Organizing Data Graphical and Tabular Descriptive Techniques презентация
Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Overall: To give students a basic understanding of best
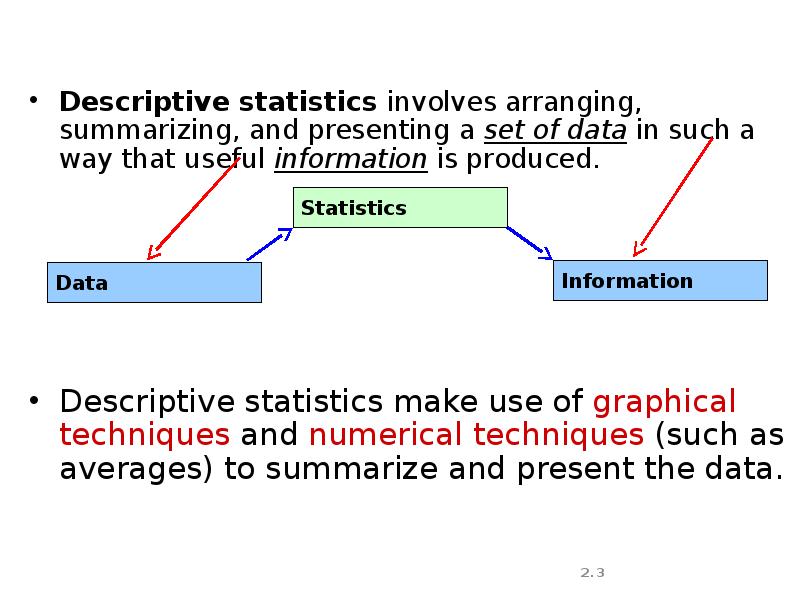
- 3. Descriptive statistics involves arranging, summarizing, and presenting a set of data
- 4. DATA MINING Most companies routinely collect data – at the cash
- 5. DATA MINING is a collection of methods for obtaining useful knowledge
- 6. 1. Marketing and sales: companies have lots of information about past
- 7. Finance: Mining of financial data can be useful in forming and
- 8. Statistical methods, such as hypothesis testing, are helpful as part of
- 9. 3. Product design: What particular combinations of features are customers ordering
- 10. 4. Production 4. Production Imagine a factory running 24/7
- 11. 5. Fraud detections: 5. Fraud detections: Fraud can affect many
- 12. YOU once received a telephone call from your credit card company
- 13. Data mining is a large task that involves combining resources from
- 14. Statistics: All of the basic activities of statistics are involved: a
- 15. Some specialized statistical methods are particularly useful, including classification analysis (also
- 16. Computer science: Efficient algorithms (computer instructions) are needed for collecting, maintaining,
- 17. Optimization: Optimization: These methods help you achieve a goal, which might
- 18. Alternatively, the goal might be more vague such as obtaining a
- 19. WHAT IS PROBABILITY? Probability is a what if tool for understanding
- 20. You might learn, for example, that an international project has only
- 21. Here are additional examples of situations where finding the appropriate answer
- 22. 3. What are the chances that a foreign country (where you
- 23. Probability is the inverse of statistics. Whereas statistics helps you go
- 24. Probability also works together with statistics by providing a solid foundation
- 26. Definitions… A variable [Typically called a “random” variable since we do
- 27. We Deal with “2” Types of Data Numerical/Quantitative Data [Real Numbers]:
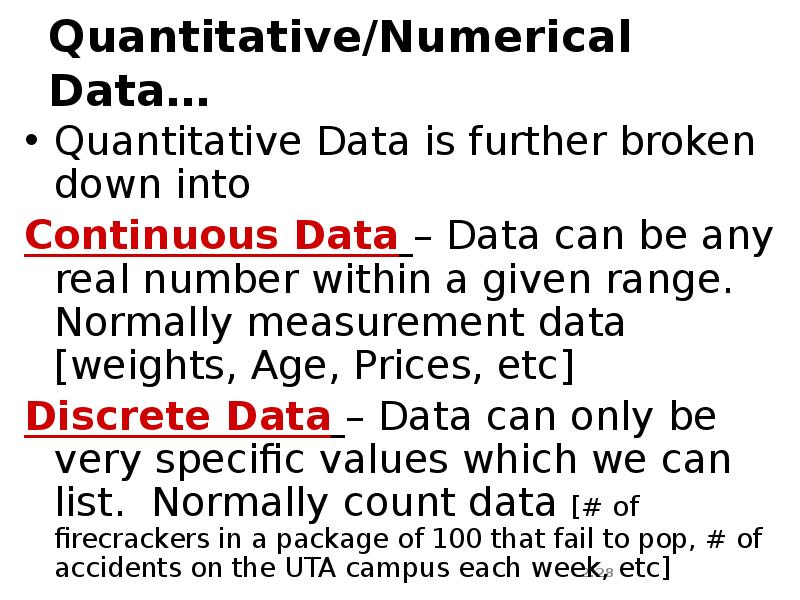
- 28. Quantitative/Numerical Data… Quantitative Data is further broken down into Continuous Data
- 29. Qualitative/Categorical Data Nominal Data [has no natural order to the values].
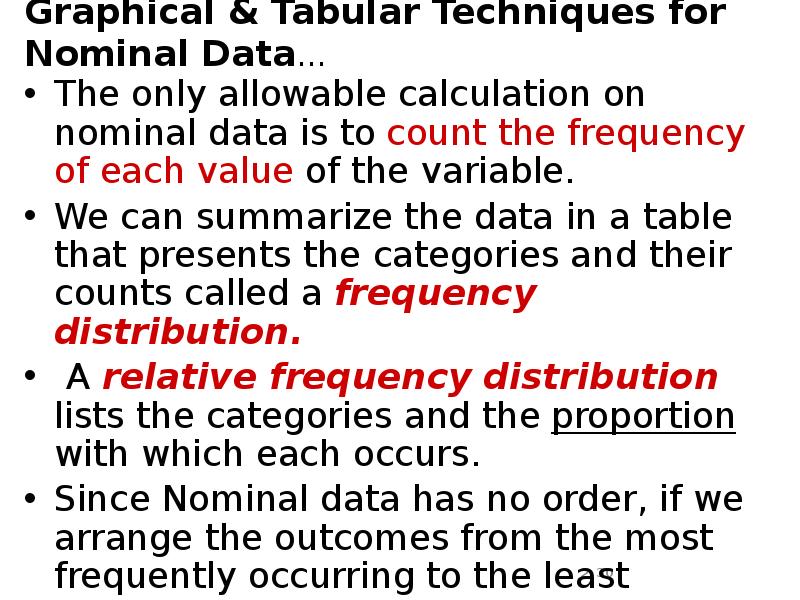
- 30. Graphical & Tabular Techniques for Nominal Data… The only allowable calculation
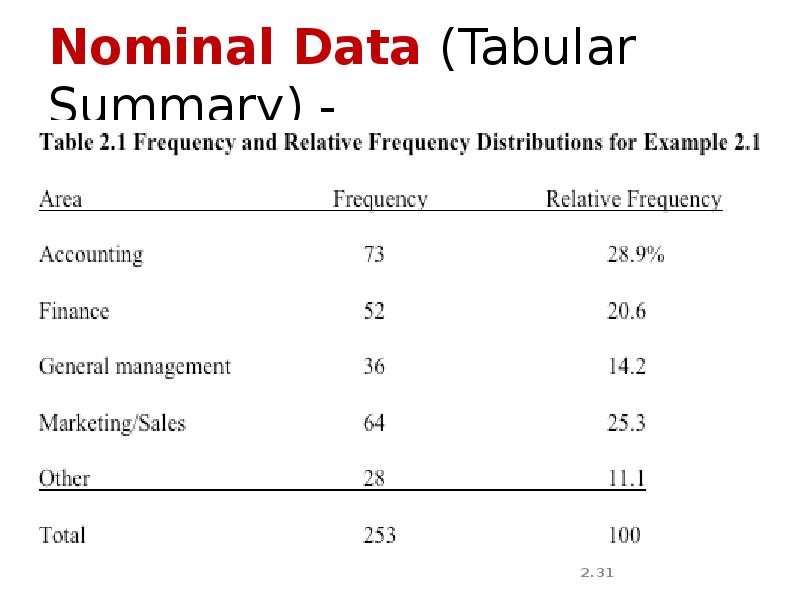
- 31. Nominal Data (Tabular Summary) -
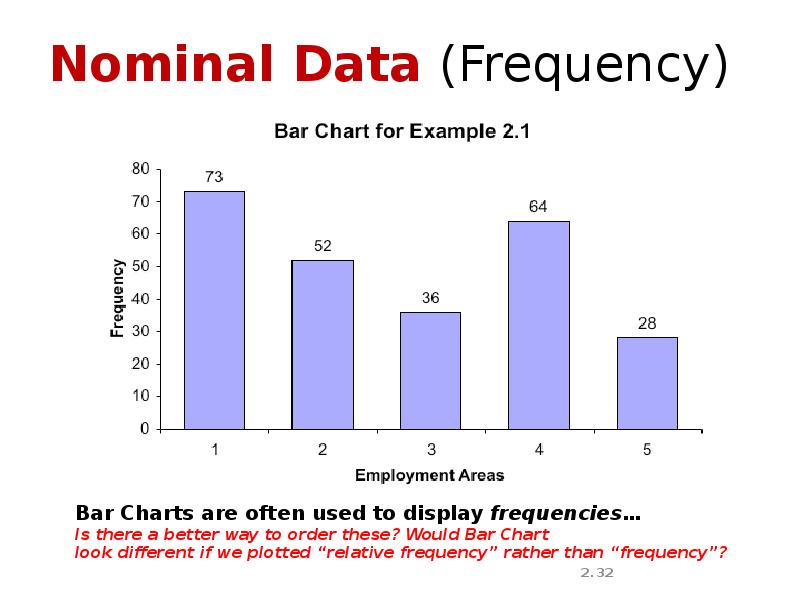
- 32. Nominal Data (Frequency)
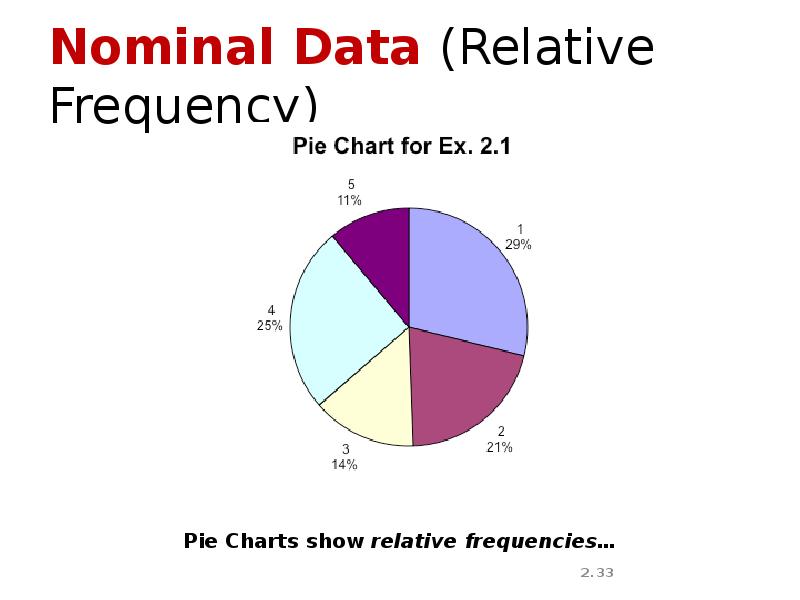
- 33. Nominal Data (Relative Frequency)
- 34. Frequency Distributions Definition A frequency distribution for qualitative data lists all
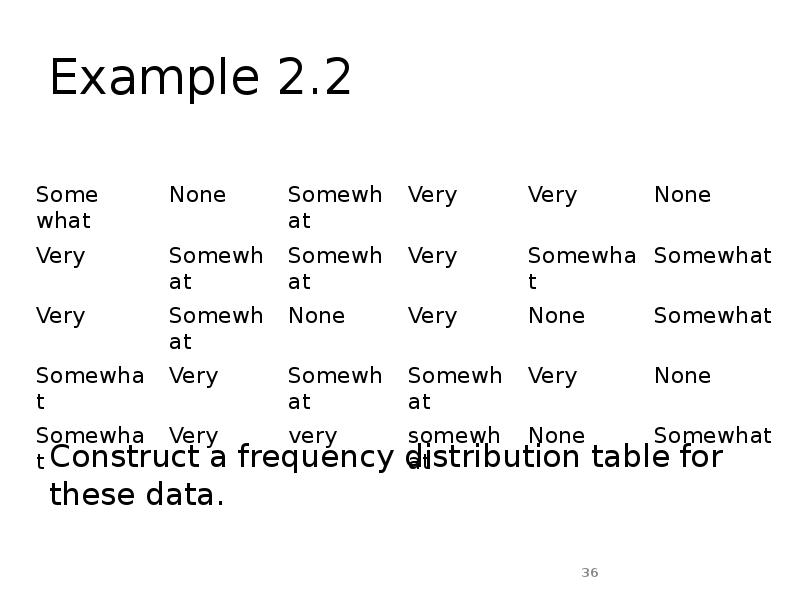
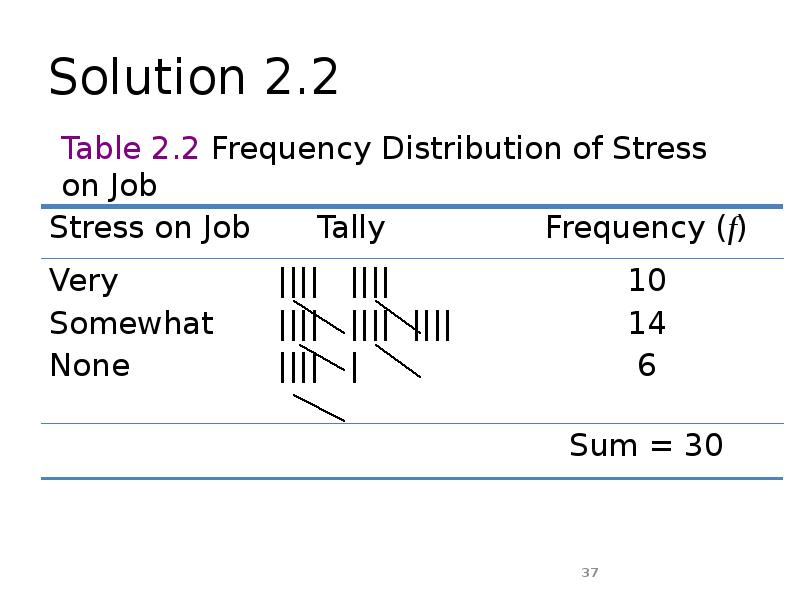
- 35. Example 2.2 A sample of 30 employees from large companies was
- 36. Example 2.2
- 37. Solution 2.2
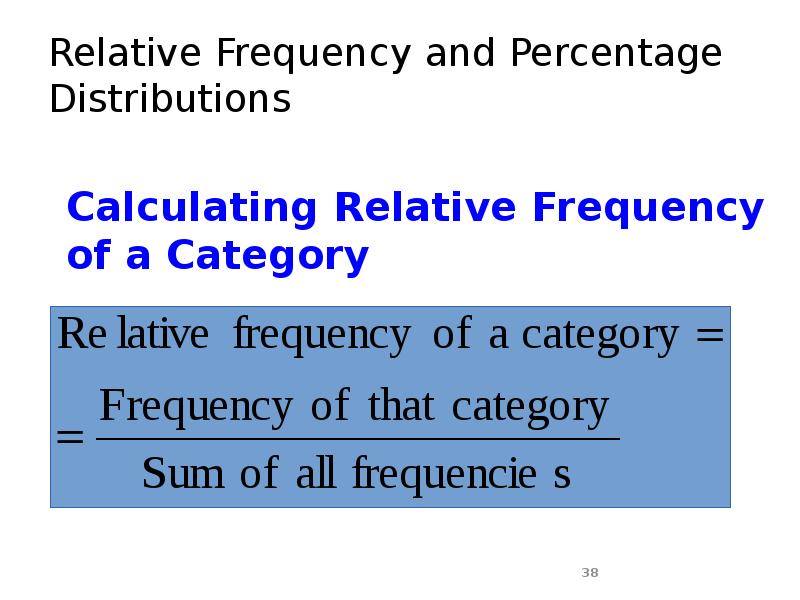
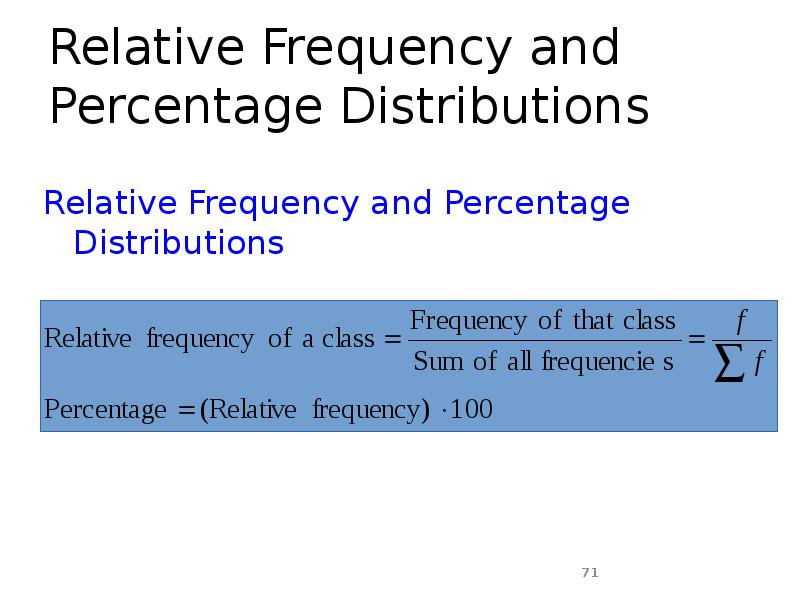
- 38. Relative Frequency and Percentage Distributions Calculating Relative Frequency of a Category
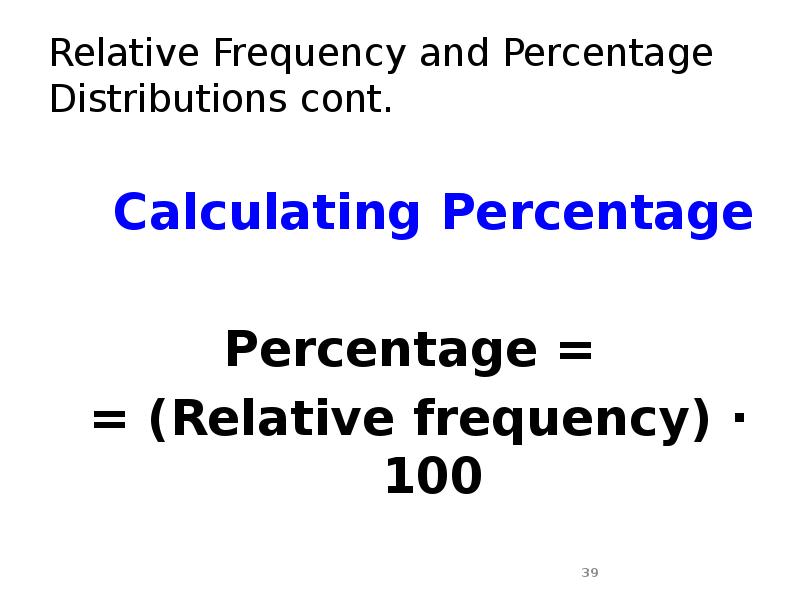
- 39. Relative Frequency and Percentage Distributions cont. Calculating Percentage Percentage =
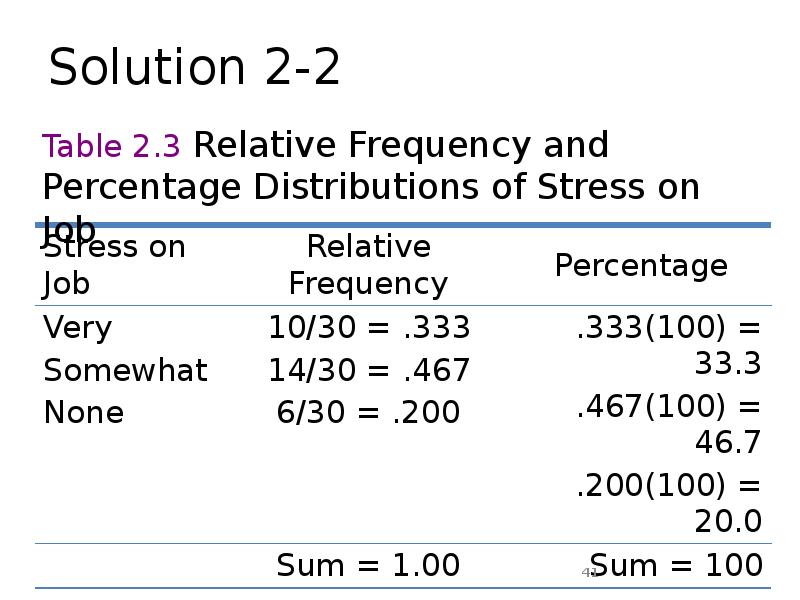
- 40. Example 2.3 Determine the relative frequency and percentage for the data
- 41. Solution 2-2
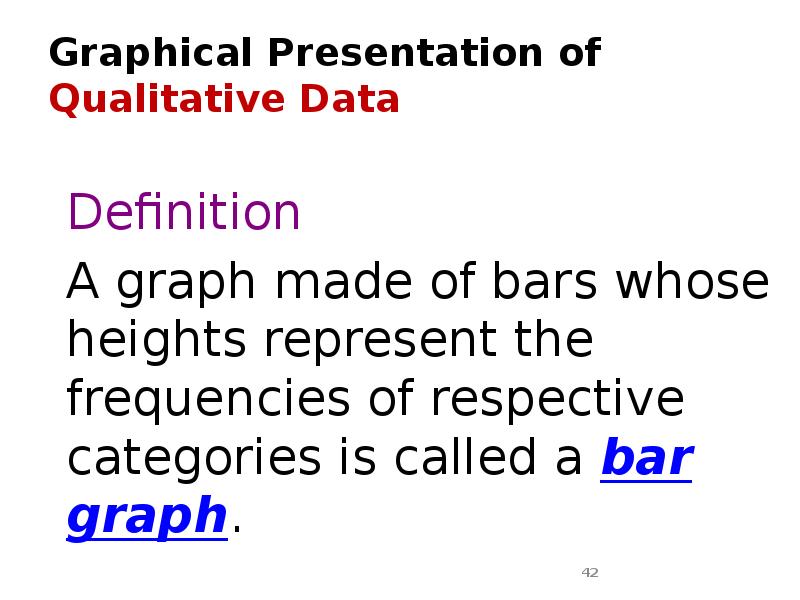
- 42. Graphical Presentation of Qualitative Data Definition A graph made of bars
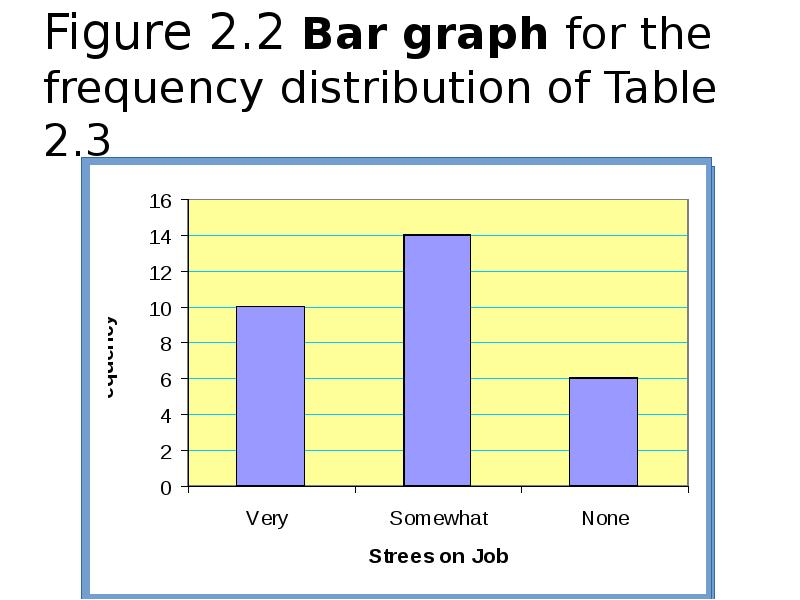
- 43. Figure 2.2 Bar graph for the frequency distribution of Table 2.3
- 44. Graphical Presentation of Qualitative Data cont. Definition A circle divided into
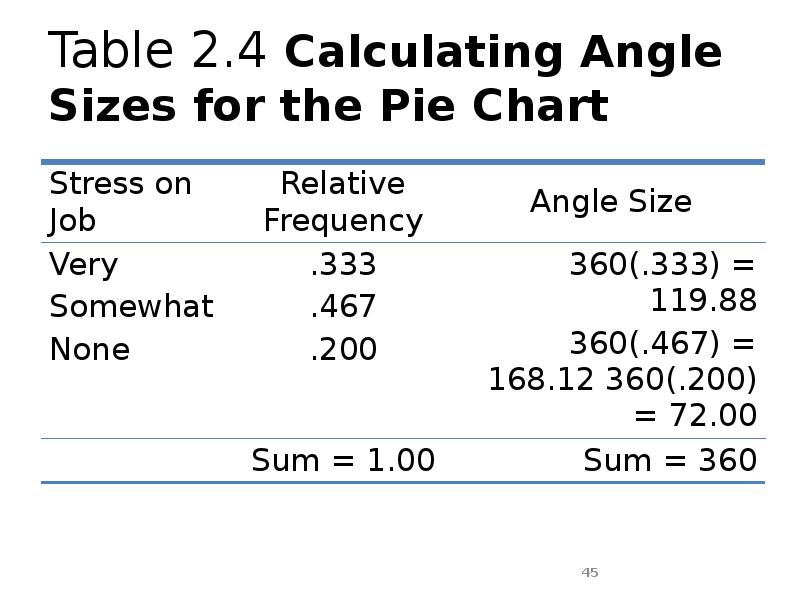
- 45. Table 2.4 Calculating Angle Sizes for the Pie Chart
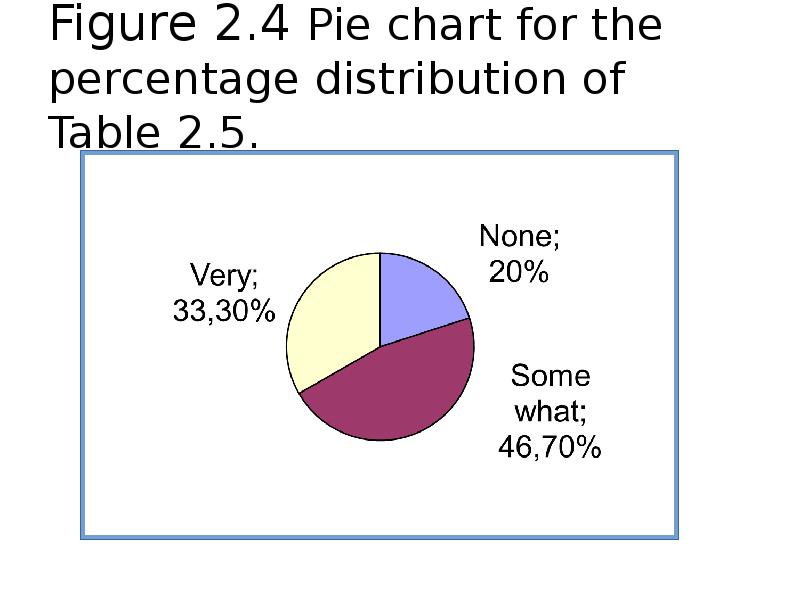
- 46. Figure 2.4 Pie chart for the percentage distribution of Table 2.5.
- 47. ORGANIZING AND GRAPHING QUANTITATIVE DATA Frequency Distributions Constructing Frequency Distribution Tables
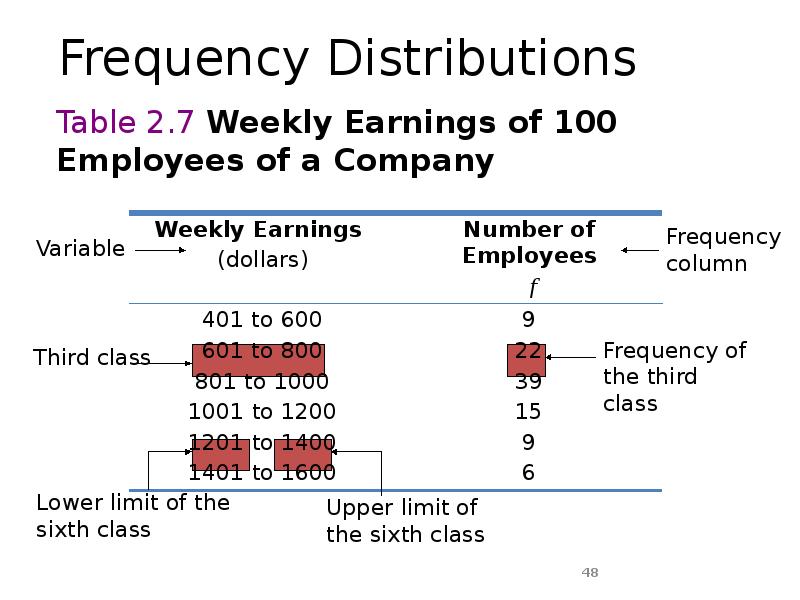
- 48. Frequency Distributions
- 49. Frequency Distributions cont. Definition A frequency distribution for quantitative data
- 50. Essential Question : How do we construct a frequency distribution table?
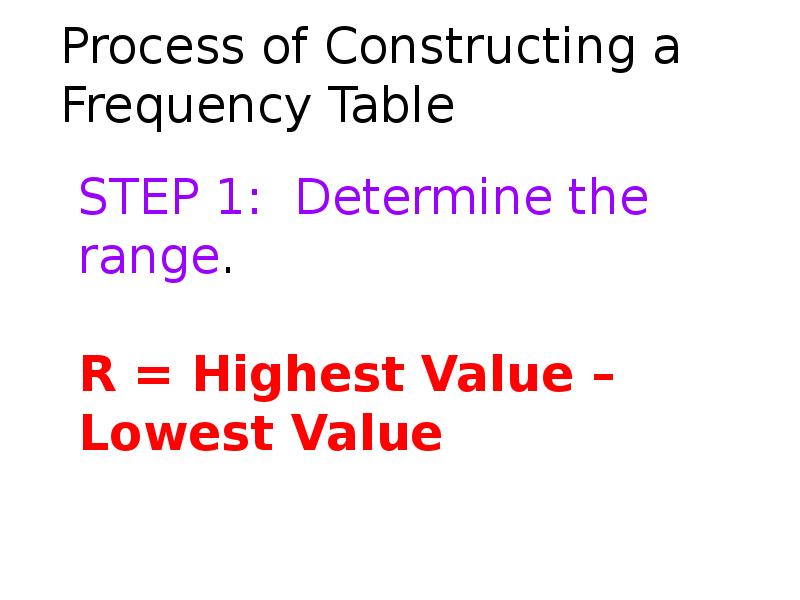
- 51. Process of Constructing a Frequency Table STEP 1: Determine the
- 52. STEP 2. Determine the tentative number of classes (k) STEP 2.
- 53. STEP 3. Find the class width by dividing the range by
- 54. STEP 4. Write the classes or categories starting with the lowest
- 55. STEP 5. Determine the frequency for each class by referring to
- 56. When constructing frequency tables, the following guidelines should be followed. The
- 57. 3. All classes should have the same width, although it is
- 58. Let’s Try!!! Time magazine collected information on all 464 people who
- 59. 19 18 30 40 41 33 73 25 19 18 30
- 60. Determine the range. Determine the range. R = Highest Value –
- 61. Determine the tentative number of classes (K). Determine the tentative number
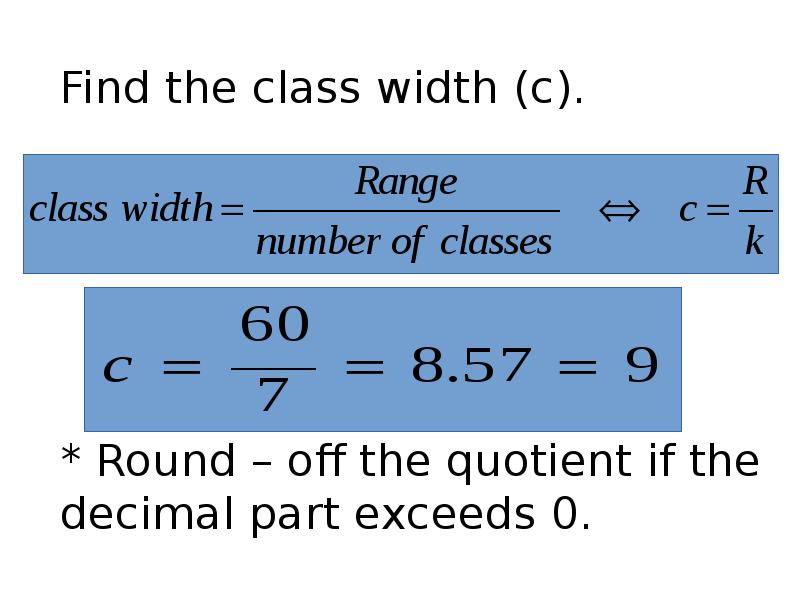
- 62. Find the class width (c). Find the class width (c). *
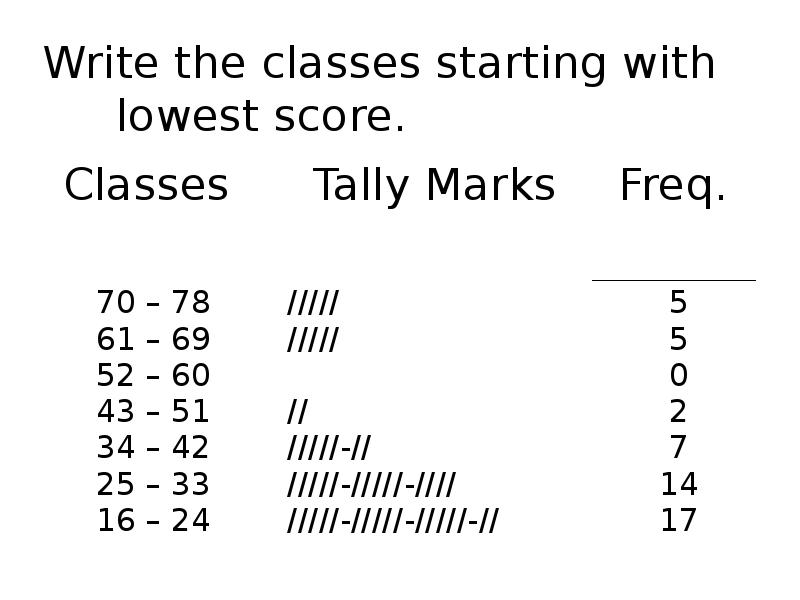
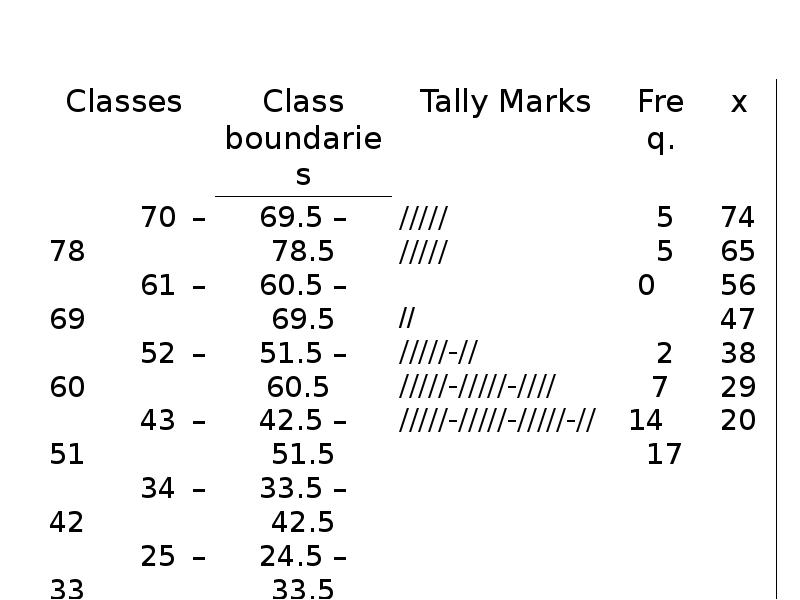
- 63. Write the classes starting with lowest score.
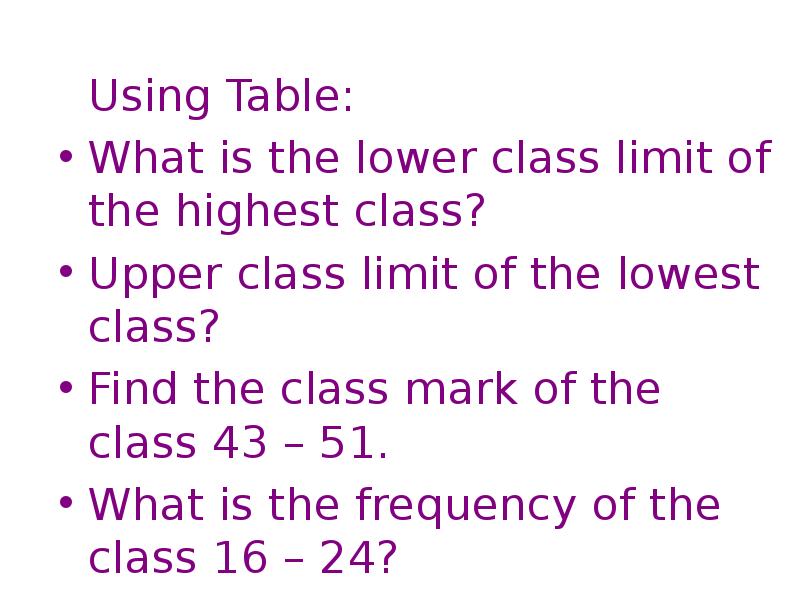
- 64. Using Table: Using Table: What is the lower class limit of
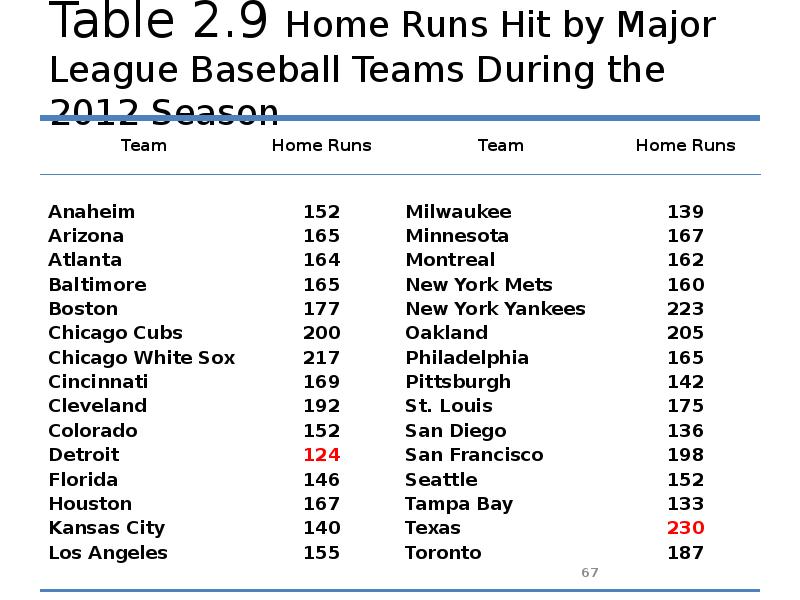
- 66. Example Table 2.9 gives the total home runs hit by
- 67. Table 2.9 Home Runs Hit by Major League Baseball Teams During
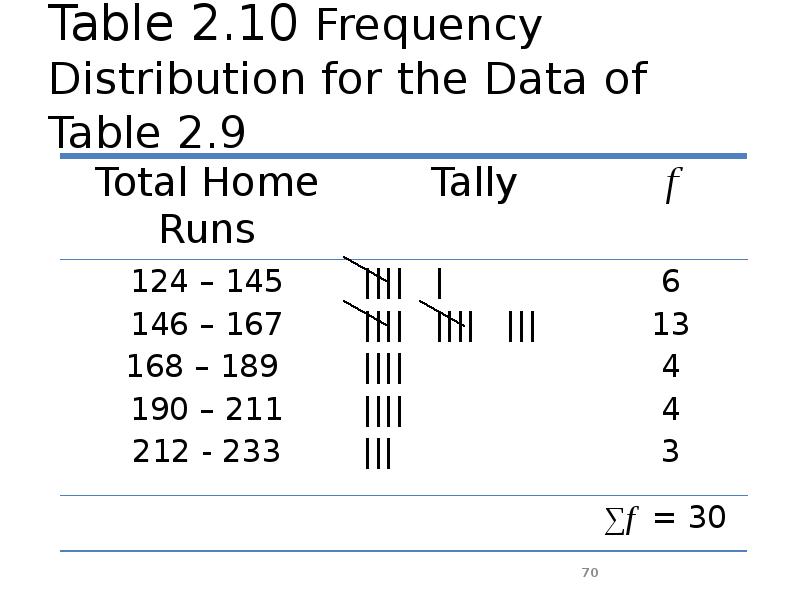
- 68. Solution 2-3
- 69. Solution 2-3 The lower limit of the first class can be
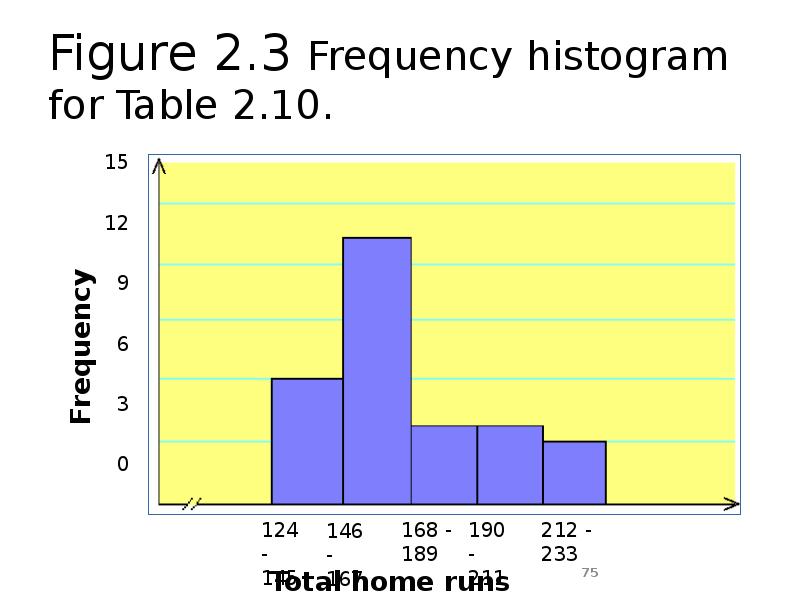
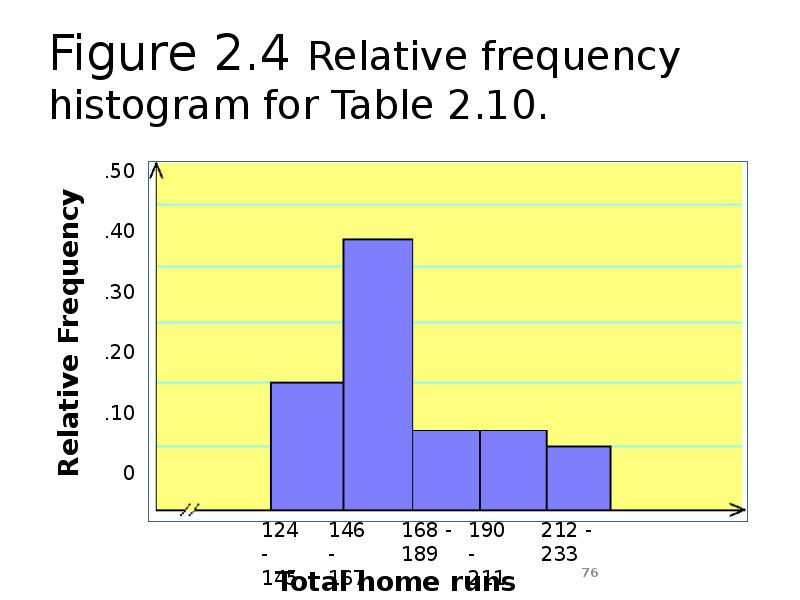
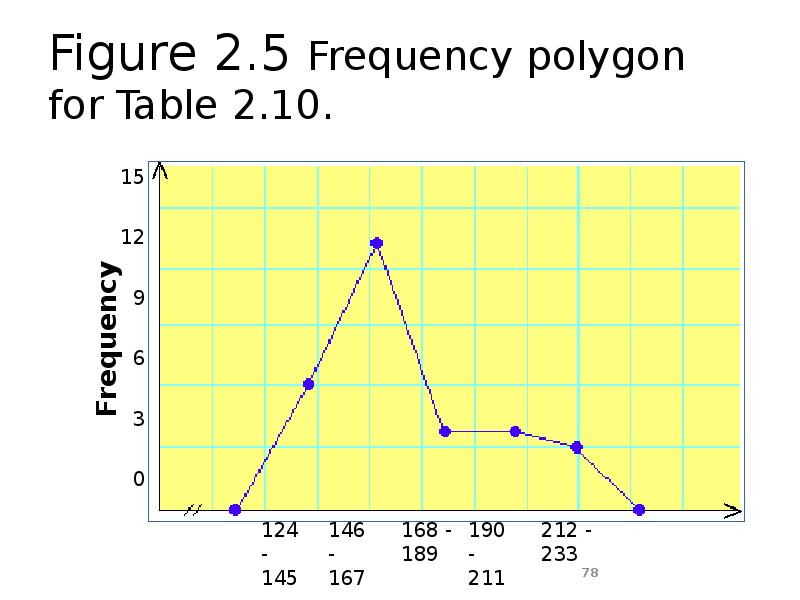
- 70. Table 2.10 Frequency Distribution for the Data of Table 2.9
- 71. Relative Frequency and Percentage Distributions Relative Frequency and Percentage Distributions
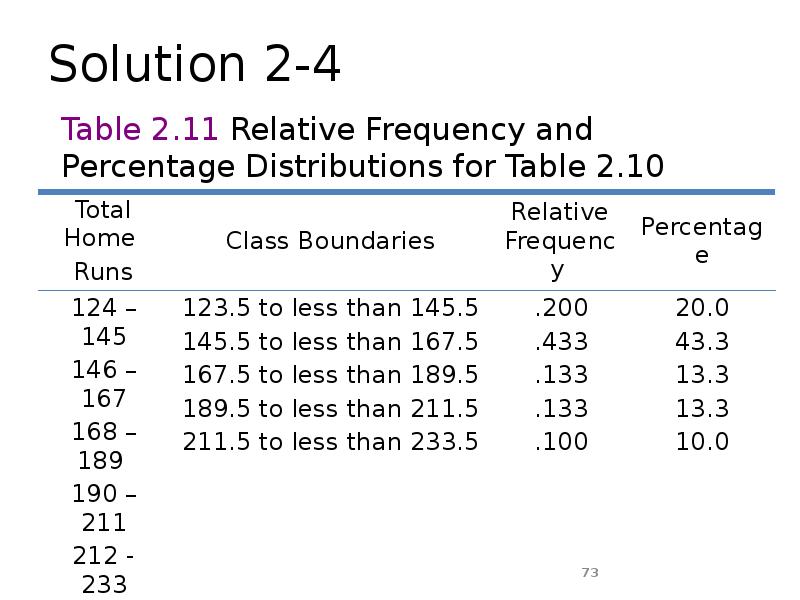
- 72. Example 2-4 Calculate the relative frequencies and percentages for Table 2.10
- 73. Solution 2-4
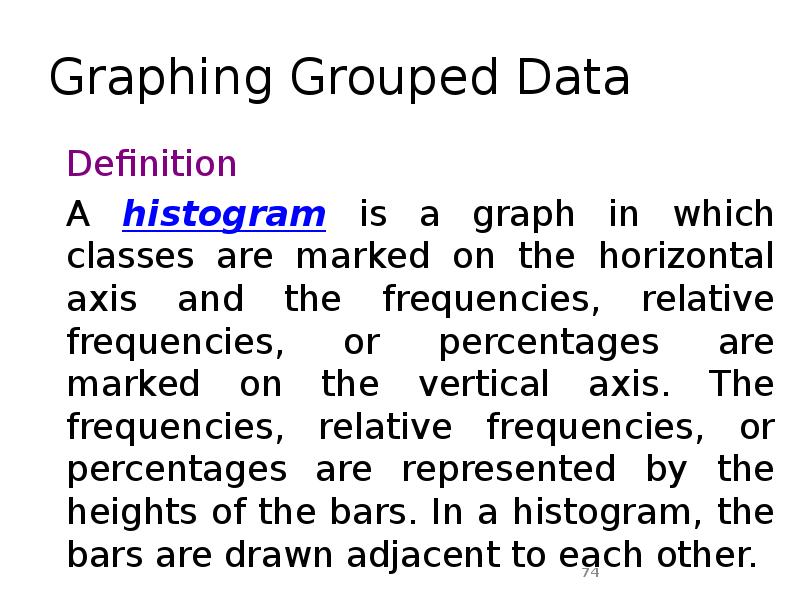
- 74. Graphing Grouped Data Definition A histogram is a graph in which
- 75. Figure 2.3 Frequency histogram for Table 2.10.
- 76. Figure 2.4 Relative frequency histogram for Table 2.10.
- 77. Graphing Grouped Data cont. Definition A graph formed by joining the
- 78. Figure 2.5 Frequency polygon for Table 2.10.
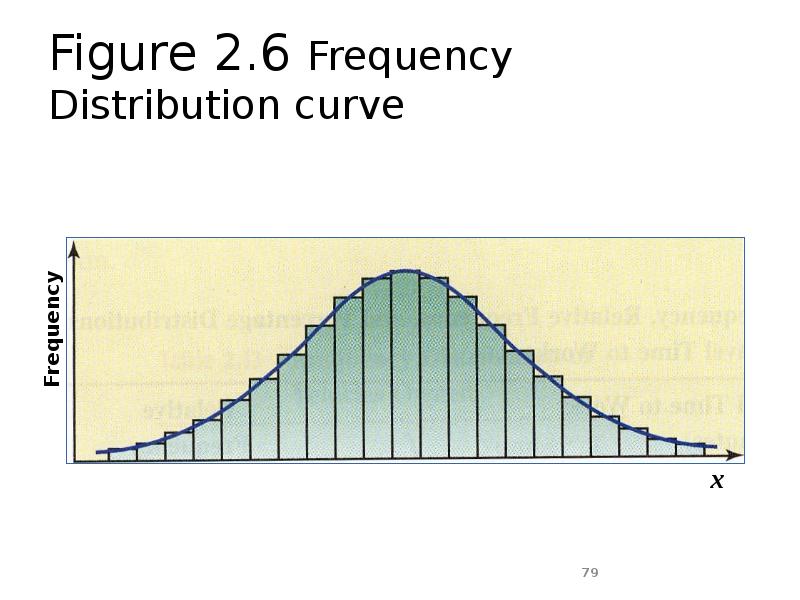
- 79. Figure 2.6 Frequency Distribution curve
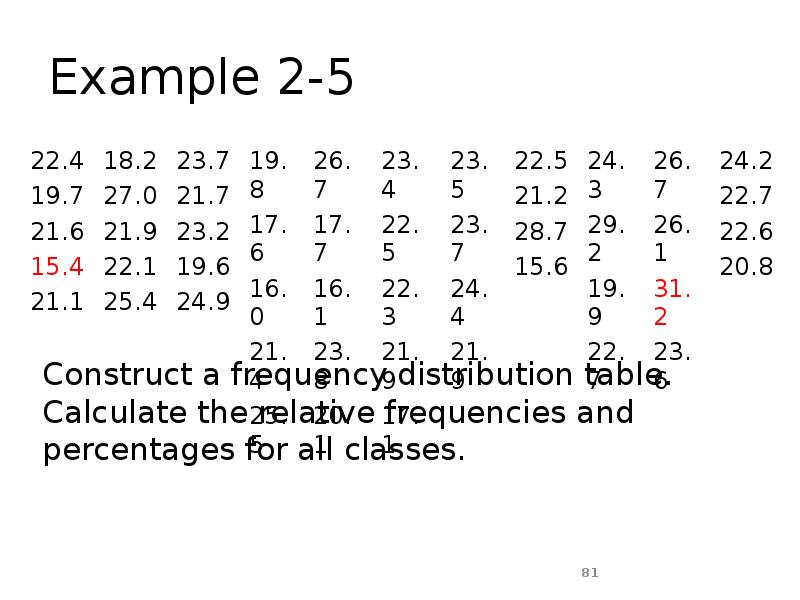
- 80. Example 2-5 The following data give the average travel time from
- 81. Example 2-5
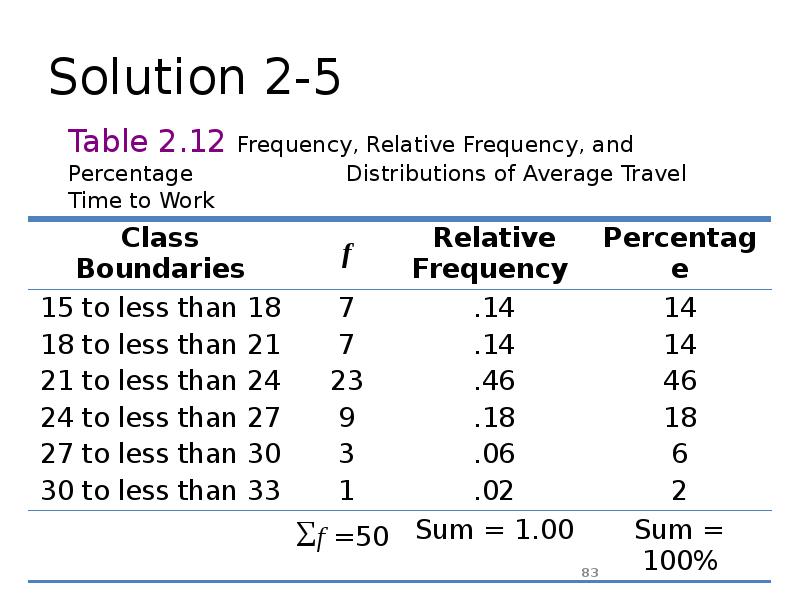
- 82. Solution 2-5
- 83. Solution 2-5
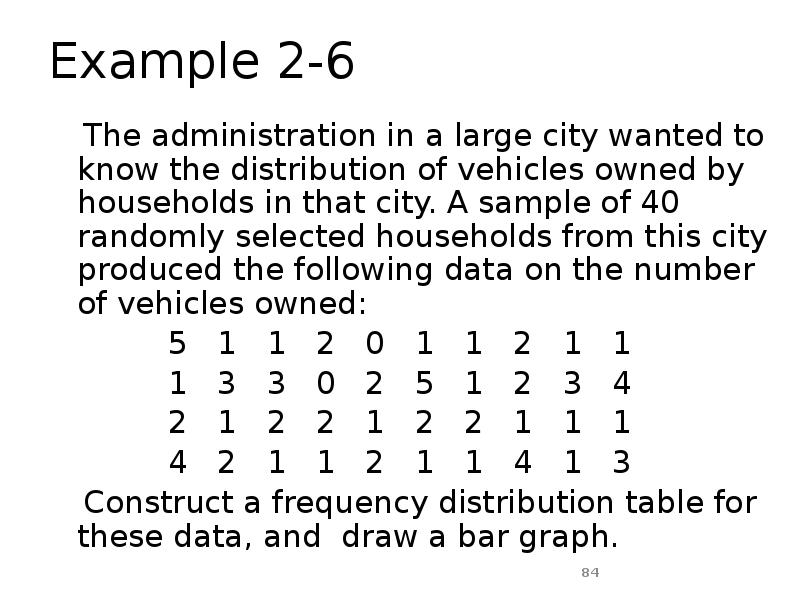
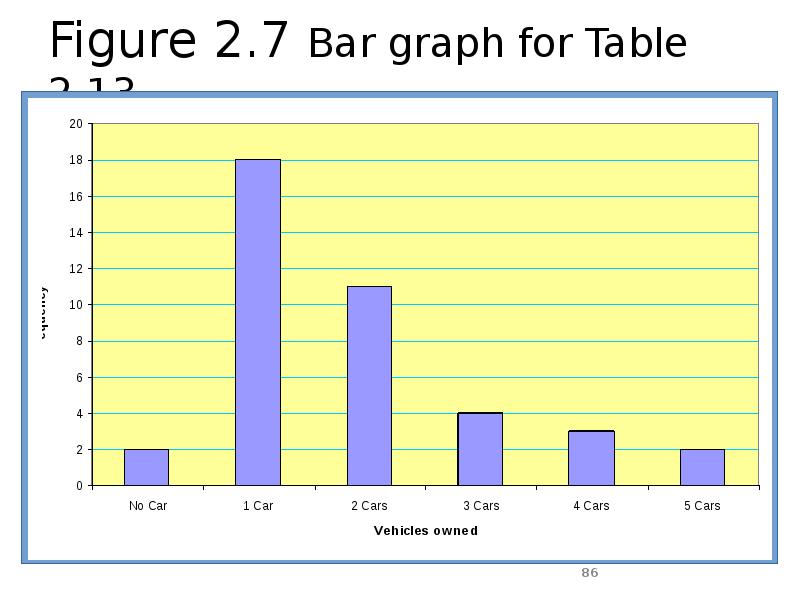
- 84. Example 2-6 The administration in a large city wanted to
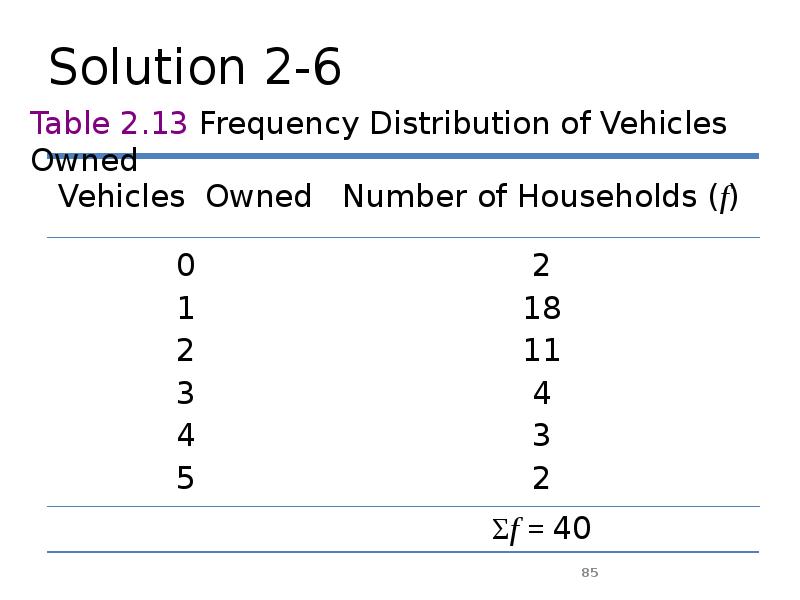
- 85. Solution 2-6
- 86. Figure 2.7 Bar graph for Table 2.13.
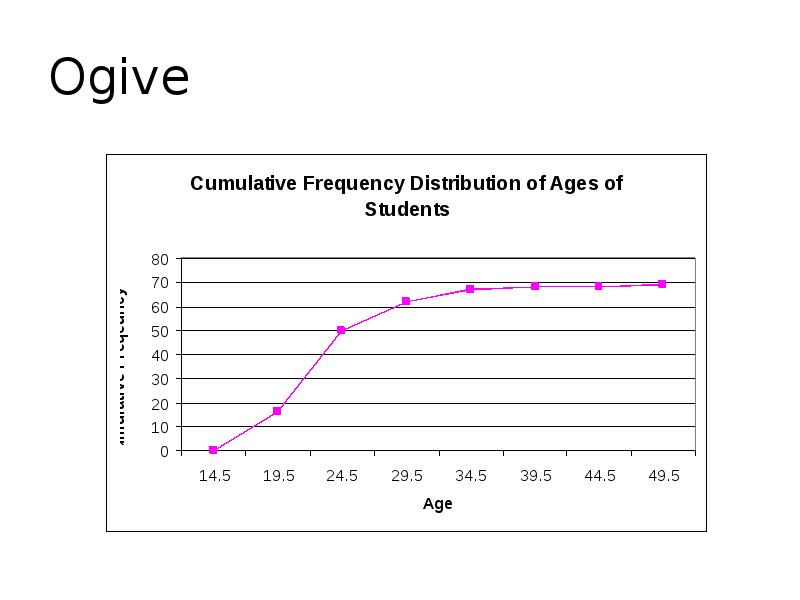
- 87. Ogive The ogive is a graph that represents the cumulative frequencies
- 88. Ogive
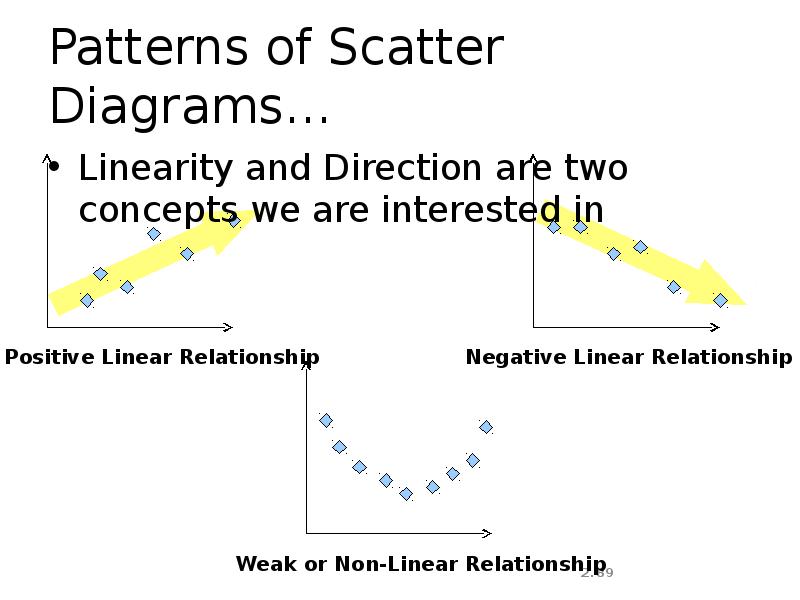
- 89. Patterns of Scatter Diagrams… Linearity and Direction are two concepts we
- 90. Скачать презентацию
























![We Deal with “2” Types of Data
Numerical/Quantitative Data [Real Numbers]:
We Deal with “2” Types of Data
Numerical/Quantitative Data [Real Numbers]:](/documents_7/c03e86ff40eb5eefeded565b0f71141a/img26.jpg)
![Qualitative/Categorical Data
Nominal Data [has no natural order to the values]. Qualitative/Categorical Data
Nominal Data [has no natural order to the values].](/documents_7/c03e86ff40eb5eefeded565b0f71141a/img28.jpg)















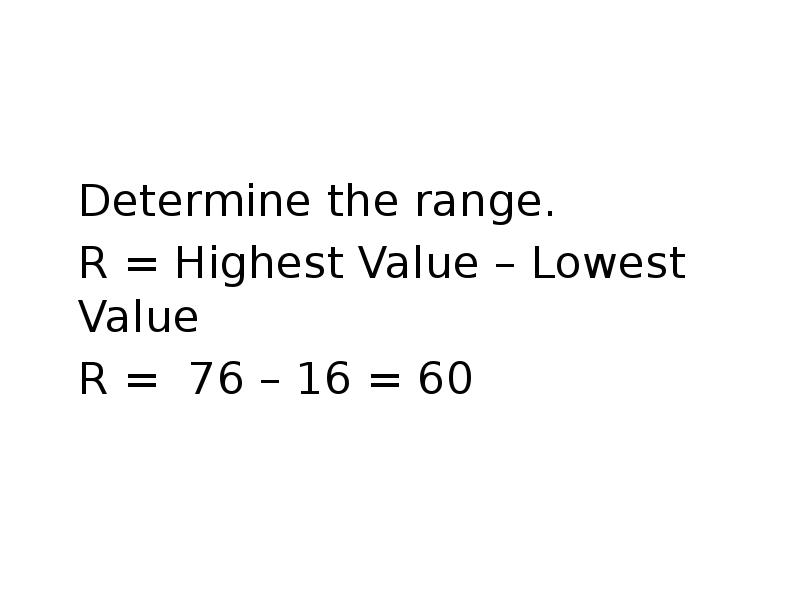









Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Organizing Data Graphical and Tabular Descriptive Techniques можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























