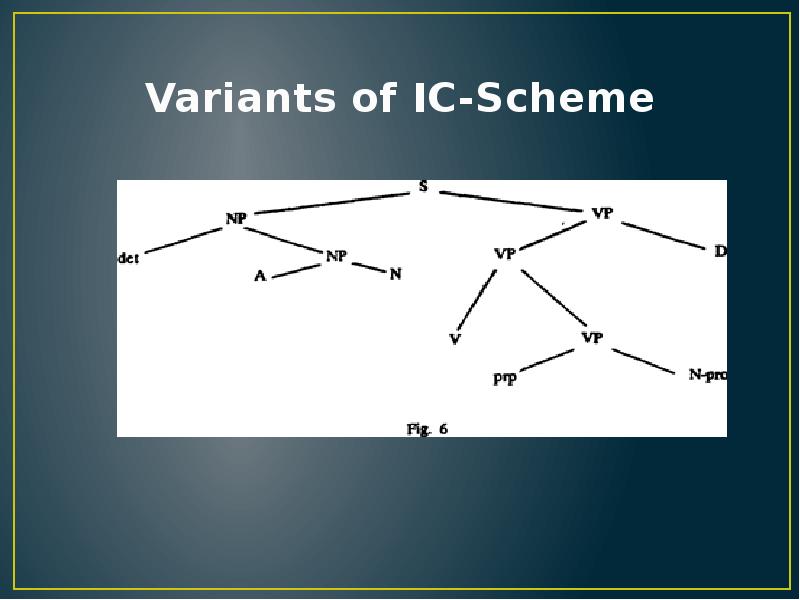
- 16. Variants of IC-Scheme
- 17. 5. Syntactic Processes Expansion / Extension (расширение) consists in adding of
- 19. Complication is a syntactic process that consists in transforming the structure
- 20. Complication of the predicate. The following three types of complication are
- 21. Complication of the object. Complication of the direct object is possible
- 22. Contamination has a restricted usage. It can be applied only to
- 23. Development (развертывание) is a modification of one element by another element
- 24. Adjunction (присоединение) is similar to development. It consists in modifying words
- 25. Substitution (замещение) is a use of words with generalized structural meaning
- 26. Ellipsis (опущение) takes place when a structurally needed element of the
- 27. Скачать презентацию



















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Constituent Structure of the Sentence. Syntactic Processes можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























