Database Systems презентация
Содержание
- 2. Objectives The difference between data and information What a database is,
- 3. Data vs. Information Data: Raw facts; building blocks of information Unprocessed
- 4. Introducing the Database and the DBMS Database—shared, integrated computer structure that
- 5. Introducing the Database and the DBMS (continued) DBMS (database management system):
- 6. Role and Advantages of the DBMS (continued) End users have better
- 7. Types of Databases Single-user: Supports only one user at a time
- 8. Types of Databases (continued) Workgroup: Multi-user database that supports a small
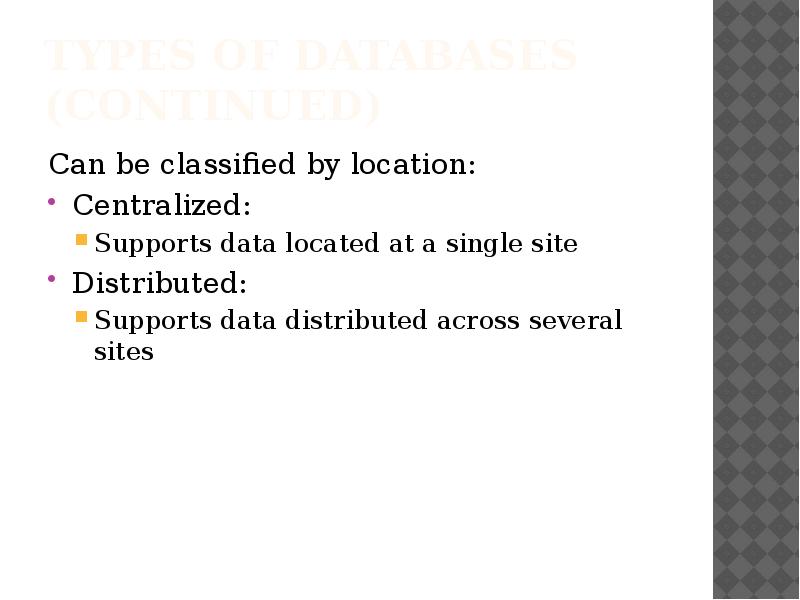
- 9. Types of Databases (continued) Can be classified by location: Centralized: Supports
- 10. Types of Databases (continued) Can be classified by use: Transactional (or
- 11. Why Database Design is Important Defines the database’s expected use Different
- 12. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems Managing data with file systems
- 13. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) Manual File systems:
- 14. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) Conversion from manual
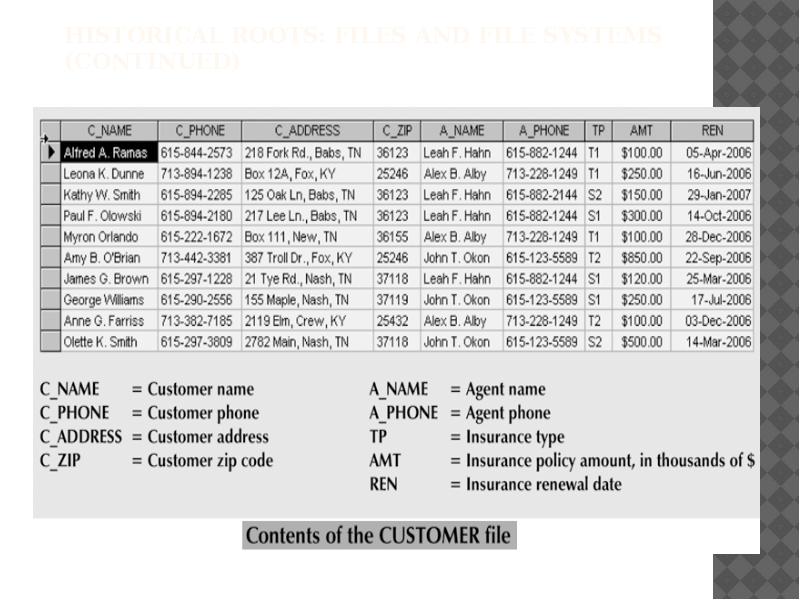
- 15. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued)
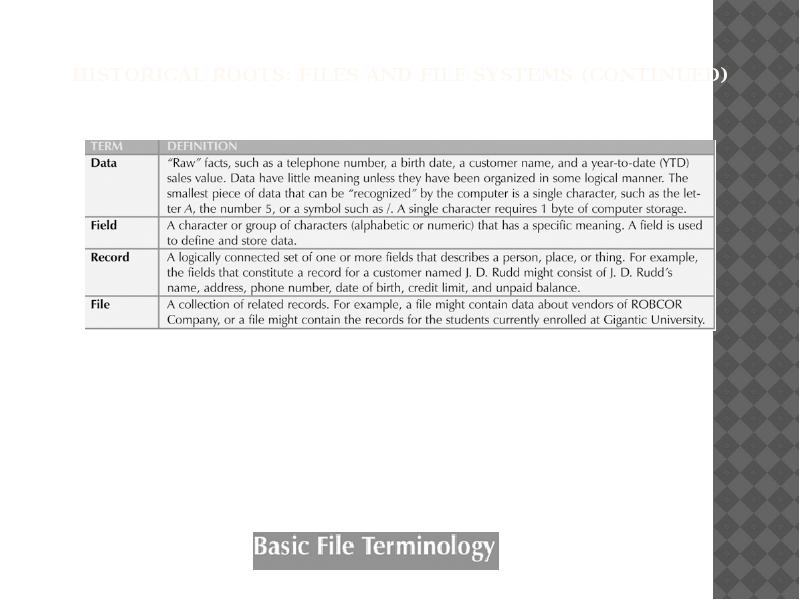
- 16. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued)
- 17. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) DP specialist wrote
- 18. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) Other departments requested
- 19. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) As number of
- 20. Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued)
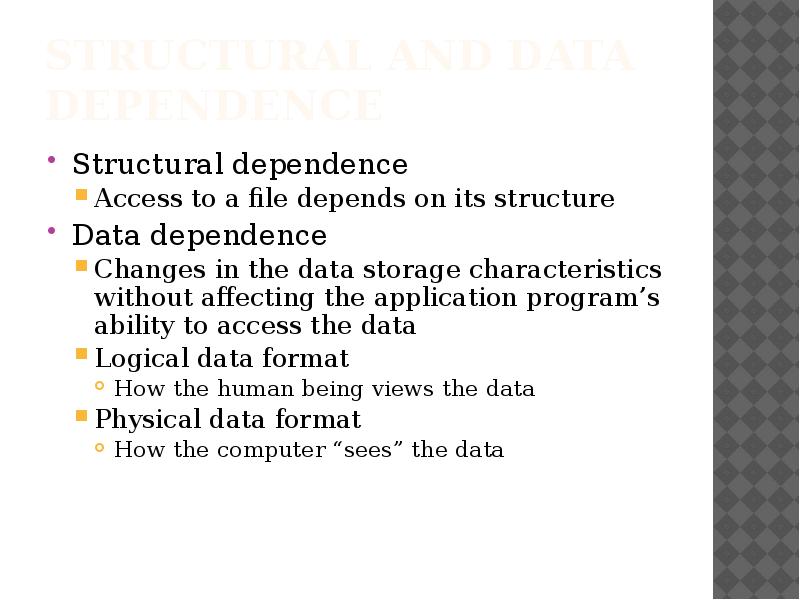
- 21. Structural and Data Dependence Structural dependence Access to a file depends
- 22. Data Redundancy Data redundancy results in data inconsistency Different and conflicting
- 23. Data Redundancy Types of data anomalies: Update anomalies Occur when changes
- 24. Database Systems Problems inherent in file systems make using a database
- 25. Database Systems
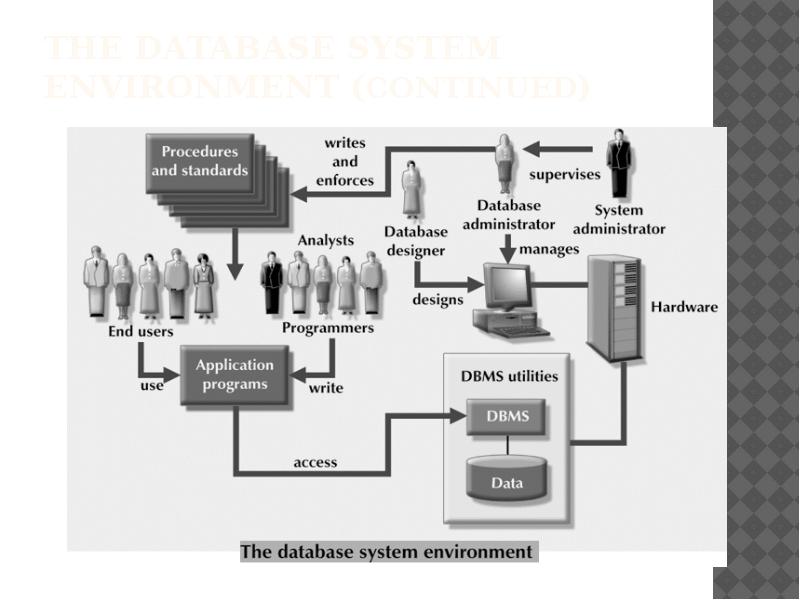
- 26. The Database System Environment Database system is composed of five
- 27. The Database System Environment (continued)
- 28. DBMS Functions DBMS performs functions that guarantee integrity and consistency of
- 29. DBMS Functions (continued) Data transformation and presentation translates logical requests into
- 30. DBMS Functions (continued) Multiuser access control uses sophisticated algorithms to ensure
- 31. DBMS Functions (continued) Database access languages and application programming interfaces provide
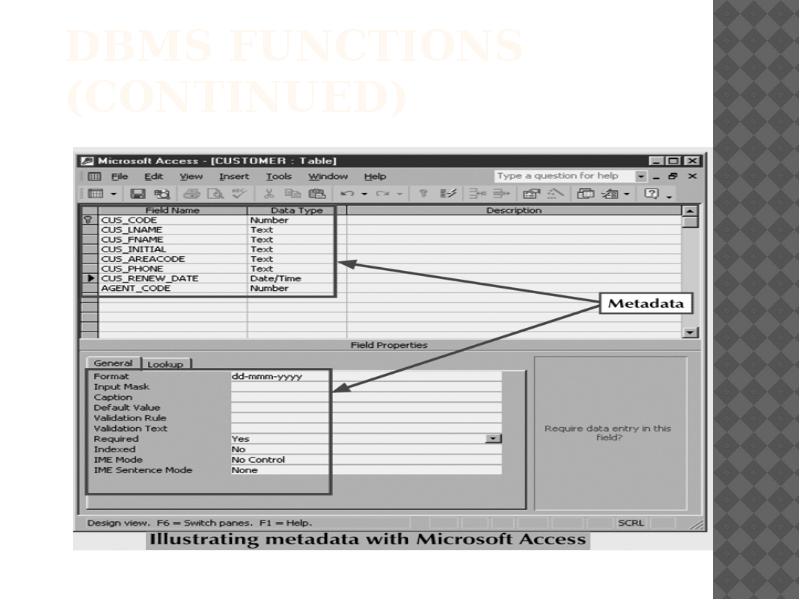
- 32. DBMS Functions (continued)
- 33. Summary Data are raw facts. Information is the result of processing
- 34. Summary (continued) Databases were preceded by file systems. Limitations of file
- 35. Скачать презентацию




























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























