The Verb: Mood and Modality презентация
Содержание
- 2. The Category of Mood - the category of the verb expressing
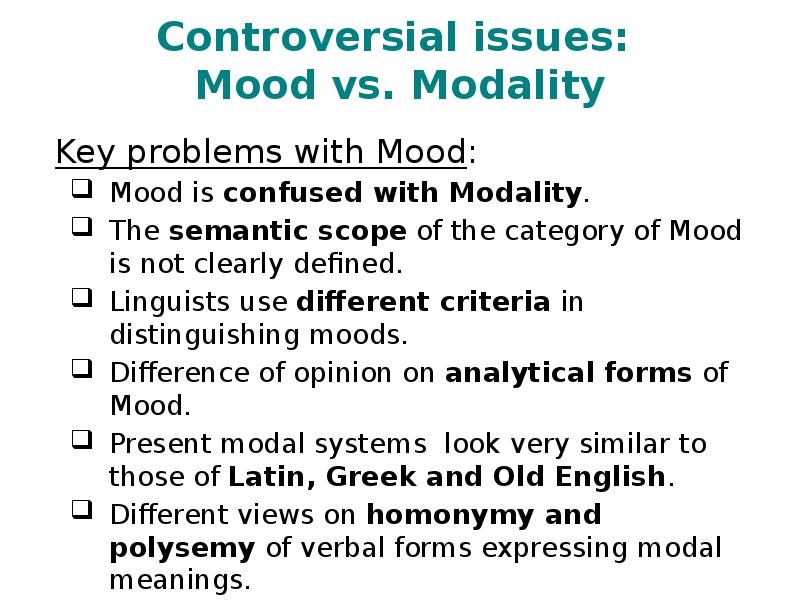
- 3. Controversial issues: Mood vs. Modality Key problems with Mood: Mood is
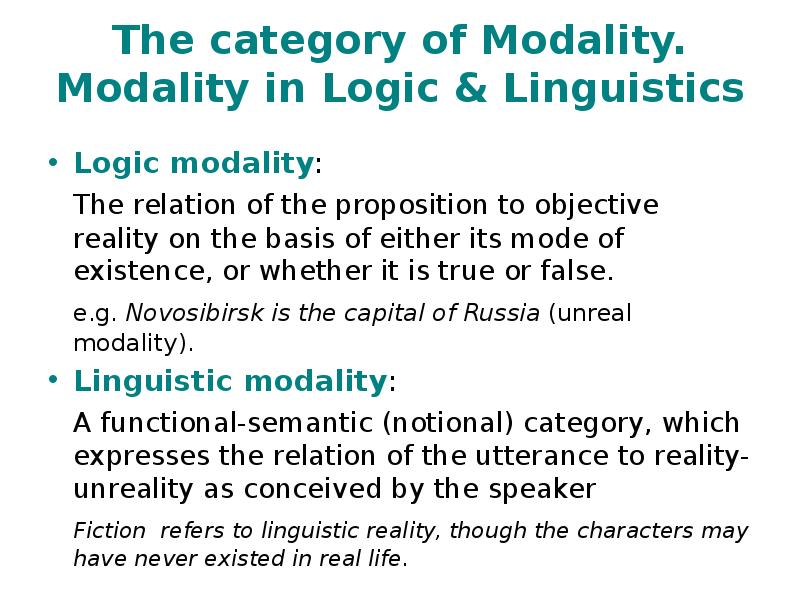
- 4. The category of Modality. Modality in Logic & Linguistics Logic modality:
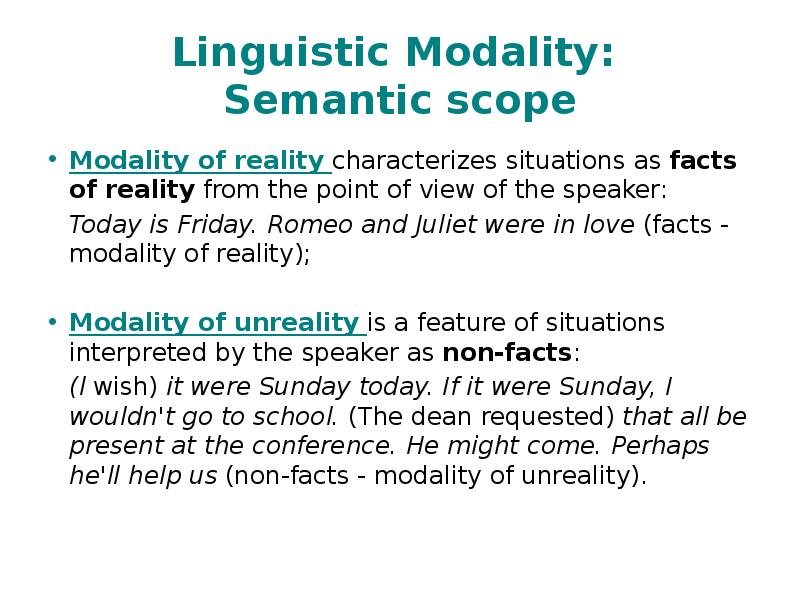
- 5. Linguistic Modality: Semantic scope Modality of reality characterizes situations as facts
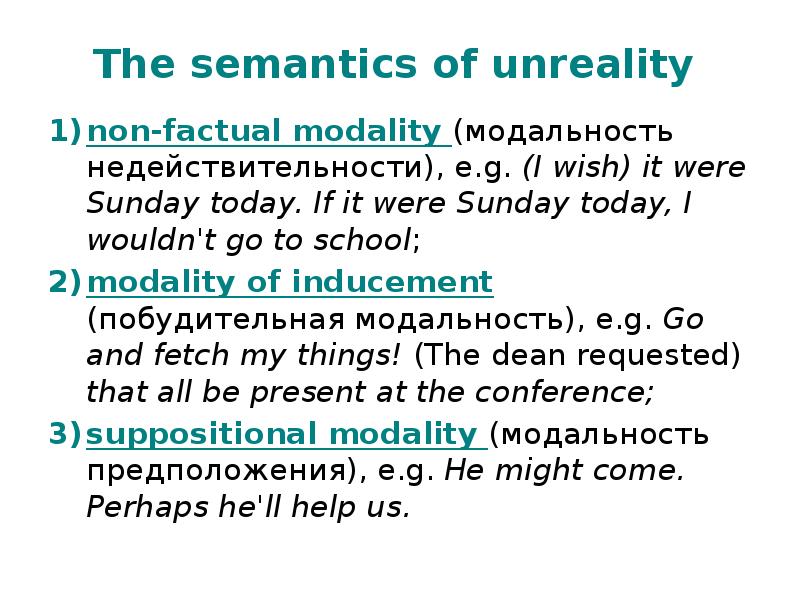
- 6. The semantics of unreality non-factual modality (модальность недействительности), e.g. (I
- 7. With respect to meaning Linguistic modality is an opposition of
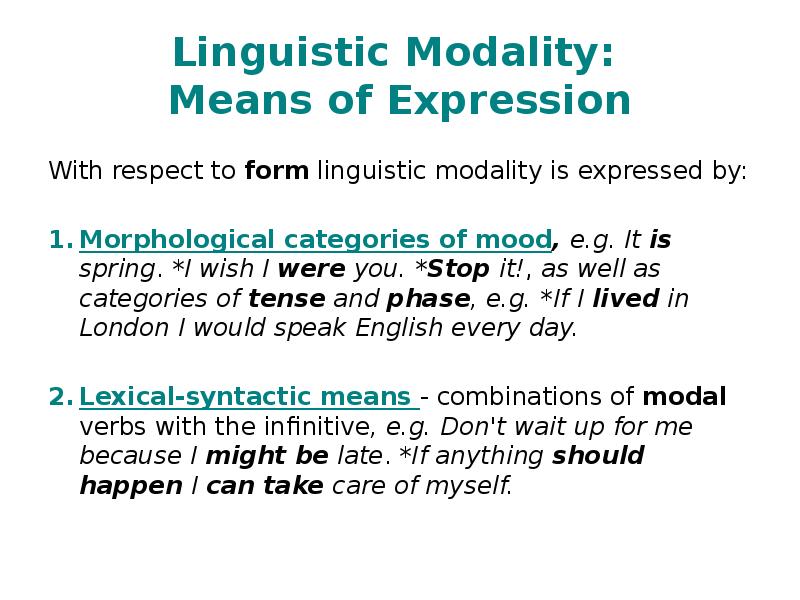
- 8. Linguistic Modality: Means of Expression With respect to form linguistic modality
- 9. Lexical means - modal words, Lexical means - modal words,
- 10. Syntactic types of sentences and subordinate clauses, e.g. *Take it easy!
- 11. The category of Mood is a set of opposed form classes,
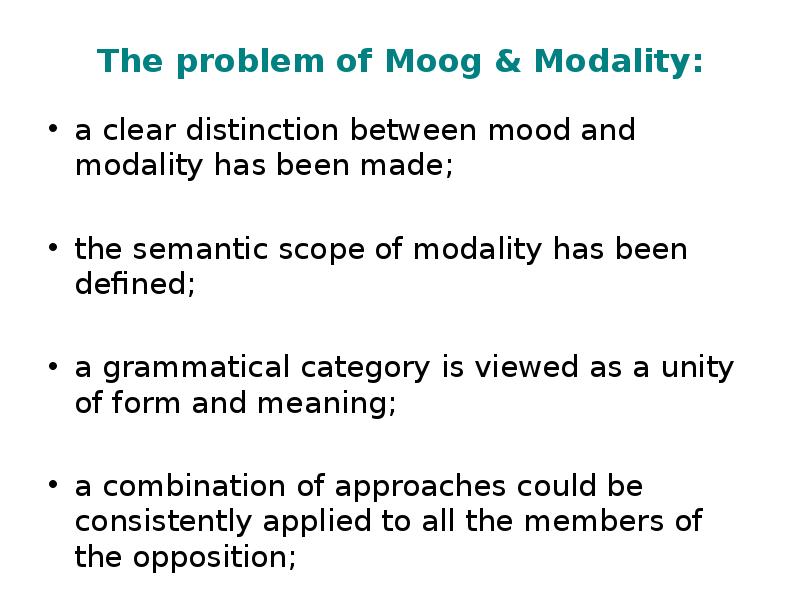
- 12. The problem of Moog & Modality: a clear distinction between mood
- 13. since combinations of modal verbs with the infinitive are not characterized
- 14. Different approaches to the system of Moods in English V. Plotkin:
- 15. A.I. Smirnitsky: a system of 6 moods Indicative: He came there.
- 16. Weak points of Smirnitsky’s theory: its semantic basis is inconsistent (the
- 17. The system of three moods in traditional grammar Indicative - Fact-Mood.
- 18. The Thought-Mood is subdivided: Subjunctive (be/were), Permissive (may/might/let + infinitive),
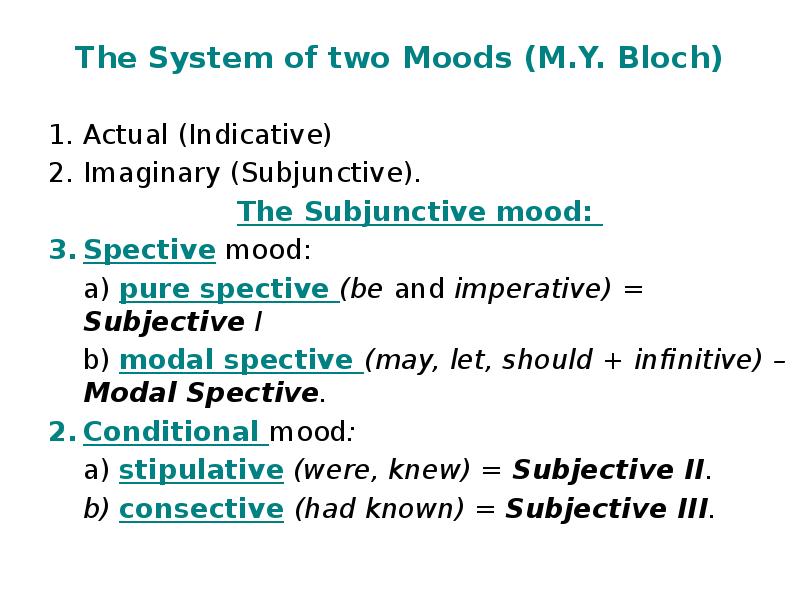
- 19. The System of two Moods (M.Y. Bloch) Actual (Indicative) Imaginary
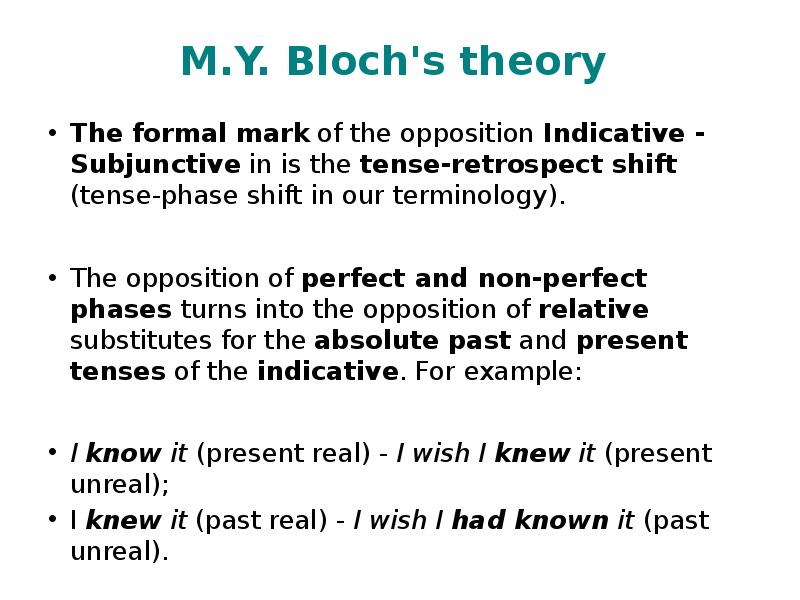
- 20. M.Y. Bloch's theory The formal mark of the opposition Indicative
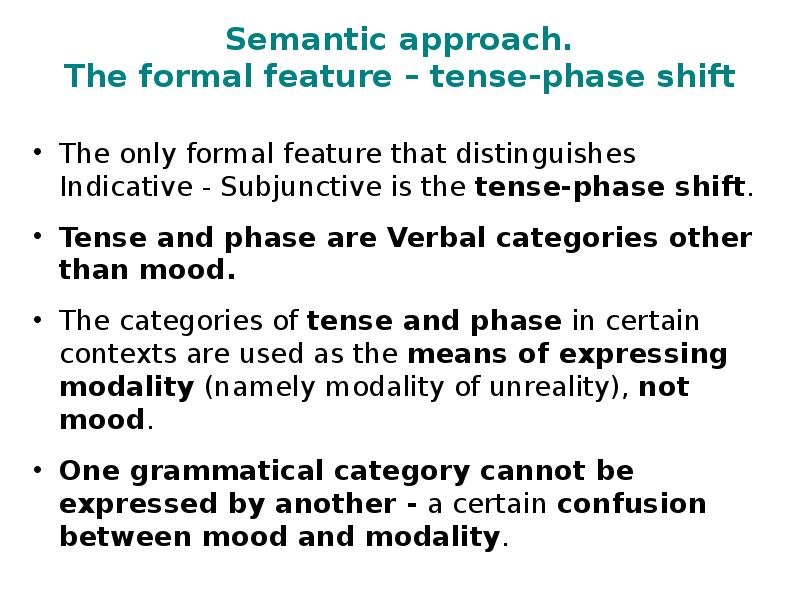
- 21. Semantic approach. The formal feature – tense-phase shift The only formal
- 22. L.S. Barchudarov’s approach to the category of Mood as twofold system
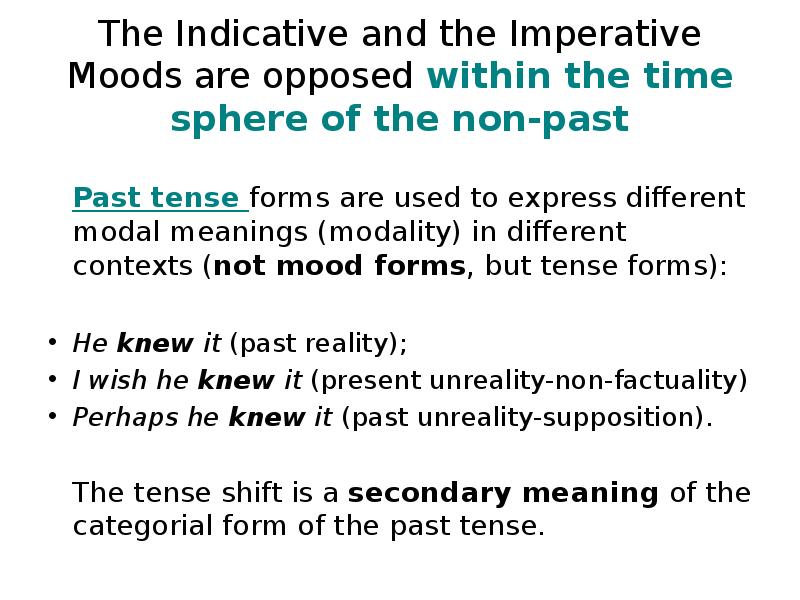
- 23. The Indicative and the Imperative Moods are opposed within the time
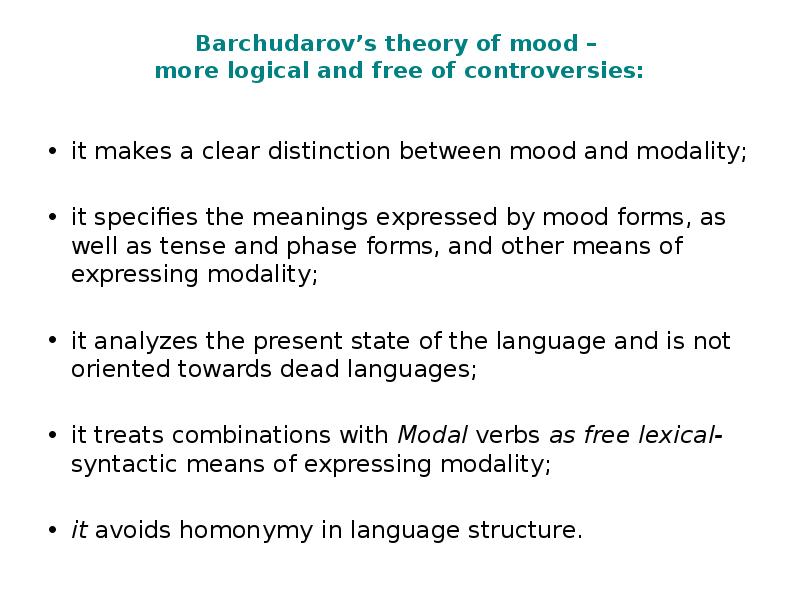
- 24. Barchudarov’s theory of mood – more logical and free of controversies:
- 25. Verbal means of expressing unreality (he) go/be (I insist that he
- 26. should + infinitive for all persons (I insist that he should
- 27. Detailed consideration of verbal means of expressing unreality (he) be/go;
- 28. knew/went; had known/had gone the forms of the past tense of
- 29. should/would + non-perfect/perfect infinitive are often referred to as the analytical
- 30. should + infinitive I insist that you should go there. It
- 31. may/might + infinitive are sometimes treated as an analytical form of
- 32. would + infinitive in conditional clauses is treated as a free
- 33. can/could + infinitive is never treated as an analytical mood form.
- 34. Free and dependent use of verbal means expressing unreality The independent
- 35. The Traditional Use of verbal means expressing unreality includes such
- 36. The independent use of forms expressing unreality Imperative mood forms in
- 37. The dependent use of verbal means expressing unreality Non-factuality: The Subjunctive
- 38. The extinct form were and forms of the past tense in
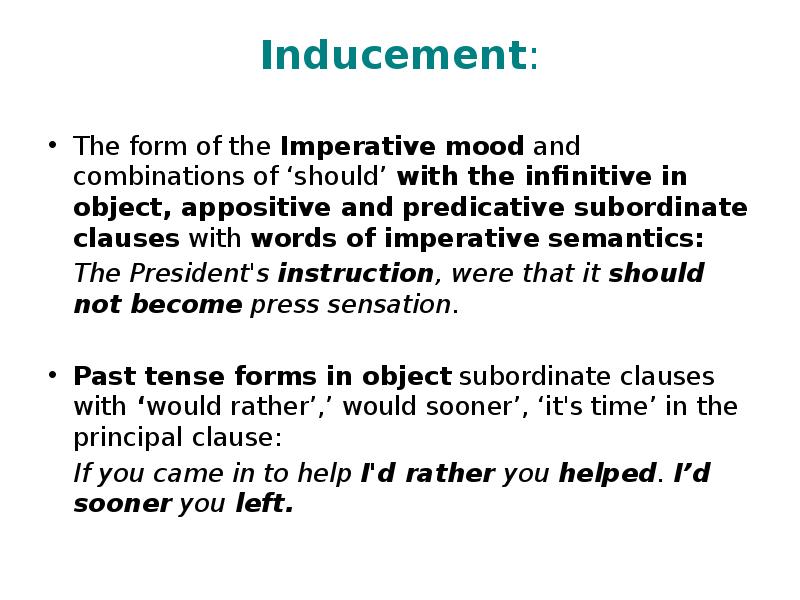
- 39. Inducement: The form of the Imperative mood and combinations of ‘should’
- 40. Supposition: Mood, tense and phase forms, combinations of modal verbs with
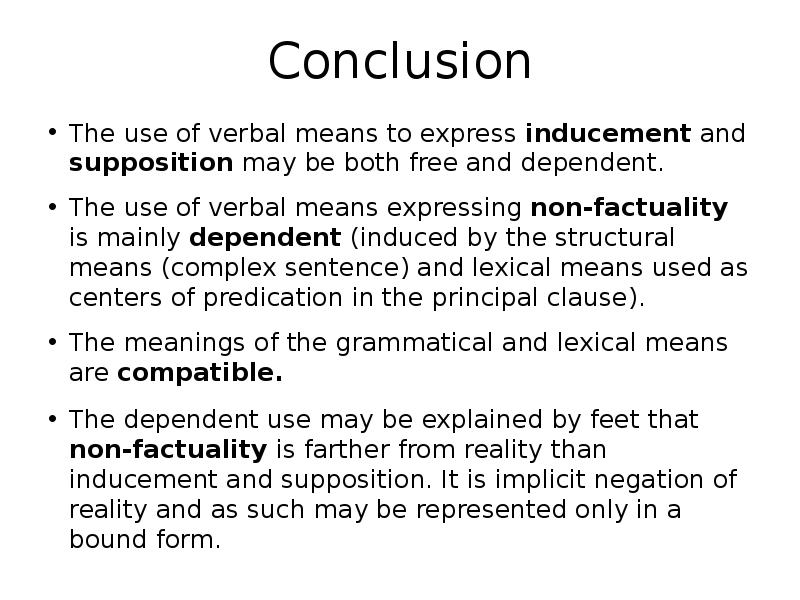
- 41. Conclusion The use of verbal means to express inducement and supposition
- 42. Скачать презентацию




























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























