Genome assembly with SPAdes презентация
Содержание
- 2. Introduction
- 3. Why to assemble?
- 4. Why to assemble? Sequencing data Billions of short reads Sequencing
- 5. Why to assemble? Sequencing data Billions of short reads Sequencing
- 6. Assembly basics
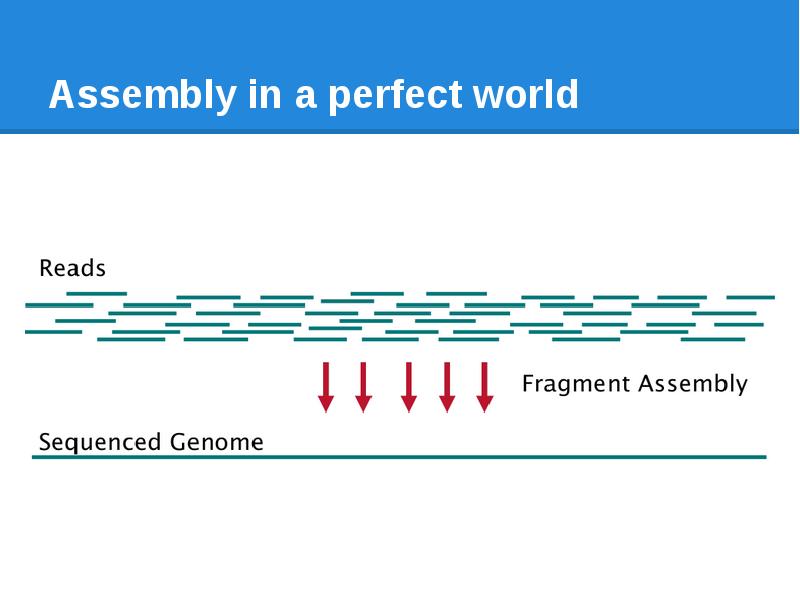
- 7. Assembly in a perfect world
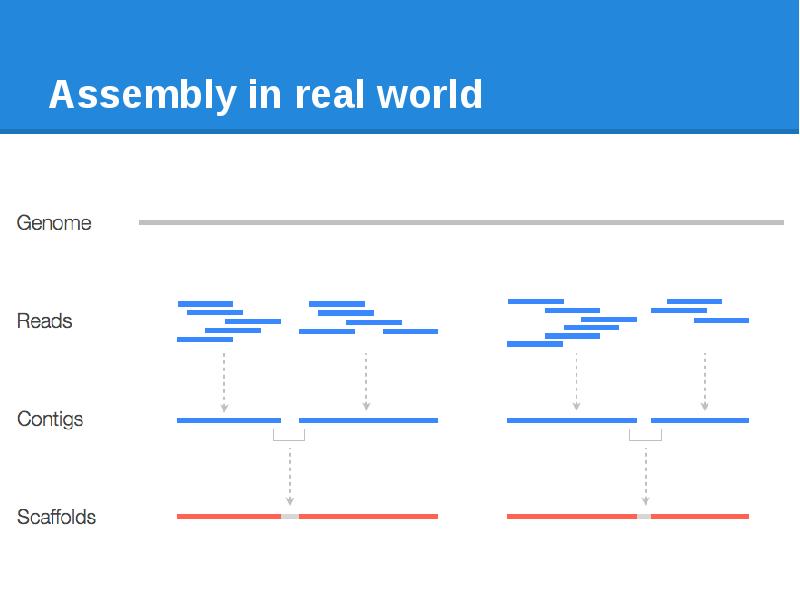
- 8. Assembly in real world
- 9. De novo whole genome assembly
- 10. De novo whole genome assembly
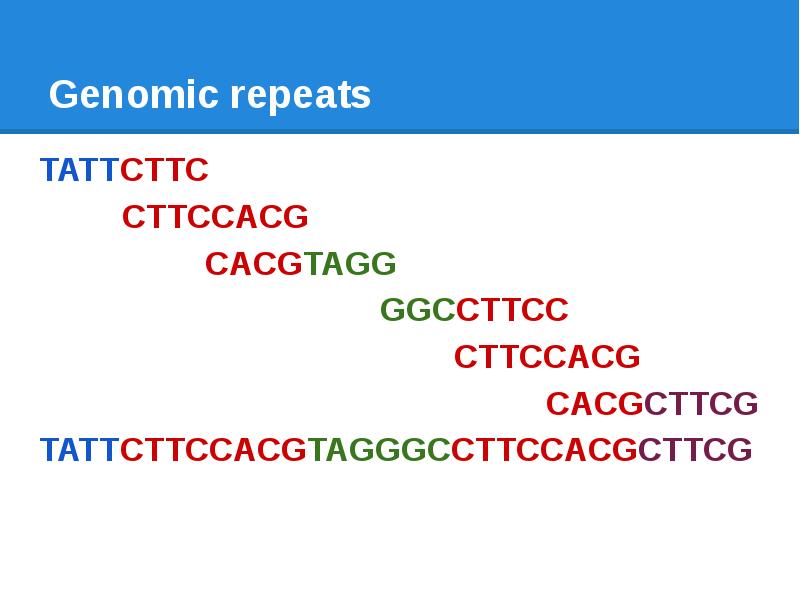
- 11. Genomic repeats TATTCTTCCACGTAGGGCCTTCCACGCTTCG
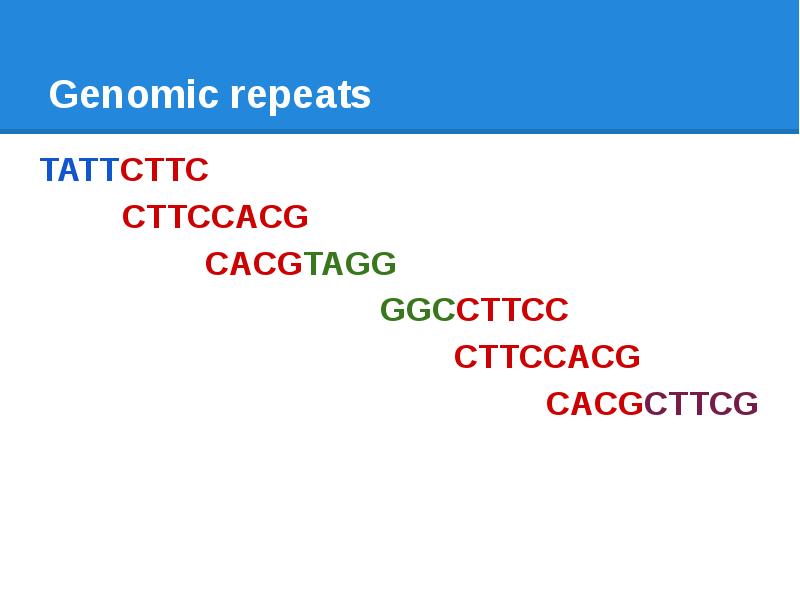
- 12. Genomic repeats TATTCTTC CTTCCACG CACGTAGG
- 13. Genomic repeats TATTCTTC CTTCCACG CACGTAGG
- 14. Genomic repeats TATTCTTCCACGTAGG GGCCTTCCACGCTTCG TATTCTTCCACGCTTCG GGCCTTCCACGTAGG
- 15. Genomic repeats TATTCTTCCACGTAGG
- 16. Genomic repeats TATTCTTCCACGTAGG
- 17. SPAdes assembler
- 18. SPAdes first steps spades.py
- 19. SPAdes first steps spades.py spades.py --help spades.py --test
- 20. SPAdes first steps spades.py spades.py --help spades.py --test -o <output_dir>
- 21. Input data formats FASTA: .fasta / .fa FASTQ: .fastq / .fq
- 22. Input data options Unpaired reads Illumina unpaired -s single.fastq -s single1.fastq
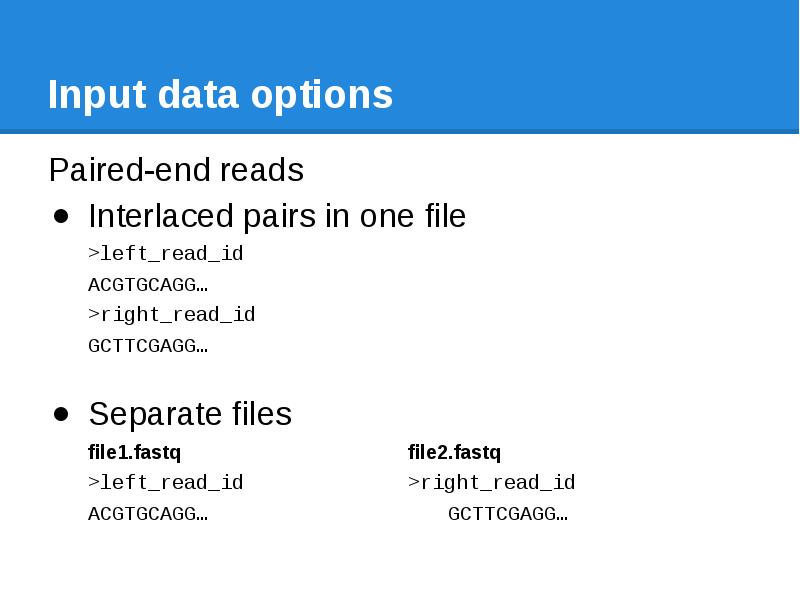
- 23. Input data options Paired-end reads Interlaced pairs in one file >left_read_id
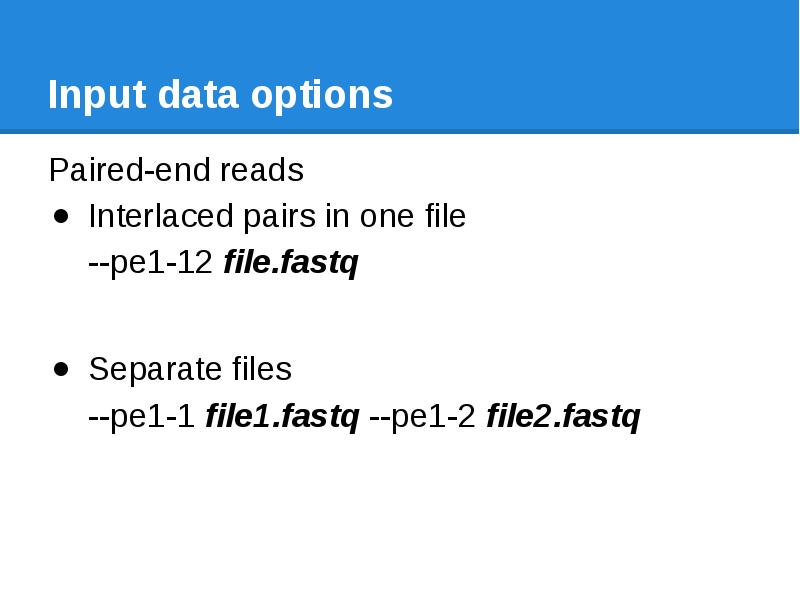
- 24. Input data options Paired-end reads Interlaced pairs in one file --pe1-12
- 25. Input data options Paired-end reads Interlaced pairs in one file --pe1-12
- 26. SPAdes performance options Number of threads -t N Maximal available RAM
- 27. Pipeline options Run only assembler (input reads are already corrected or
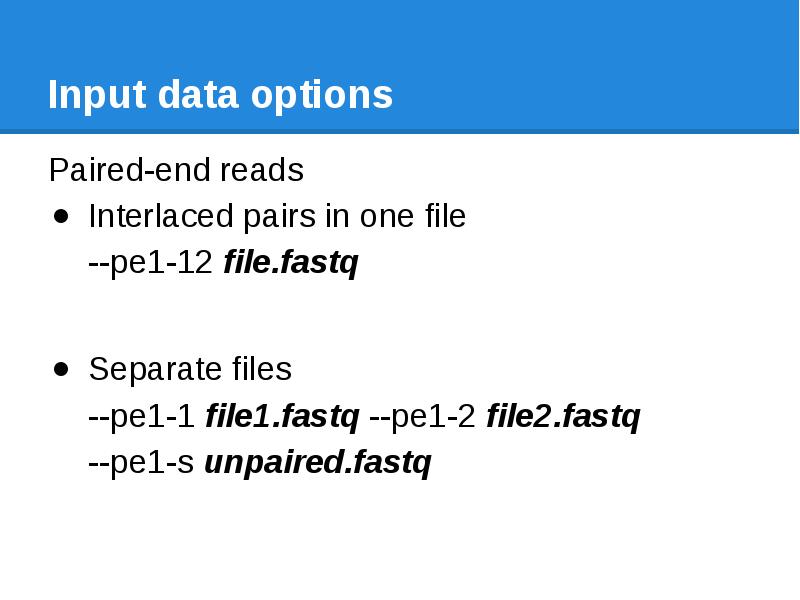
- 28. Input data options Mate-pair reads Cannot be used separately Interlaced
- 29. Hybrid assembly options PacBio CLR --pacbio pb.fastq Oxford Nanopore reads
- 30. Restarting SPAdes SPAdes / system crashed --continue -o your_output_dir
- 31. Genome assembly evaluation with QUAST Center for Algorithmic Biotechnology SPbU
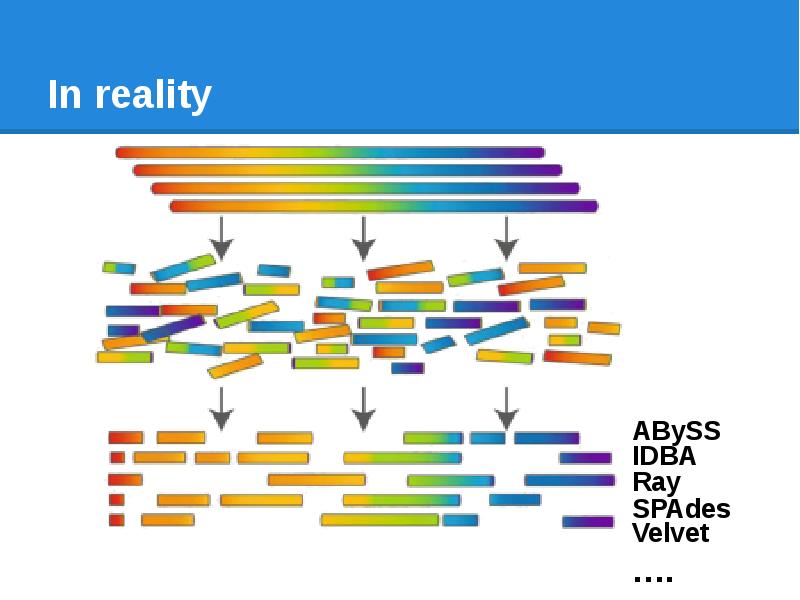
- 32. In reality
- 33. Which assembler to use? ABySS ALLPATHS-LG CLC IDBA-UD MaSuRCA MIRA Ray
- 34. Which assembler to use? Different technologies (Illumina, 454, IonTorrent, ...) Genome
- 35. There is no best assembler
- 36. Which assembler to use? Assemblathon 1 & 2 Simulated and real
- 37. Assembly evaluation Basic evaluation No extra input Very quick Reference-based evaluation
- 38. Basic statistics
- 39. Contig sizes Number of contigs
- 40. Contig sizes Number of contigs Number of large contigs (i.e. >
- 41. Contig sizes Number of contigs Number of large contigs (i.e. >
- 42. Contig sizes Number of contigs Number of large contigs (i.e. >
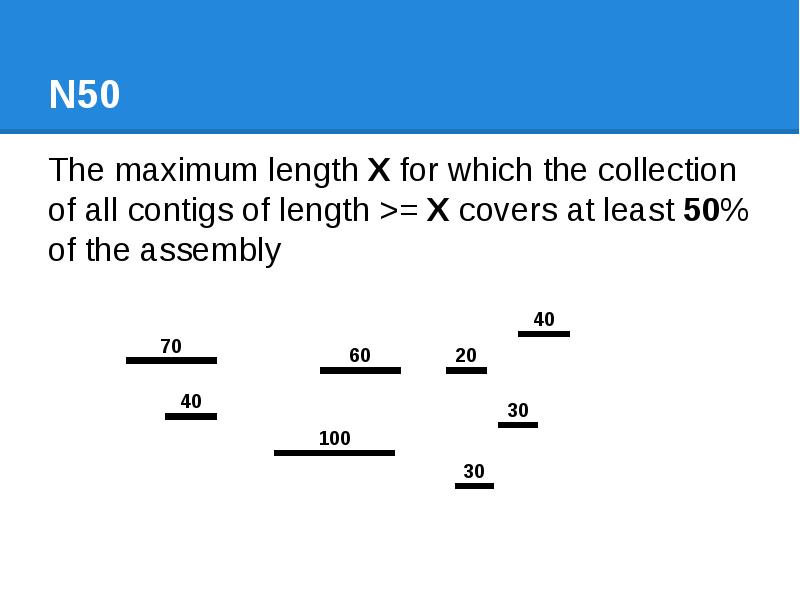
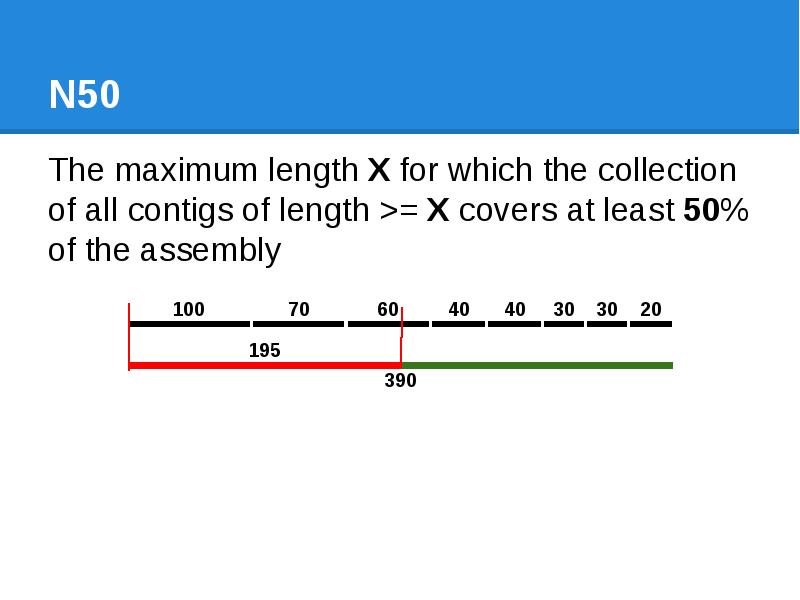
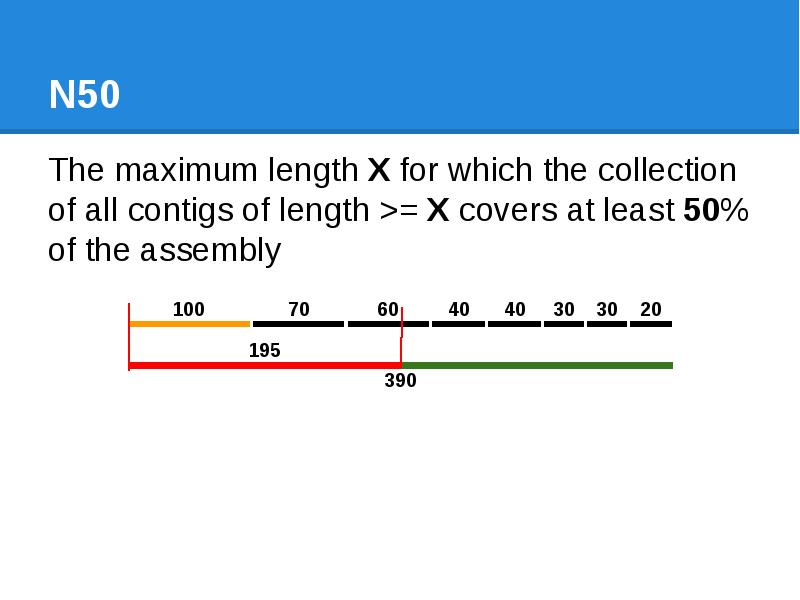
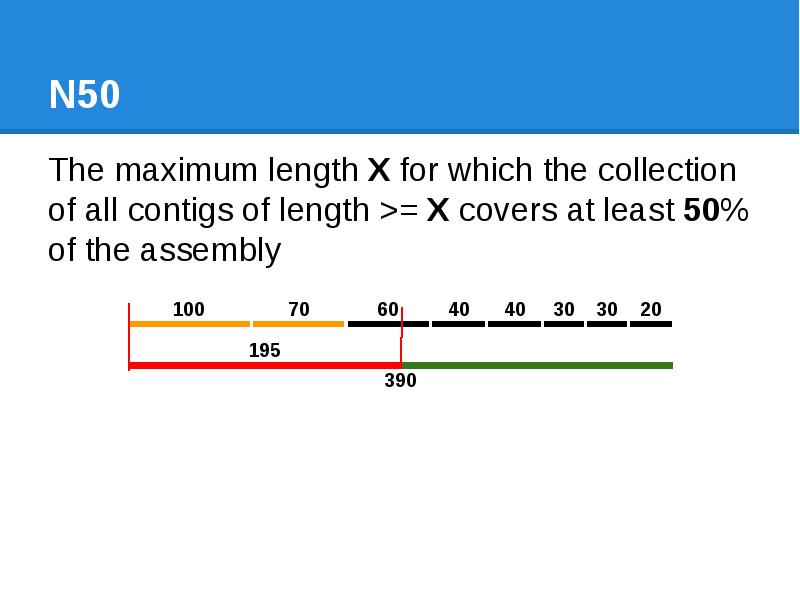
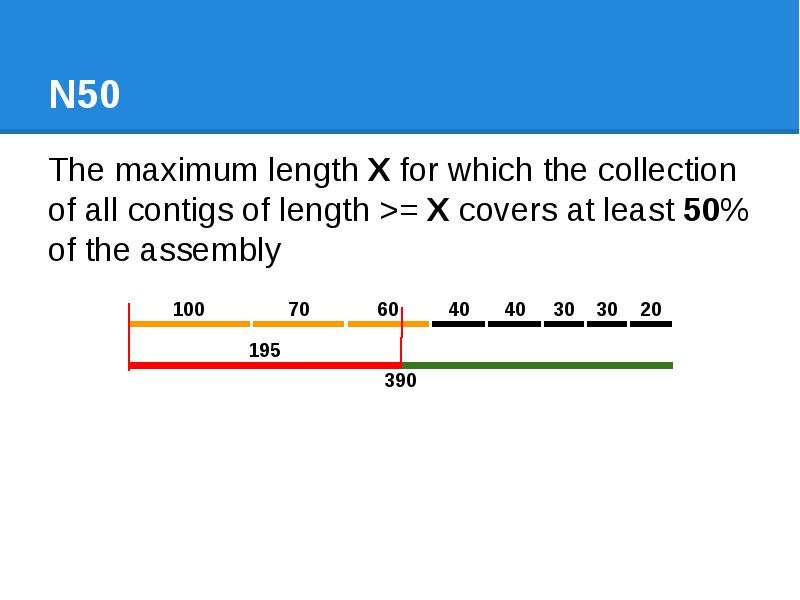
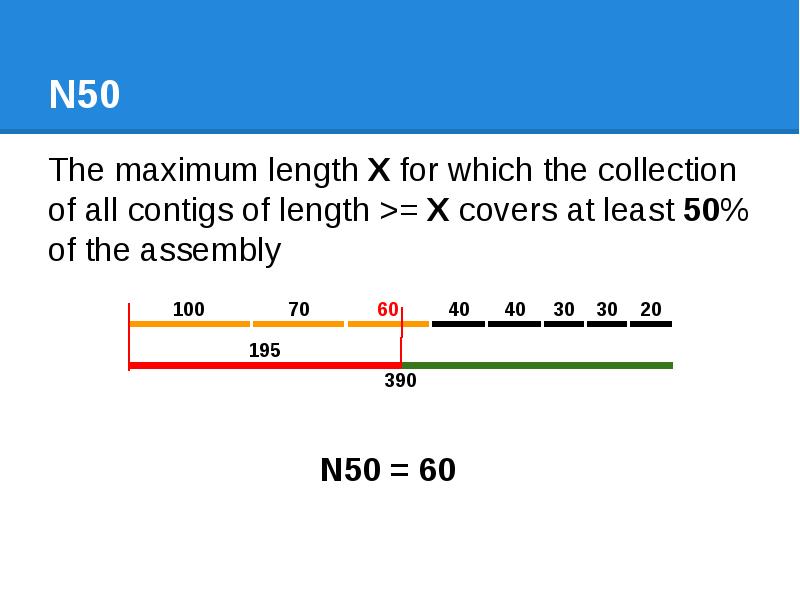
- 43. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 44. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 45. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 46. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 47. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 48. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 49. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
- 50. N50 The maximum length X for which the collection of all
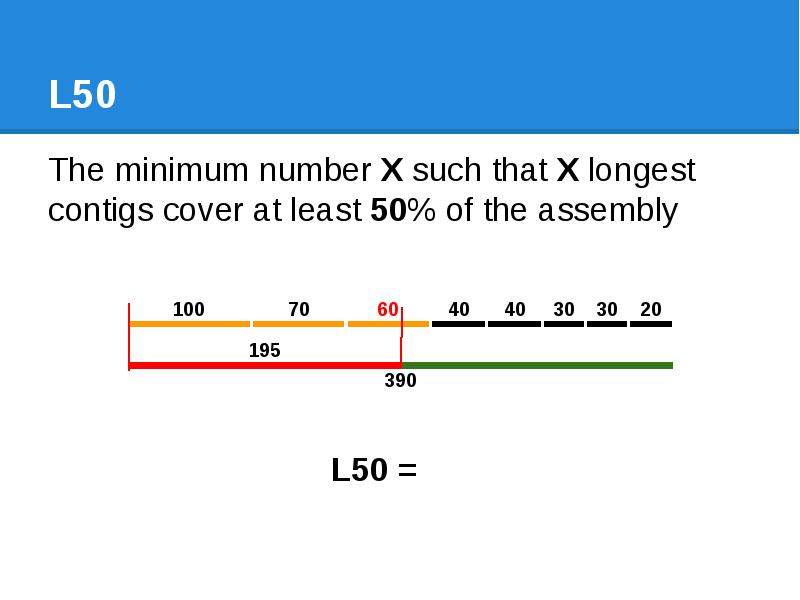
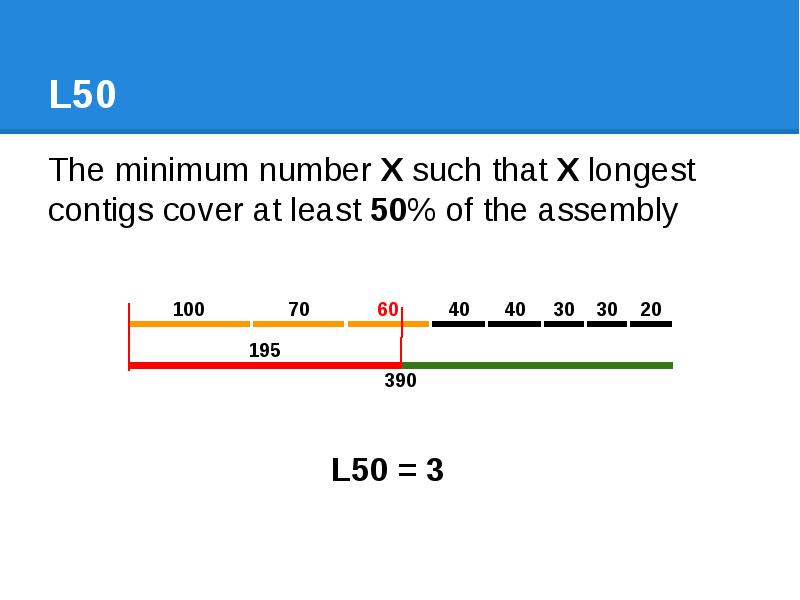
- 51. L50 The minimum number X such that X longest contigs cover
- 52. L50 The minimum number X such that X longest contigs cover
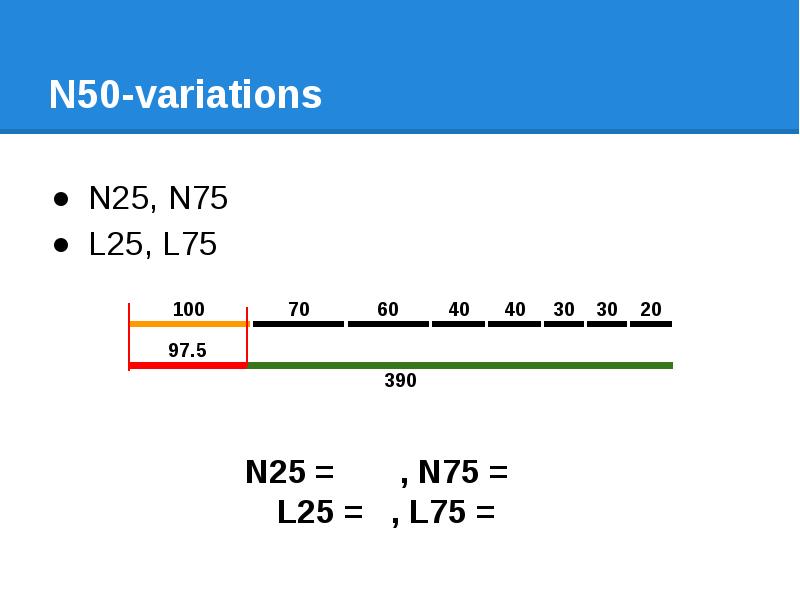
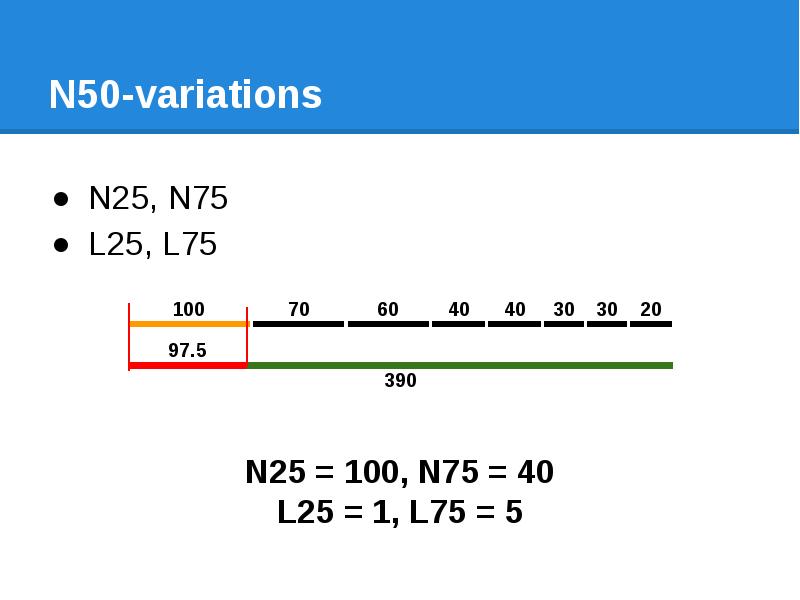
- 53. N50-variations N25, N75 L25, L75
- 54. N50-variations N25, N75 L25, L75
- 55. N50-variations N25, N75 L25, L50, L75
- 56. N50-variations N25, N75 L25, L50, L75 Nx, Lx
- 57. Other Number of N’s per 100 kbp
- 58. Other Number of N’s per 100 kbp GC %
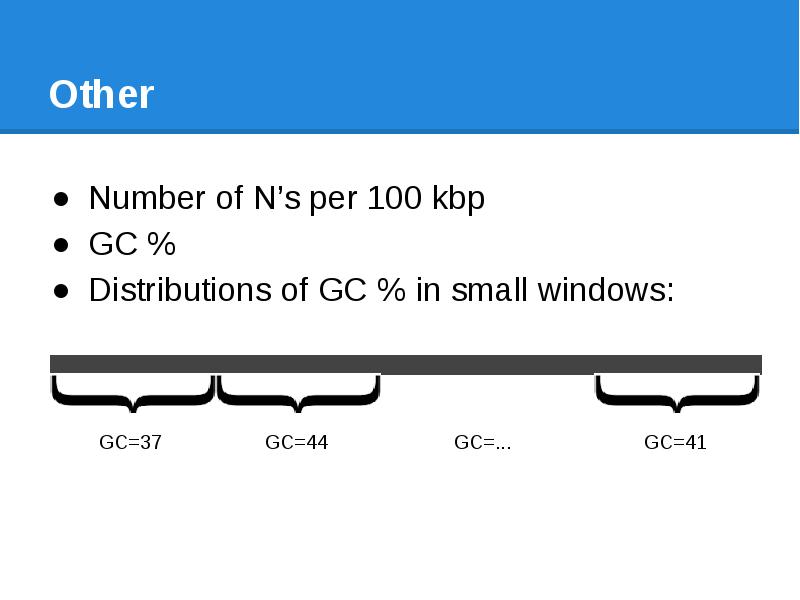
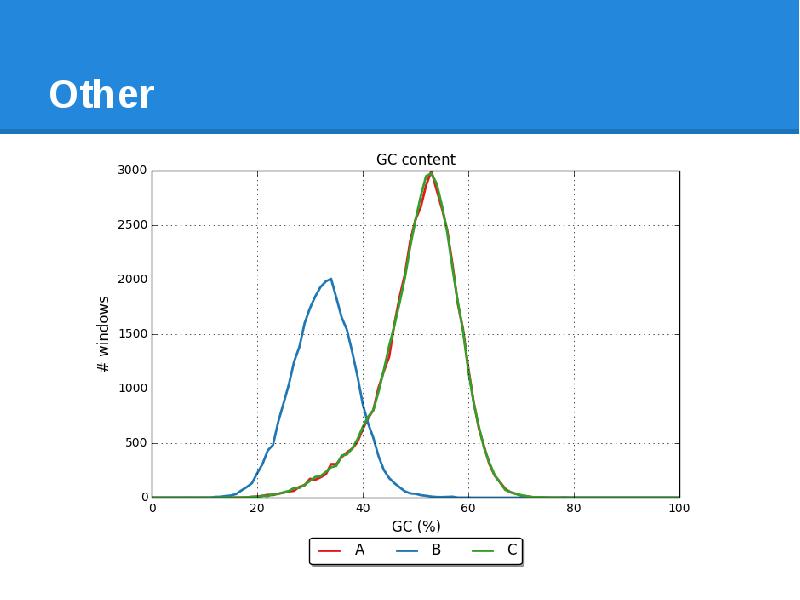
- 59. Other Number of N’s per 100 kbp GC % Distributions of
- 60. Other
- 61. Reference-based metrics
- 62. Basic reference statistics Reference length Reference GC % Number of chromosomes
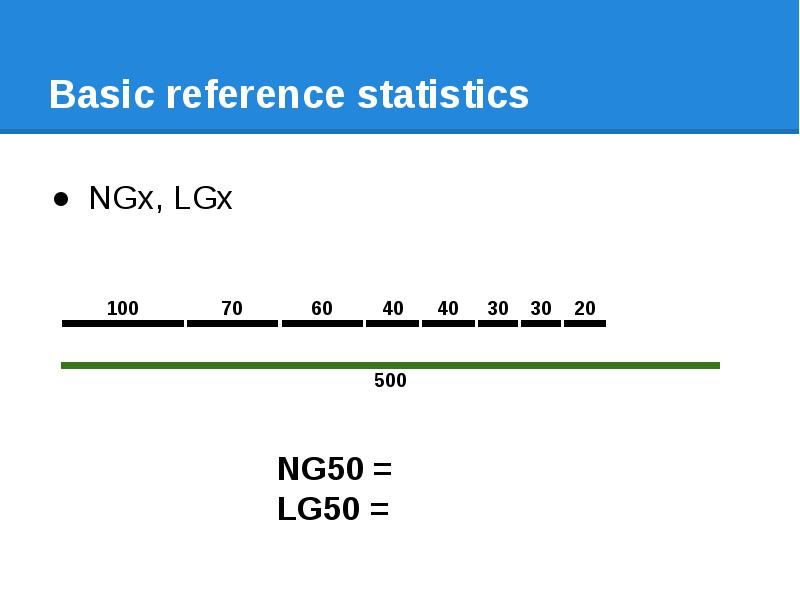
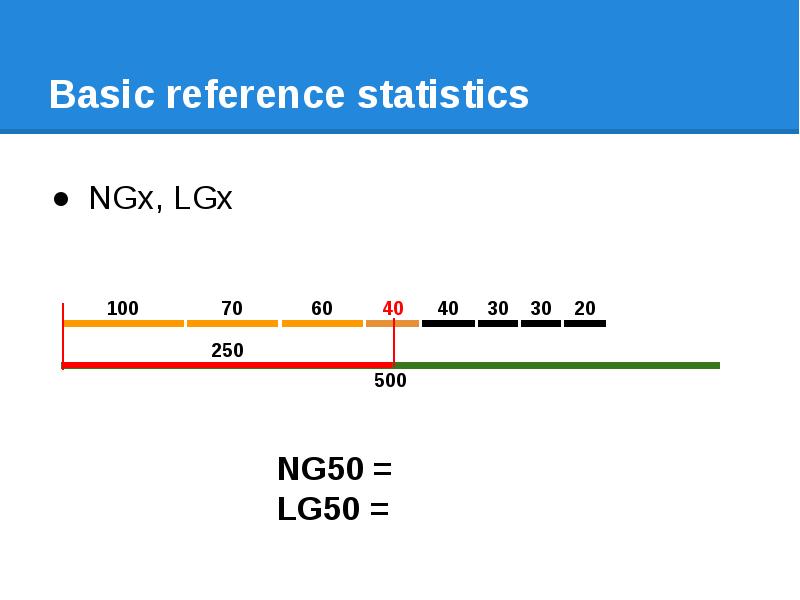
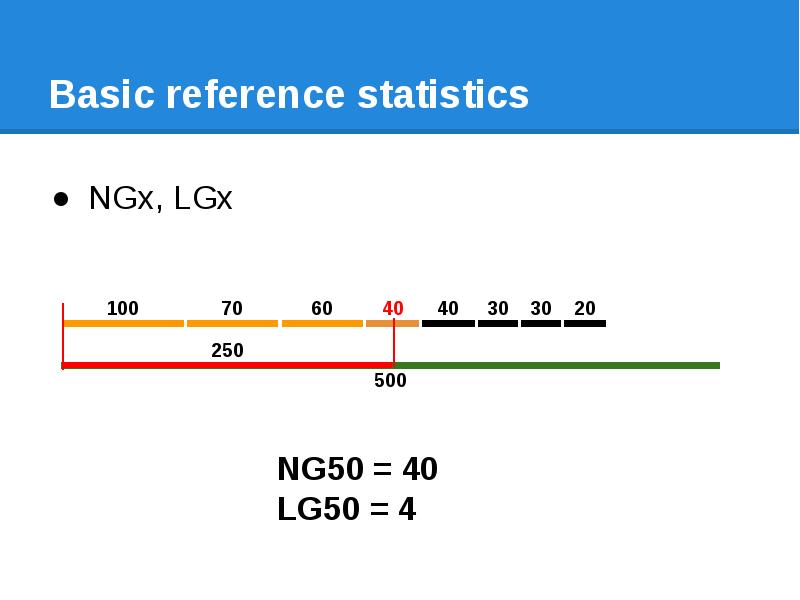
- 63. Basic reference statistics NGx, LGx
- 64. Basic reference statistics NGx, LGx
- 65. Basic reference statistics NGx, LGx
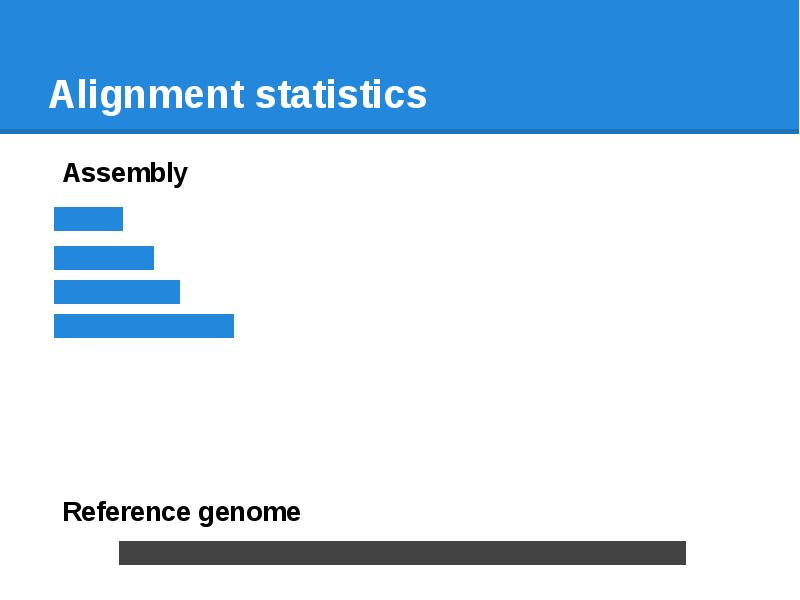
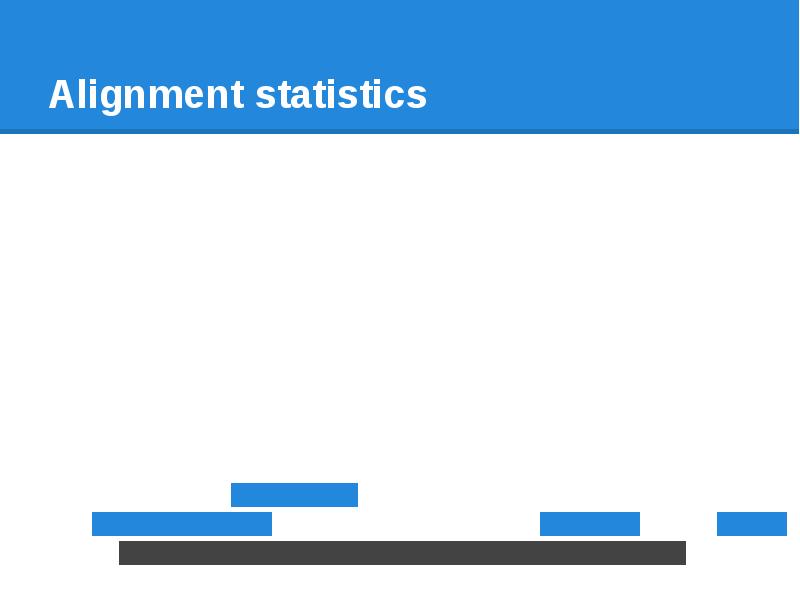
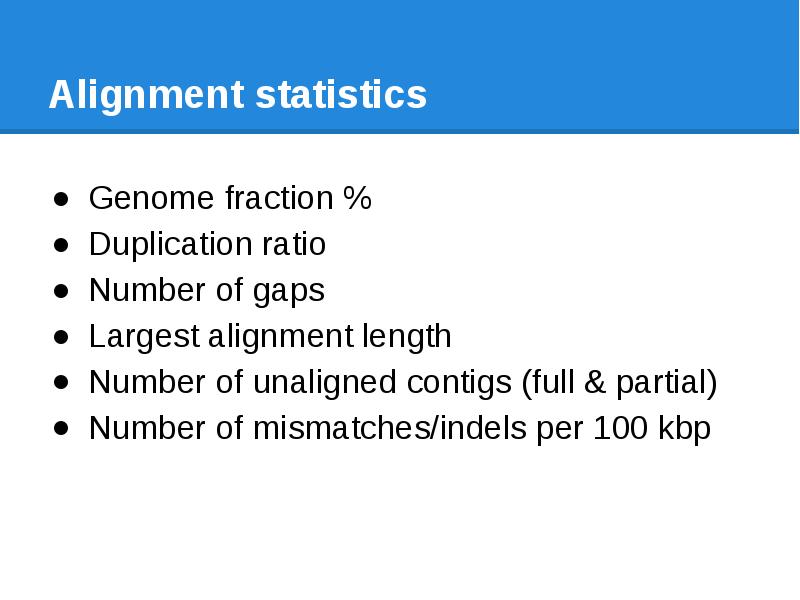
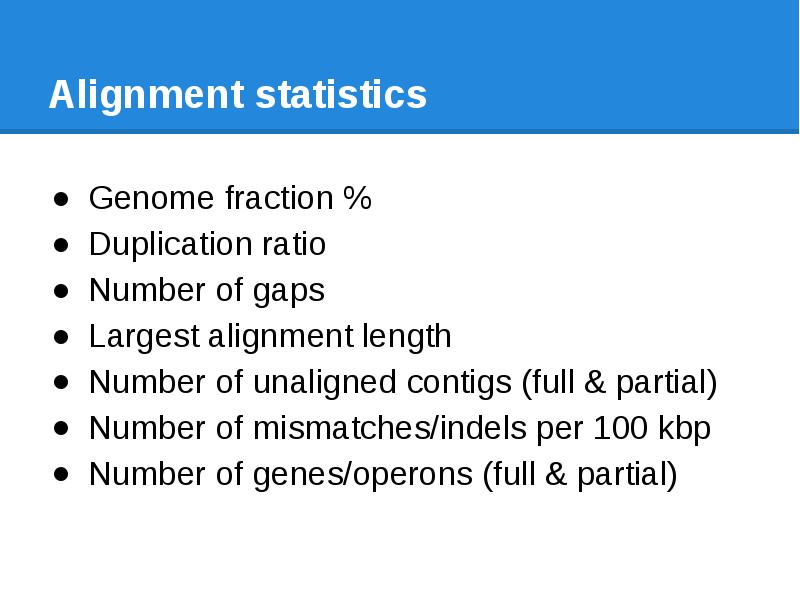
- 66. Alignment statistics
- 67. Alignment statistics
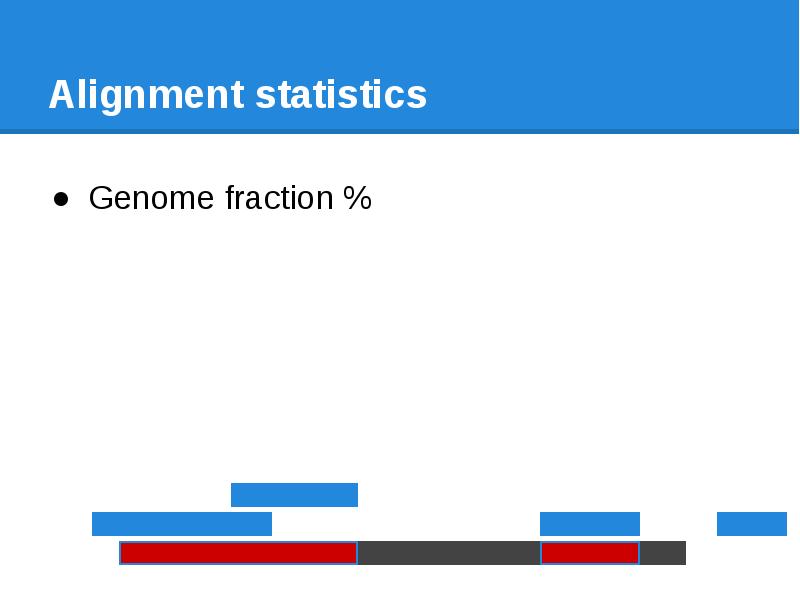
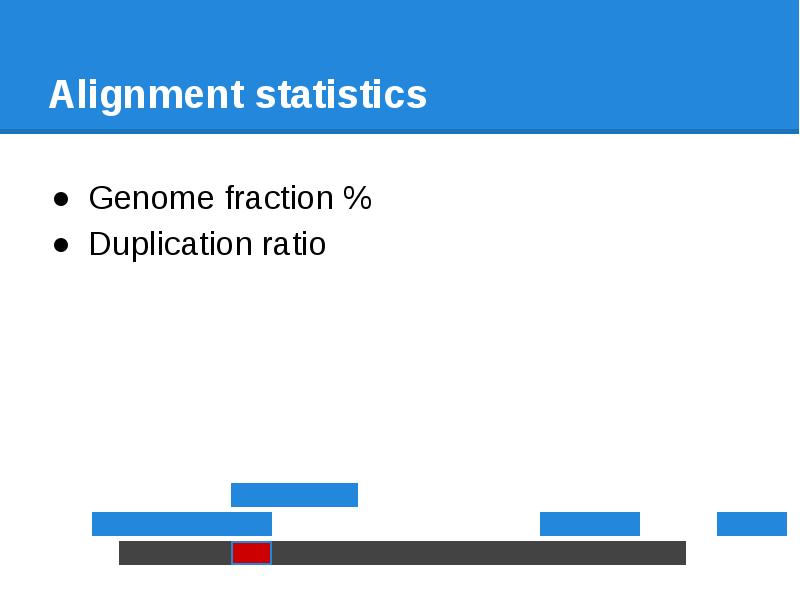
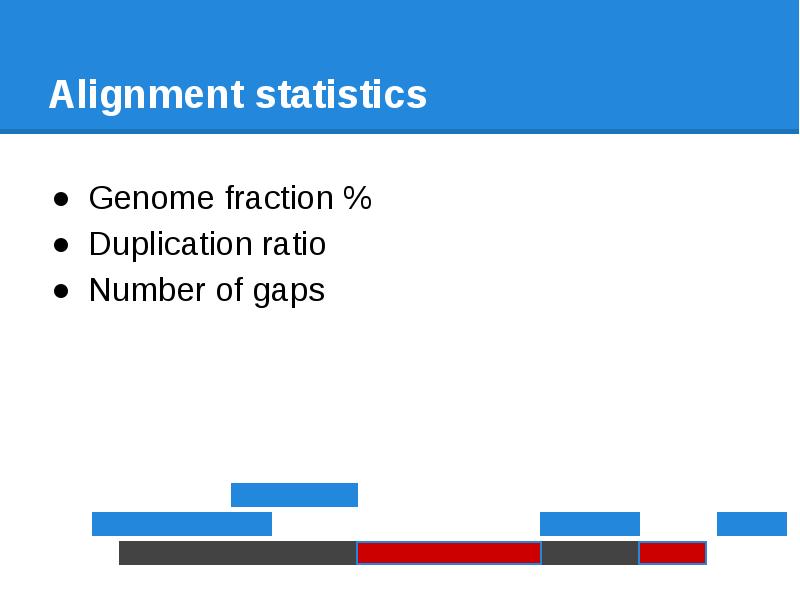
- 68. Alignment statistics Genome fraction %
- 69. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio
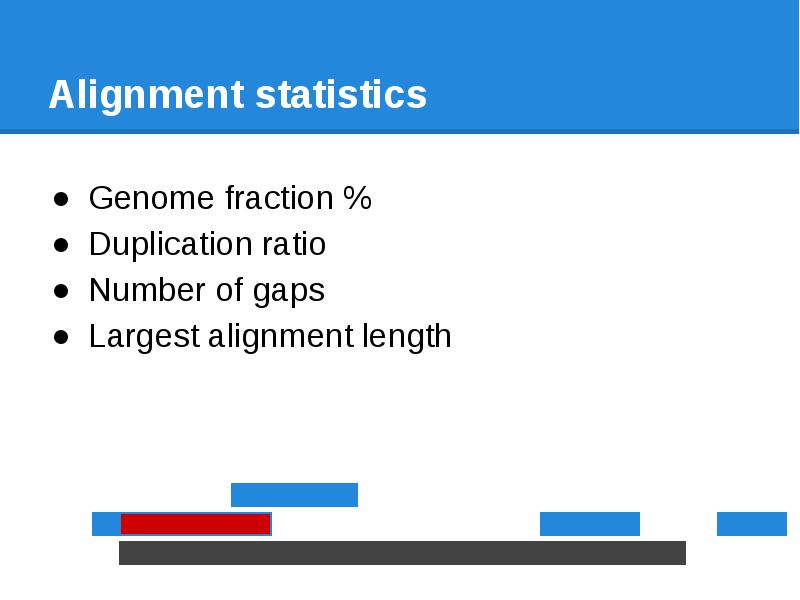
- 70. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio Number of gaps
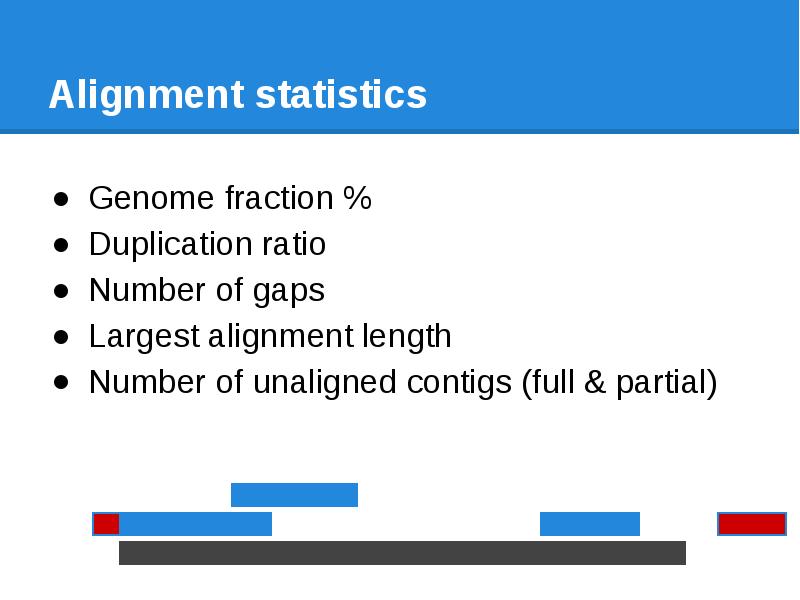
- 71. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio Number of gaps Largest
- 72. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio Number of gaps Largest
- 73. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio Number of gaps Largest
- 74. Alignment statistics Genome fraction % Duplication ratio Number of gaps Largest
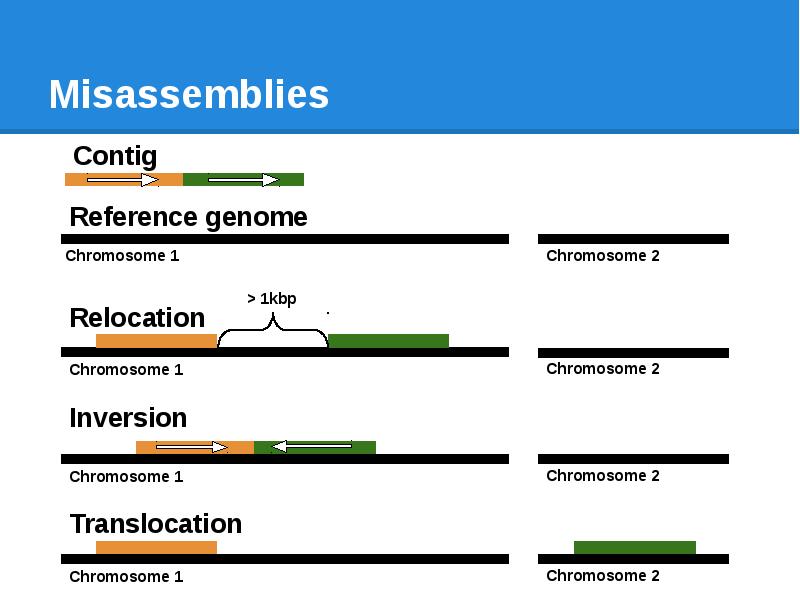
- 75. Misassemblies
- 76. Misassemblies
- 77. There is no best metric
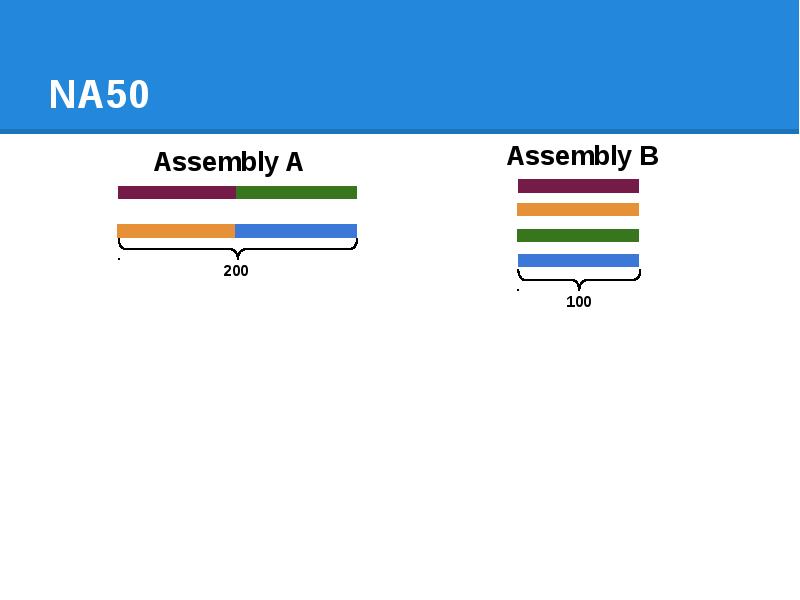
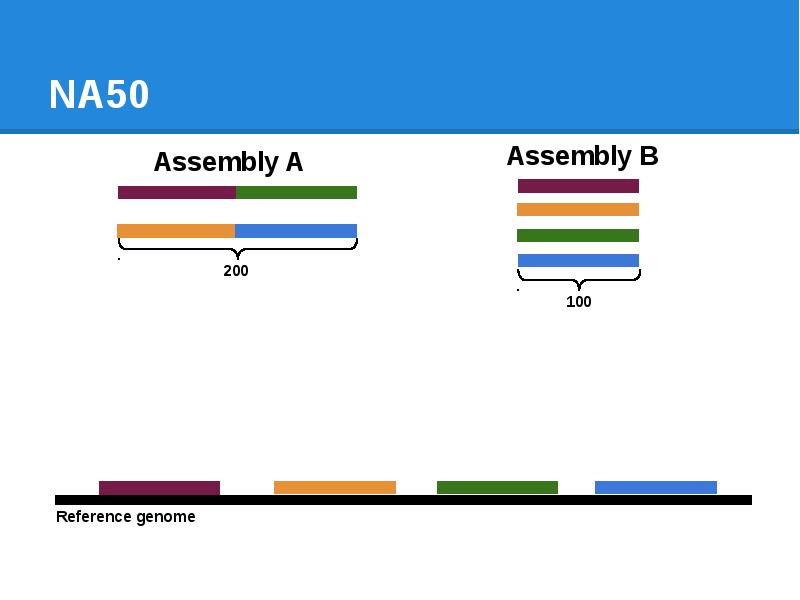
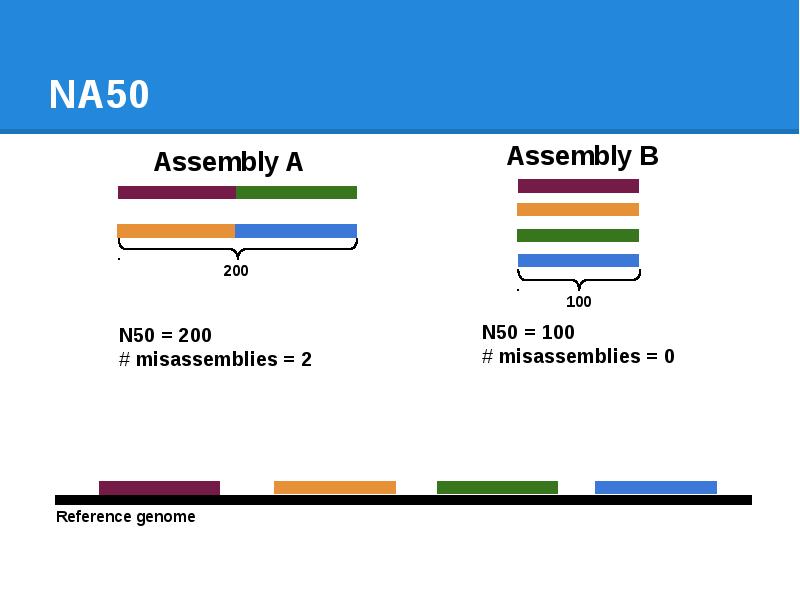
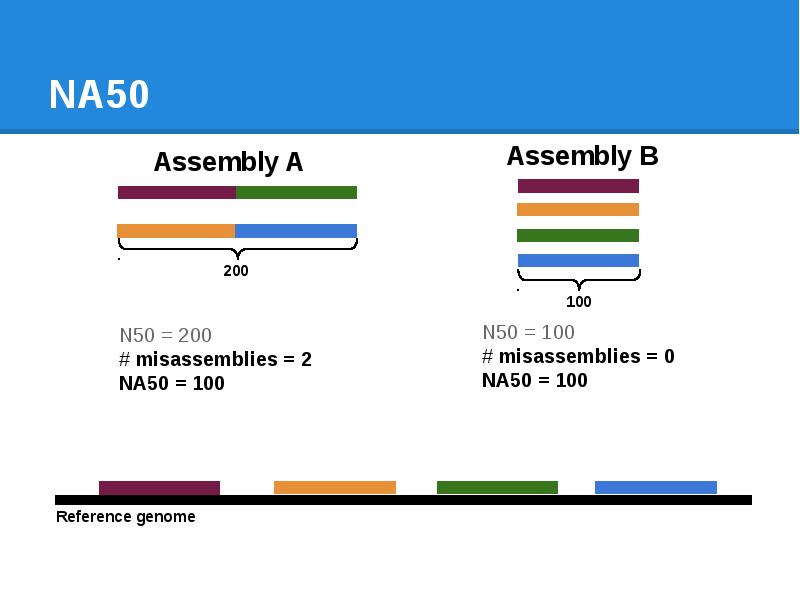
- 78. NA50
- 79. NA50
- 80. NA50
- 81. NA50
- 82. QUality ASsesment Tool for Genome Assemblies
- 83. QUAST Assembly statistics Basic statistics Reference-based evaluation Simple de novo
- 84. QUAST: console tool quast.py quast.py --help
- 85. QUAST basics quast.py quast.py --help quast.py contigs.fasta quast.py [options] contigs.fasta quast.py
- 86. Reference options Reference genome -R reference.fasta Gene annotation -G genes.gff
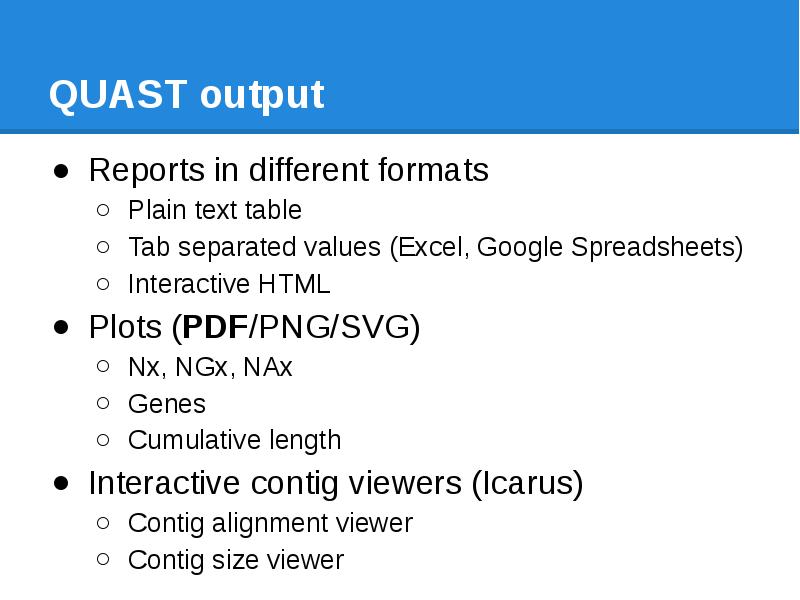
- 87. QUAST output Reports in different formats Plain text table Tab separated
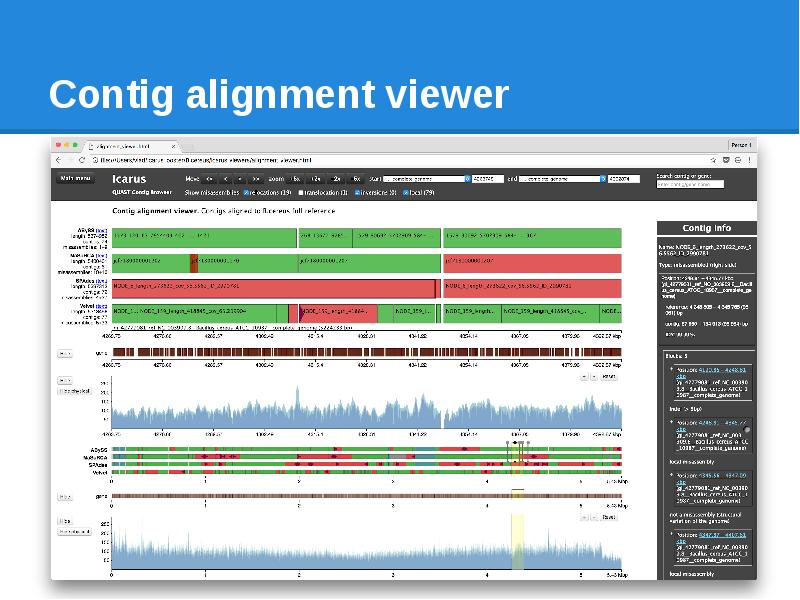
- 88. Contig alignment viewer All alignments for each contig Misassembly details
- 89. Contig alignment viewer
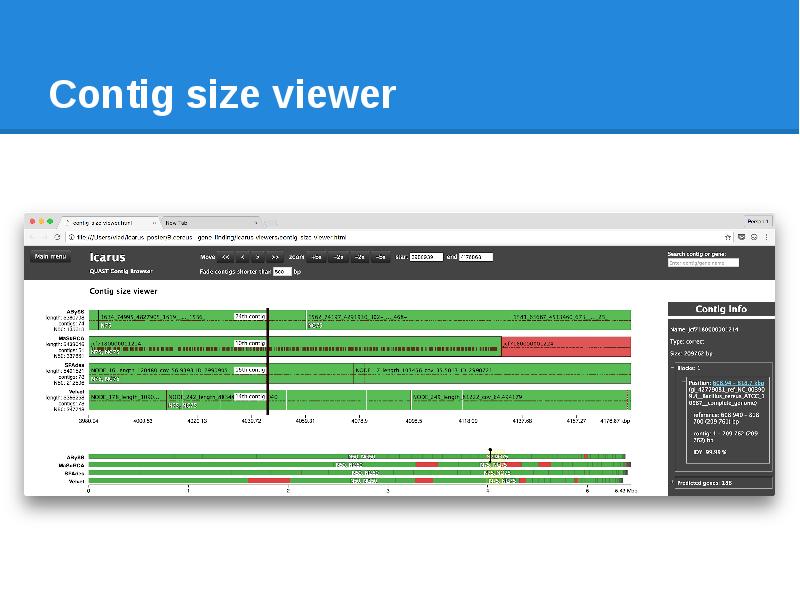
- 90. Contig size viewer Contigs ordered from longest to shortest N50, N75
- 91. Contig size viewer
- 92. De novo evaluation
- 93. Read-based statistics Number of aligned/unaligned reads % of assembly covered
- 94. Read-based statistics Number of aligned/unaligned reads % of assembly covered
- 95. Annotation-based statistics Number of ORFs
- 96. Annotation-based statistics Number of ORFs Number of gene/operon-like regions GeneMarkS (Borodovsky
- 97. Annotation-based statistics Number of ORFs Number of gene/operon-like regions GeneMarkS (Borodovsky
- 98. Thank you! Questions?
- 99. Скачать презентацию













































![QUAST basics
quast.py
quast.py --help
quast.py contigs.fasta
quast.py [options] contigs.fasta
quast.py QUAST basics
quast.py
quast.py --help
quast.py contigs.fasta
quast.py [options] contigs.fasta
quast.py](/documents_7/2cc7b8b3ef43e20c22698c8879960ccf/img84.jpg)






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























