Database systems. B asic concepts of databases. Databases and database презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Database What, Why, How Evolution of Database File System Data
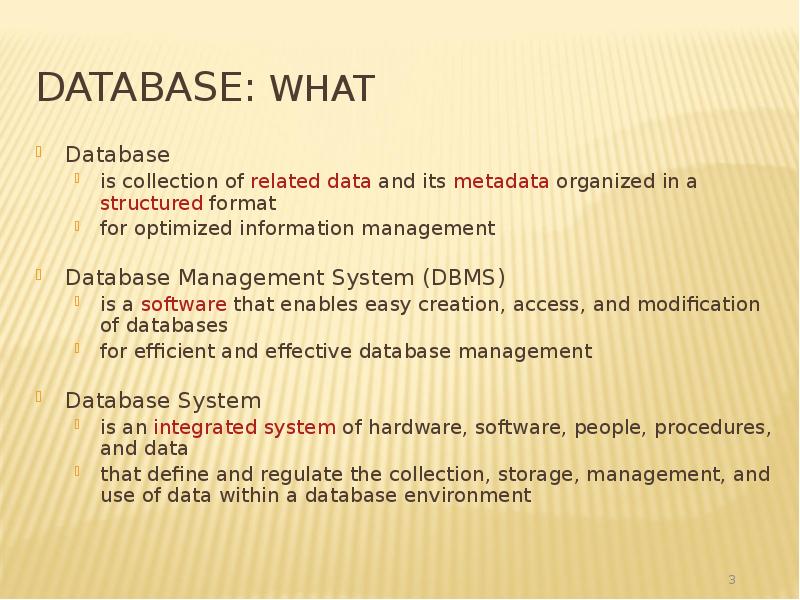
- 3. Database: What Database is collection of related data and its metadata
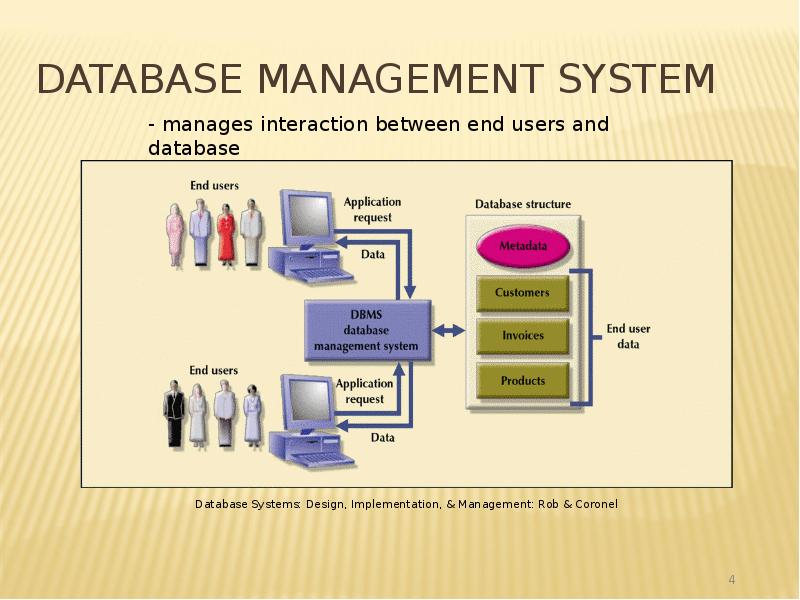
- 4. Database Management System
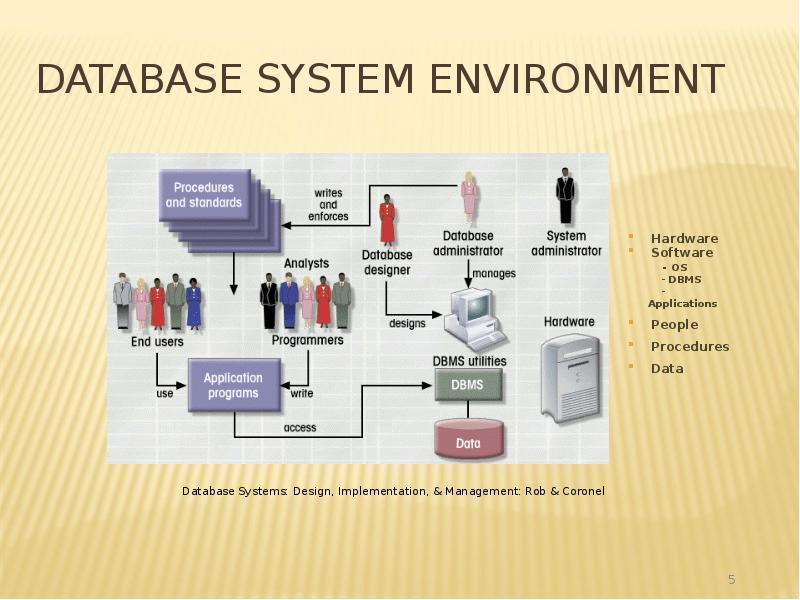
- 5. Database System Environment
- 6. Database: Why Purpose of Database Optimizes data management Transforms data
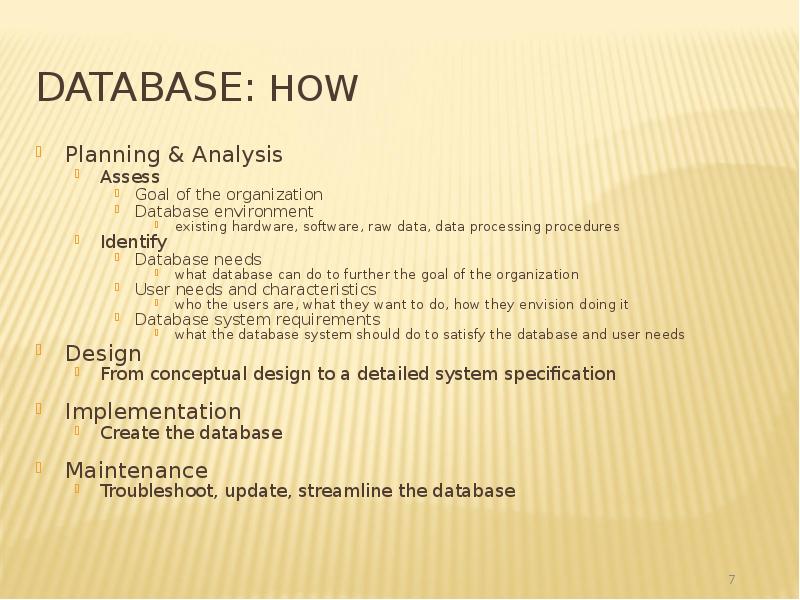
- 7. Database: How Planning & Analysis Assess Goal of the organization
- 8. Business Rules What Brief, precise, and unambiguous descriptions of operations in
- 9. Database: User-centered Perspective The user is always right. If there is
- 10. Database: Data Models Importance Abstraction of complex real-word data structures in
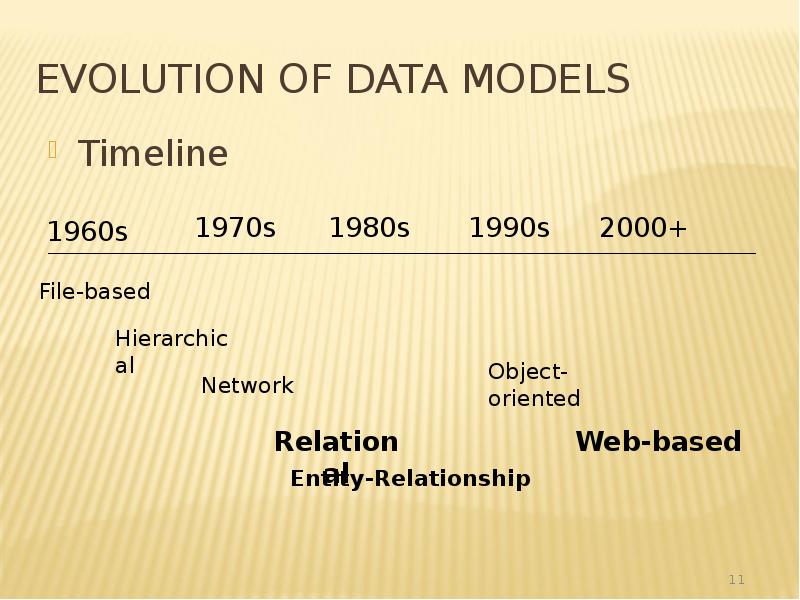
- 11. Evolution of Data Models Timeline
- 12. Database: Historical Roots Manual File System to keep track of data
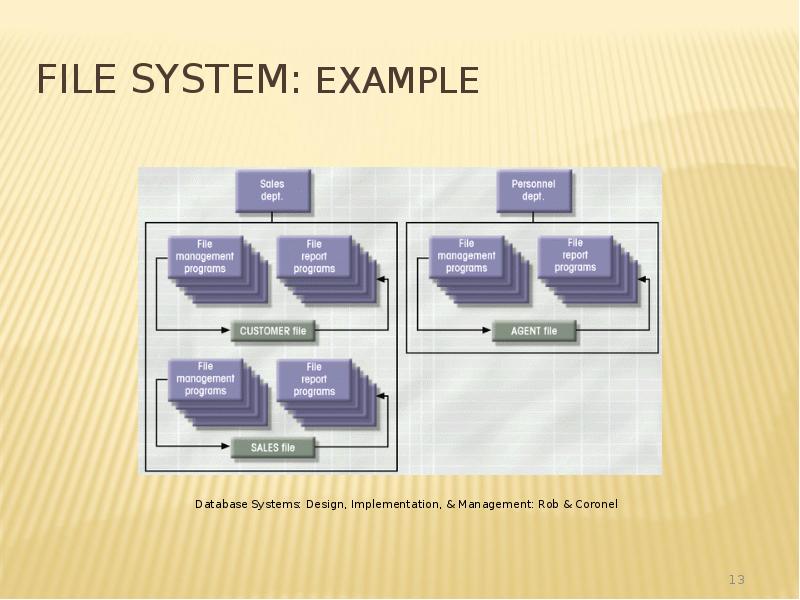
- 13. File System: Example
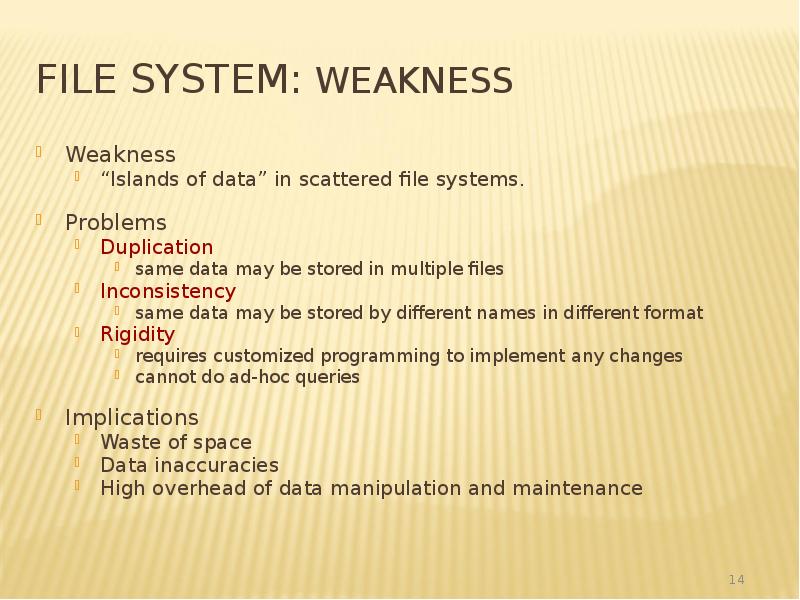
- 14. File System: Weakness Weakness “Islands of data” in scattered file systems.
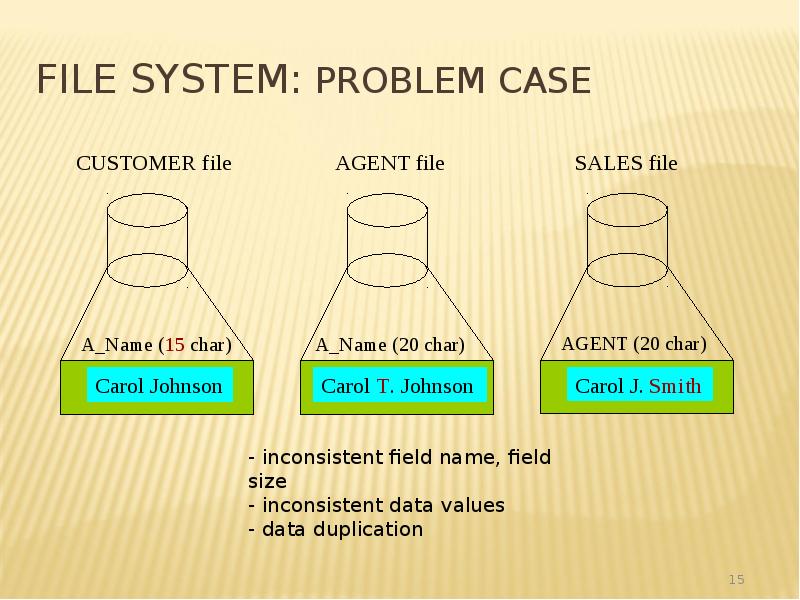
- 15. File System: Problem Case
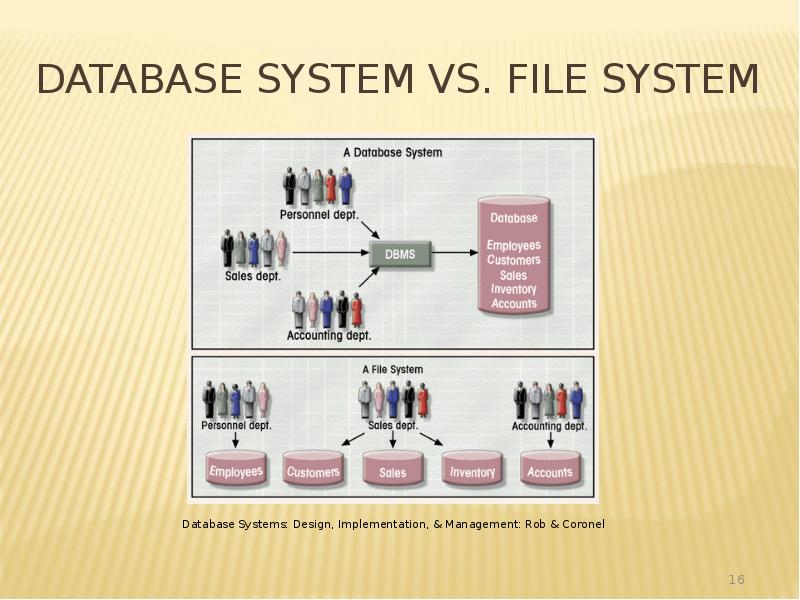
- 16. Database System vs. File System
- 17. Hierarchical Database Background Developed to manage large amount of data for
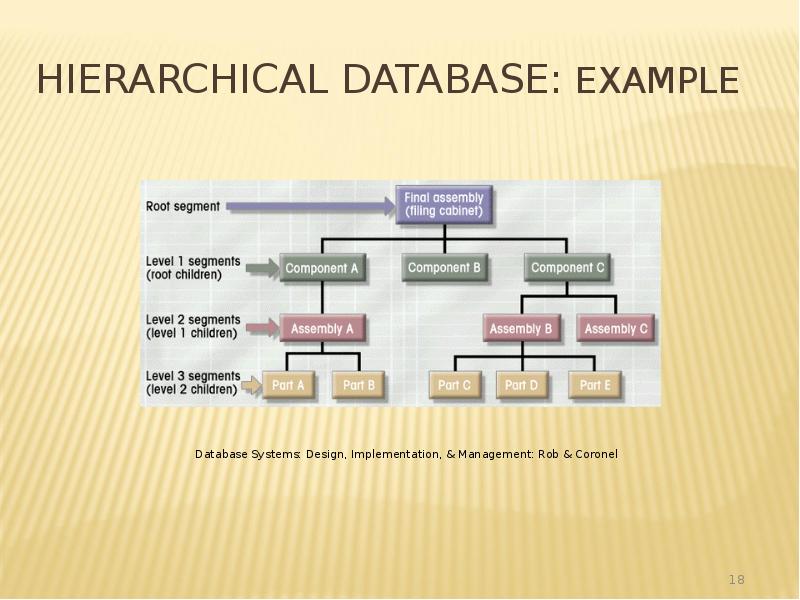
- 18. Hierarchical Database: Example
- 19. Hierarchical Database: Pros & Cons Advantages Conceptual simplicity groups of data
- 20. Network Database Objectives Represent more complex data relationships Improve database performance
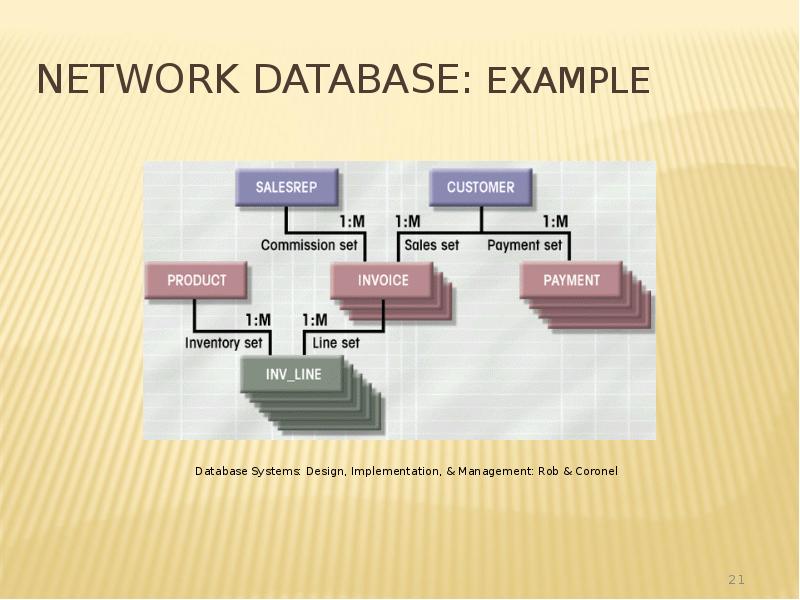
- 21. Network Database: Example
- 22. Network Database: Pros & Cons Advantages More data relationship types More
- 23. Relational Database Problems with legacy database systems Required excessive effort to
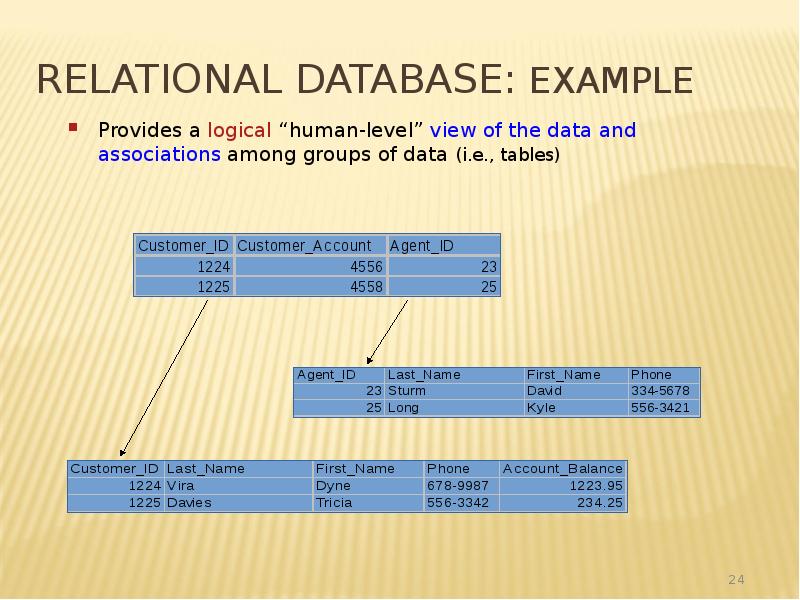
- 24. Relational Database: Example
- 25. Relational Database: Pros & Cons Advantages Structural independence Separation of database
- 26. Entity Relationship Model Peter Chen’s Landmark Paper in 1976 “The Relationship
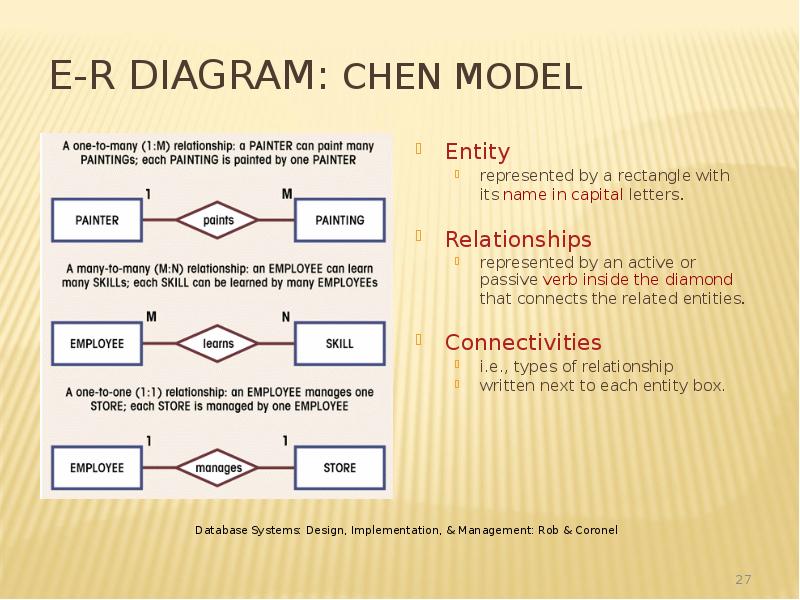
- 27. E-R Diagram: Chen Model Entity represented by a rectangle with its
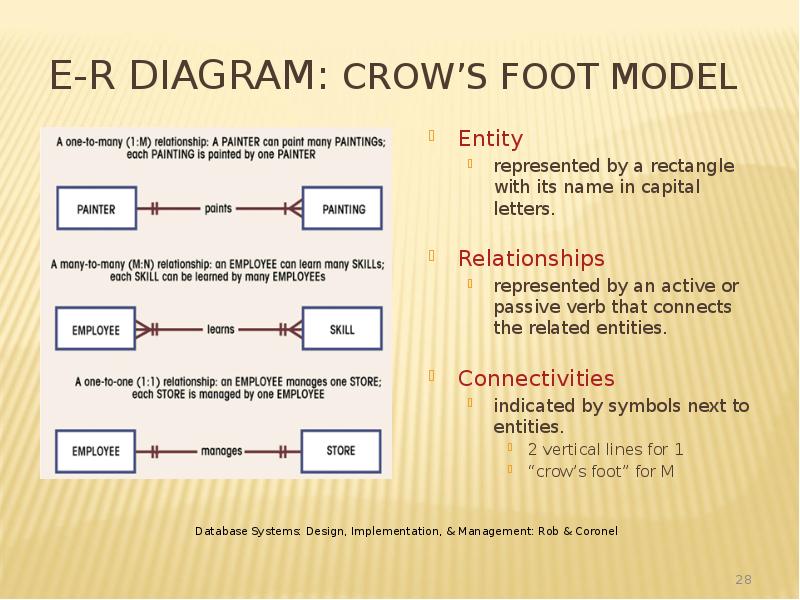
- 28. E-R Diagram: Crow’s Foot Model Entity represented by a rectangle with
- 29. E-R Model: Pros & Cons Advantages Exceptional conceptual simplicity easily
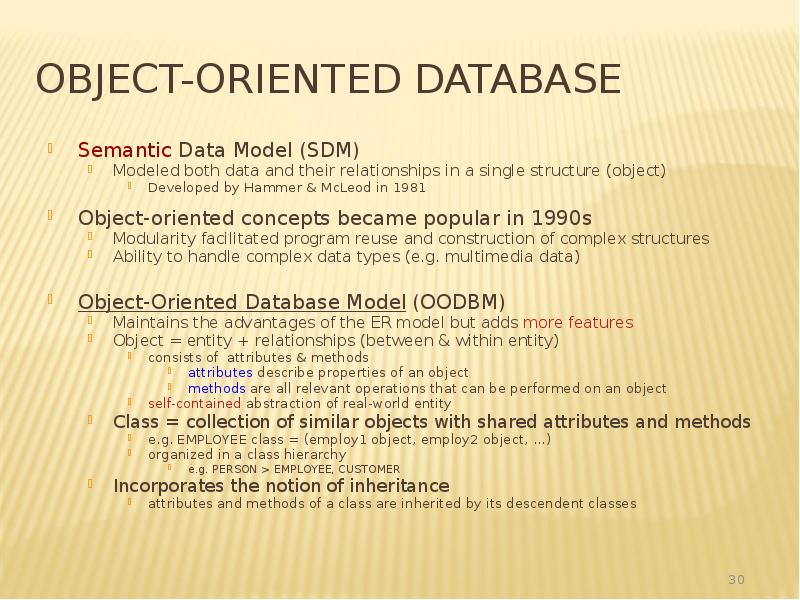
- 30. Object-Oriented Database Semantic Data Model (SDM) Modeled both data and their
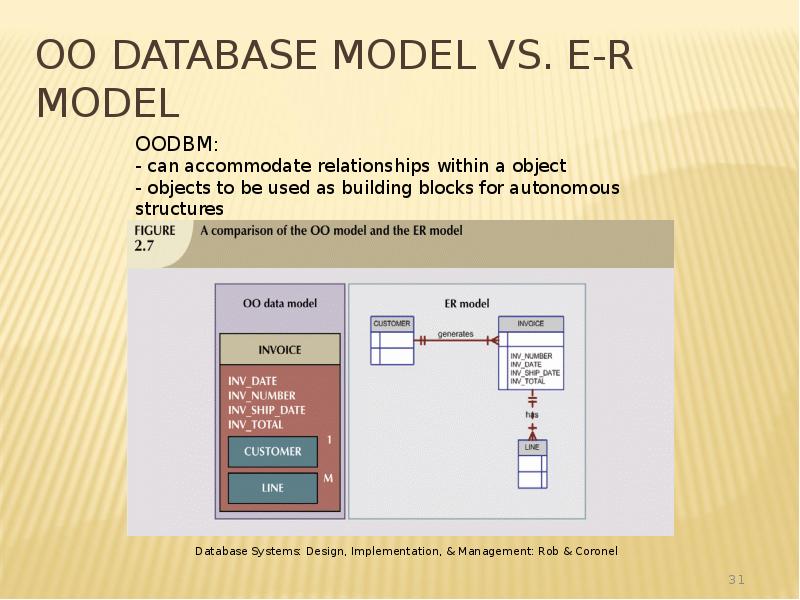
- 31. OO Database Model vs. E-R Model
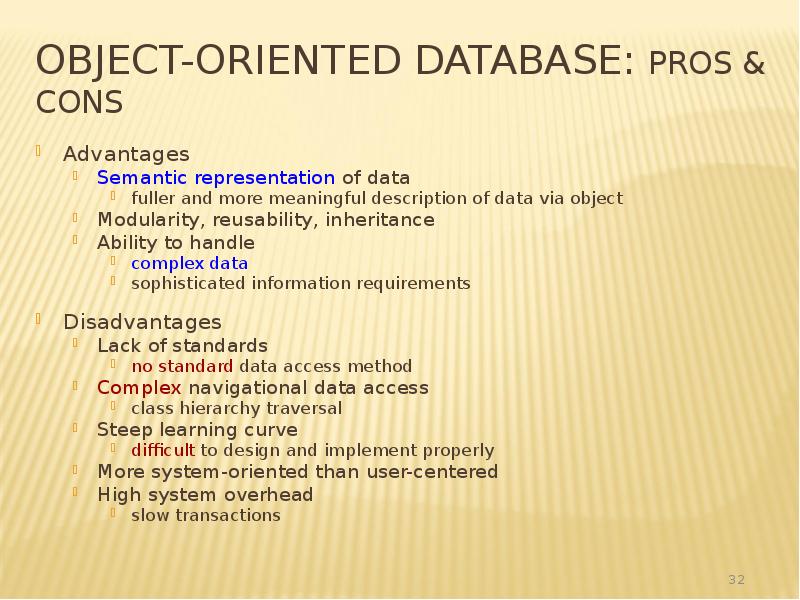
- 32. Object-Oriented Database: Pros & Cons Advantages Semantic representation of data fuller
- 33. Скачать презентацию









Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Database systems. B asic concepts of databases. Databases and database можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























