SQL SERVER ENCRYPTION презентация
Содержание
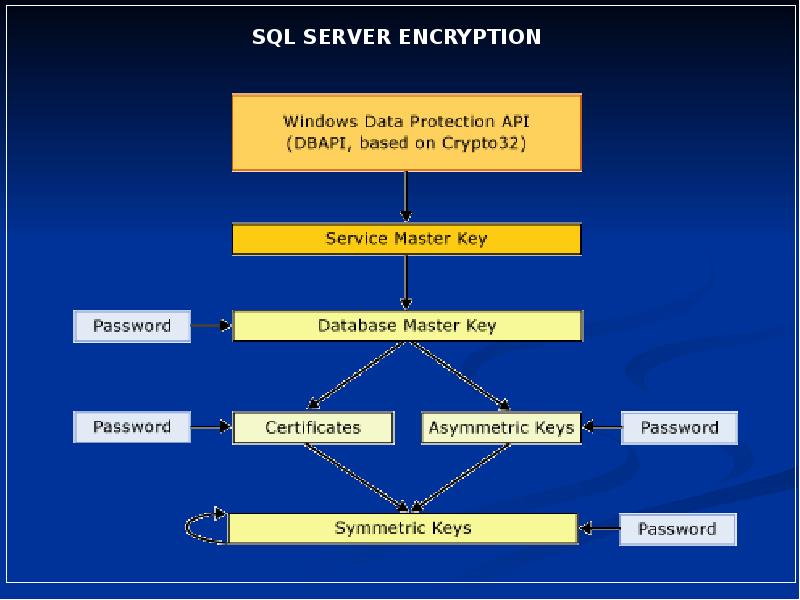
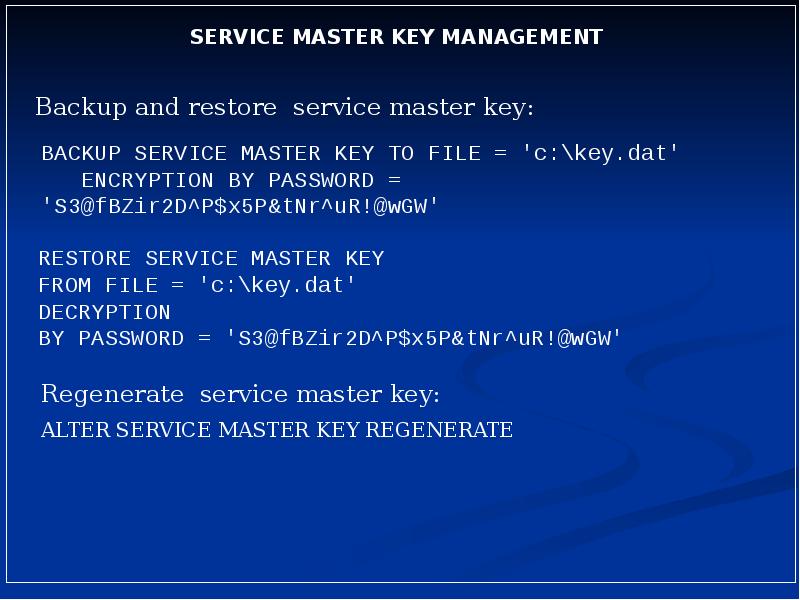
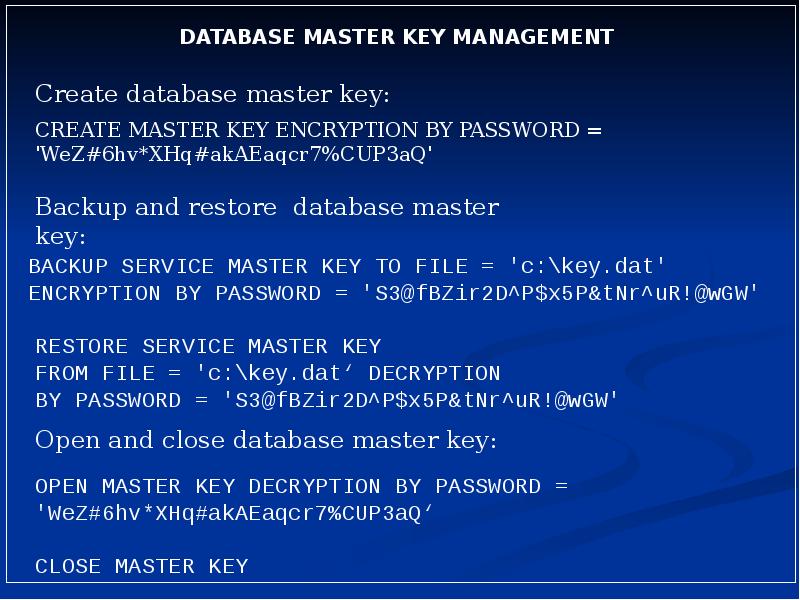
- 2. Service Master Key Service Master Key Root – Top Level Key
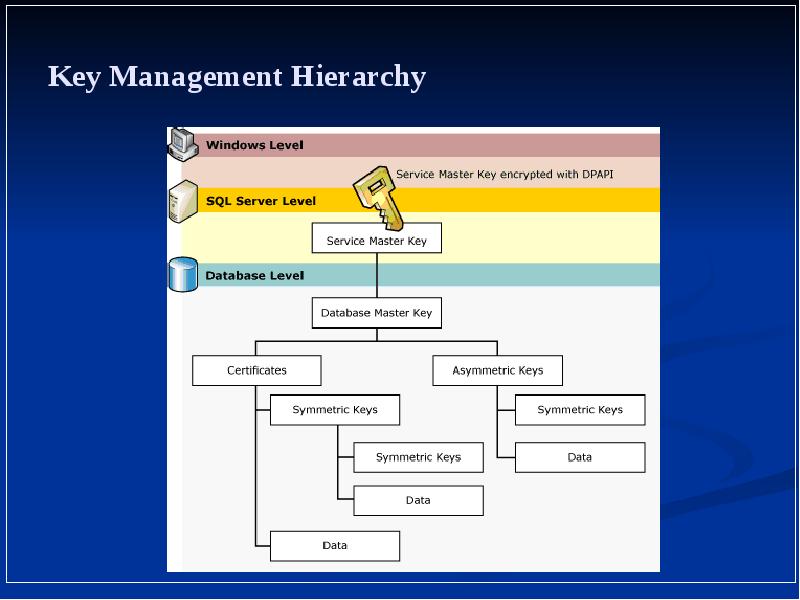
- 3. Key Management Hierarchy Key Management Hierarchy Database Master Keys Symmetric key
- 4. Key Management Hierarchy
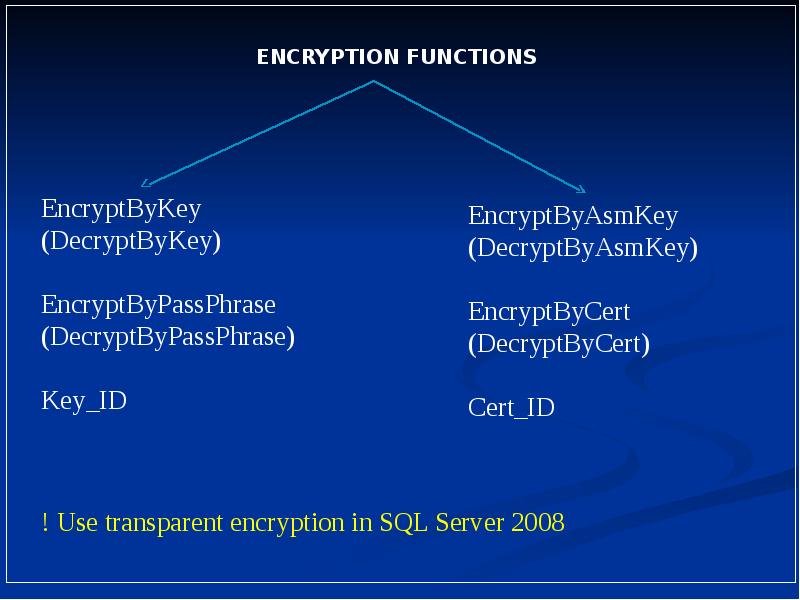
- 5. MS SQL Server Protecting Password Avoid storing passwords if possible Use
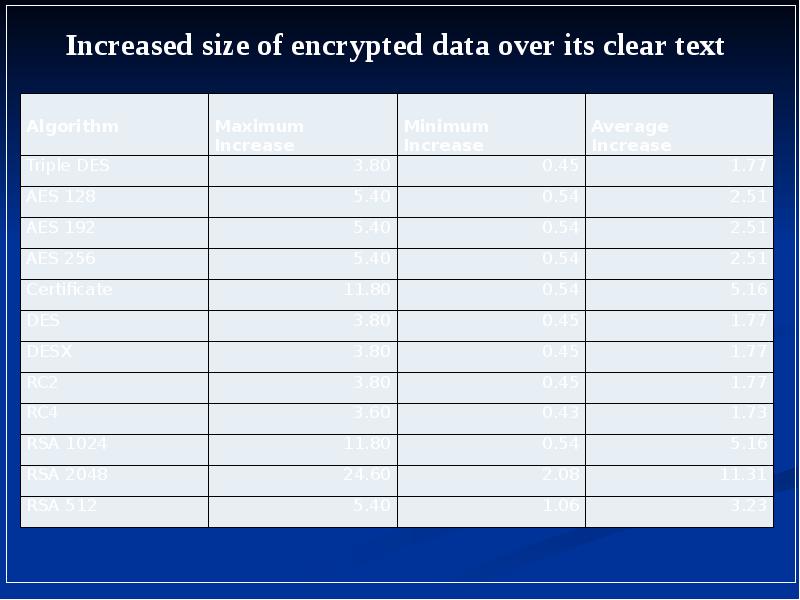
- 6. MS SQL Server Checklist Use either the AES192 or AES256 algorithm
- 12. Encryption for Oracle 8i-11g Oracle DBMS Obfuscation Toolkit (DOTK) (Only
- 13. Oracle DOTK Checklist Use only the 3DES encryption rather than DES
- 14. Oracle DBMS Obfuscation Toolkit DOTK Encryption Procedure: DBMS_OBFUSCATION_TOOLKIT.DES3Encrypt( input_string IN VARCHAR2,
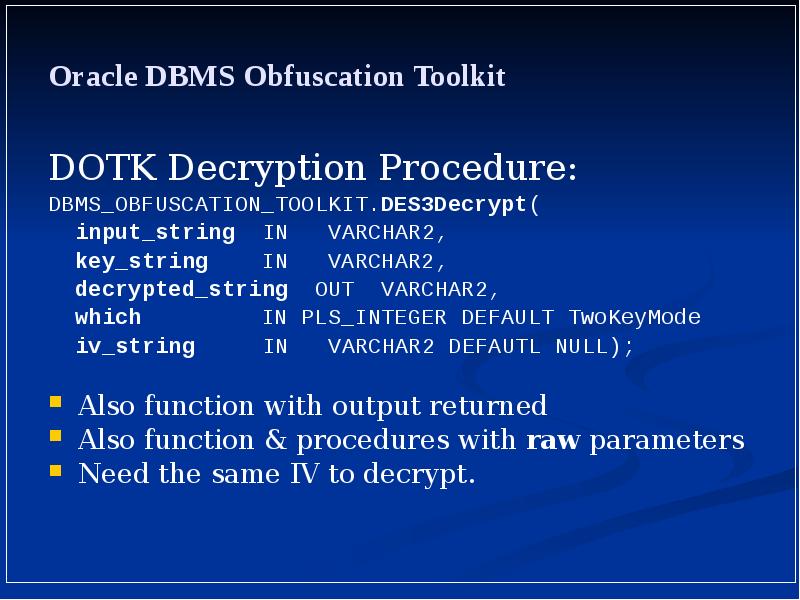
- 15. Oracle DBMS Obfuscation Toolkit DOTK Decryption Procedure: DBMS_OBFUSCATION_TOOLKIT.DES3Decrypt( input_string IN VARCHAR2,
- 16. Oracle DBMS Obfuscation Toolkit DOTK DES3 Generate Key Procedure: DBMS_OBFUSCATION_TOOLKIT.DES3GetKey( which
- 17. Oracle DBMS Crypto Checklist Use either the AES192 or AES256 algorithm
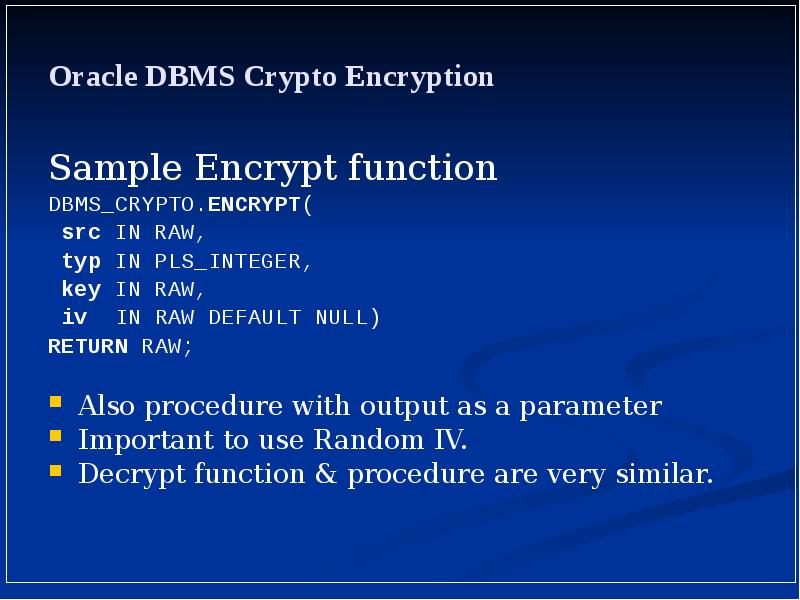
- 18. Oracle DBMS Crypto Encryption Sample Encrypt function DBMS_CRYPTO.ENCRYPT( src IN RAW,
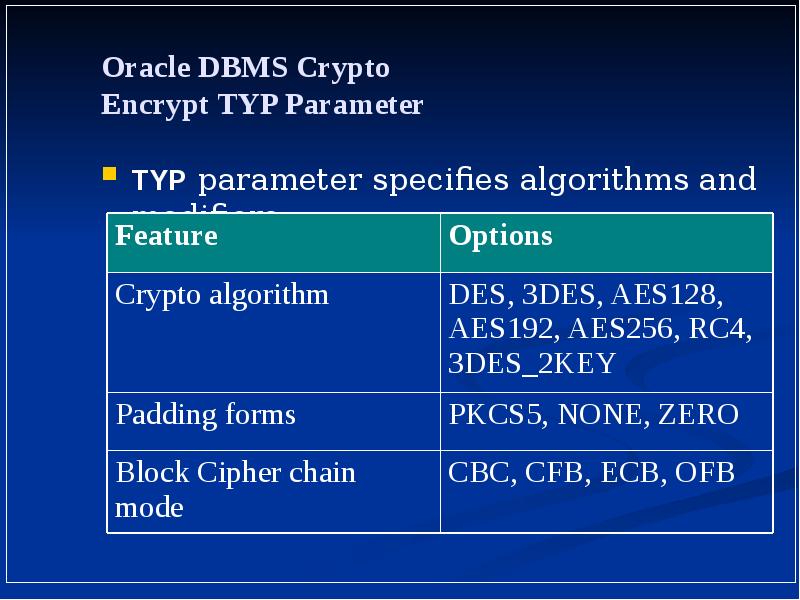
- 19. Oracle DBMS Crypto Encrypt TYP Parameter TYP parameter specifies algorithms and
- 20. Oracle DBMS Crypto Encryption DBMS Crypto Generate Random Bytes: DBMS_CRYPTO.RANDOMBYTES (
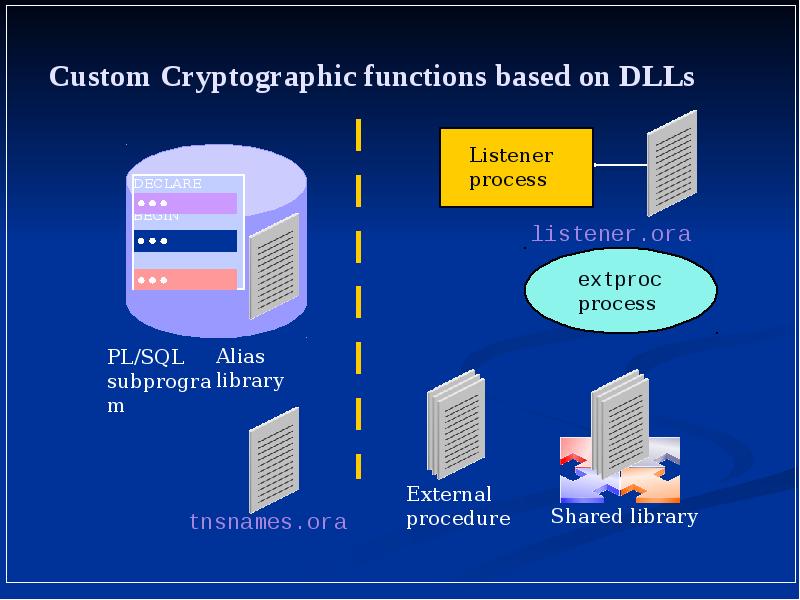
- 21. Custom Cryptographic functions based on DLLs
- 22. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























