Lung Examination: Abnormal презентация
Содержание
- 5. Illustrative Pathological problems Consolidation Atelectasis Pleural effusion Pneumothorax Mass Diffuse lung
- 12. Steps General Examination Mediastinal position Chest expansion Lung resonance Breath sounds
- 13. General Examination Respiratory rate Pattern of breathing Cyanosis Clubbing Weight Cough
- 14. Respiratory Rate Bradypnea: rate less than 8 per minute Tachypnea:
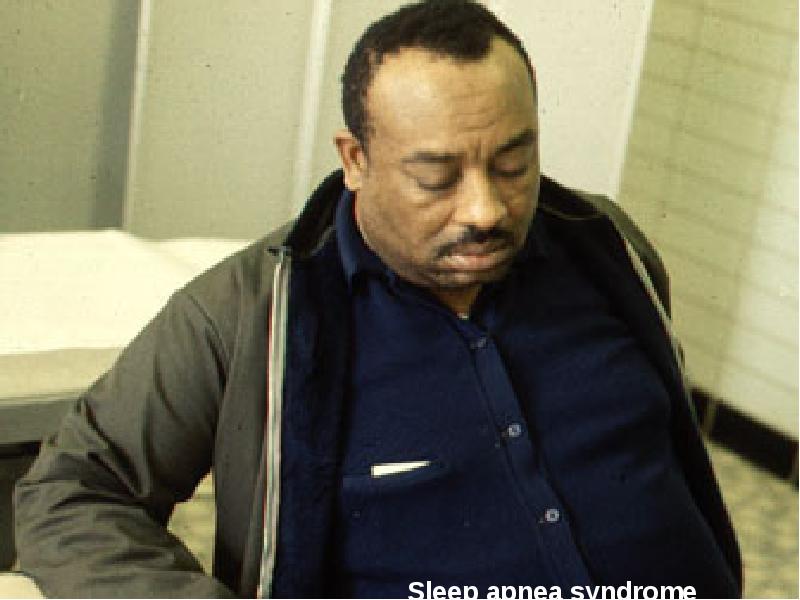
- 15. Pattern of Breathing Kussmals Sleep apnea Cheyne strokes Pursed lip breathing
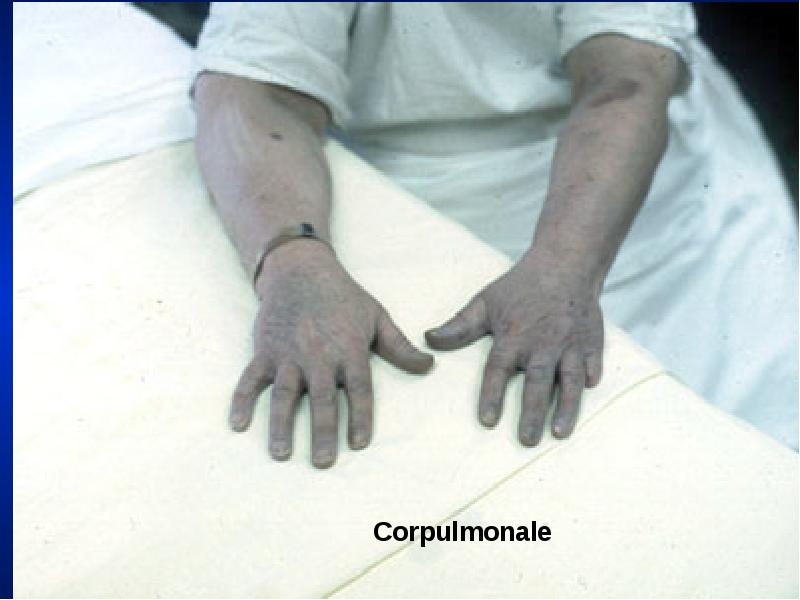
- 17. Central Cyanosis Results from pulmonary dysfunction, the mucous membrane of conjunctiva
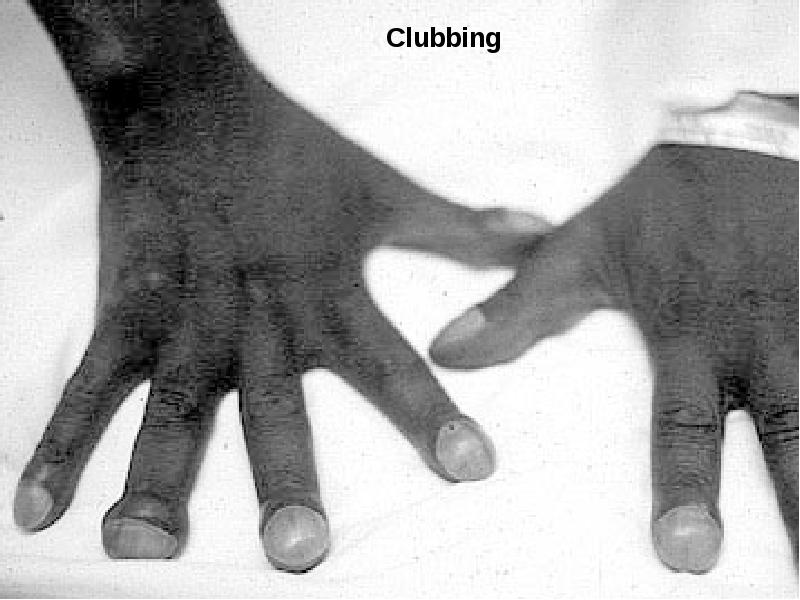
- 21. Clubbing In clubbing, there is widening of the AP and lateral
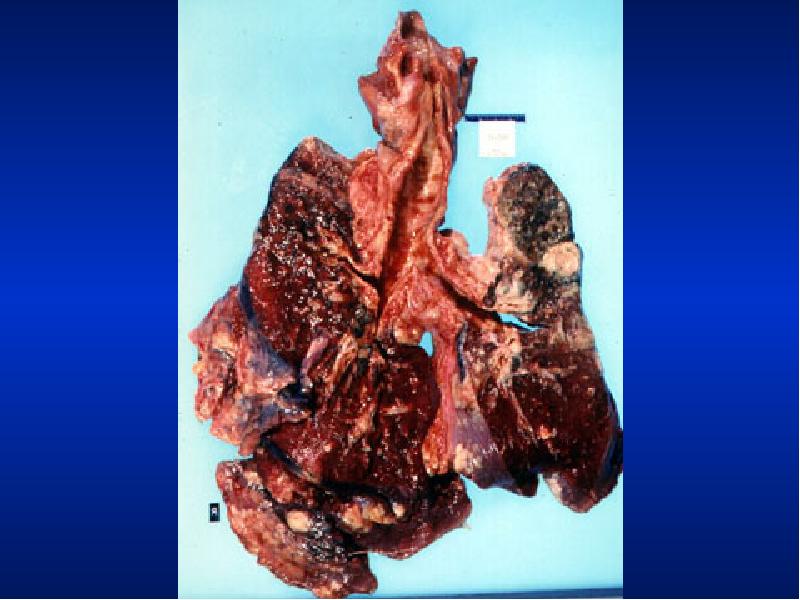
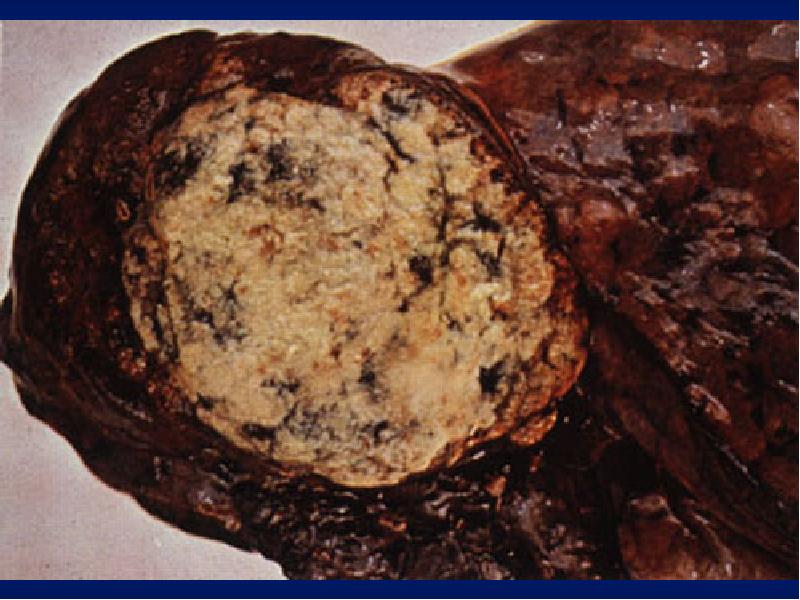
- 22. Significance: Clubbing Observed In: Intrathoracic malignancy: Primary or secondary (lung, pleural,
- 24. Weight Emaciation cachectic Malignancy Tuberculosis
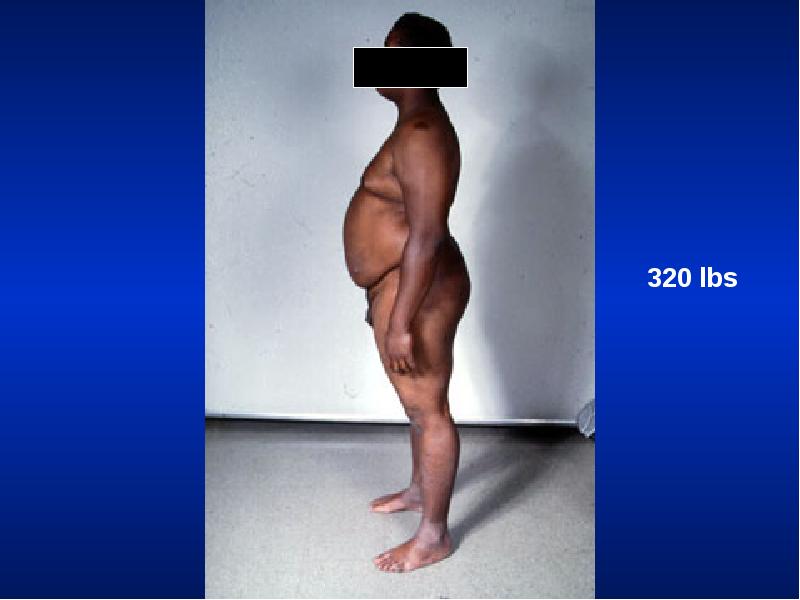
- 26. Weight Obese: Sleep apnea syndrome
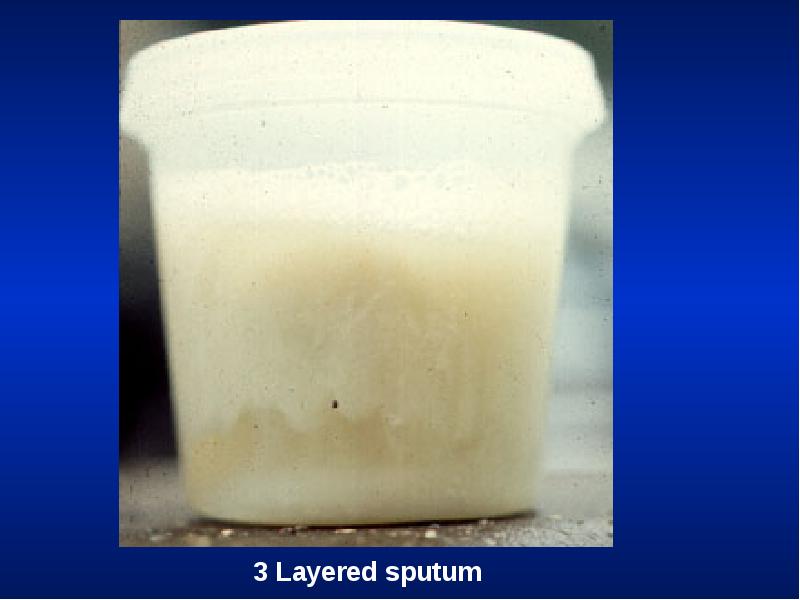
- 28. Cough Productive Dry Whooping Bovine
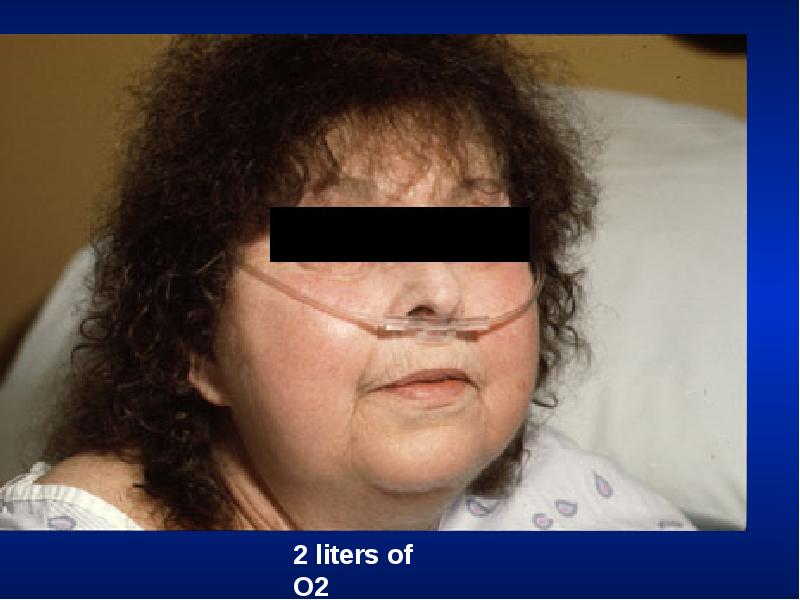
- 30. Hospital Setting Isolation room Oxygen set up
- 31. Effort of Ventilation Person appears uncomfortable. Breathing seems voluntary. Accessory muscles
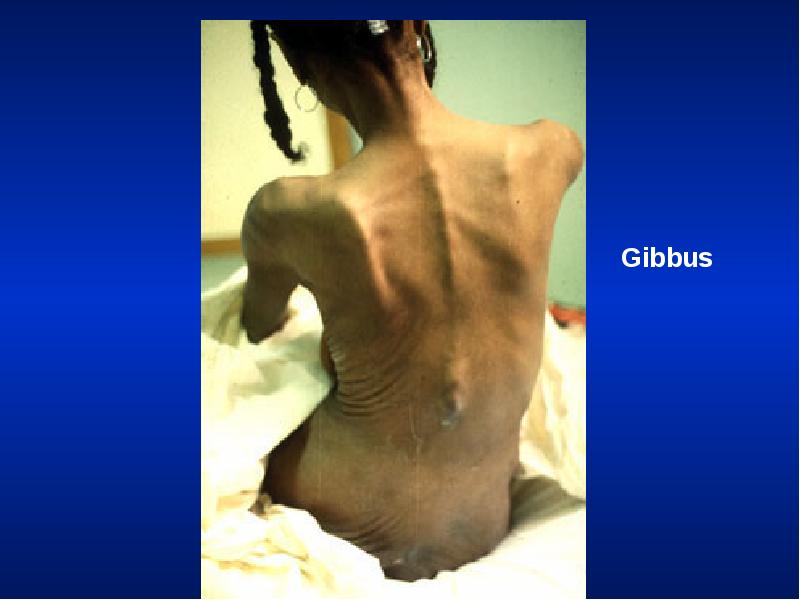
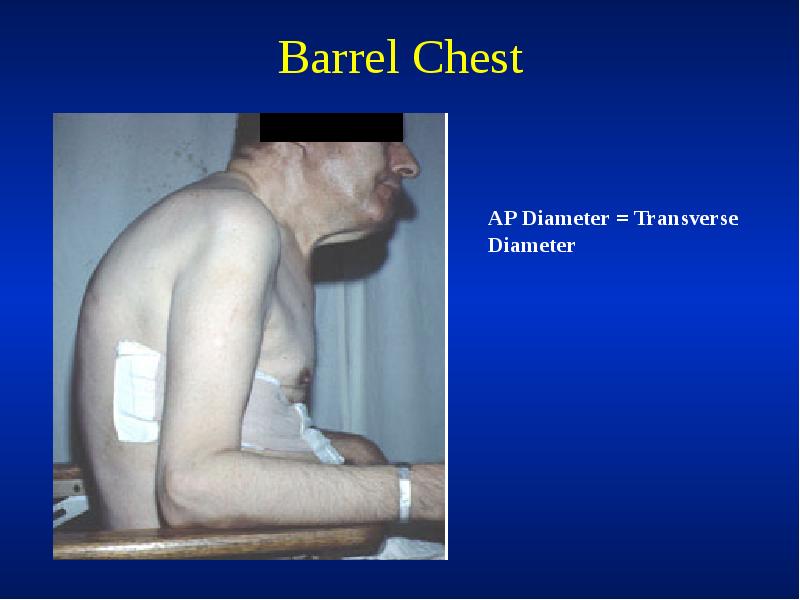
- 32. Resting Size and Shape of Thorax Barrel chest Kyphosis Scoliosis Pectus
- 33. Barrel Chest
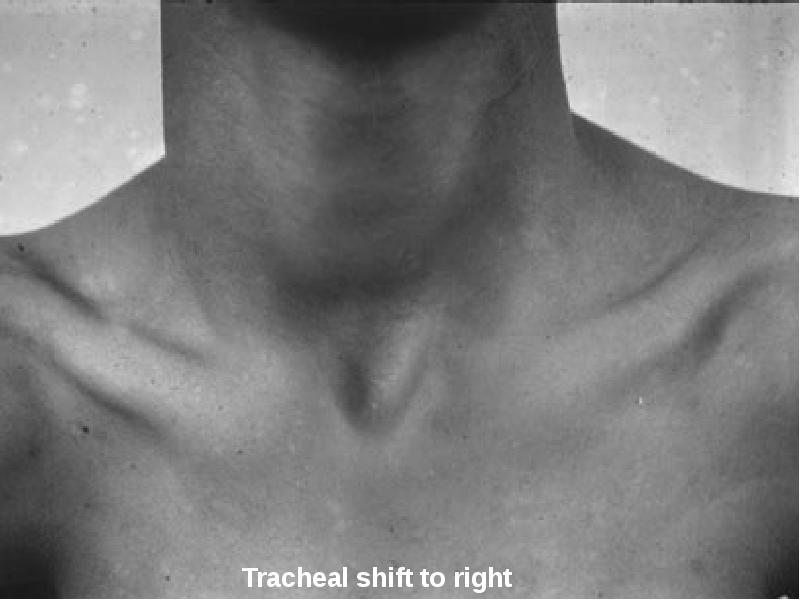
- 34. Tracheal Position: Mediastinum Any deviation of the mediastinum is abnormal Lateral
- 36. Chest Expansion Asymmetrical chest expansion is abnormal The abnormal side expands
- 37. Percussion: Decreased or Increased Resonance is Abnormal Dullness Decreased resonance is
- 38. Breath Sounds: Diminished or Absent Intensity of breath sounds, in general,
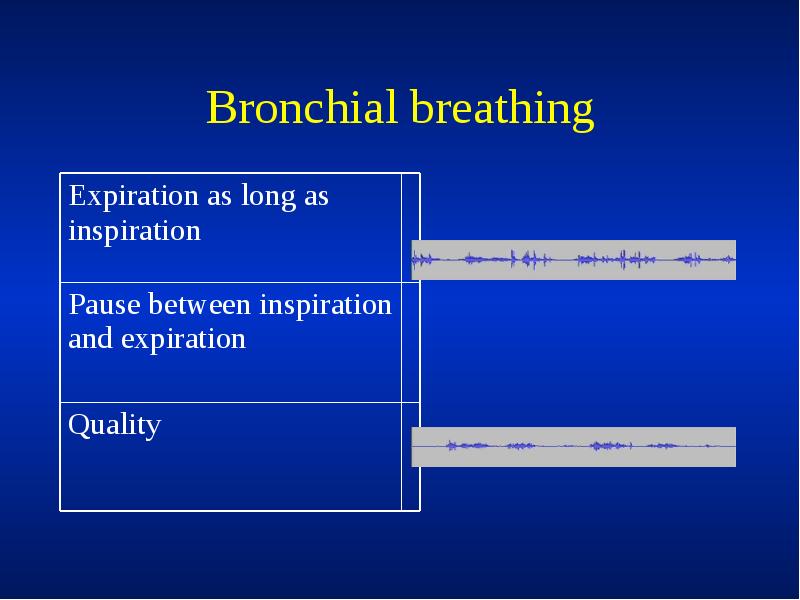
- 39. Bronchial Bronchial breathing anywhere other than over the trachea, right clavicle
- 40. Bronchial breathing
- 41. Rhonchi Rhonchi are long continuous adventitious sounds, generated by obstruction to
- 42. Rhonchi
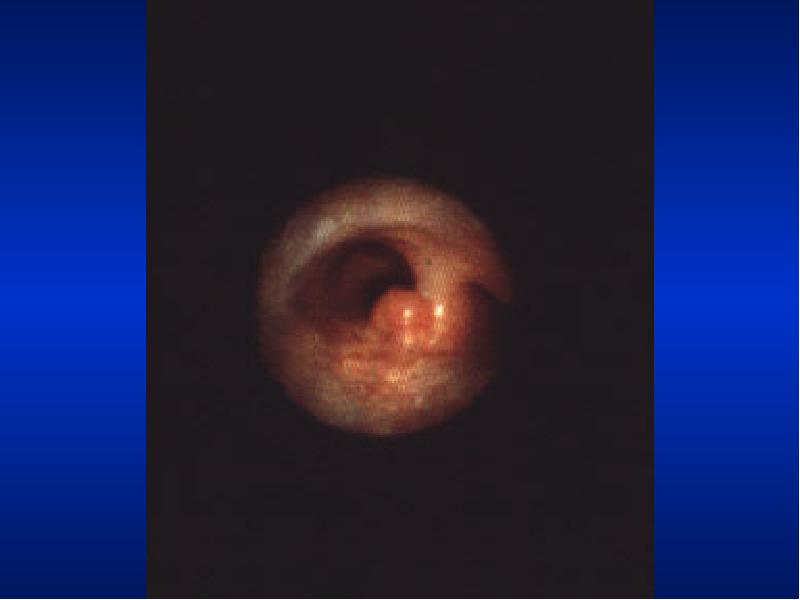
- 43. Rhonchi Localized rhonchi suggests obstruction of any etiology e.g., tumor, foreign
- 44. Pleural Rub Normal parietal and visceral pleura glide smoothly during respiration.
- 45. Pleural rub
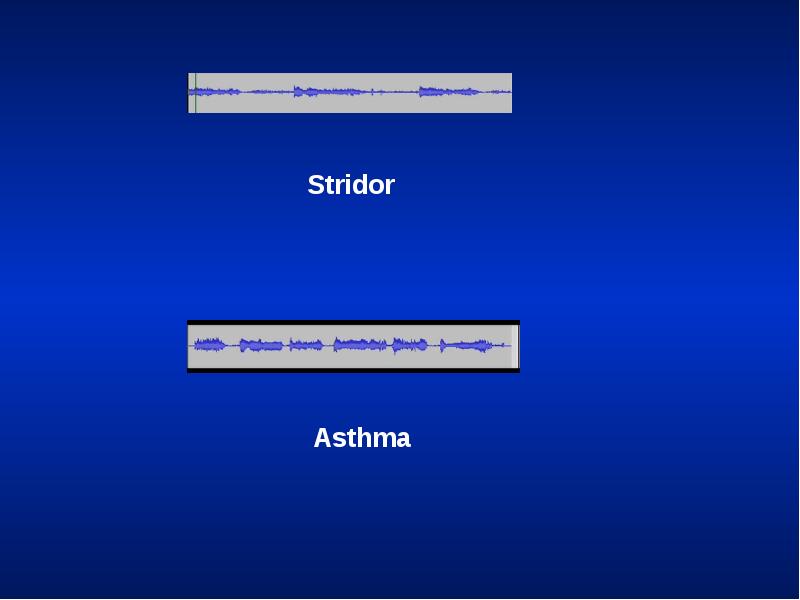
- 46. Stridor Loud audible inspiratory rhonchi is called a stridor. Inspiratory rhonchi
- 48. Crackles Interrupted adventitious sounds are called crackles. Make a notation about
- 49. Crackles When the crackles are heard at the end of inspiration
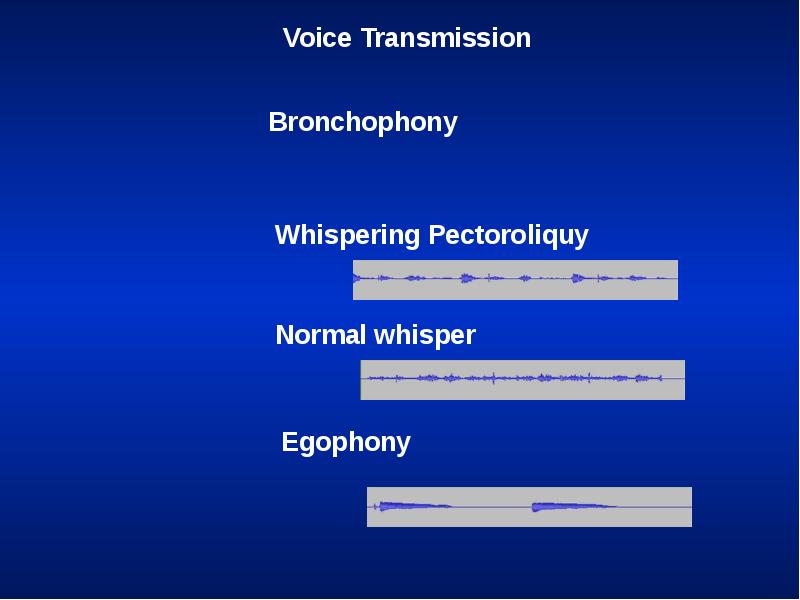
- 50. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance) Asymmetrical voice transmission points to
- 51. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance) Decreased: A quantitative decrease in
- 53. Скачать презентацию


































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























