Digestive tract презентация
Содержание
- 2. DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO COLIC IN ADULT HORSES PAIN – degree,
- 3. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF COLIC IN ADULT HORSES Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- 4. Decompression - gastric decompression via a nasogastric tube, cecal enterocentesis in
- 5. LAXATIVES – mineral oil at 0.5-1 gallon via NGT in
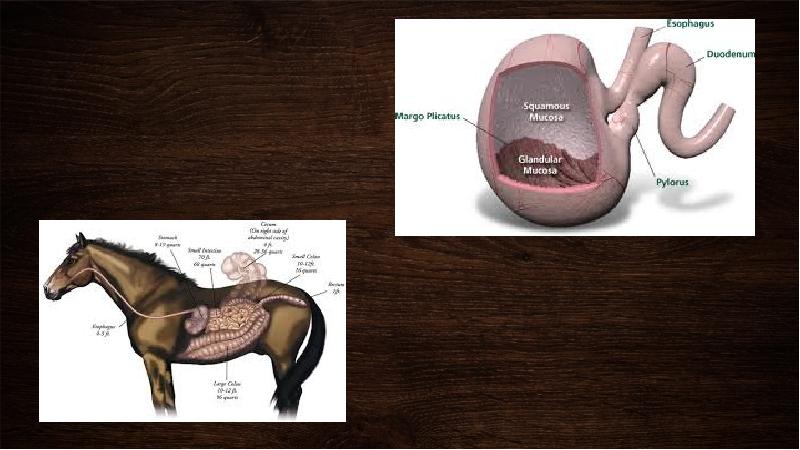
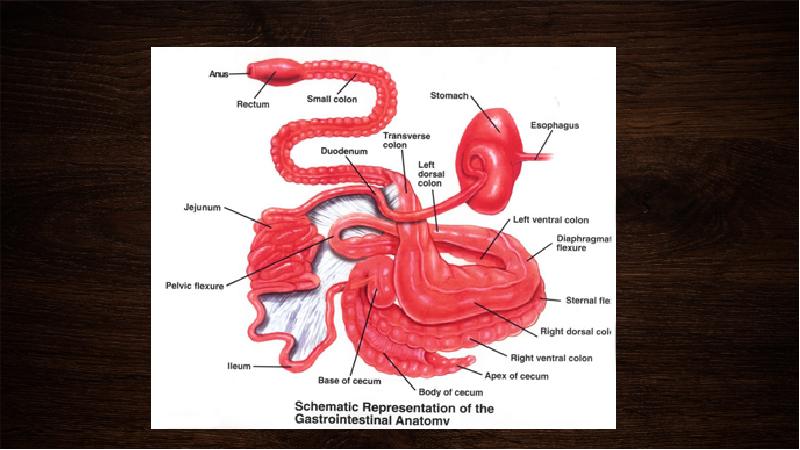
- 6. stomach The horse’s stomach is relatively small, with a capacity of
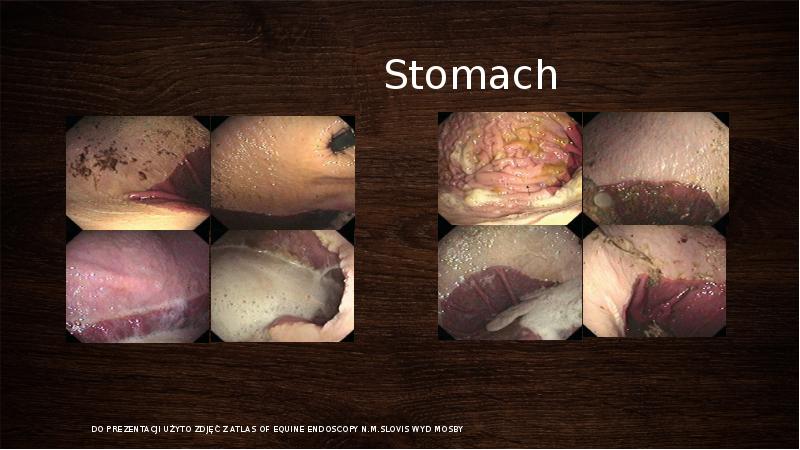
- 8. Stomach
- 9. Gastritis Gastritis is an inflammation and irritation of the lining of
- 10. Acute Gastritis Acute gastritis is caused by ingesting moldy or spoiled
- 11. Chronic Gastritis Chronic gastritis is associated with the long-standing ingestion of
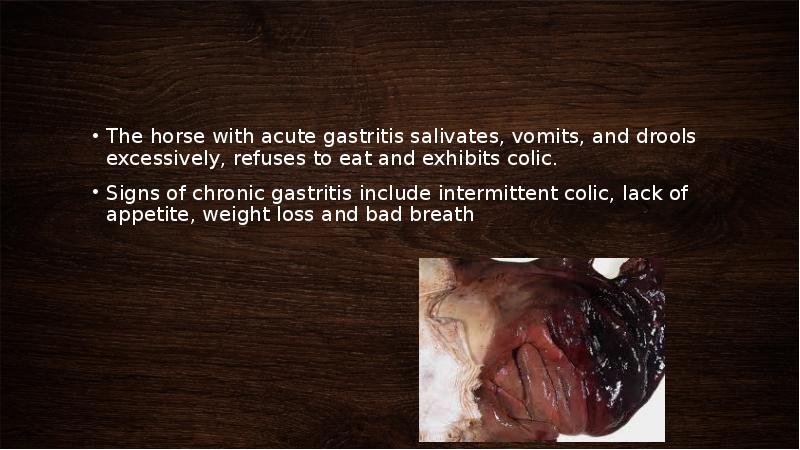
- 12. The horse with acute gastritis salivates, vomits, and drools excessively, refuses
- 13. treatment H2 receptors blockers – ranitidin 6-7 mg/kg every 8 hours,
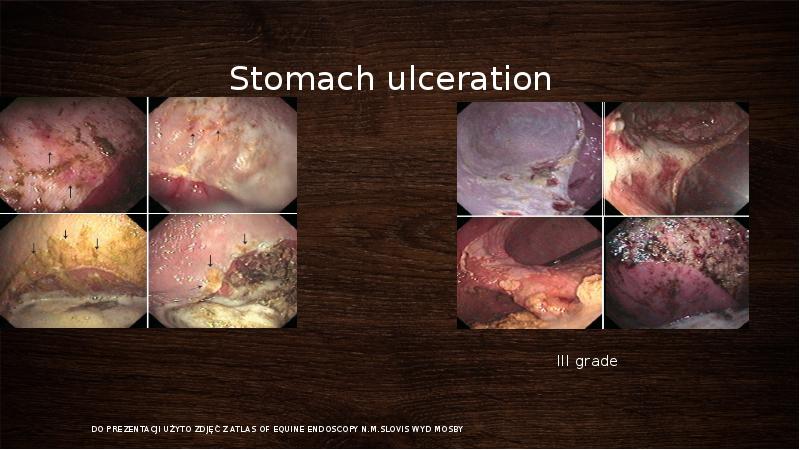
- 14. Gastric ulcers Ulcers are a common medical condition in horses and
- 15. Stomach is divided into two distinct parts. The non-glandular portion (also
- 16. Causes of gastric ulcers Fasting (not eating) - Horses evolved to
- 17. Signs of gastric ulcers in horses In foals, signs of gastric
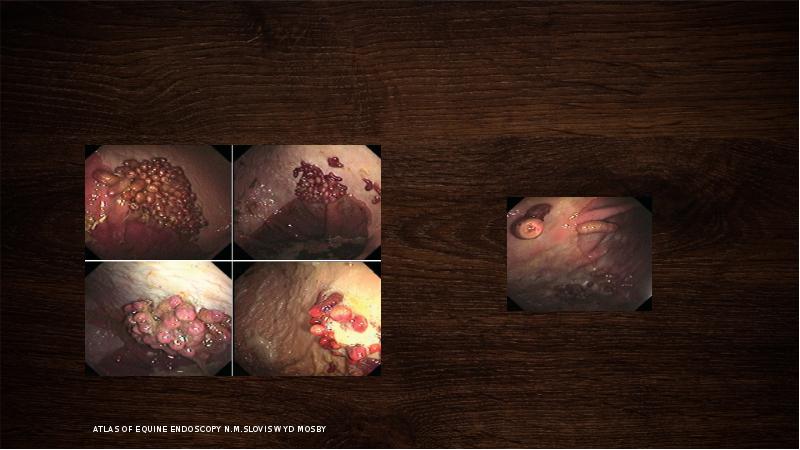
- 18. Stomach ulceration I grade
- 19. Treatment of gastric ulcers in horses H2 blockers: These are
- 20. In addition to medications, changes in management are almost always necessary
- 21. Gastric parasites Horse bots, which are found in the stomach, are
- 22. The larvae of all 3 species apparently stay embedded in the
- 23. Bots cause a mild gastritis, but large numbers may be present
- 25. Gastric dilatation and rupture Gastric dilatation can be classified as
- 26. Secondary gastric dilatation occurs more commonly and can result from primary
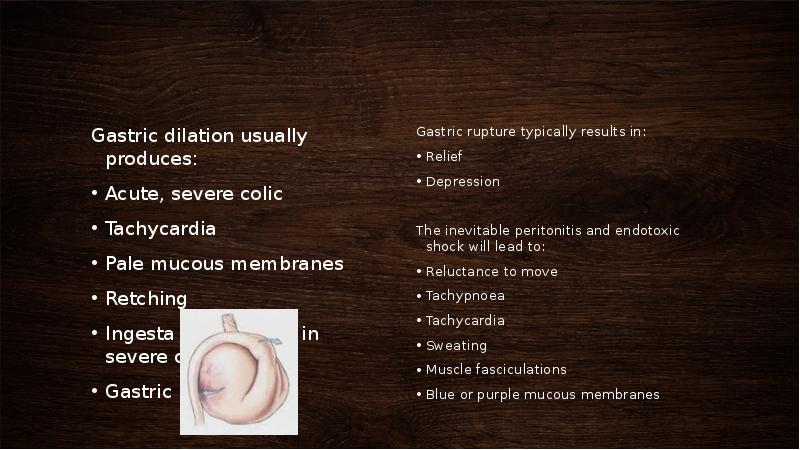
- 27. Gastric dilation usually produces: Acute, severe colic Tachycardia
- 28. Primary gastric dilation should be suspected : copious amounts of gastric
- 29. Gastric rupture results in septic peritonitis which will be reflected in
- 30. treatment Gastric lavage (water or oil) Treat underlying disease
- 31. Gastric Impaction (Obstruction) Gastric impaction can result in either acute or
- 32. Clinical signs The colic associated with gastric impaction varies from mild
- 33. treatment gastric lavage with water IV fluid therapy and analgesia the
- 34. prevention Regular dental care Ensure sugar beet nuts are adequately
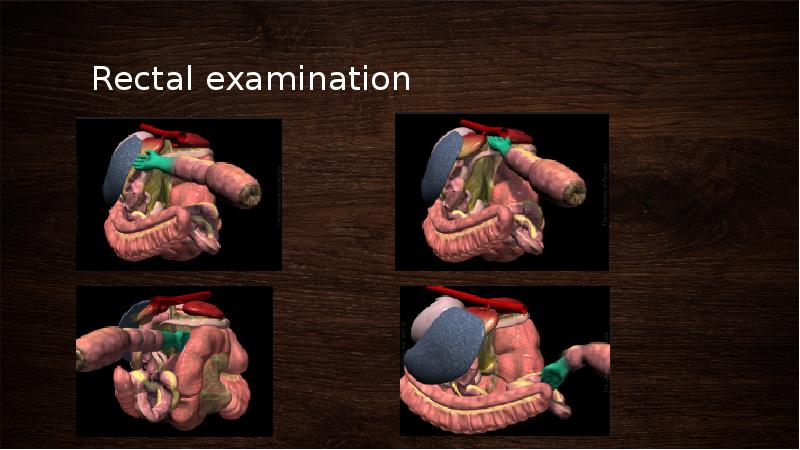
- 36. Rectal examination
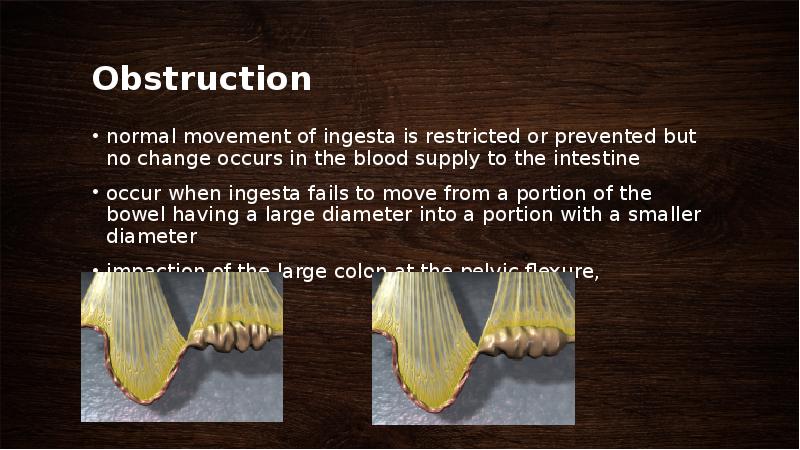
- 37. Obstruction normal movement of ingesta is restricted or prevented but no
- 38. Pelvic Flexure Impaction occur when dry or inadequately digested feed fails
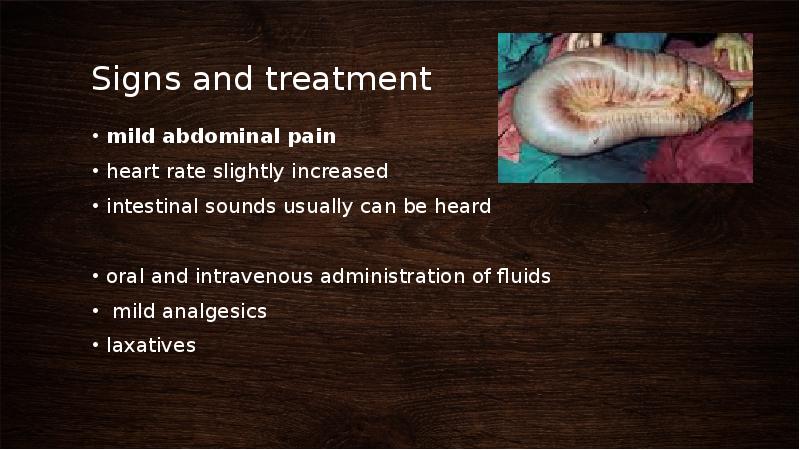
- 39. Signs and treatment mild abdominal pain heart rate slightly increased intestinal
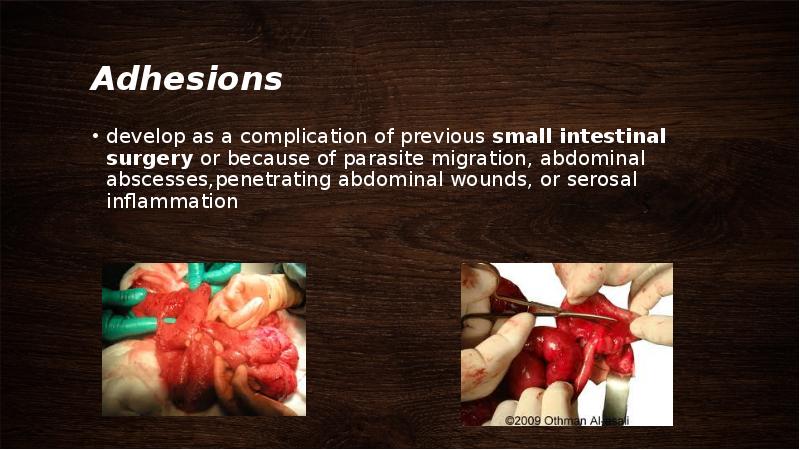
- 40. Adhesions develop as a complication of previous small intestinal surgery or
- 41. history of a gradual onset of colic and weight loss, and
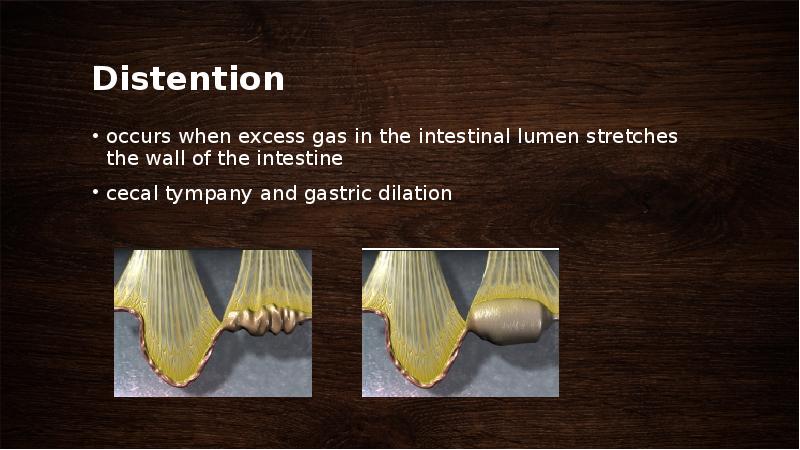
- 42. Distention occurs when excess gas in the intestinal lumen stretches the
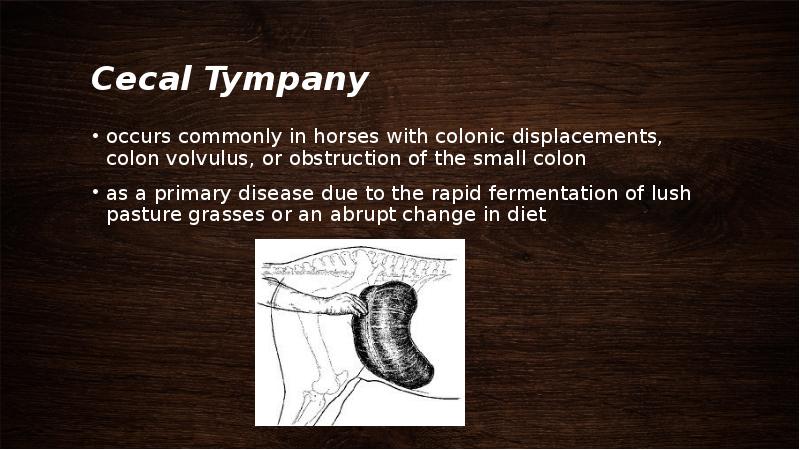
- 43. Cecal Tympany occurs commonly in horses with colonic displacements, colon volvulus,
- 44. distention of the abdomen tight paralumbar fossae pain tachycardia and
- 45. Spasm abnormal, uncoordinated contractions of smooth muscle cells in the wall
- 46. Spasmodic Colic occurs due to spasm or cramping of intestinal musculature
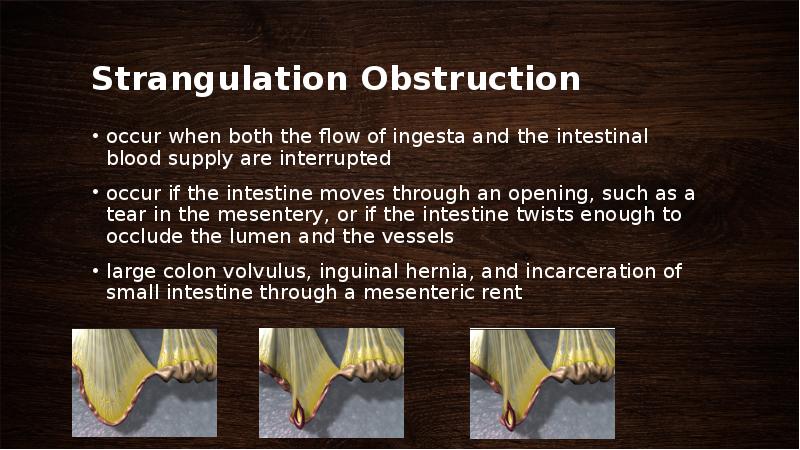
- 47. Strangulation Obstruction occur when both the flow of ingesta and the
- 48. Small Intestinal Strangulation through Mesenteric Rent defect in the small intestinal
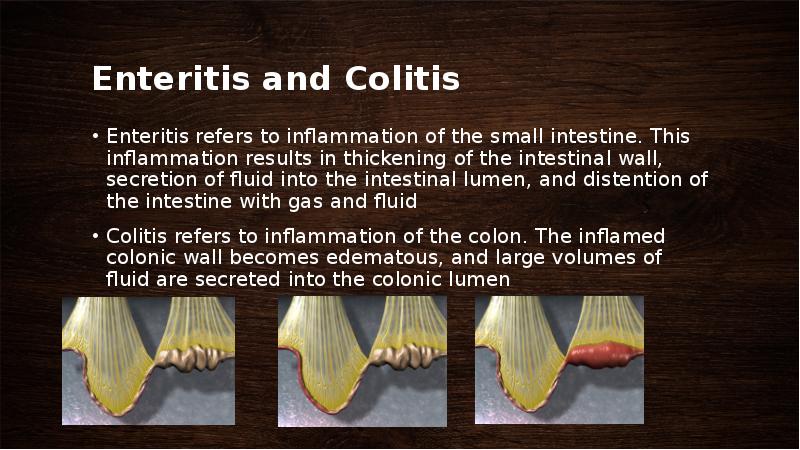
- 49. Enteritis and Colitis Enteritis refers to inflammation of the small intestine.
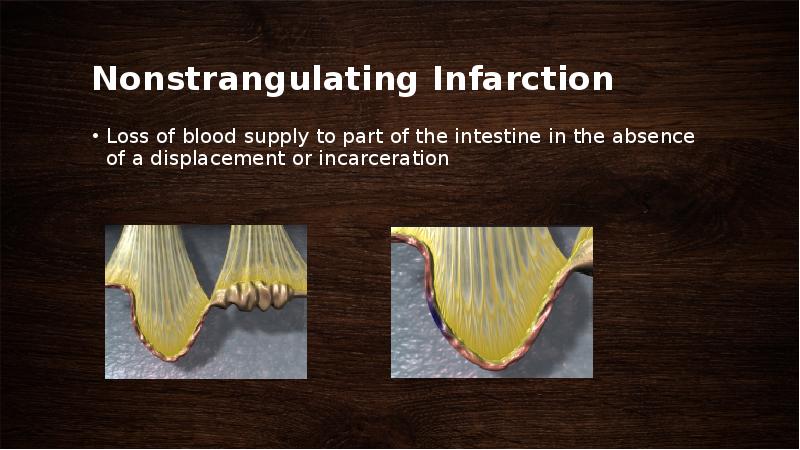
- 50. Nonstrangulating Infarction Loss of blood supply to part of the intestine
- 51. thromboembolism or a reduction in local blood flow secondary to parasitism
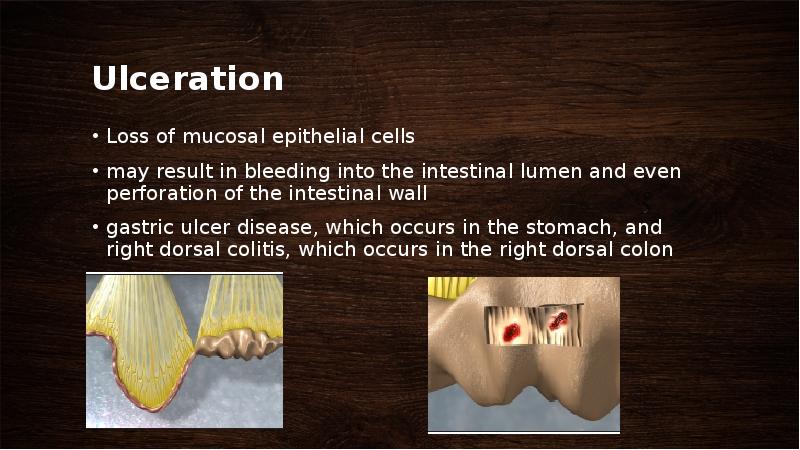
- 52. Ulceration Loss of mucosal epithelial cells may result in bleeding into
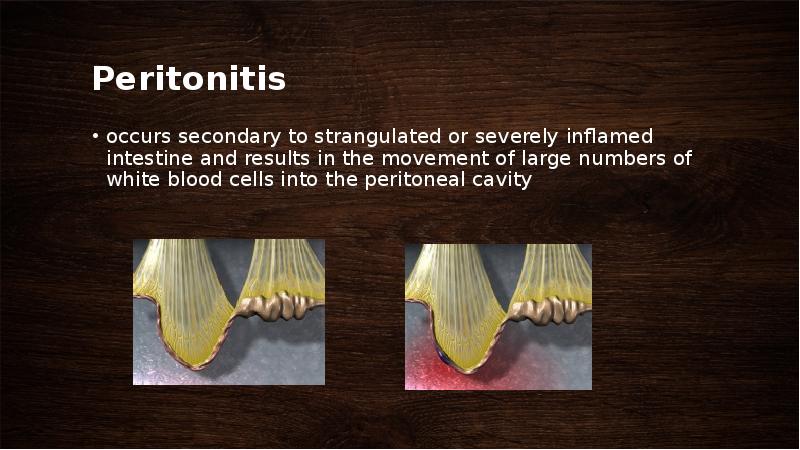
- 53. Peritonitis occurs secondary to strangulated or severely inflamed intestine and results
- 54. Скачать презентацию


































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























