Introduction to the Field of Organizational Behavior презентация
Содержание
- 2. What are Organizations? Groups of people who work interdependently toward some
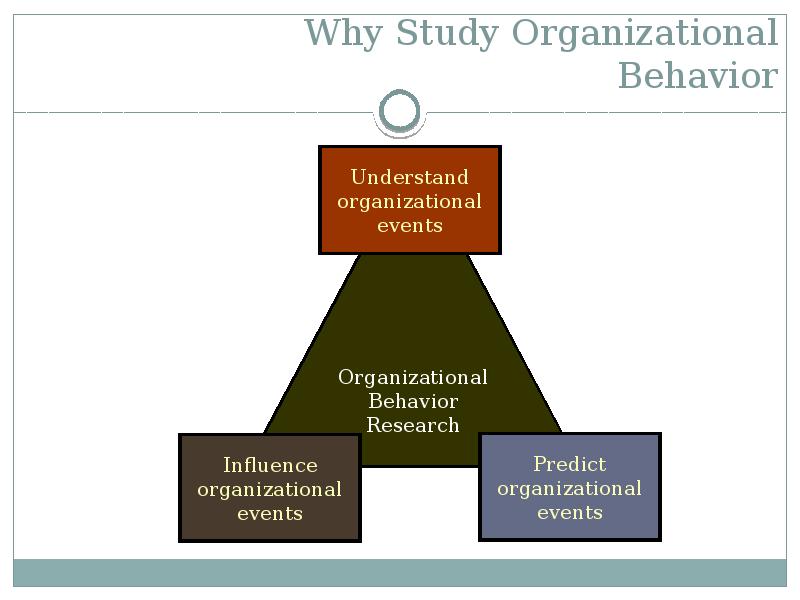
- 3. Why Study Organizational Behavior
- 4. Trends: Globalization Economic, social, and cultural connectivity with people in other
- 5. Trends: Information Technology Blurs temporal and spatial boundaries between employees and
- 6. Telecommuting An alternative work arrangement where employees work at home or
- 7. Trends: Changing Workforce Primary and secondary diversity -- but concerns about
- 8. Trends: Employment Relationship Employability “New deal” employment relationship Continuously learn new
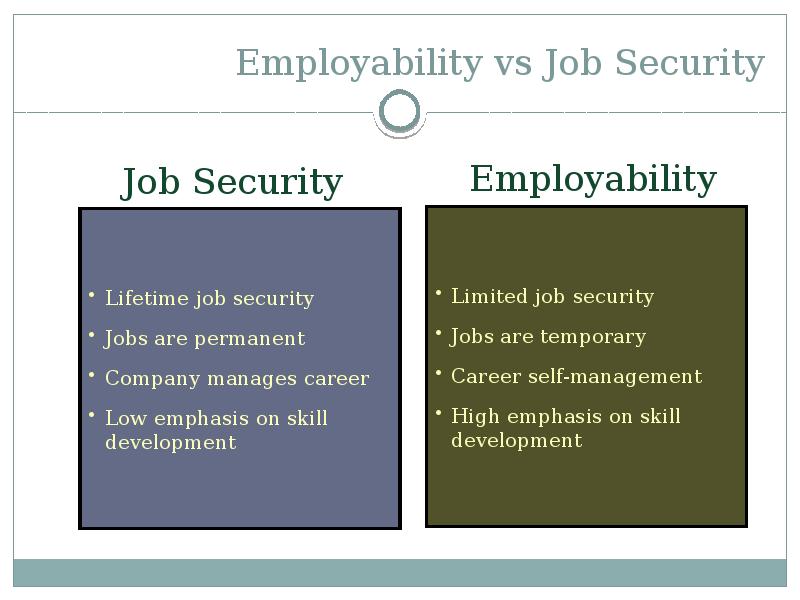
- 9. Employability vs Job Security
- 10. Trends: Workplace Values & Ethics Values are long-lasting beliefs about what
- 11. Corporate Social Responsibility Corporate Social Responsibility Organization’s moral obligation toward
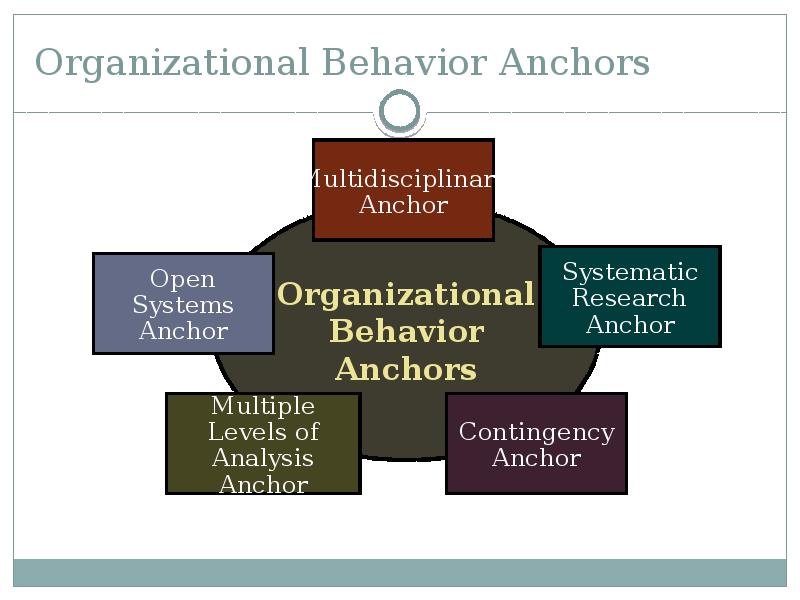
- 12. Organizational Behavior Anchors
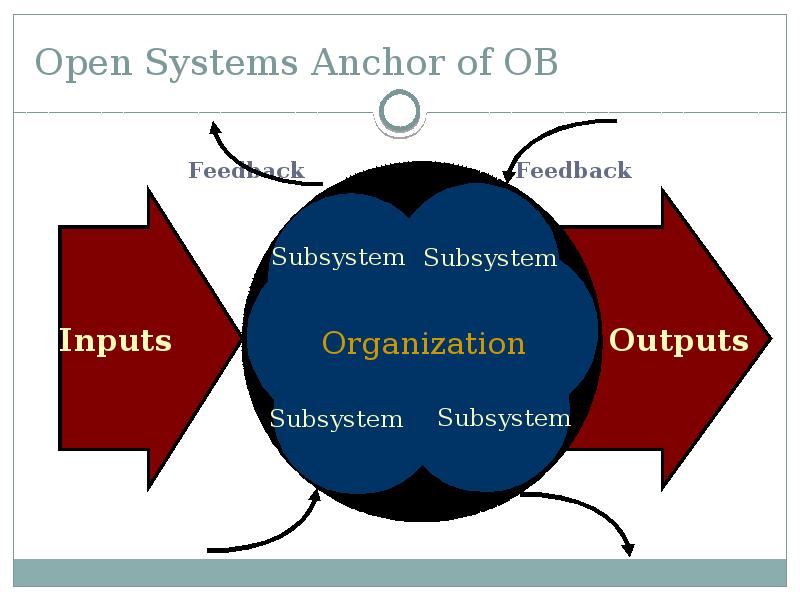
- 13. Open Systems Anchor of OB
- 14. Knowledge Management Defined Any structured activity that improves an organization’s capacity
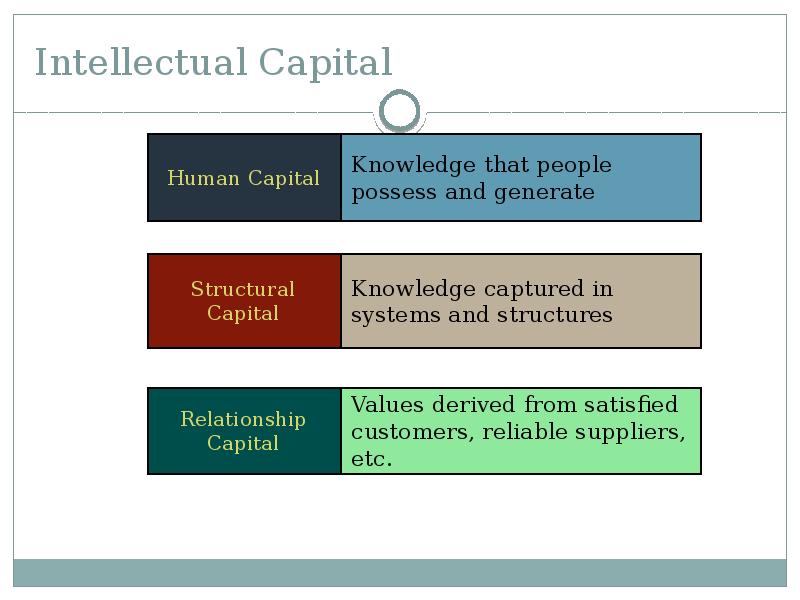
- 15. Intellectual Capital
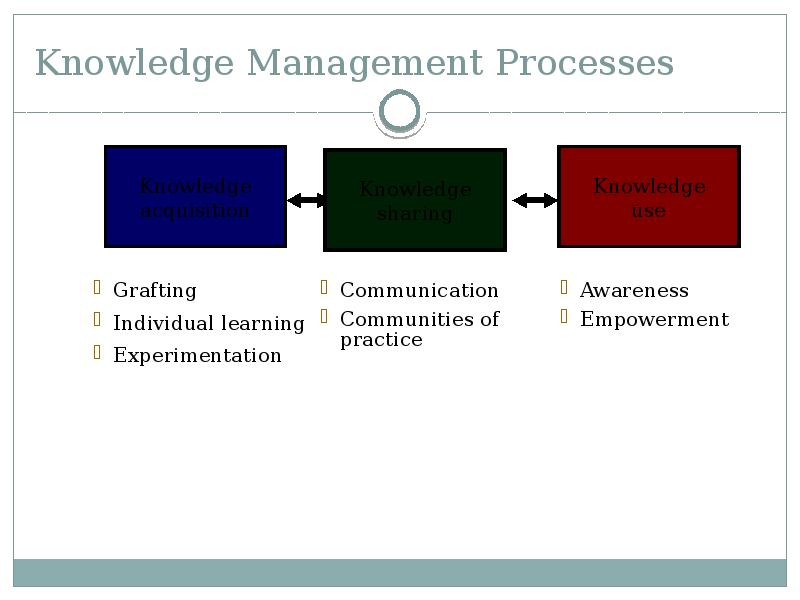
- 16. Knowledge Management Processes
- 17. Organizational Behaviour . . . a field of study that
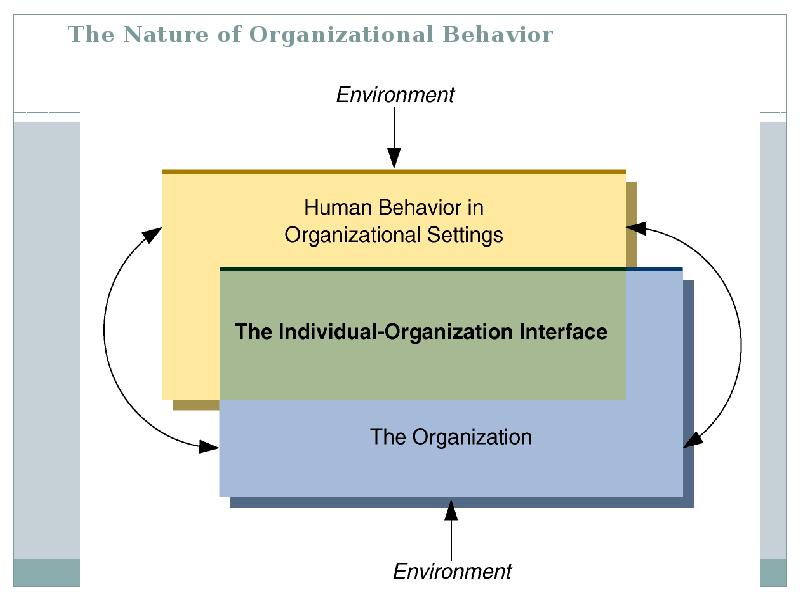
- 18. The Nature of Organizational Behavior
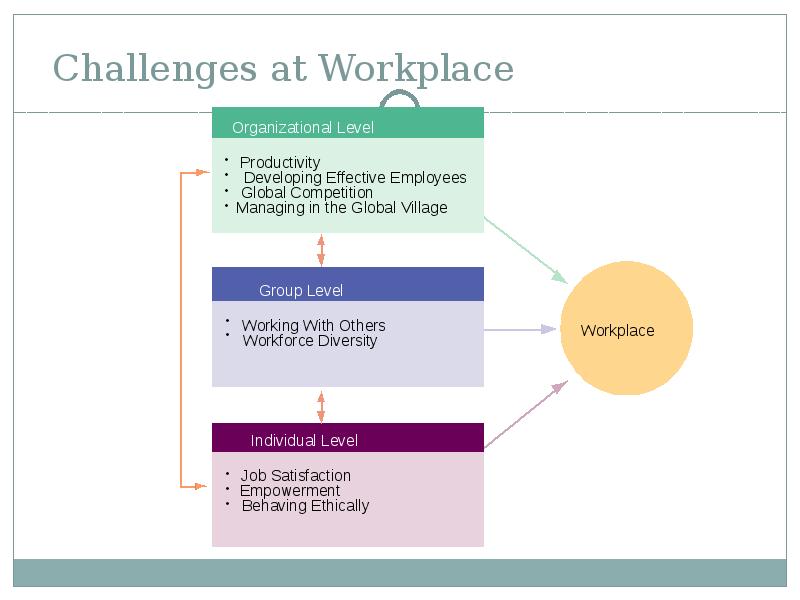
- 19. Challenges at Workplace
- 20. The Rigour of OB OB looks at consistencies What is common
- 21. Beyond Common Sense Systematic Study Looking at relationships, attempting to attribute
- 22. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field Psychology Sociology Social Psychology Anthropology
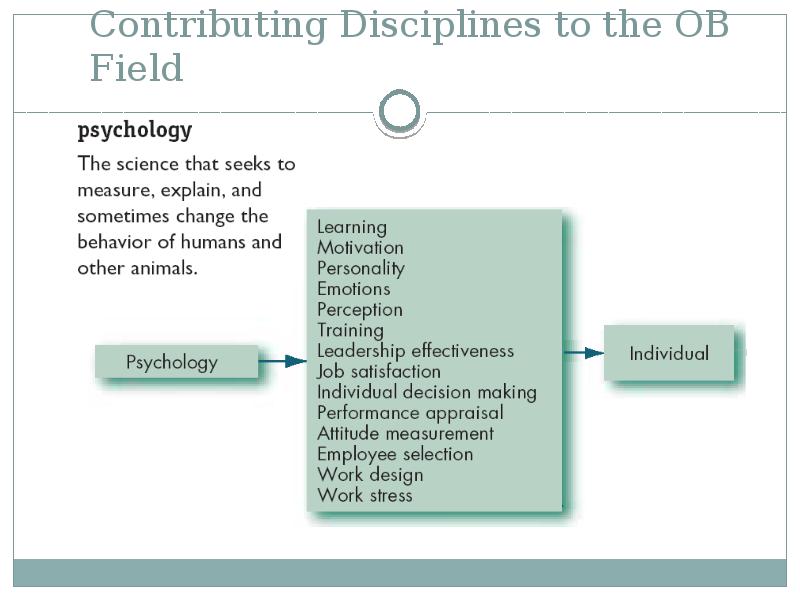
- 23. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field
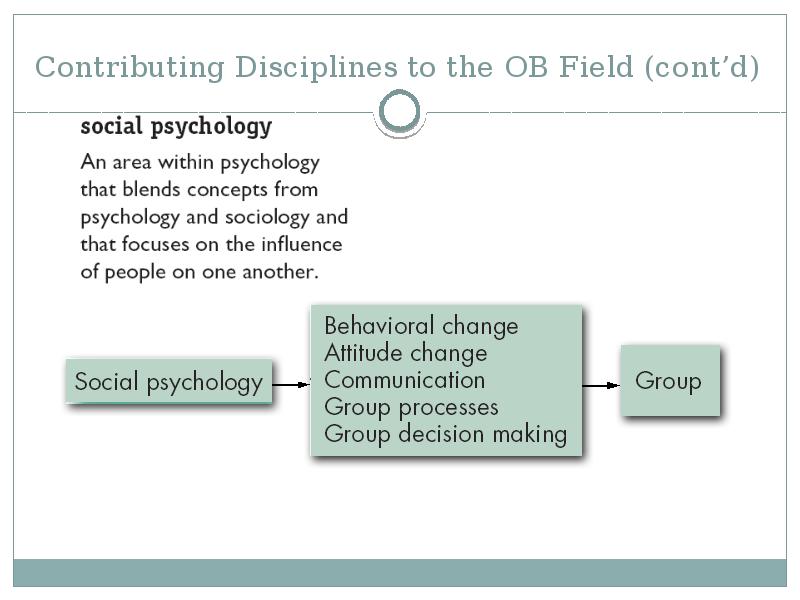
- 24. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field (cont’d)
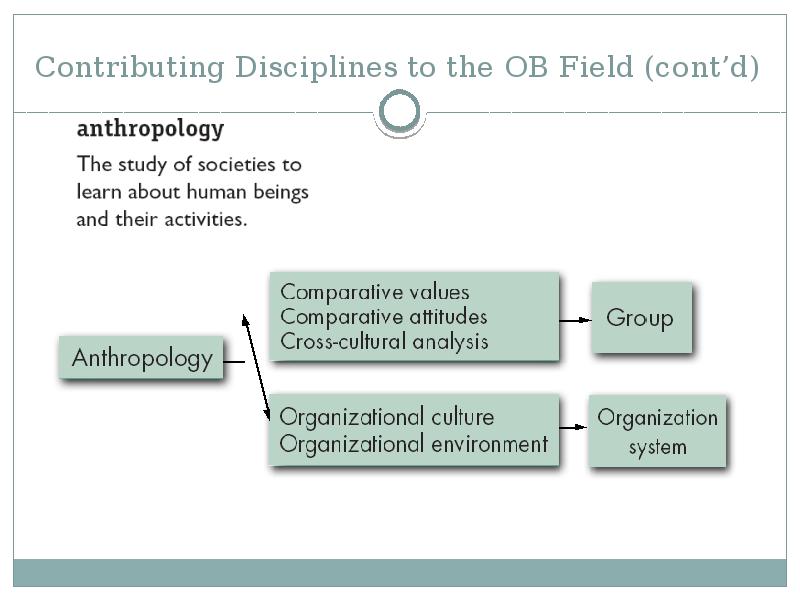
- 25. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field (cont’d)
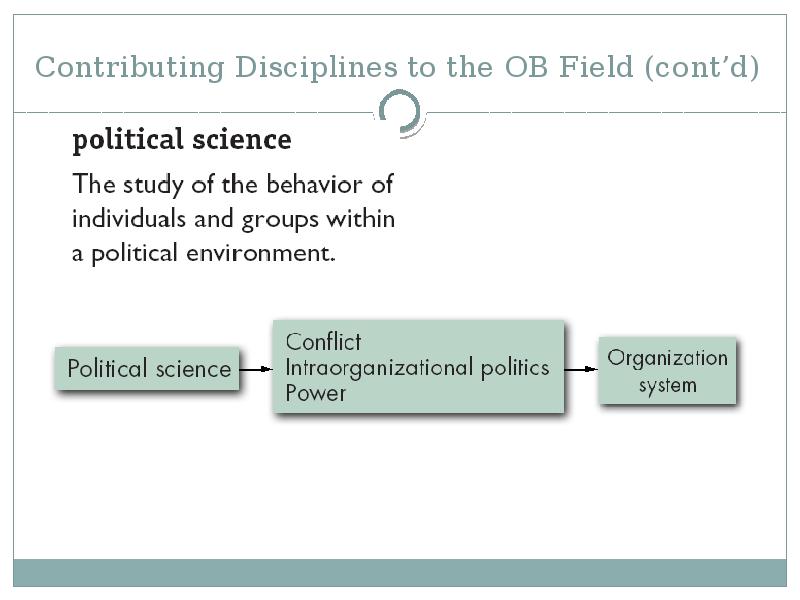
- 26. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field (cont’d)
- 27. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field (cont’d)
- 28. Summary and Implications OB is a field of study that investigates
- 29. The Historical Roots of Organizational Behavior Scientific Management Era (early 1900s)
- 30. Scientific Management Positive Attributes Facilitated job specialization and mass production. Demonstrated
- 31. The Historical Roots of Organizational Behavior Classical Organization Theory This perspective
- 32. Major Contributors to Classical Organization Theory Henri Fayol French executive and
- 33. The Emergence of Organizational Behavior Legacy of Scientific Management and Classical
- 34. The Hawthorne Studies (1927–1932) Involved two studies conducted by Elton Mayo
- 35. The Emergence of Organizational Behavior The Human Relations Movement People respond
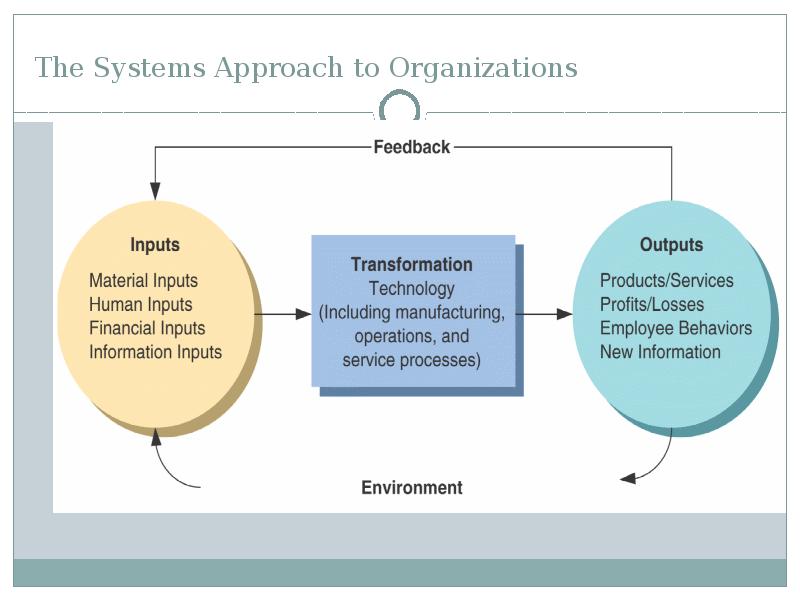
- 36. Contextual Perspectives on Organizational Behavior The Systems Perspective A system is
- 37. Contextual Perspectives on Organizational Behavior The Universal Perspective Suggests that whenever
- 38. The Systems Approach to Organizations
- 39. Contextual Perspectives on Organizational Behavior Interactionalism: People and Situations First presented
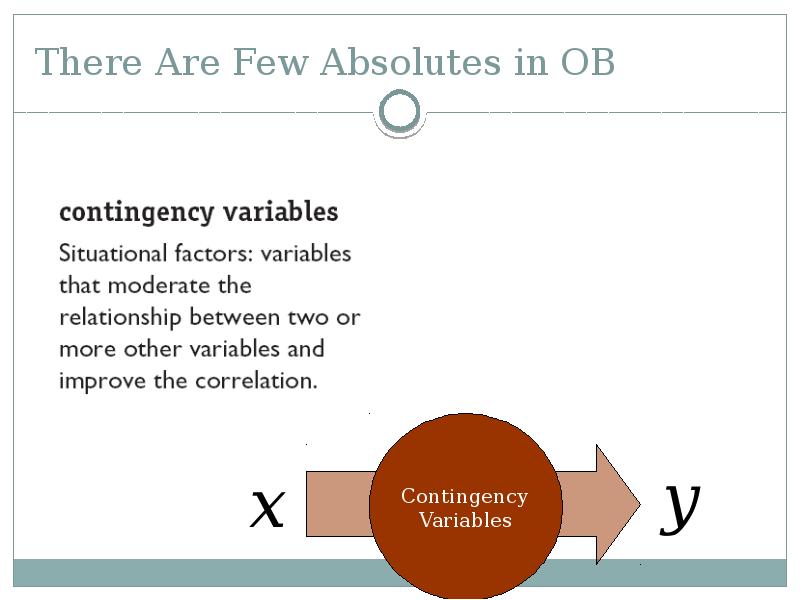
- 40. There Are Few Absolutes in OB
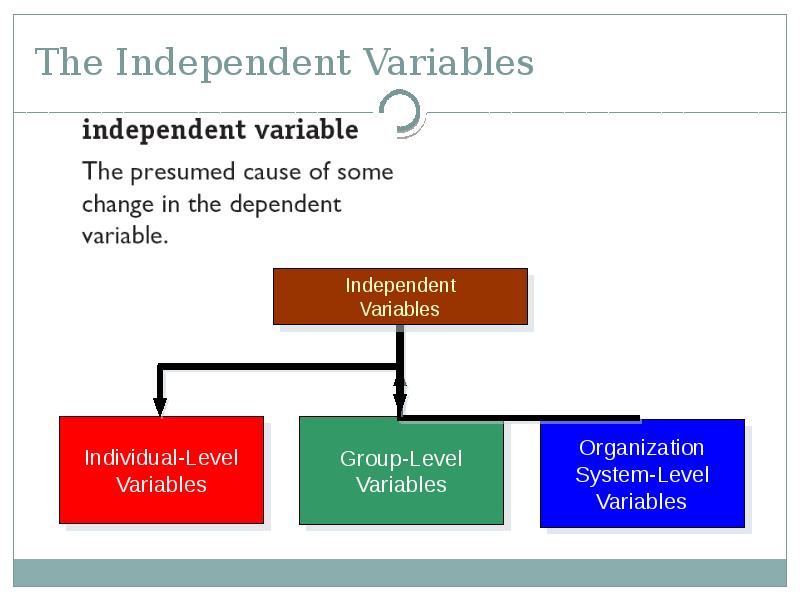
- 41. The Independent Variables
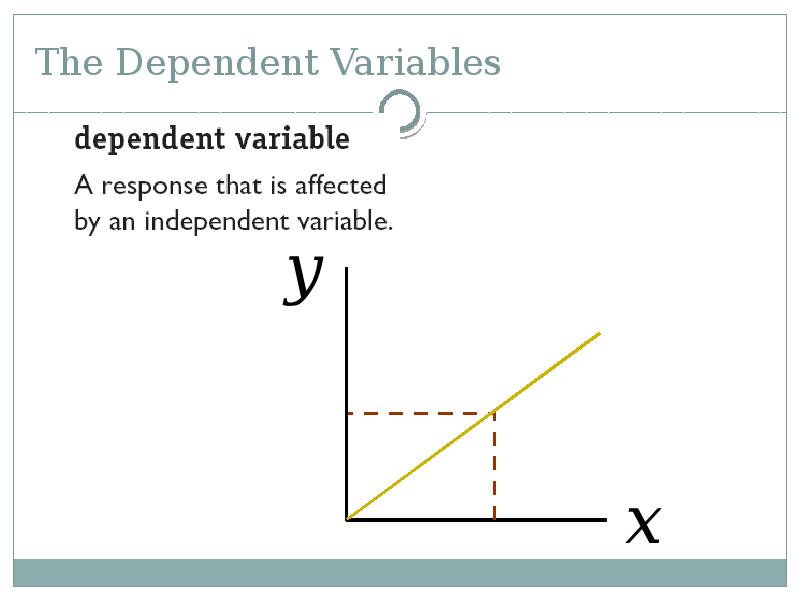
- 42. The Dependent Variables
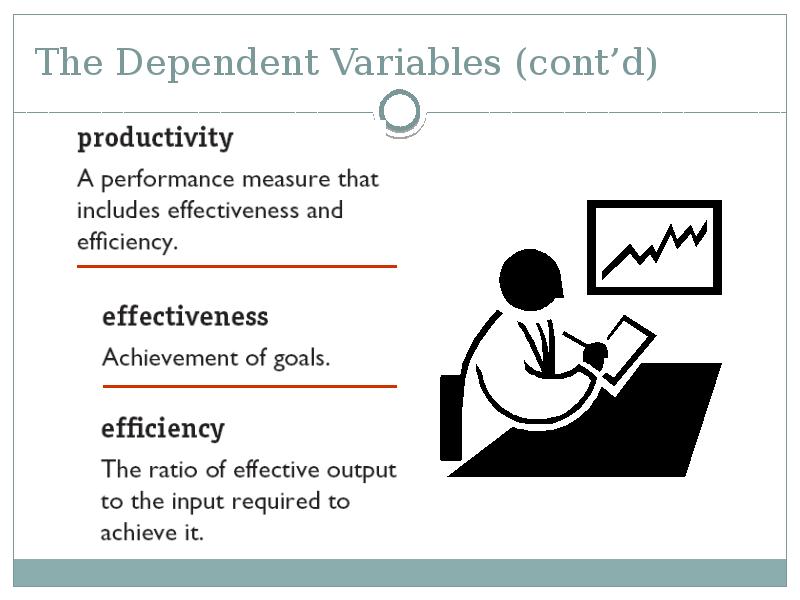
- 43. The Dependent Variables (cont’d)
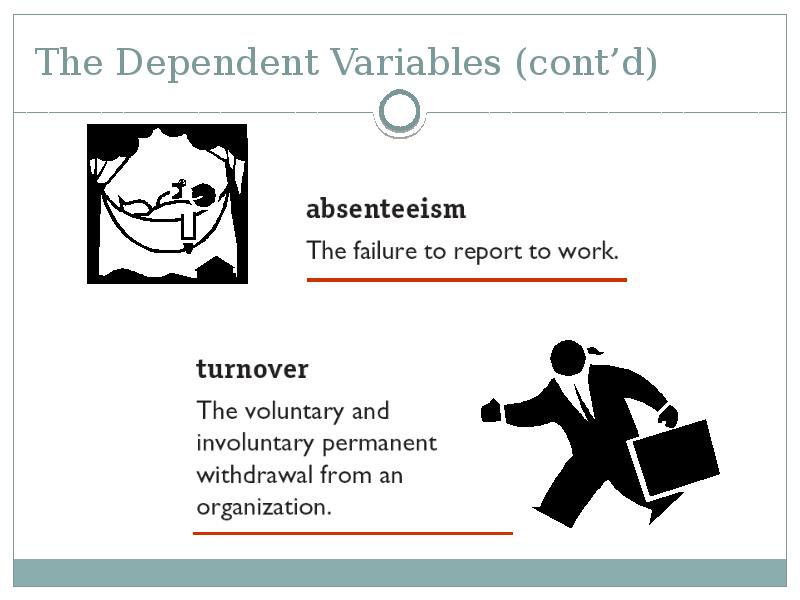
- 44. The Dependent Variables (cont’d)
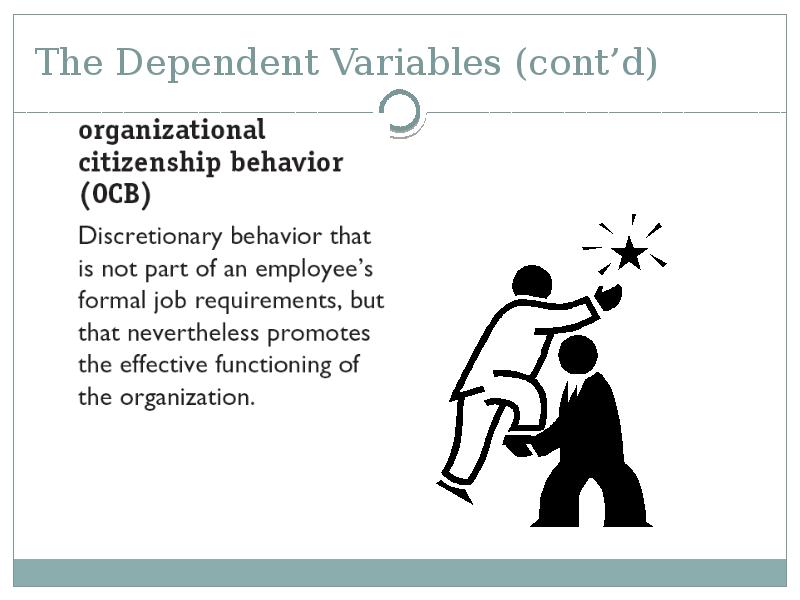
- 45. The Dependent Variables (cont’d)
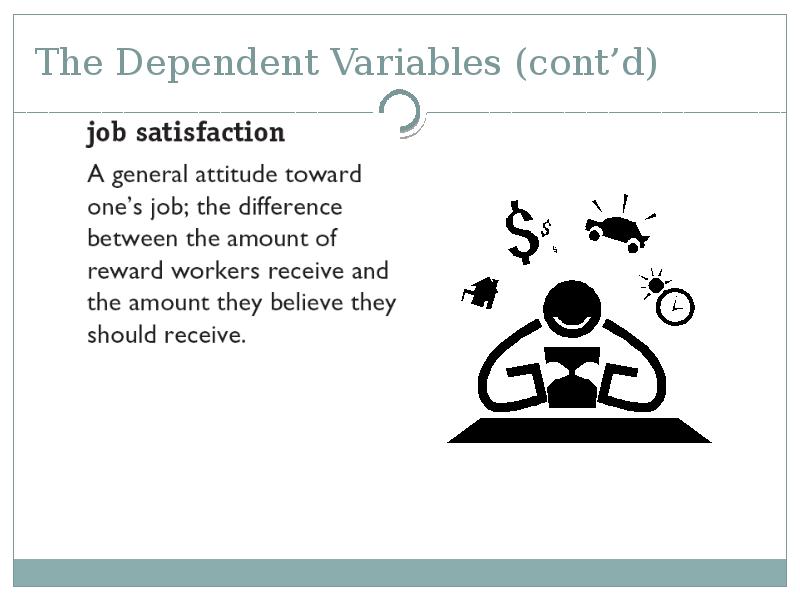
- 46. The Dependent Variables (cont’d)
- 47. Скачать презентацию


























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Introduction to the Field of Organizational Behavior можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























