Understanding Feature Space in Machine Learning презентация
Содержание
- 2. My journey so far
- 3. Why machine learning?
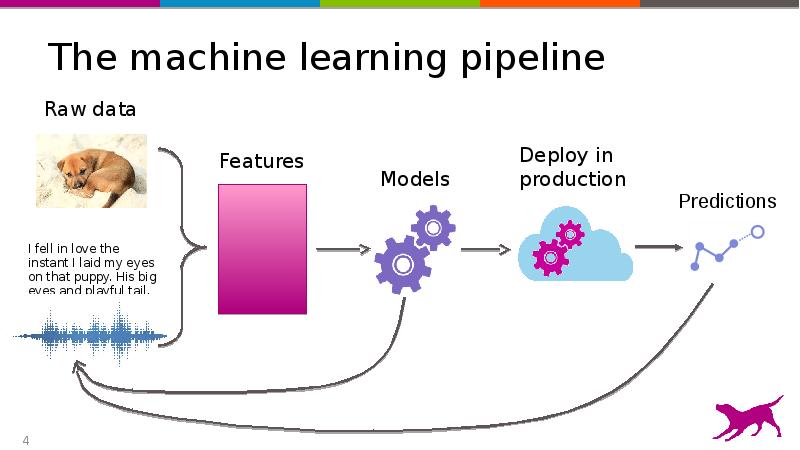
- 4. The machine learning pipeline
- 5. Feature = numeric representation of raw data
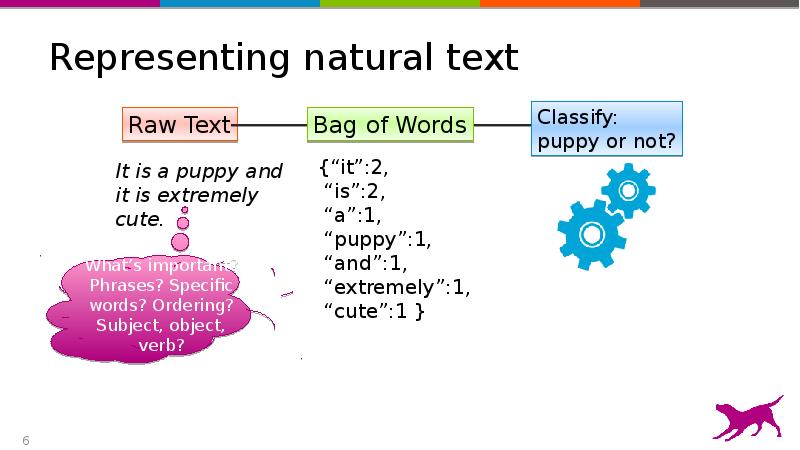
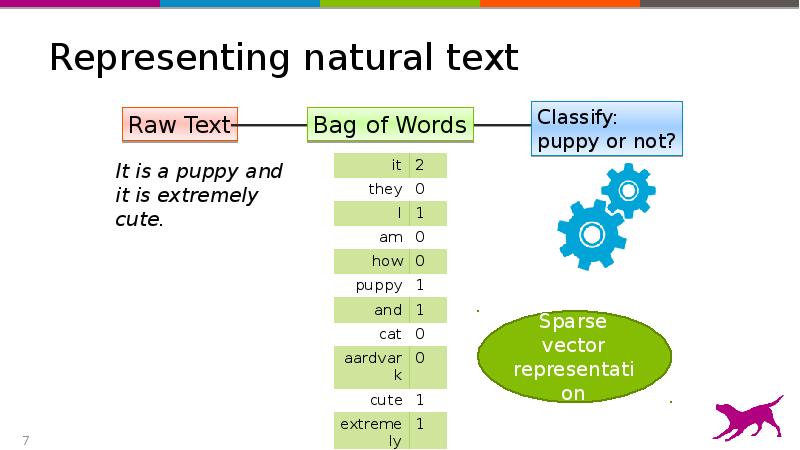
- 6. Representing natural text
- 7. Representing natural text
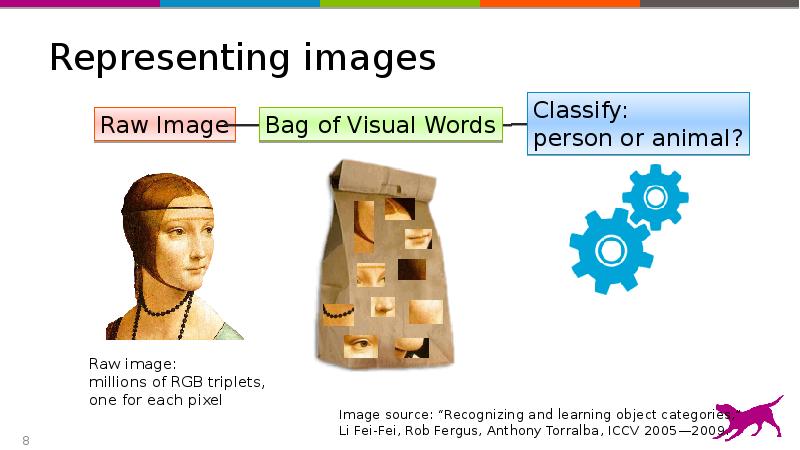
- 8. Representing images
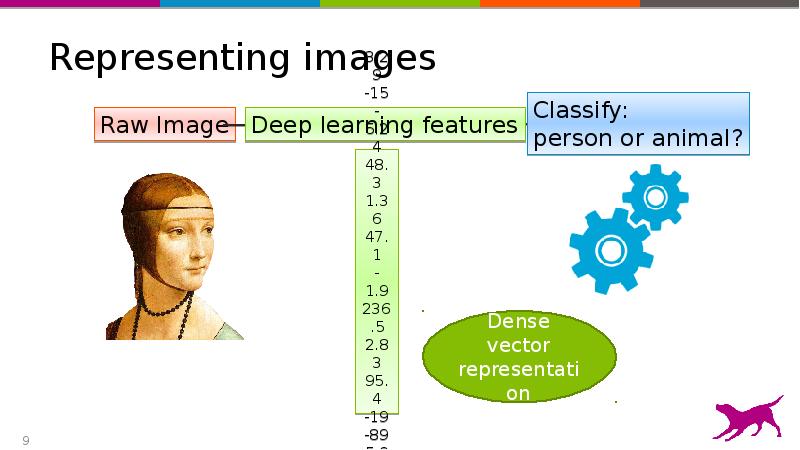
- 9. Representing images
- 10. Feature space in machine learning Raw data high dimensional vectors
- 11. Crudely speaking, mathematicians fall into two categories: the algebraists, who find
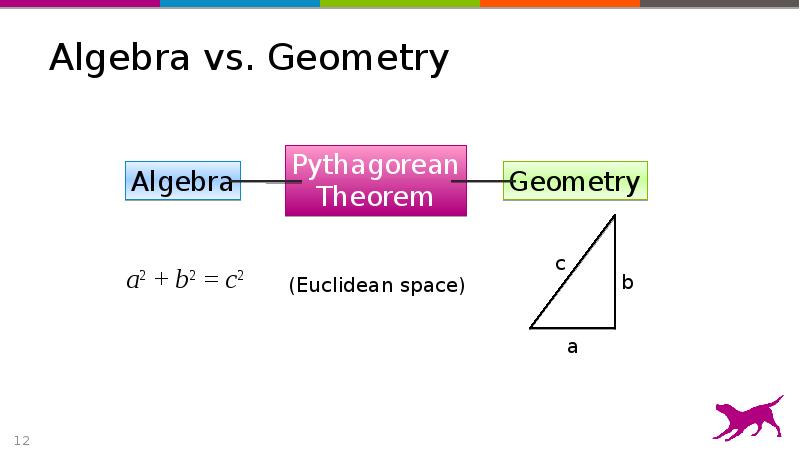
- 12. Algebra vs. Geometry
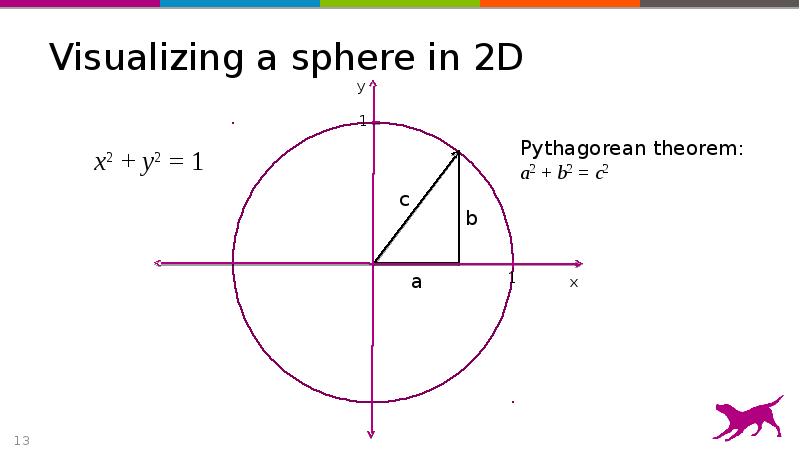
- 13. Visualizing a sphere in 2D
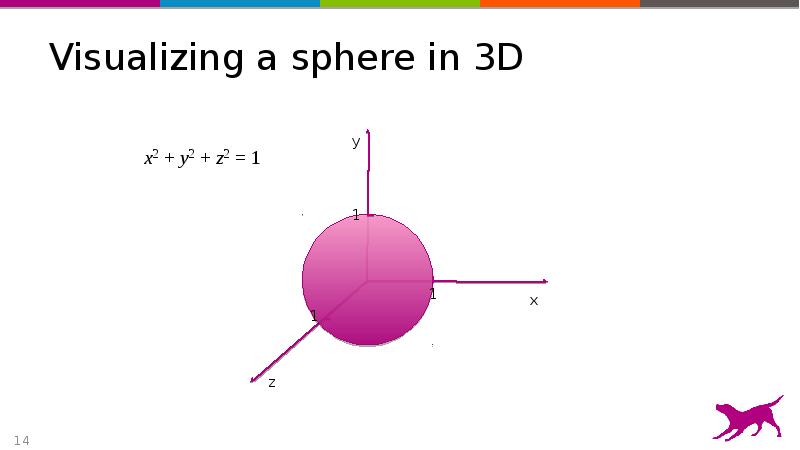
- 14. Visualizing a sphere in 3D
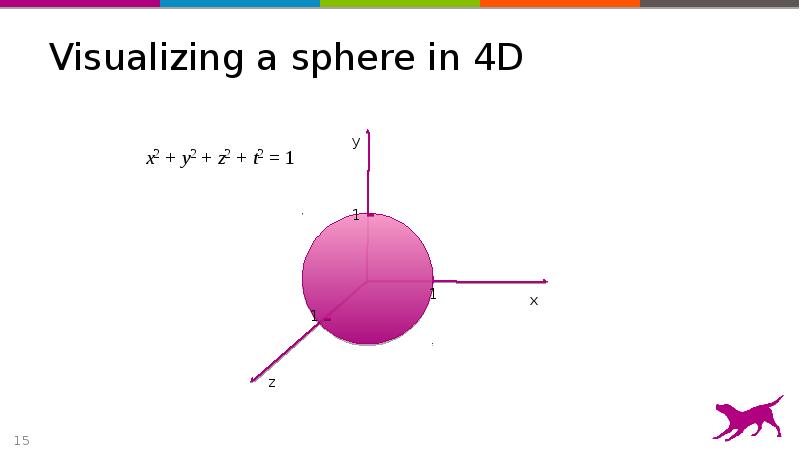
- 15. Visualizing a sphere in 4D
- 16. Why are we looking at spheres?
- 17. The power of higher dimensions A sphere in 4D can model
- 18. Visualizing Feature Space
- 19. The challenge of high dimension geometry Feature space can have hundreds
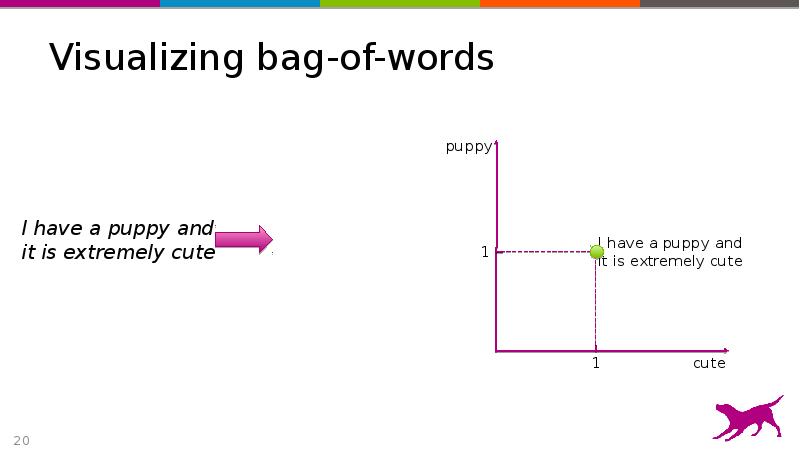
- 20. Visualizing bag-of-words
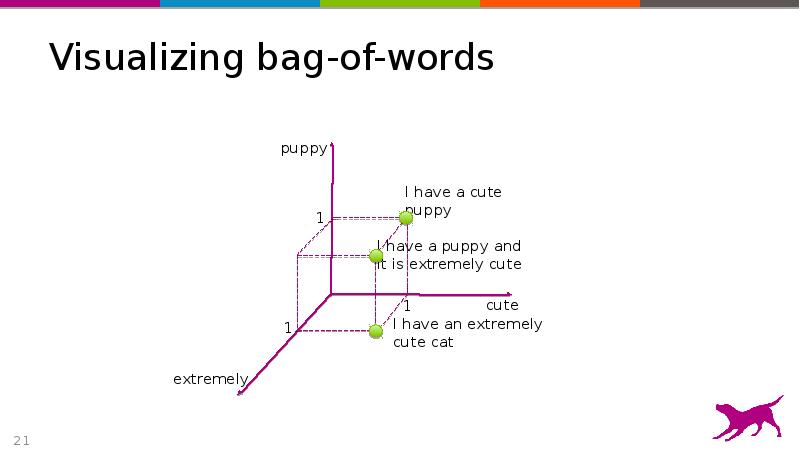
- 21. Visualizing bag-of-words
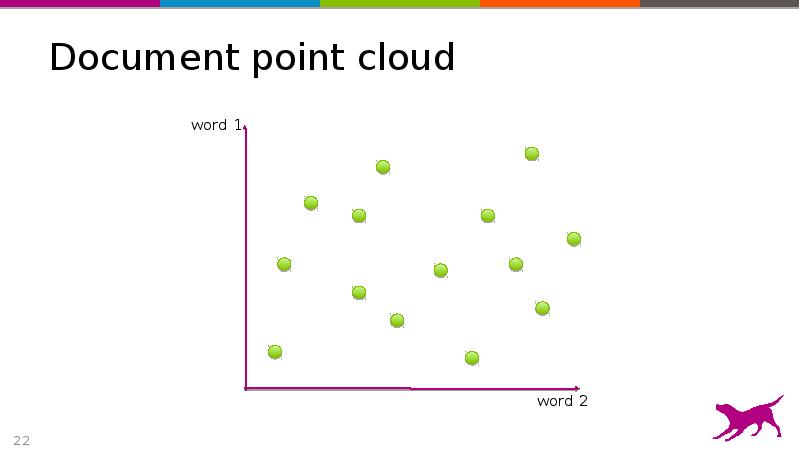
- 22. Document point cloud
- 23. What is a model? Model = mathematical “summary” of data What’s
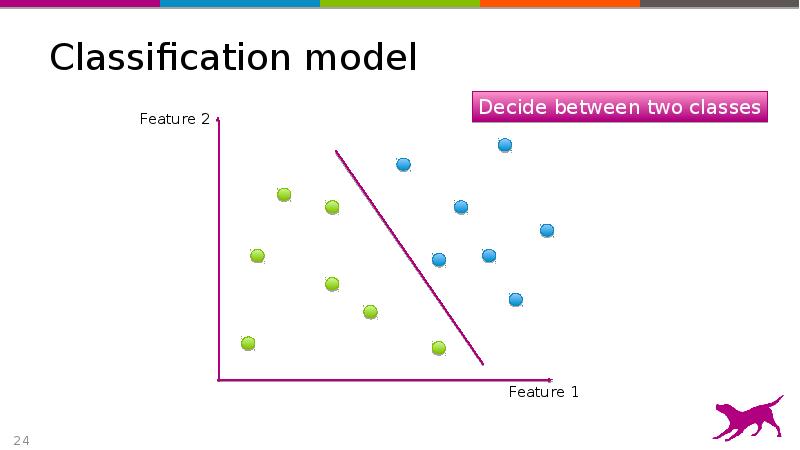
- 24. Classification model
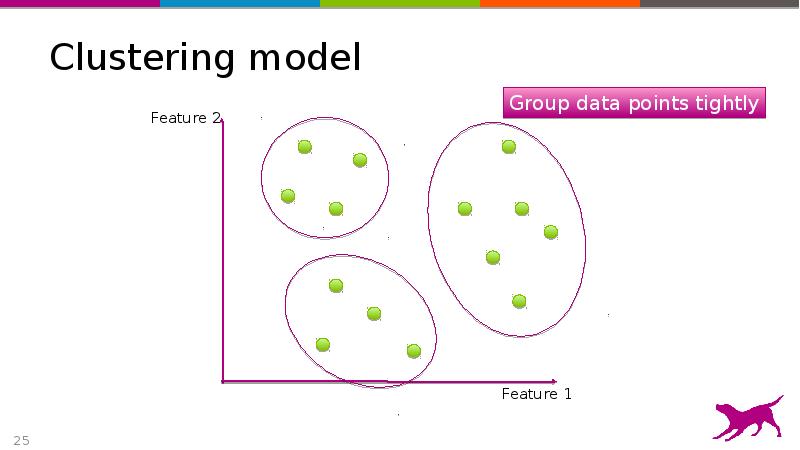
- 25. Clustering model
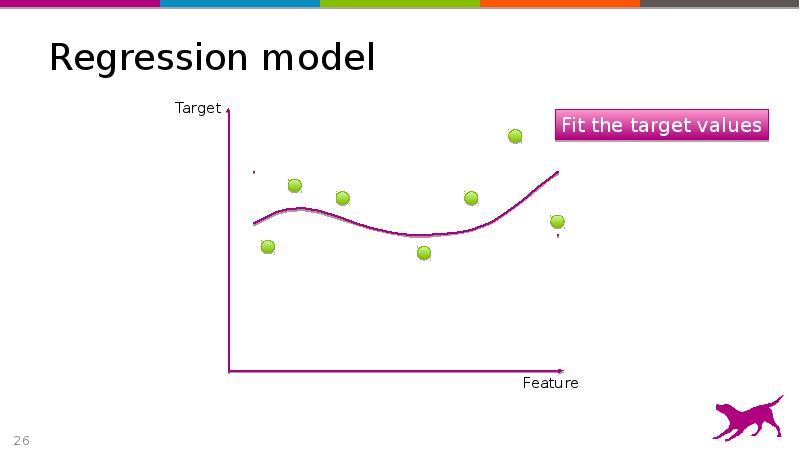
- 26. Regression model
- 27. Visualizing Feature Engineering
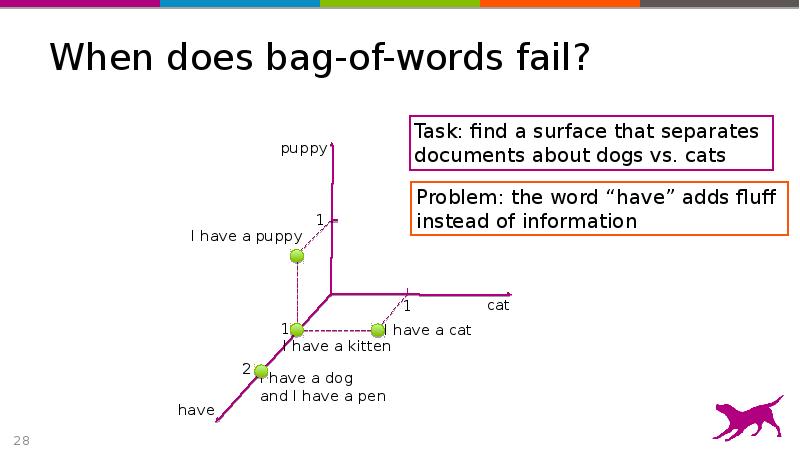
- 28. When does bag-of-words fail?
- 29. Improving on bag-of-words Idea: “normalize” word counts so that popular words
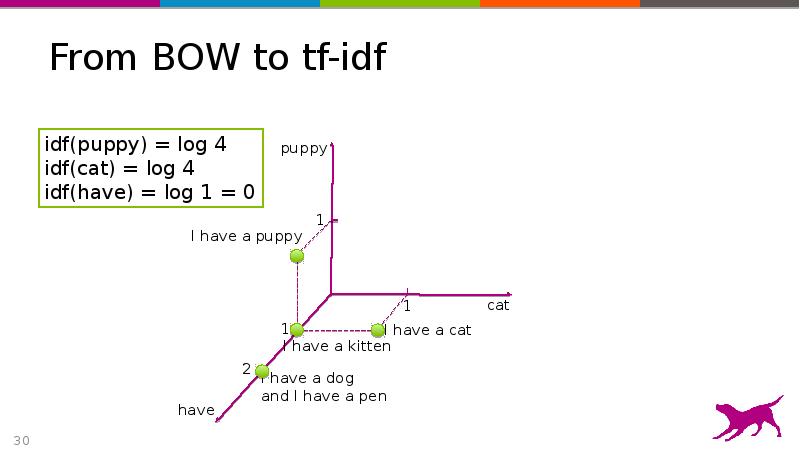
- 30. From BOW to tf-idf
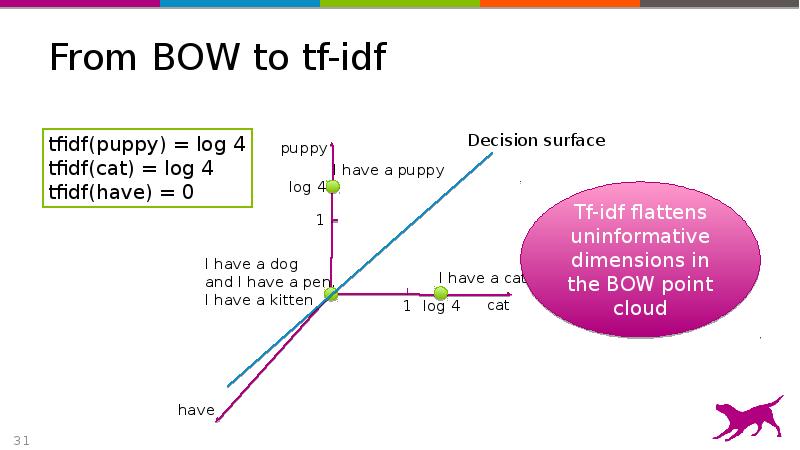
- 31. From BOW to tf-idf
- 32. Entry points of feature engineering Start from data and task What’s
- 33. That’s not all, folks! There’s a lot more to feature engineering:
- 34. Скачать презентацию










Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Understanding Feature Space in Machine Learning можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























