Problems of social inequality, social stratification and political elites презентация
Содержание
- 2. Understanding Inequality Inequality is the unequal access to scarce goods or
- 3. Understanding Social Stratification Social stratification is the division of society into
- 4. Social Stratification Every society has some form of social stratification, but
- 5. Systems of Stratification (Cont’d) Social class refers to a system of
- 6. Social Classes in the United States The upper class (capitalist class):
- 7. Social Classes in the United States The upper-middle class: Professionals and
- 8. Social Classes in the United States The working (lower-middle) class: “Blue-collar”
- 9. Social Classes in the United States The lower class (the working
- 10. Theories of Social Class Karl Marx believed that there were two
- 11. Theories of Social Class Max Weber offered a similar model that
- 12. Theories of Social Class More recently, Pierre Bourdieu argued each generation
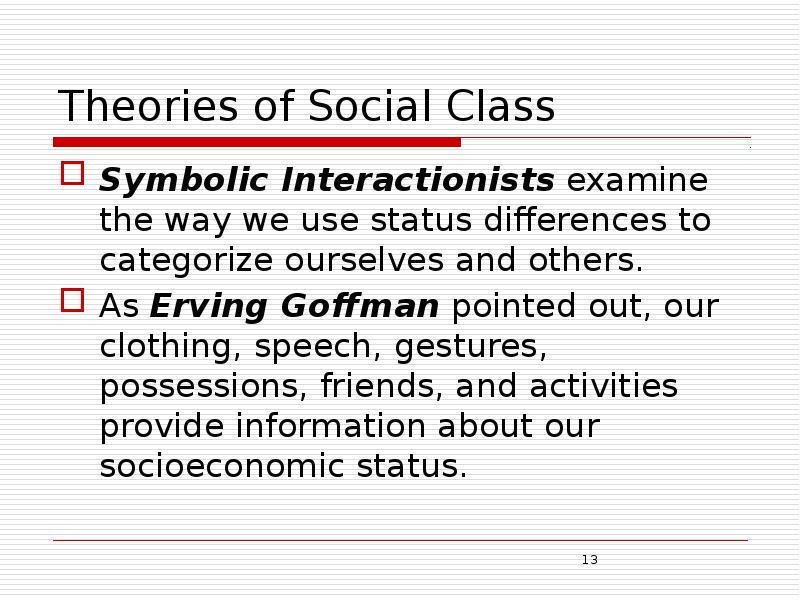
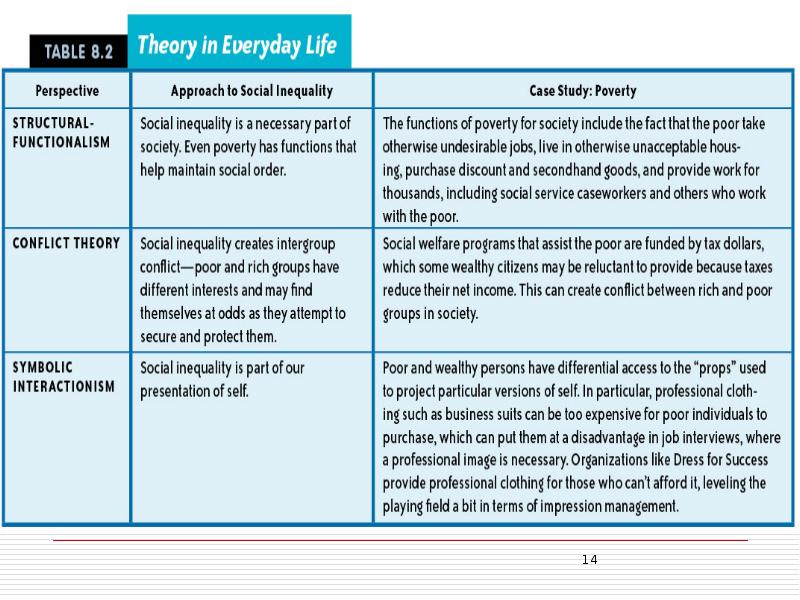
- 13. Theories of Social Class Symbolic Interactionists examine the way we use
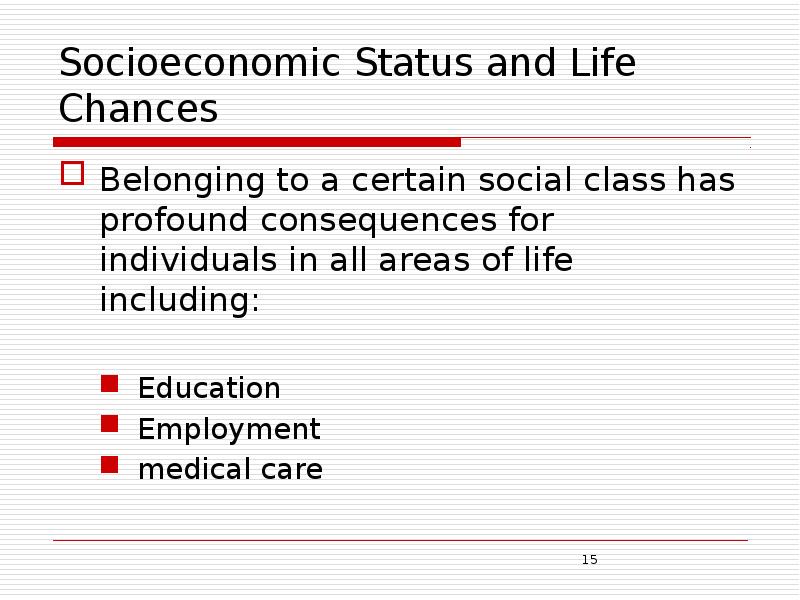
- 15. Socioeconomic Status and Life Chances Belonging to a certain social class
- 16. Social Mobility Social mobility is the movement of individuals or groups
- 17. Poverty The culture of poverty refers to learned attitudes that can
- 18. Political elite In every society there is a class of people
- 19. Characteristics of political elites Small in number Organised Monopoly over political
- 20. Elitist Theorists “pluralists” or “functionalists” Mosca, Parsons Mosca's enduring
- 21. Lesson Quiz True or False: 1. Every society has some
- 22. Lesson Quiz 2. The tendency of social classes to remain relatively
- 23. Lesson Quiz 3. Entrenched attitudes that can develop among poor communities
- 24. Lesson Quiz 4. Max Weber argued that there were several important
- 25. Скачать презентацию





















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Problems of social inequality, social stratification and political elites можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























