TAKAYASU’S ARTERITIS презентация
Содержание
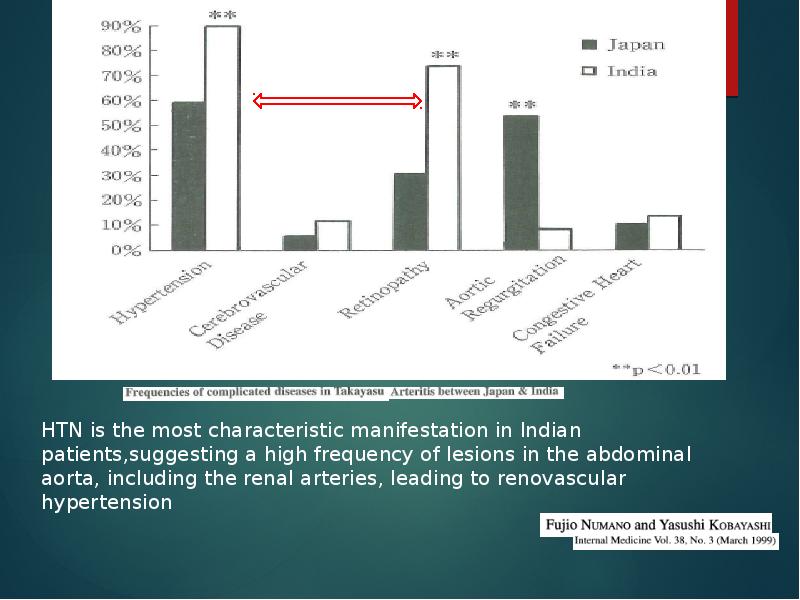
- 2. EPIDEMIOLOGY More case reports from Japan ,India, South-east Asia, Mexico No
- 3. Age Age Mc-2nd & 3rd decade May range from
- 4. Genetics Japan - HLA-B52 and B39 Mexican and Colombian patients
- 5. Histopathology Idiopathic c/c infla arteritis of elastic arteries resulting in occlusive
- 7. Gross Gross
- 8. Wall thickening, Fibrosis, Stenosis, & Thrombus formation →end organ ischaemia More
- 9. Associated pathology-TB (LN)-55% Associated pathology-TB (LN)-55%
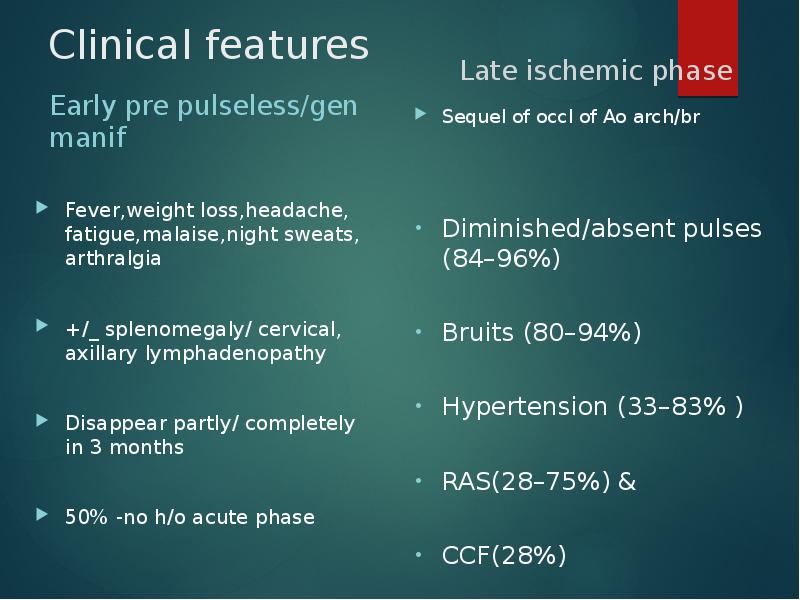
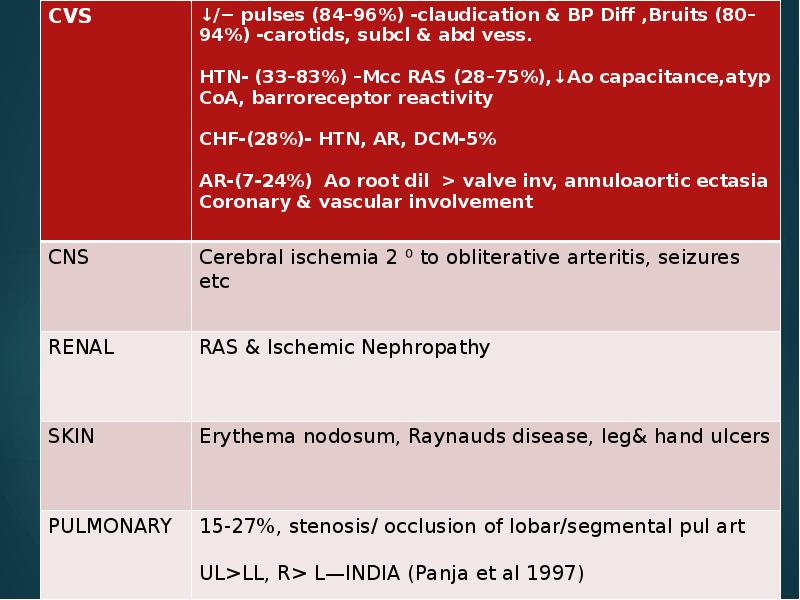
- 10. Clinical features Early pre pulseless/gen manif
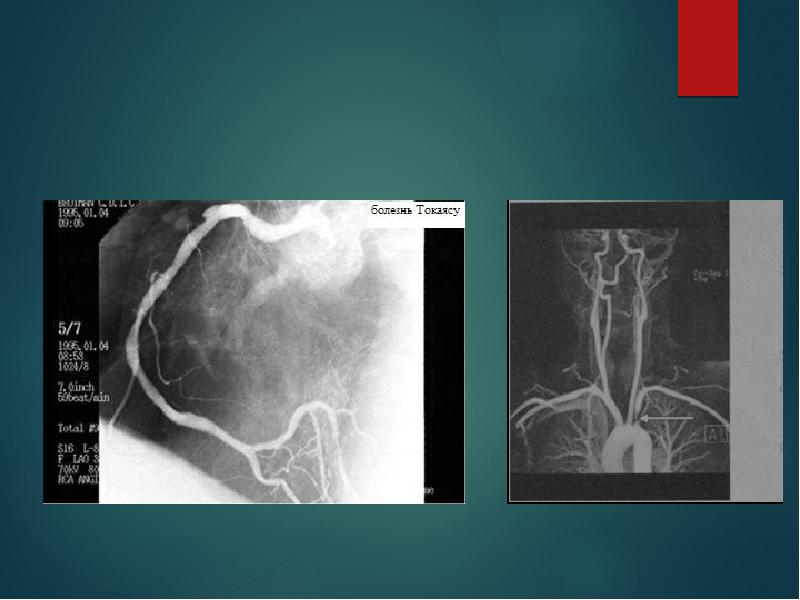
- 12. Coronary involvement in TA Occurs in 10~30% Often fatal Classified into
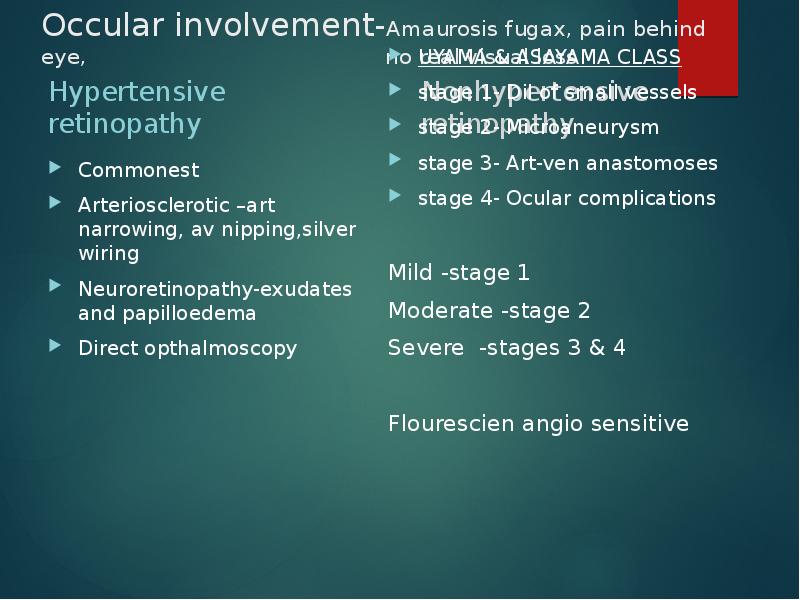
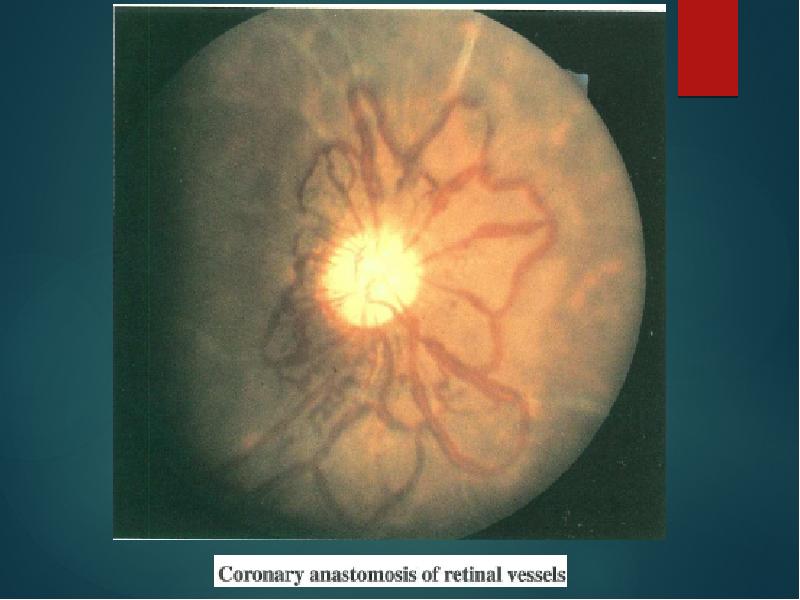
- 13. Occular involvement-Amaurosis fugax, pain behind eye,
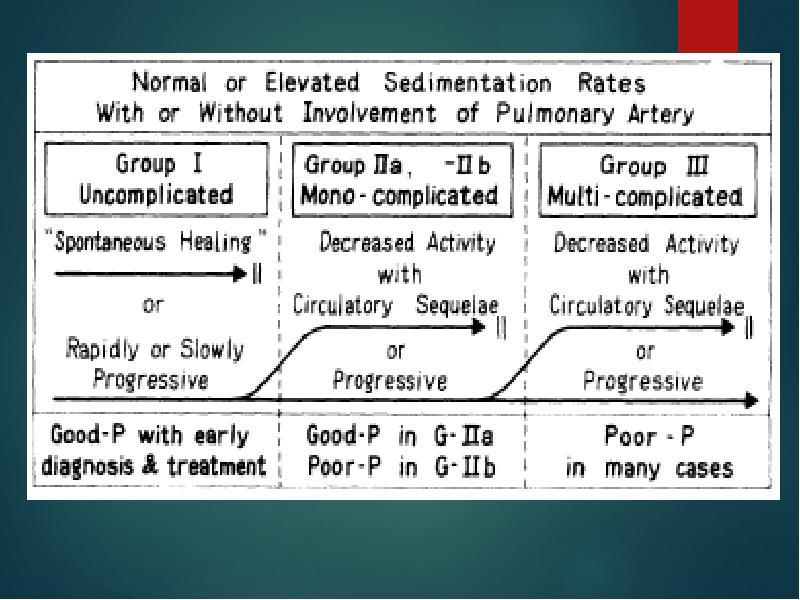
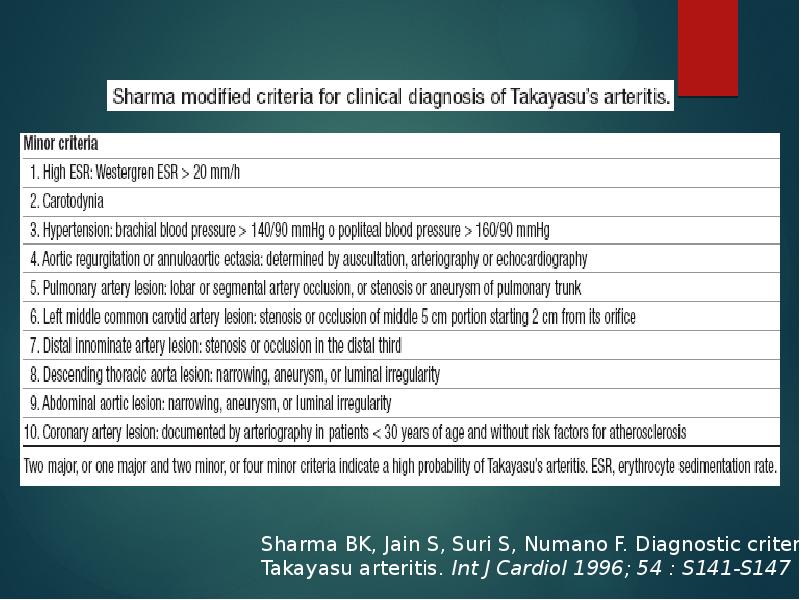
- 16. Ishikawa clinical classification of Takayasu arteritis 1978
- 18. Cumulative survival Cumulative survival 5years -91% (event free survival
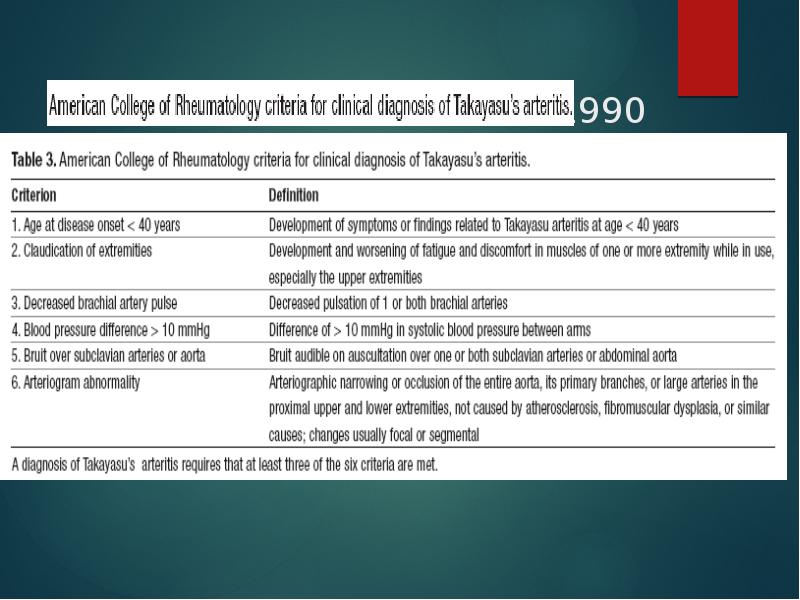
- 19. 1990
- 20. 1995
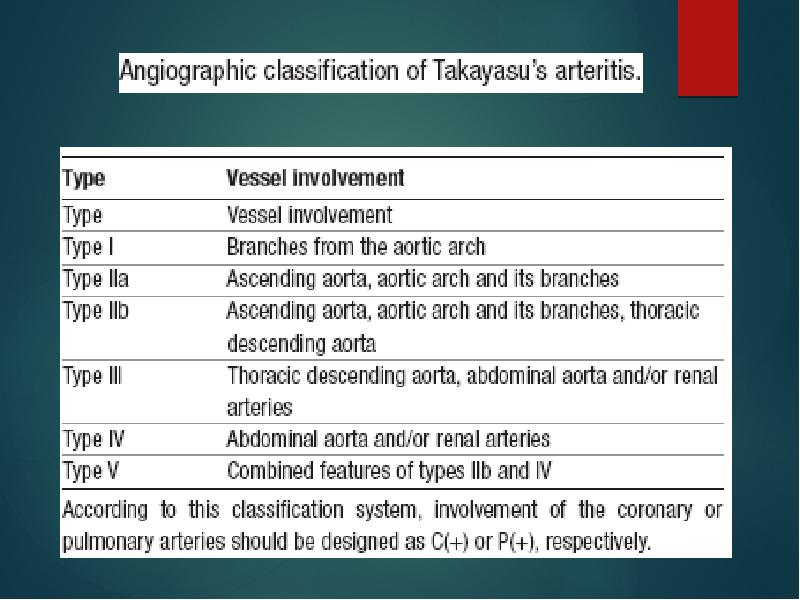
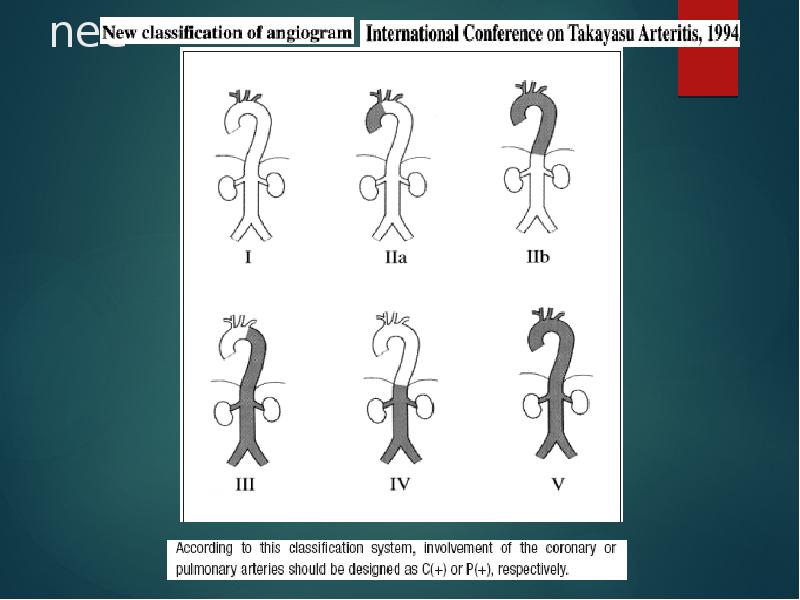
- 23. nee
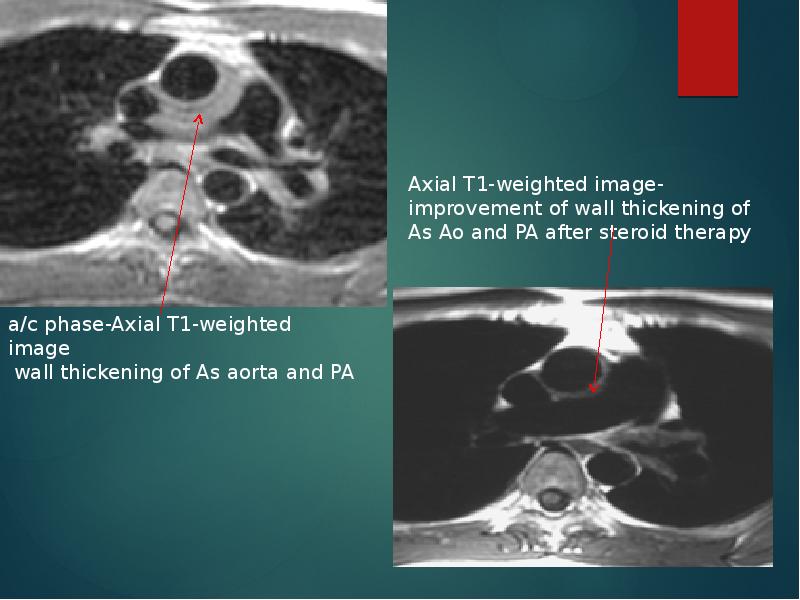
- 25. Findings of TA on MRI mural thrombi signal alterations within
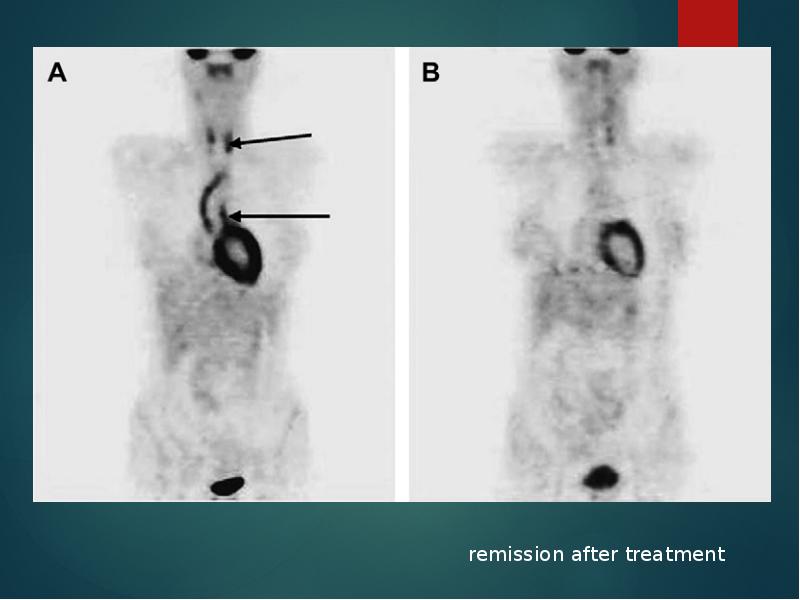
- 26. [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose PET for diagnosing Takayasu’s arteritis common [18F]FDG uptake pattern TA
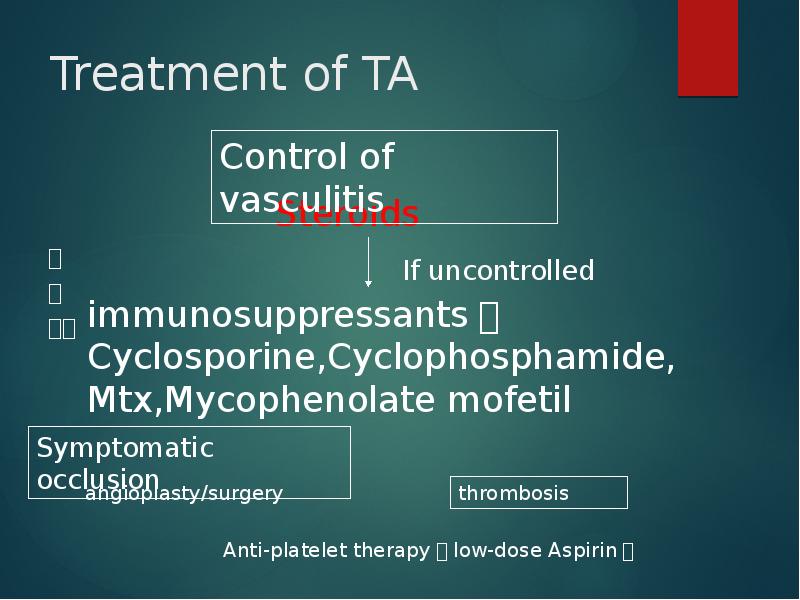
- 28. Treatment of TA ・
- 29. Medical treatment
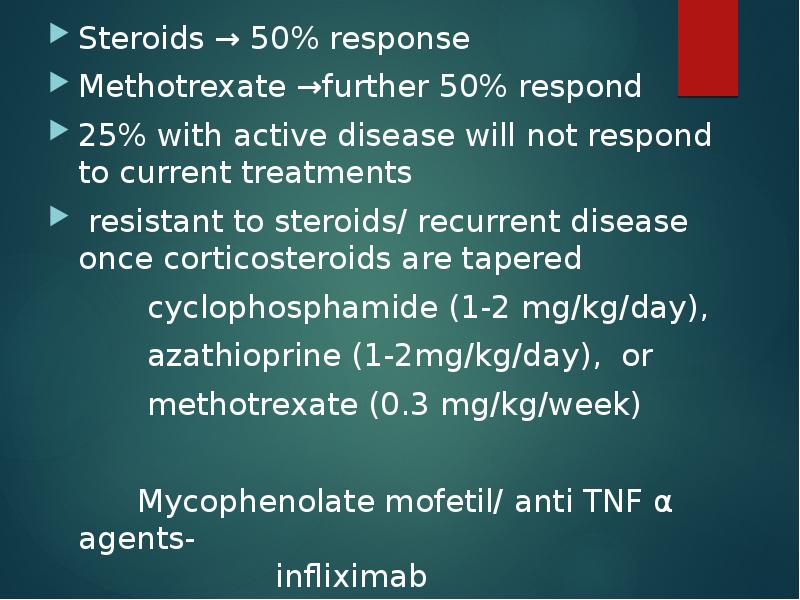
- 30. Steroids → 50% response Methotrexate →further 50% respond 25% with active
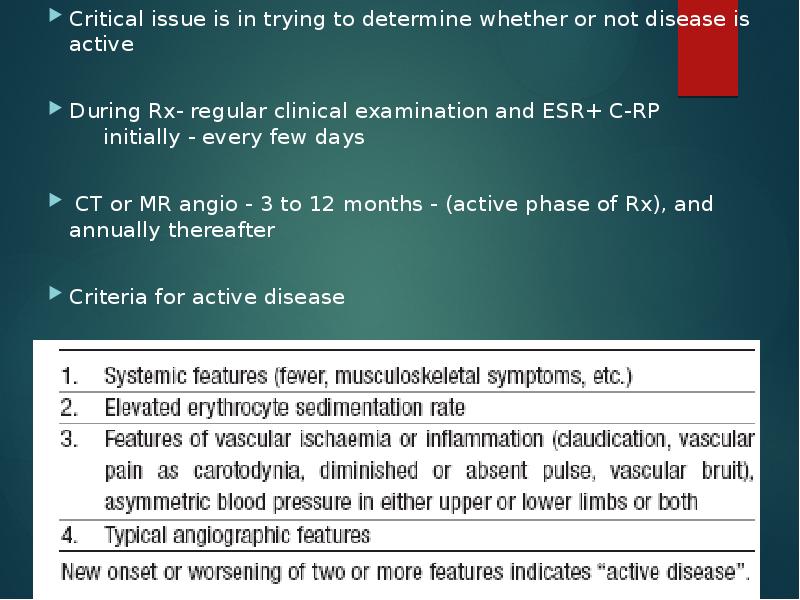
- 31. Critical issue is in trying to determine whether or not disease
- 32. chronic phase- persistent inflammation steroids should be continued –
- 33. Surgical treatment HTN with critical RAS Extremity claudication limiting daily activities
- 34. Surgical techniques Carry high morbidity & mortality Steno /aneurysm -anastomotic points
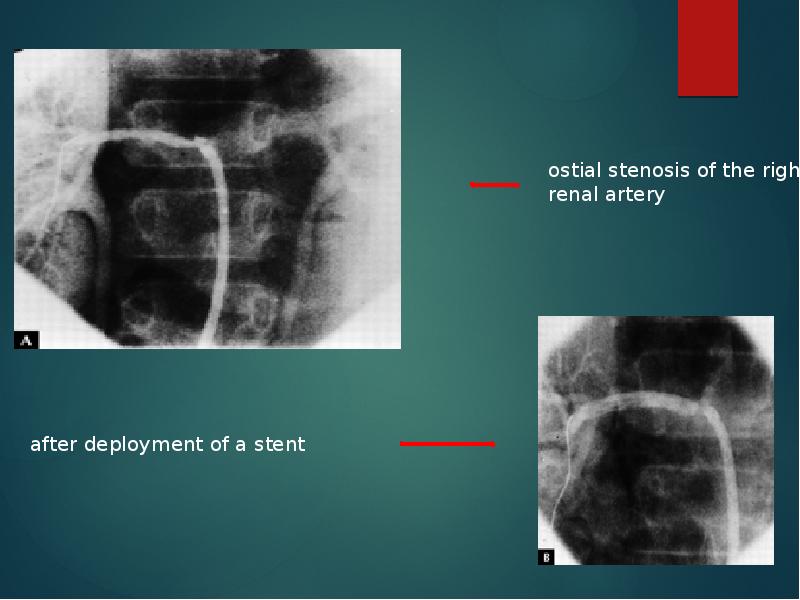
- 35. Renal artery involvement Best treated by PTA Stent placement following PTA
- 37. Renal PTA - 33 stenoses (20 pts) Renal PTA -
- 38. Aortoarteritic lesions Balloon dilation safe & reasonably effective Can be
- 40. Joseph s et al, SCT J Vasc Interv Radiol 1994;5:573–580
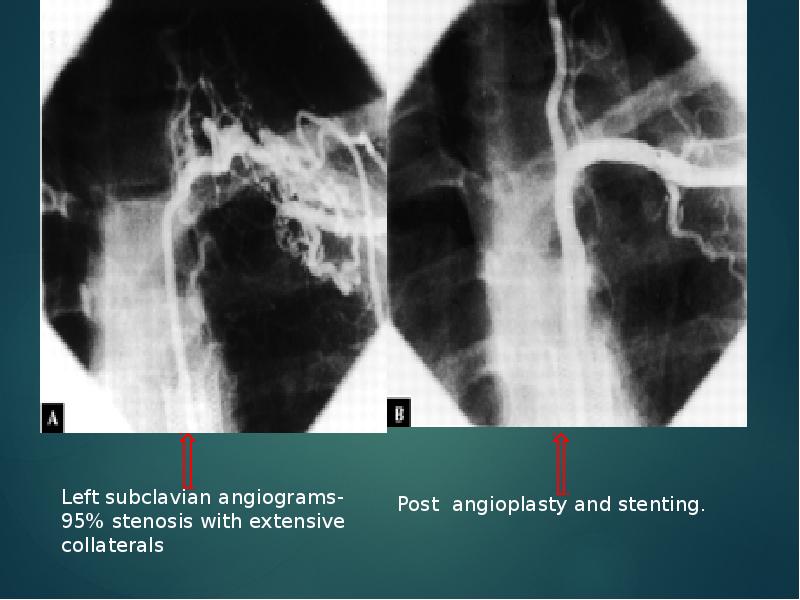
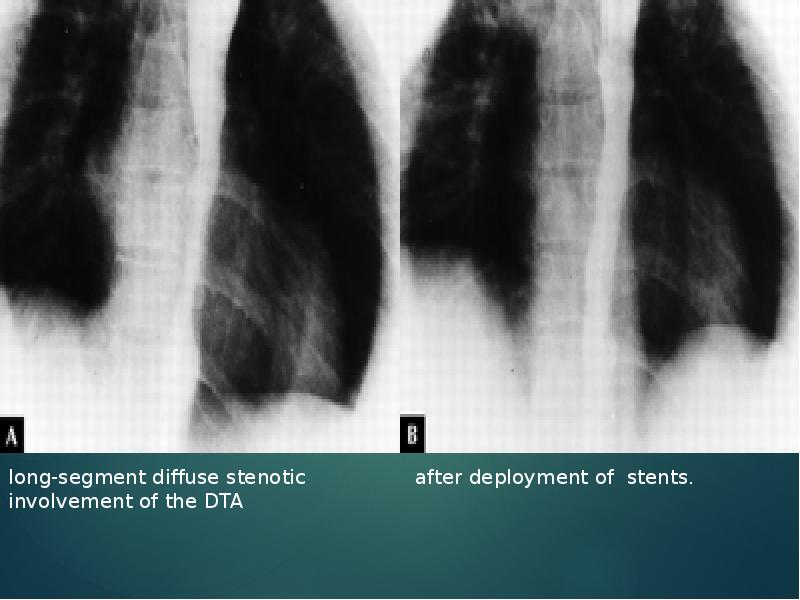
- 41. Aortoplasty and Stenting PTA -desc thoracic and/or abd Ao (TA) stenosis
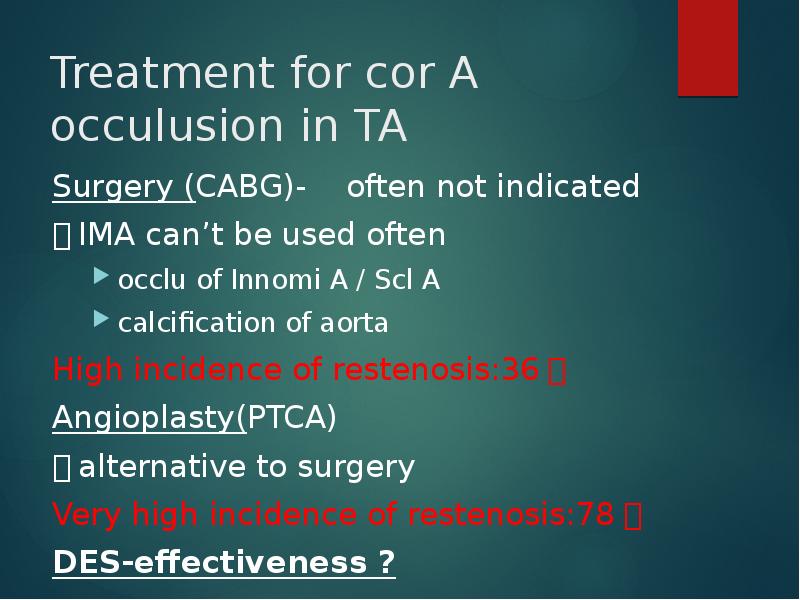
- 43. Treatment for cor A occulusion in TA Surgery (CABG)- often not
- 44. Percutaneous Management of Aneurysmal Lesions Aneurysmal dilatation- isolation or
- 45. Скачать презентацию













![[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose PET for diagnosing Takayasu’s arteritis
common [18F]FDG uptake pattern TA
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose PET for diagnosing Takayasu’s arteritis
common [18F]FDG uptake pattern TA](/documents_7/abd878846bb6411996012e1885b5c582/img25.jpg)










Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























