Old English Pronouns презентация
Содержание
- 2. Types of pronouns in Old English: 1)Personal 2)Possessive 3)Demonstrative 4)Interrogative 5)Definite
- 3. Personal pronouns As in Gothic, there were singular, plural and dual
- 4. Personal pronouns
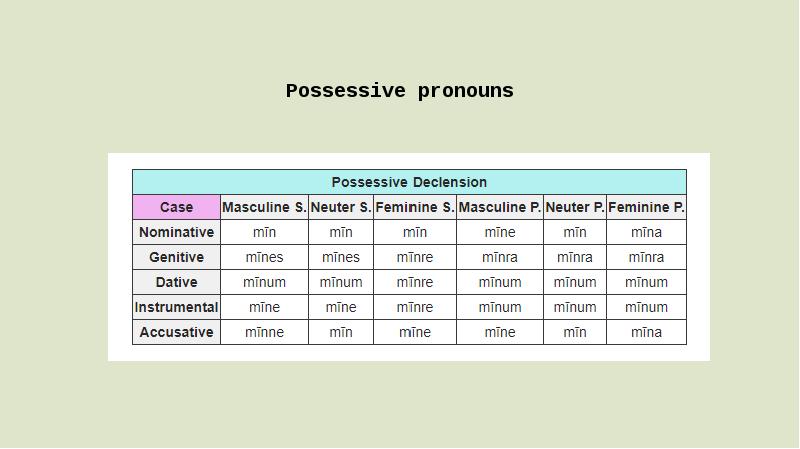
- 5. Possessive pronouns This type is derived from the genitive case of
- 6. Possessive pronouns
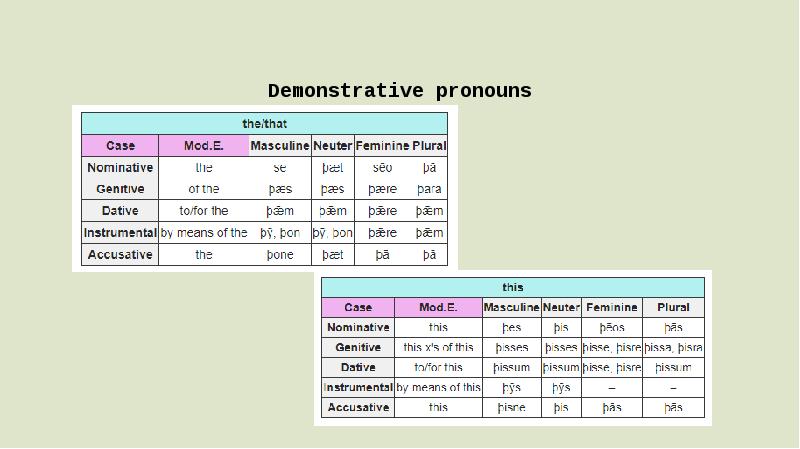
- 7. Demonstrative pronouns There were two demonstrative pronouns: sē, which could function
- 8. Demonstrative pronouns
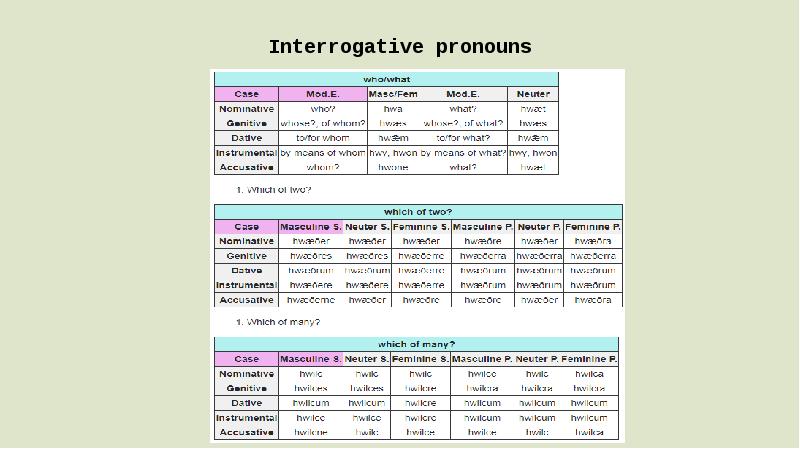
- 9. Interrogative pronouns The pronouns hwā ‘who’ and hwæt ‘what’ agreed with
- 10. Interrogative pronouns
- 11. Definite pronouns There were the pronouns ᵹehwā ‘every’ (declined as the
- 12. Indefinite pronouns The indefinite pronouns sum ‘some’ and ǣniᵹ ‘any’ were
- 13. Negative pronouns Included pronouns nān and nǣniᵹ (both with meaning ‘no’,
- 14. Relative pronouns They included the most popular pronoun þe and
- 15. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























