Patients With Traumatic Injuries презентация
Содержание
- 3. Objectives contd.. In order to: Identify the differences between a Category
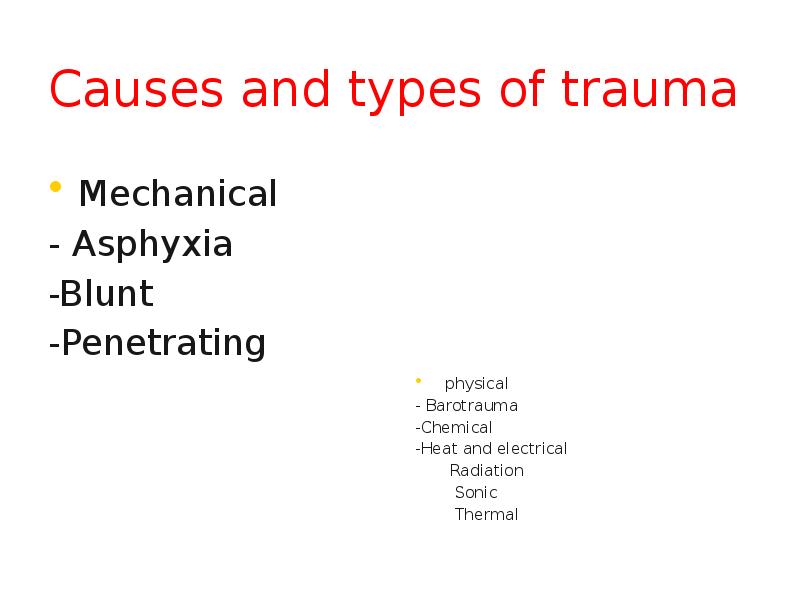
- 5. Causes and types of trauma Mechanical - Asphyxia -Blunt -Penetrating
- 6. Level I Trauma Centers Prepared and committed to handle all
- 7. Level II Trauma Centers Increased commitment to trauma care for the
- 8. Trauma Transport Systolic B/P < 90 on 2 consecutive readings (or
- 9. Trauma Transport... Traumatic arrest, isolated burns >20% Transport to the closest
- 10. Mechanism of Injury The process and forces that cause trauma Mentally
- 11. Injury Patterns – Pedestrians Adults Generally turn away & present lateral
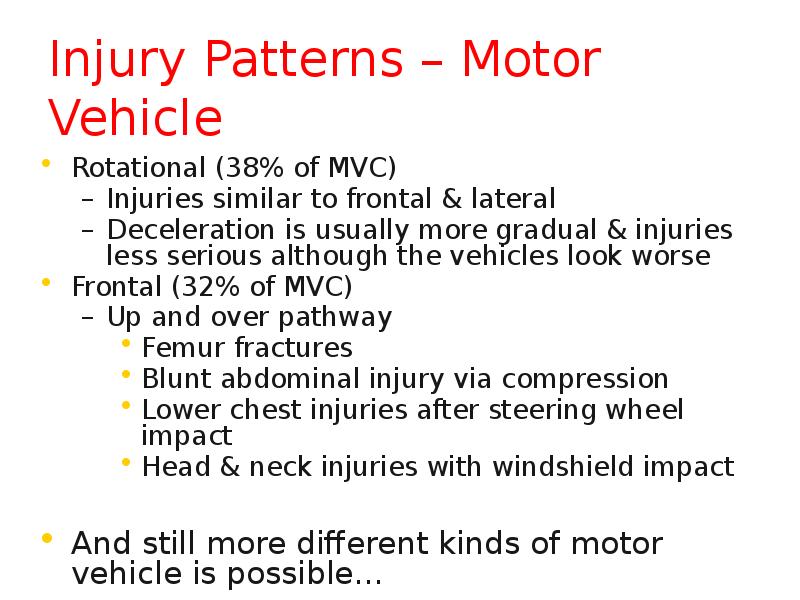
- 12. Injury Patterns – Motor Vehicle Rotational (38% of MVC) Injuries similar
- 13. Index of Suspicion Your anticipation of injury to a body, region,
- 14. Documentation To Include of The Complaint O - onset P –
- 15. Trauma Care – Amputated Parts Routine trauma care To remove gross
- 16. Care of Amputated Parts Place part in a plastic zip lock
- 17. GCS – Motor Response 1-6 Points Obeys command (6) Localizes pain
- 18. Скачать презентацию















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























