Lesson 10 Java File I/O (NIO.2) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to: Use
- 3. New File I/O API (NIO.2)
- 4. Limitations of java.io.File
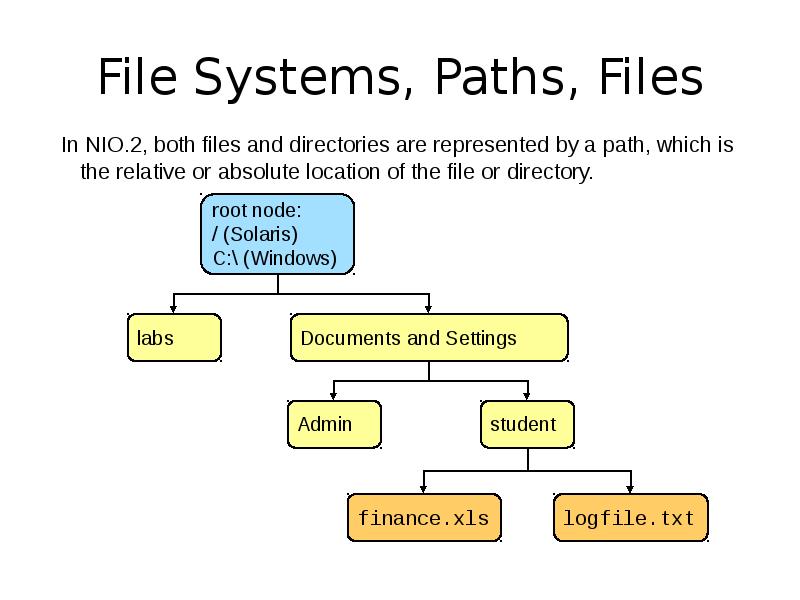
- 5. File Systems, Paths, Files In NIO.2, both files and directories are
- 6. Relative Path Versus Absolute Path A path is either relative or
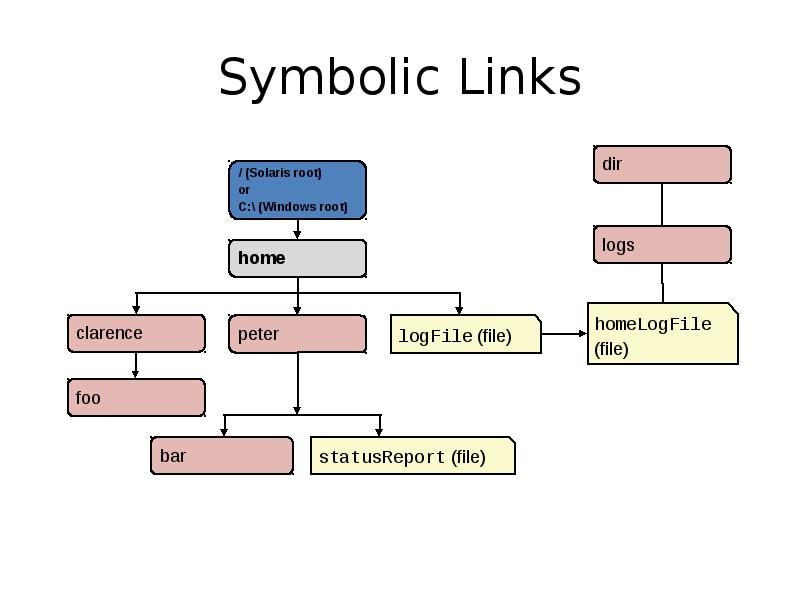
- 7. Symbolic Links
- 8. Java NIO.2 Concepts Prior to JDK 7, the java.io.File class was
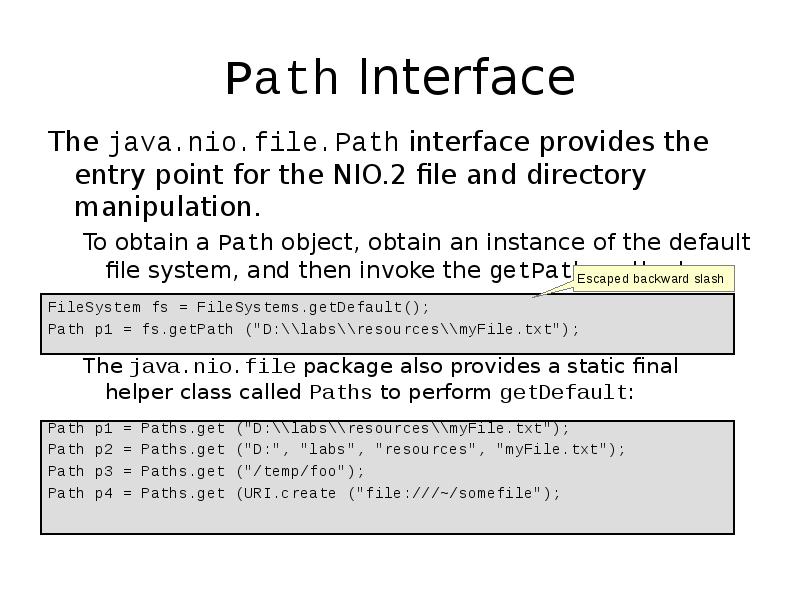
- 9. Path Interface The java.nio.file.Path interface provides the entry point for the
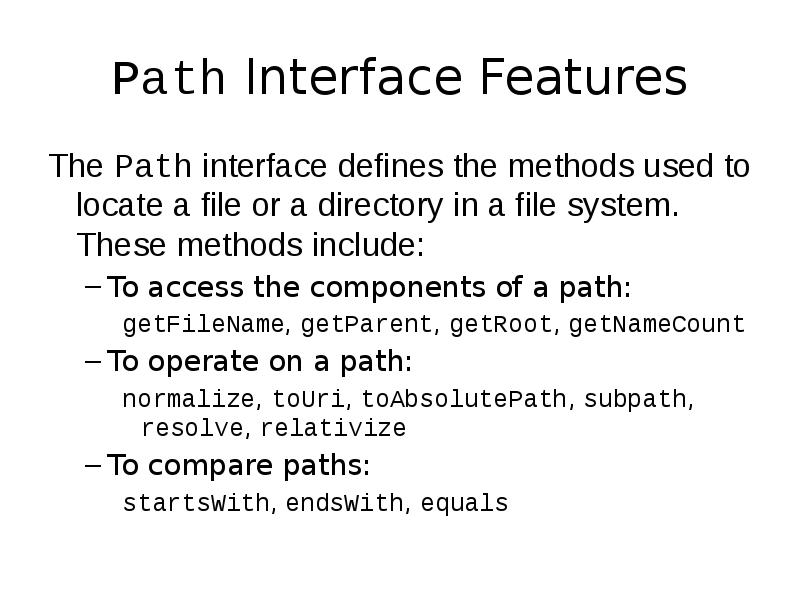
- 10. Path Interface Features The Path interface defines the methods used to
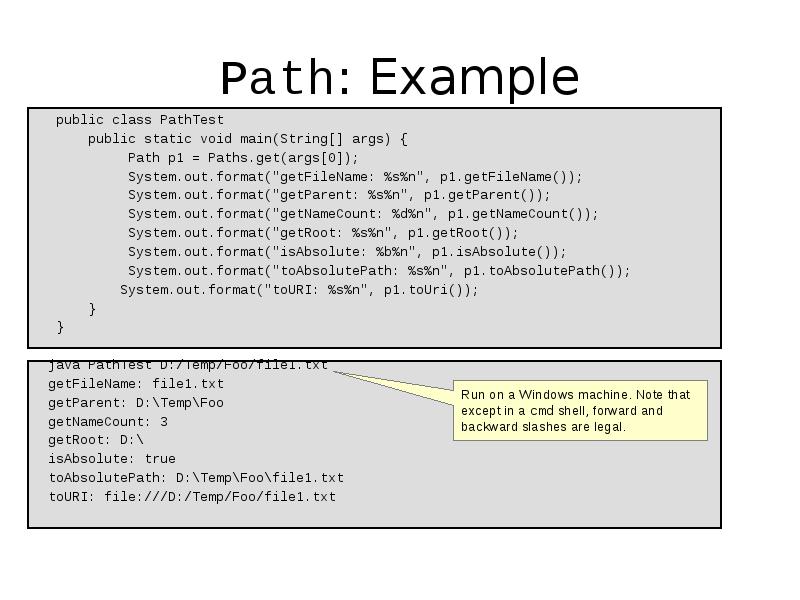
- 11. Path: Example public class PathTest public static void main(String[] args)
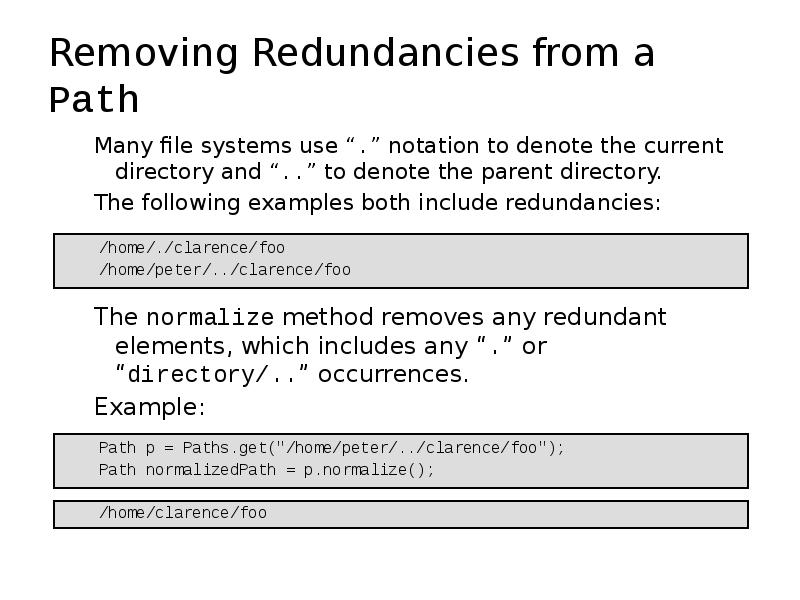
- 12. Removing Redundancies from a Path Many file systems use “.” notation
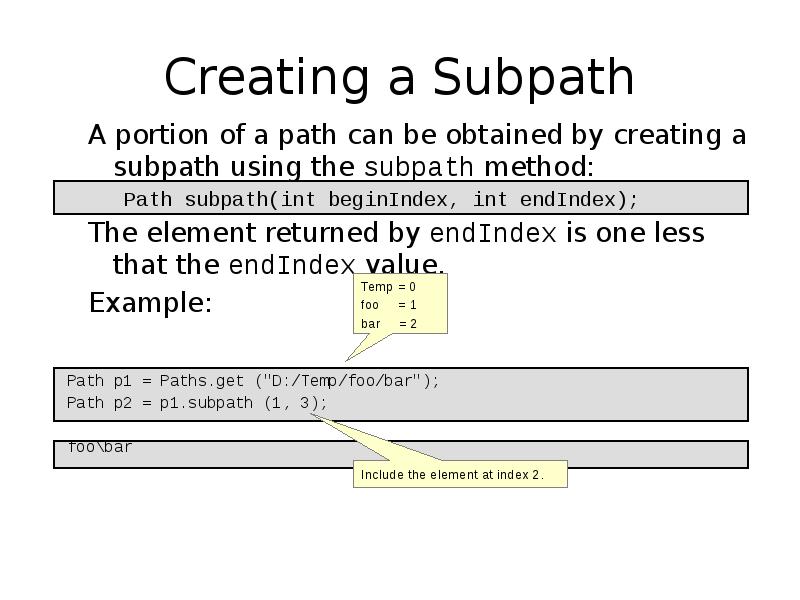
- 13. Creating a Subpath A portion of a path can be obtained
- 14. Joining Two Paths The resolve method is used to combine two
- 15. Creating a Path Between Two Paths The relativize method enables you
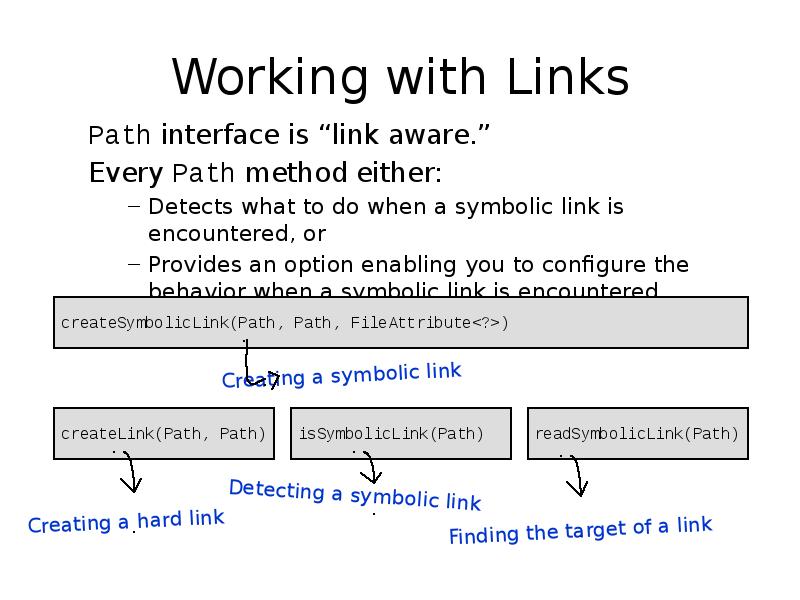
- 16. Working with Links Path interface is “link aware.” Every Path method either: Detects
- 17. Quiz Given a Path object with the following path: /export/home/heimer/../williams/./documents
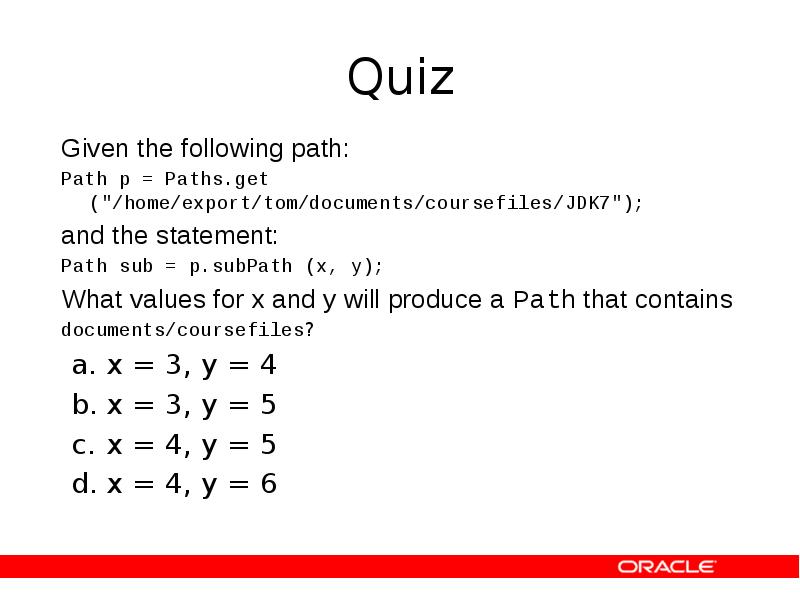
- 18. Quiz Given the following path: Path p = Paths.get ("/home/export/tom/documents/coursefiles/JDK7"); and
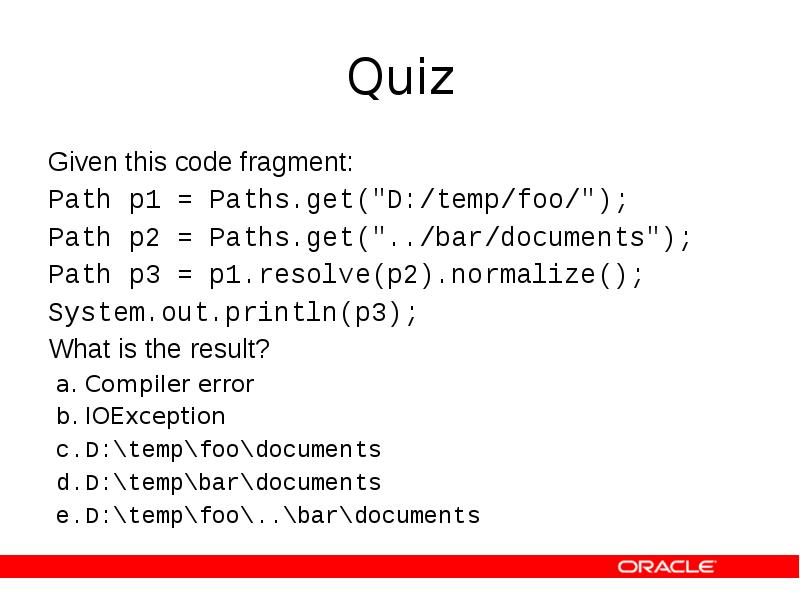
- 19. Quiz Given this code fragment: Path p1 = Paths.get("D:/temp/foo/"); Path p2
- 20. File Operations
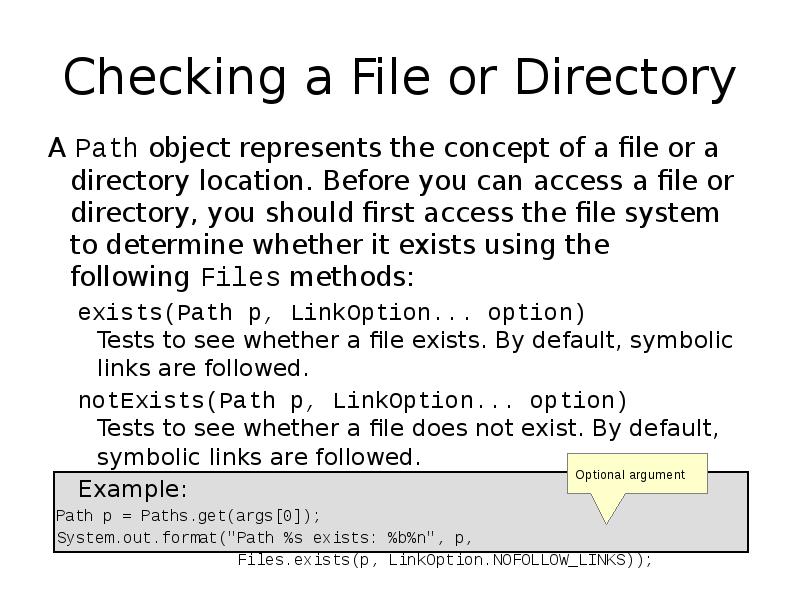
- 21. Checking a File or Directory A Path object represents the concept
- 22. Checking a File or Directory To verify that a file can
- 23. Creating Files and Directories Files and directories can be created using
- 24. Deleting a File or Directory You can delete files, directories, or
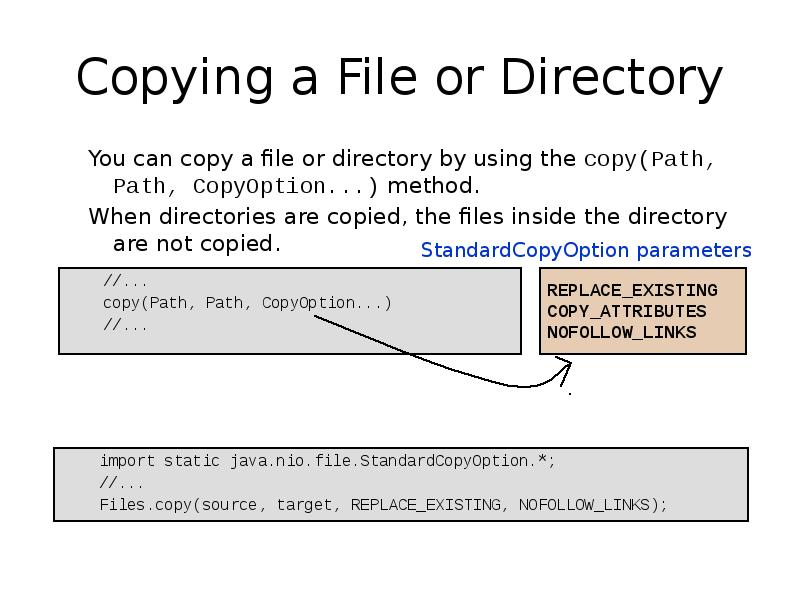
- 25. Copying a File or Directory You can copy a file or
- 26. Copying Between a Stream and Path You may also want to
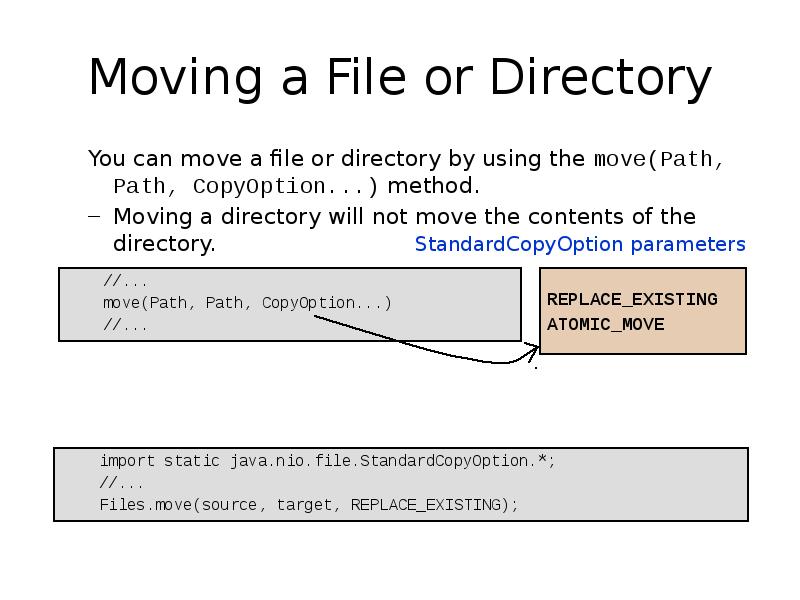
- 27. Moving a File or Directory You can move a file or
- 28. Listing a Directory’s Contents The DirectoryStream class provides a mechanism to
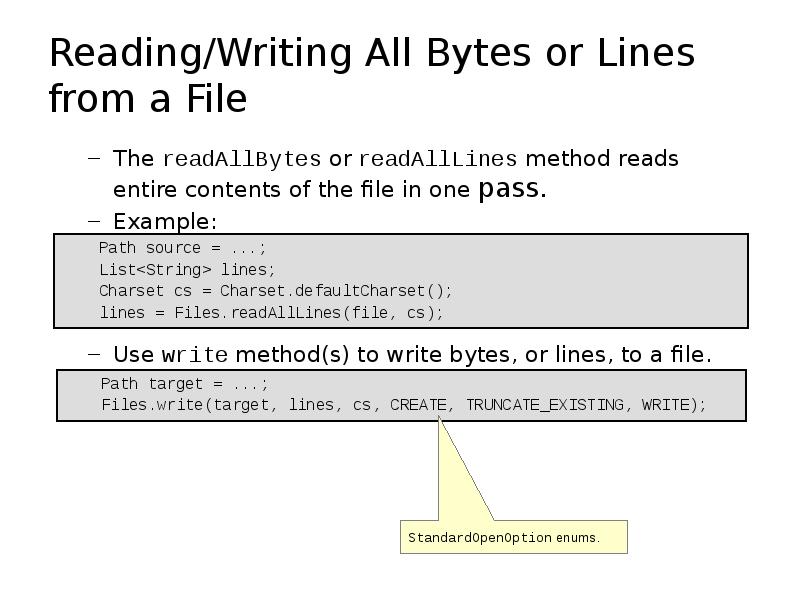
- 29. Reading/Writing All Bytes or Lines from a File The readAllBytes or
- 30. Channels and ByteBuffers Stream I/O reads a character at a time,
- 31. Random Access Files Random access files permit non-sequential, or random, access
- 32. Buffered I/O Methods for Text Files The newBufferedReader method opens a
- 33. Byte Streams NIO.2 also supports methods to open byte streams. To
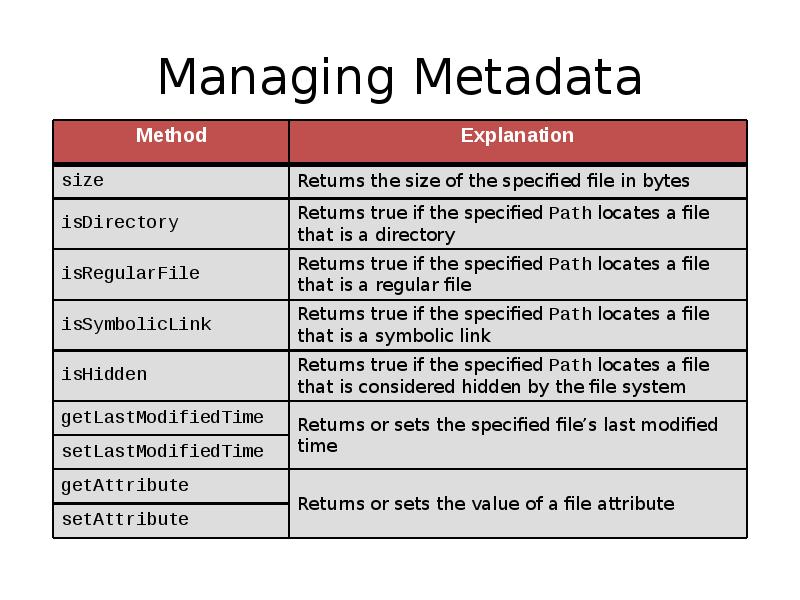
- 34. Managing Metadata
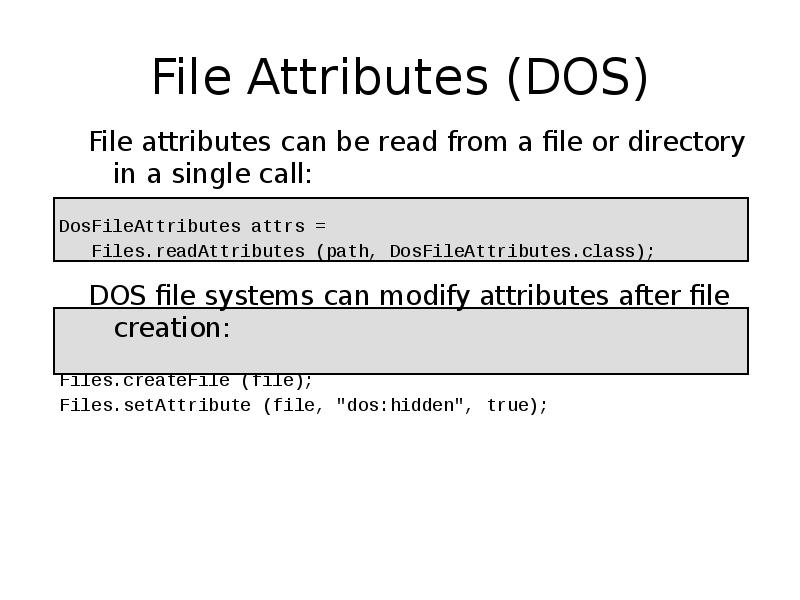
- 35. File Attributes (DOS) File attributes can be read from a file
- 36. DOS File Attributes: Example DosFileAttributes attrs = null; Path file =
- 37. POSIX Permissions With NIO.2, you can create files and directories on
- 38. Quiz Given the following fragment: Path p1 = Paths.get("/export/home/peter"); Path p2
- 39. Quiz Given this fragment: Path source = Paths.get(args[0]); Path target =
- 40. Quiz Given this fragment: Path source = Paths.get("/export/home/mcginn/HelloWorld.java"); Path newdir =
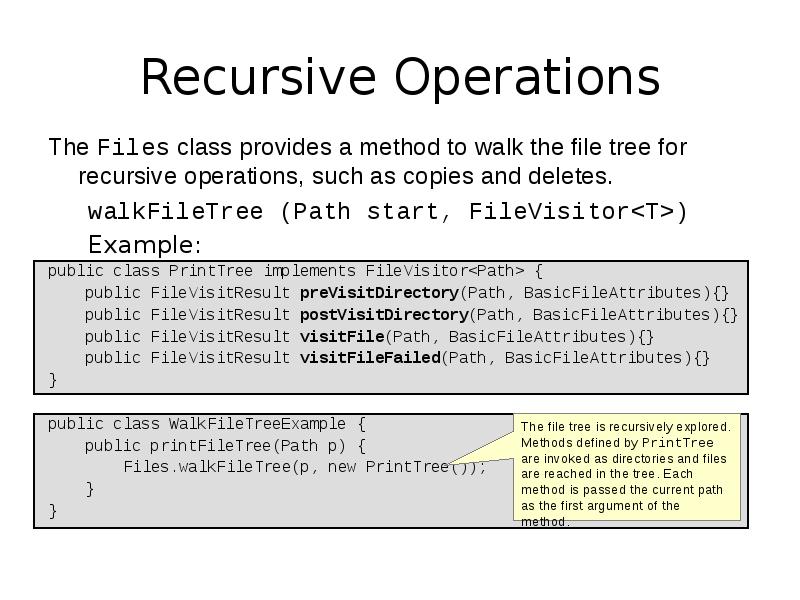
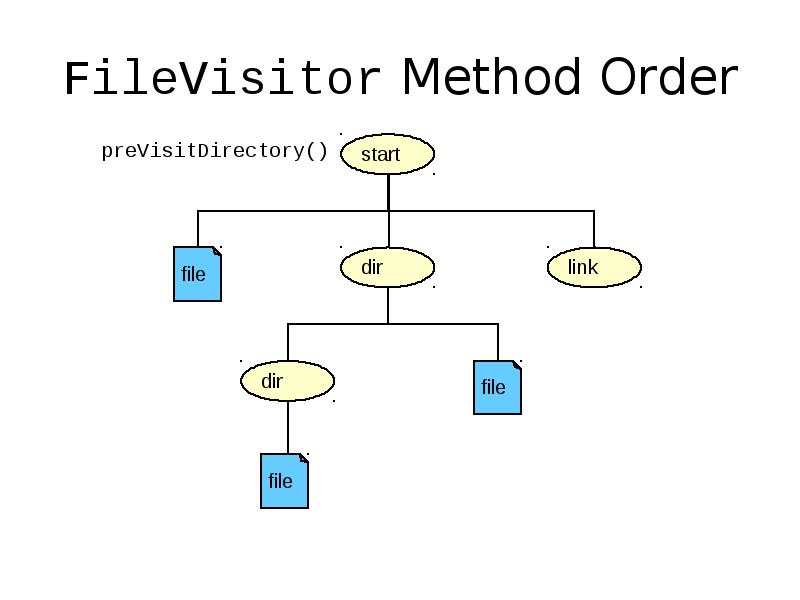
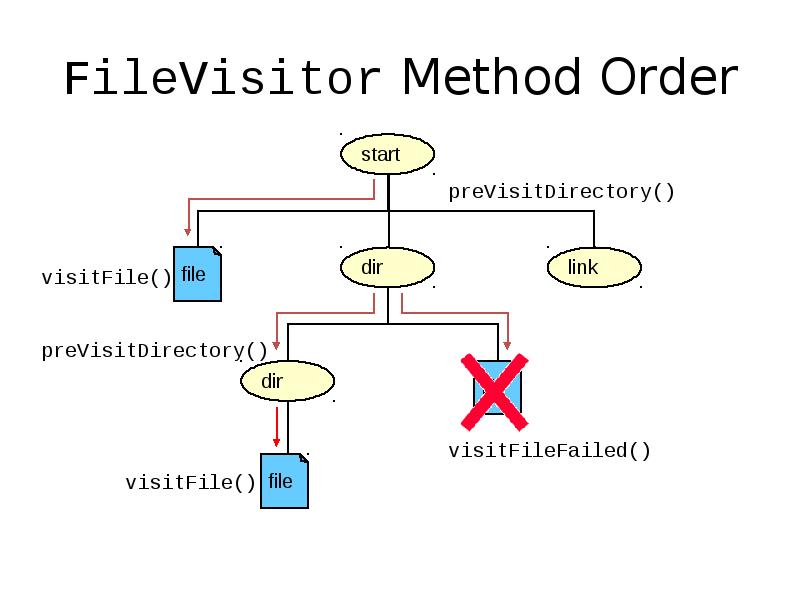
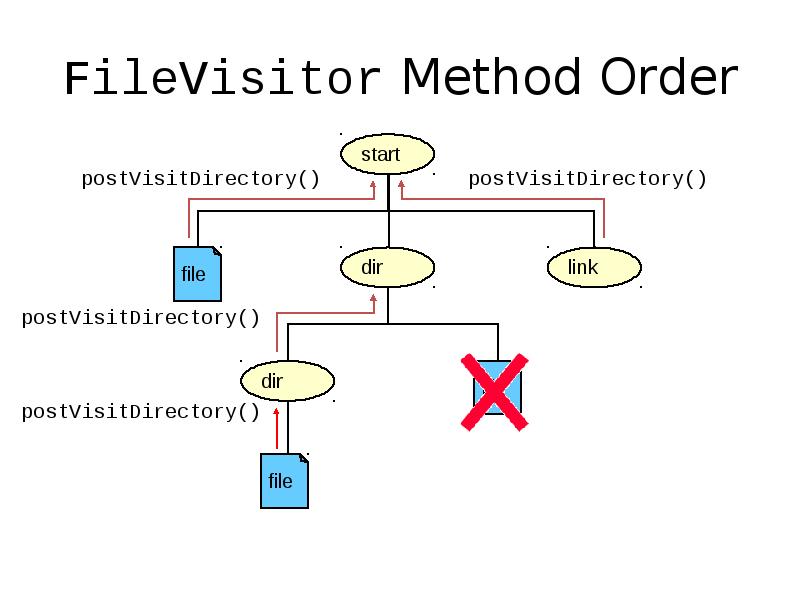
- 41. Recursive Operations The Files class provides a method to walk the
- 42. FileVisitor Method Order
- 43. FileVisitor Method Order
- 44. FileVisitor Method Order
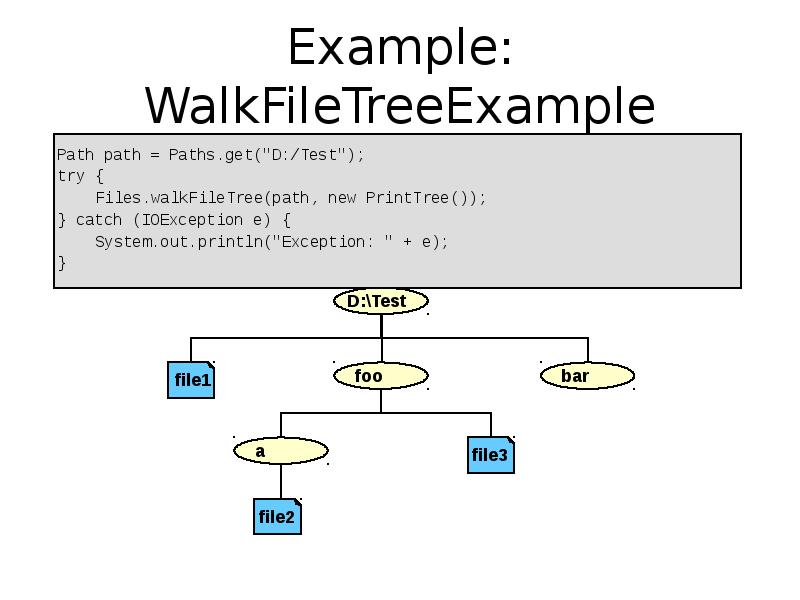
- 45. Example: WalkFileTreeExample Path path = Paths.get("D:/Test"); try { Files.walkFileTree(path, new
- 46. Finding Files To find a file, typically, you would search a
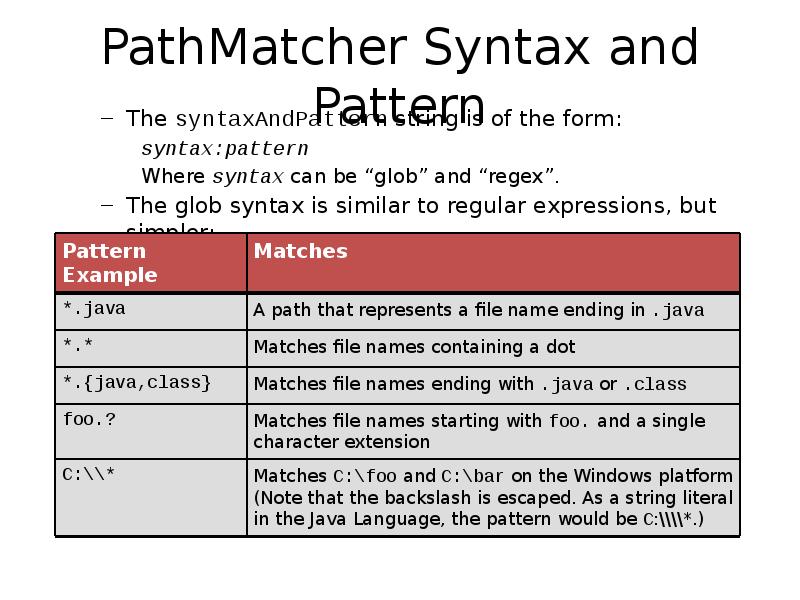
- 47. PathMatcher Syntax and Pattern The syntaxAndPattern string is of the form:
- 48. PathMatcher: Example public static void main(String[] args) { // ...
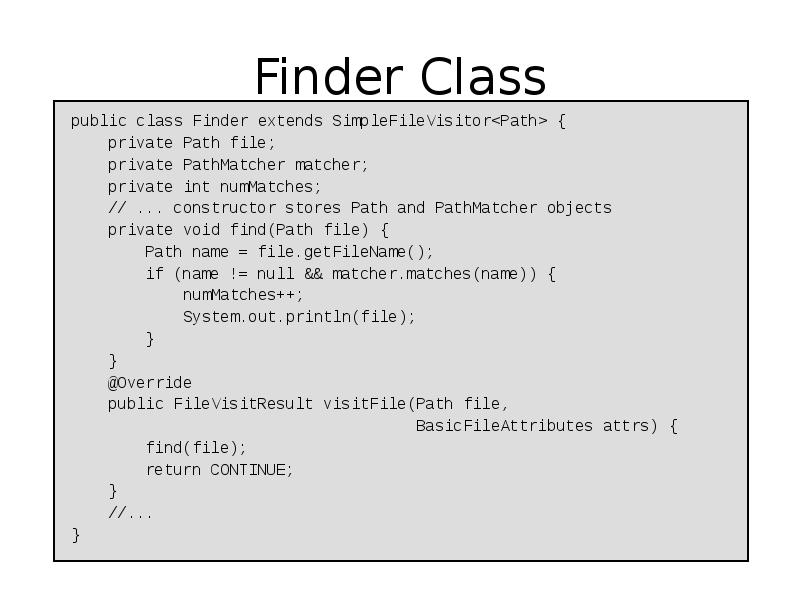
- 49. Finder Class public class Finder extends SimpleFileVisitor<Path> { private Path
- 50. Other Useful NIO.2 Classes The FileStore class is useful for providing
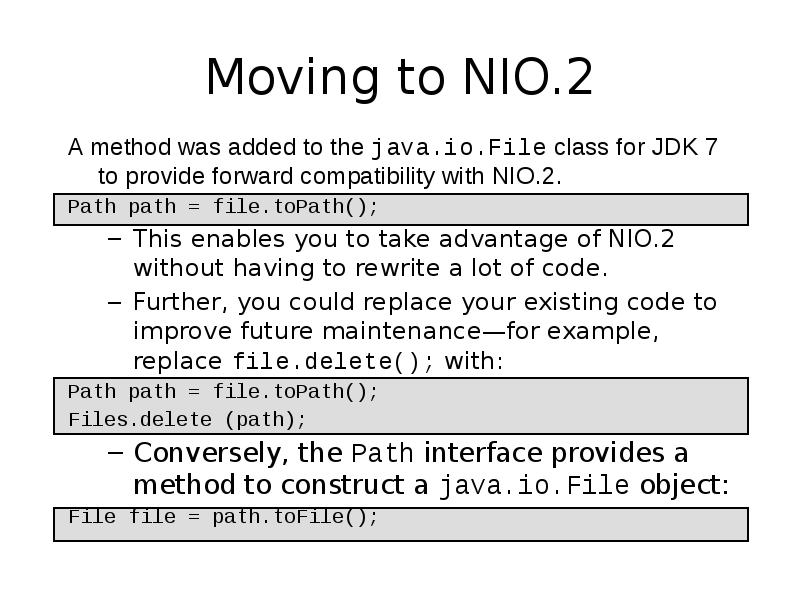
- 51. Moving to NIO.2 A method was added to the java.io.File class
- 52. Summary In this lesson, you should have learned how to: Use
- 53. Quiz To copy, move, or open a file or directory using
- 54. Quiz Given any starting directory path, which FileVisitor method(s) would you
- 55. Quiz Given an application where you want to count the depth
- 56. Скачать презентацию



















![Quiz
Given this fragment:
Path source = Paths.get(args[0]);
Path target = Quiz
Given this fragment:
Path source = Paths.get(args[0]);
Path target =](/documents_7/72e3268b143e878eab07a4523a90f1b3/img38.jpg)


![PathMatcher: Example
public static void main(String[] args) {
PathMatcher: Example
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_7/72e3268b143e878eab07a4523a90f1b3/img47.jpg)





Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























