Importing, Exporting, and Sourcing Chapter 8 презентация
Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Compare and contrast export selling and export marketing. Identify
- 3. Export Selling vs. Export Marketing Export selling involves selling the
- 4. Requirements for Export Marketing An understanding of the target market environment
- 5. Organizational Export Activities The firm is unwilling to export; it will
- 6. Organizational Export Activities (Cont.) The firm is an experienced exporter to
- 7. Potential Export Problems
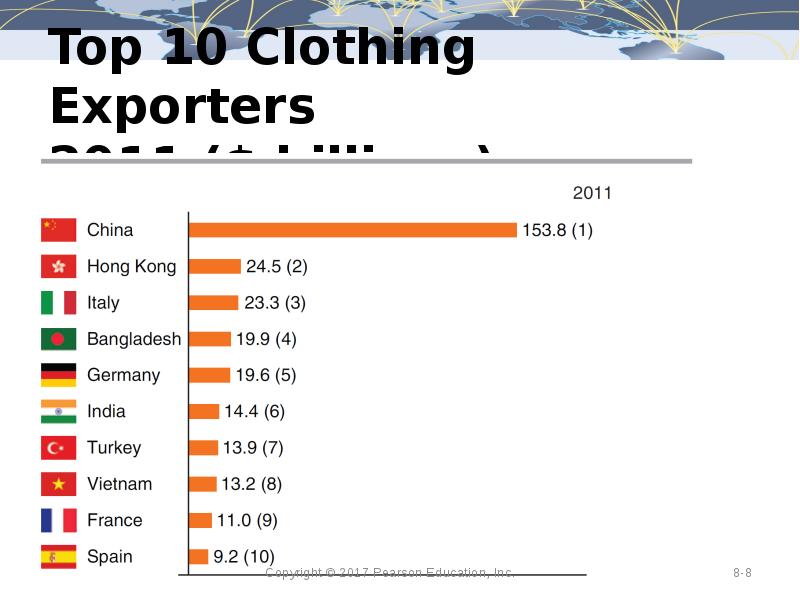
- 8. Top 10 Clothing Exporters 2011 ($ billions)
- 9. National Policies Governing Exports and Imports Most nations encourage exports and
- 10. Government Programs that Support Exports Governments concerned about trade deficits or
- 11. Government Programs that Support Exports Tax incentives Subsidies Governmental assistance Free
- 12. Governmental Actions to Discourage Imports and Block Market Access Tariffs: 3
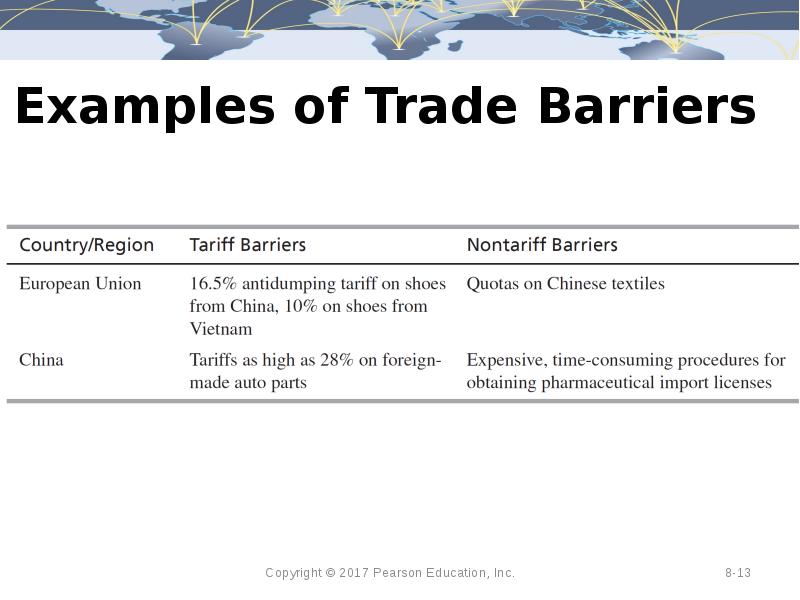
- 13. Examples of Trade Barriers
- 14. Harmonized Tariff System Developed by the World Customs Organization Effective January
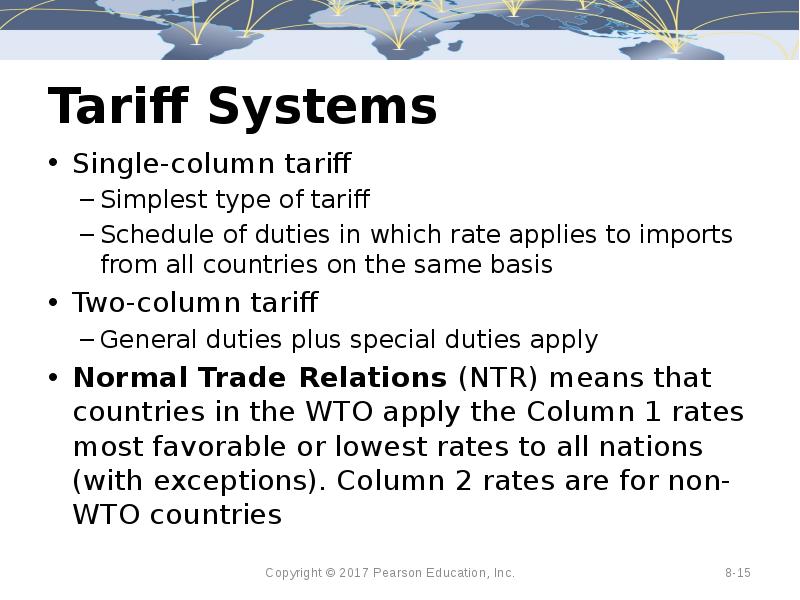
- 15. Tariff Systems Single-column tariff Simplest type of tariff Schedule of
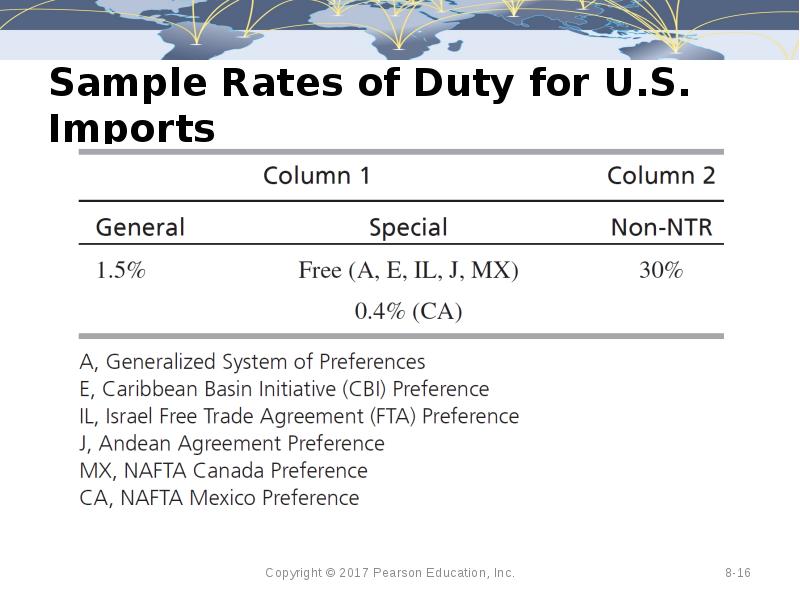
- 16. Sample Rates of Duty for U.S. Imports
- 17. Preferential Tariff Reduced tariff rate applied to imports from certain countries
- 18. Customs Duties Ad valorem duty Expressed as percentage of value of
- 19. Other Duties and Import Charges Anti-dumping Duties Dumping is the sale
- 20. Key Export Participants Foreign purchasing agents Export brokers Export merchants
- 21. Organizing for Exporting in the Manufacturer’s Country Exports can be handled
- 22. Organizing for Exporting in the Market Country Direct market representation Advantages:
- 23. Trade Financing and Methods of Payment Documentary credits (letter of credit)
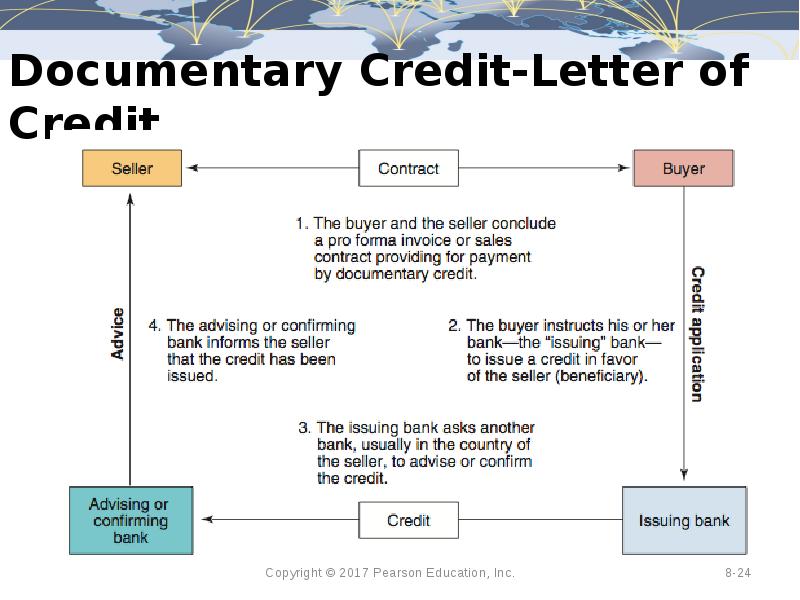
- 24. Documentary Credit-Letter of Credit
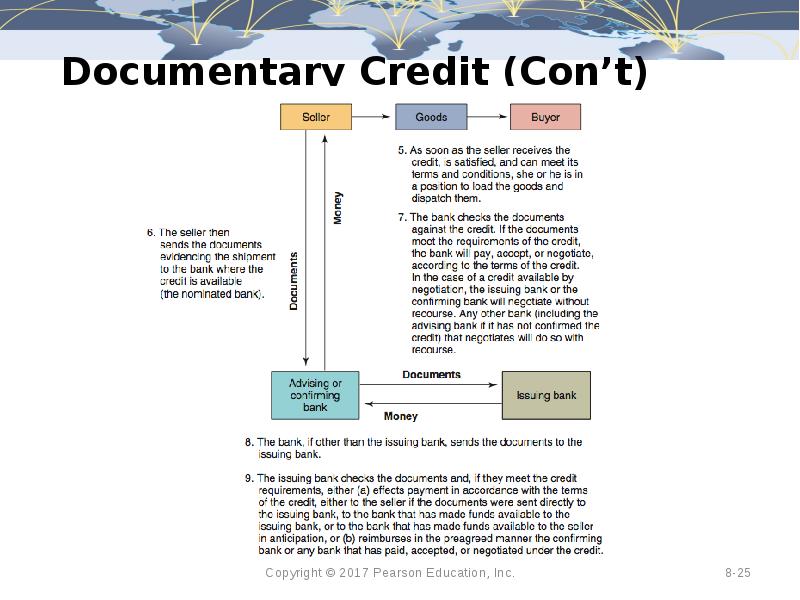
- 25. Documentary Credit (Con’t)
- 26. Methods of Payment Documentary Collections (Sight or Time Drafts) use a
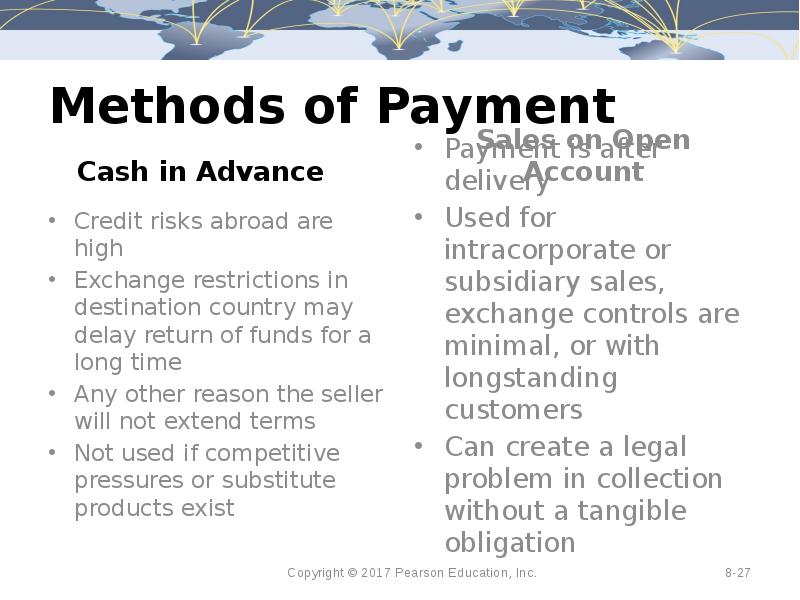
- 27. Methods of Payment Cash in Advance
- 28. Customs Trade Partnership Against Terrorism The U.S. Customs and Border Patrol
- 29. Duty Drawback Refunds of duties paid on imports that are processed
- 30. Sourcing
- 31. Factors that Affect Sourcing Management vision Factor costs and conditions Customer
- 32. Other Export/Import Issues
- 33. Other Export/Import Issues Customer Needs Needs can trump low cost; Dell
- 34. Other Export/Import Issues Political Factors Political risk is higher in less
- 35. Looking Ahead to Chapter 9 Global Market-Entry Strategies: Licensing, Investment, and
- 36. Скачать презентацию


























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Importing, Exporting, and Sourcing
Chapter 8 можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























