Ethnicity, Culture and Alcohol презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Background Alcohol consumption/drinking patterns Alcohol impacts Ethnic and cultural influences
- 3. Background Race (physical aspects) Culture (socio-cultural structures aspects) Ethnicity (group identity
- 4. Background (continued) Ethnoculturally competent practice leads to better outcomes Requires: Self-awareness
- 5. Alcohol Patterns Typical study of “between group” differences: White/Caucasian Americans
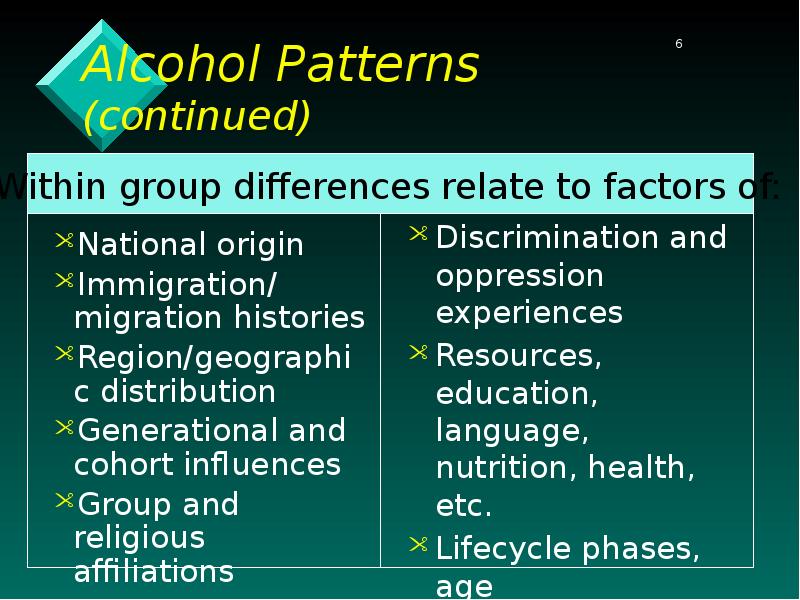
- 6. Alcohol Patterns (continued) National origin Immigration/ migration histories Region/geographic distribution Generational
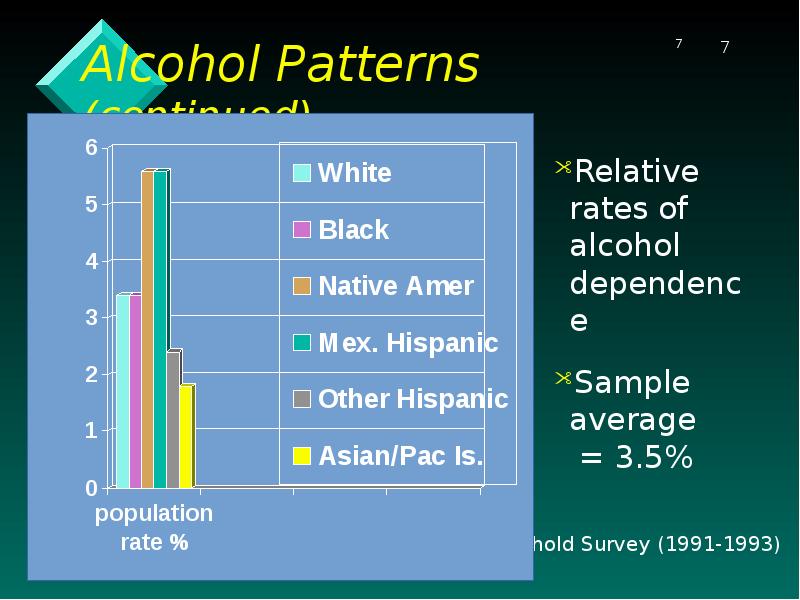
- 7. Alcohol Patterns (continued) Relative rates of alcohol dependence Sample average
- 8. Alcohol Patterns (continued) Importance of distinguishing aggregate versus disaggregate data Examples:
- 9. Alcohol Impacts Differential consequences of alcohol consumption relate to: Differing (intrinsic,
- 10. Alcohol Impacts (continued) Differential consequences of alcohol consumption also relate to:
- 11. Alcohol Impacts (continued) Mental health and other social effects Alcohol-related problems
- 12. Ethnic/Cultural Influences Drinking is influenced by: Social norms, customs, and traditions
- 13. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Alcohol-related cultural norms/values affect: Drinking patterns, reasons Alcohol
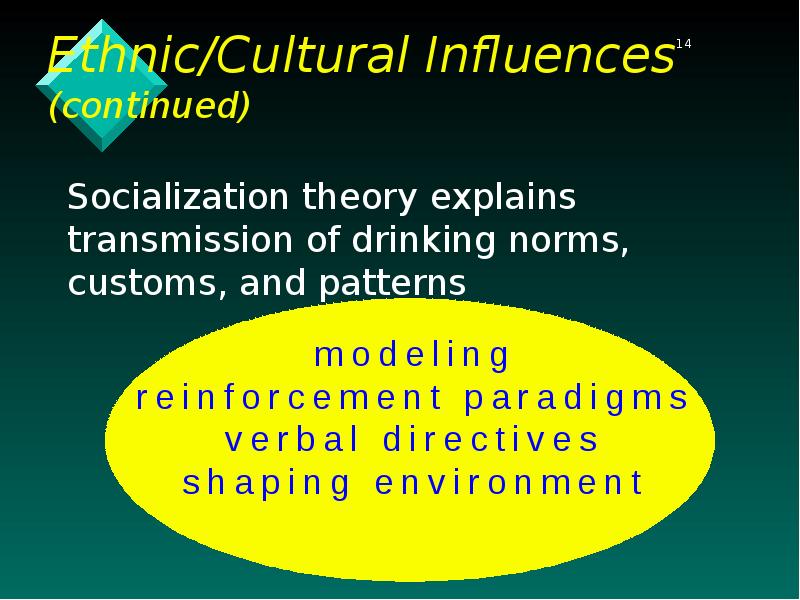
- 14. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Socialization theory explains transmission of drinking norms, customs,
- 15. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Alcohol risk perceptions vary with cultural norms, may
- 16. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Practice and research influence drinking by: Influencing perceptions
- 17. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Ethnicity x Gender (e.g., Hispanic communities) Religion,
- 18. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued)
- 19. Ethnic/Cultural Influences (continued) Alcohol access differs Neighborhoods differ in concentration of
- 20. Prevention & Intervention Ethnocultural competence in prevention and intervention: Strategy #1
- 21. Prevention & Intervention (continued) Different cultural and ethnic group approaches to
- 22. Prevention & Intervention (continued) Screening, assessment, diagnosis needs differ:
- 23. Prevention & Intervention (continued) Different “best practice” approaches may be more
- 24. Contribute to Alcohol Use Discrimination Racism Oppression Social injustice Ethnocentrism Economic
- 25. Prevention & Intervention (continued) Community practice addresses: Messages about risk/protective factors
- 26. Скачать презентацию





















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























