Polysemy and homonymy презентация
Содержание
- 2. Contents 1. What polysemantic words are. 2. Types of meaning of
- 3. Monosemantic words - words having only one meaning are comparatively few
- 4. Different meanings of a polysemantic word may come together due to
- 5. Polysemantic words should be studied synchronically and diachronically. Polysemantic words should
- 6. Types of meaning Polysemantic words have: 1) primary meaning; 2) derived
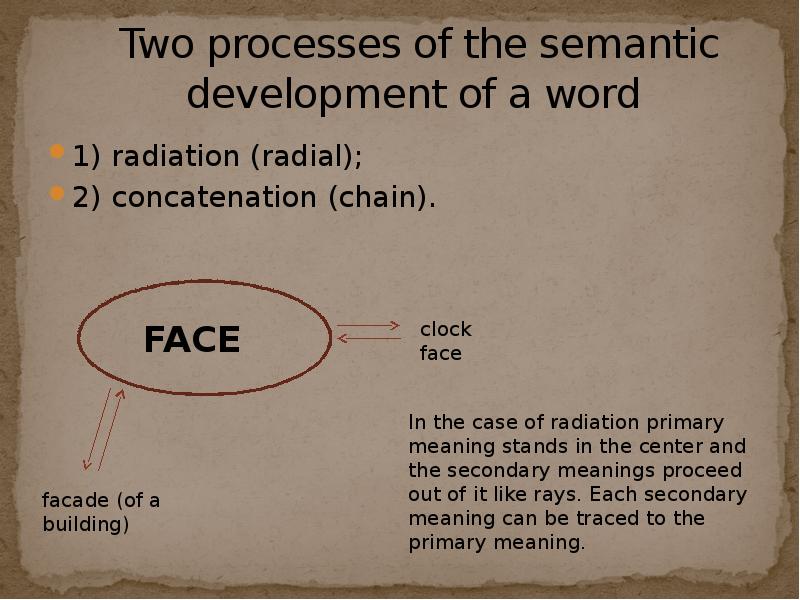
- 7. Two processes of the semantic development of a word 1)
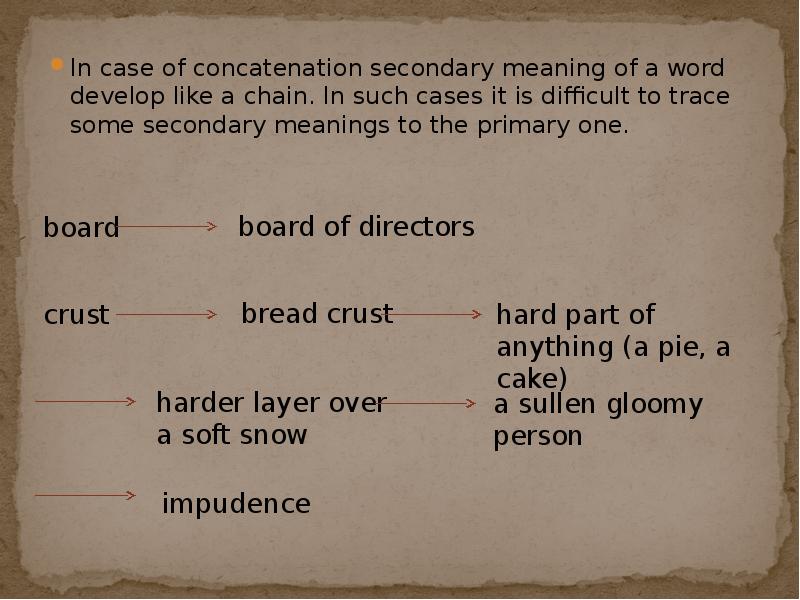
- 8. In case of concatenation secondary meaning of a word develop like
- 9. The last meanings have nothing to do with the primary ones.
- 10. Homonymy and homonyms Homonyms ( Greek homoios - identical and
- 11. English is rich in homonyms due to its monosyllabic character. The
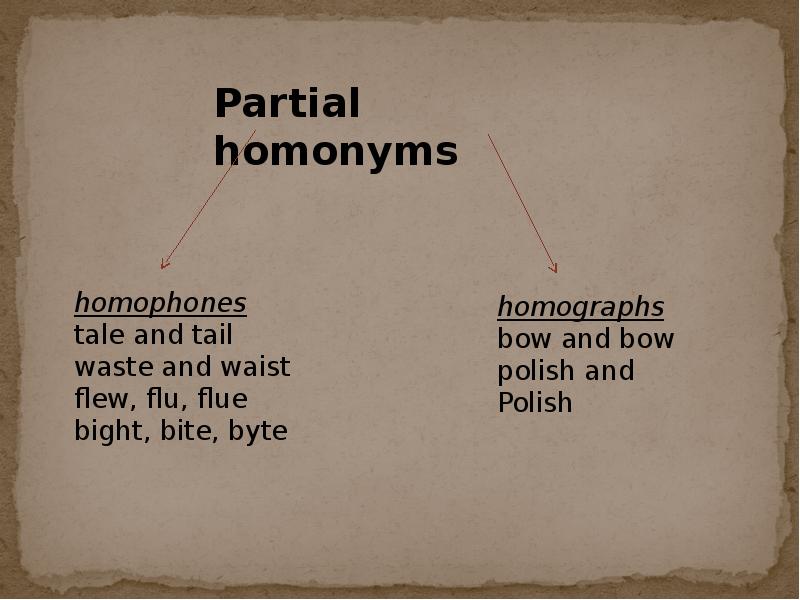
- 12. Full and partial homonyms There is the case of full and
- 14. Not only notional words can demonstrate homonymy but functional words as
- 15. Classification of homonyms according to the type of meaning Lexical
- 16. Sources of homonymy 1. Phonetic changes words undergo during the
- 17. 3. Word-building (conversion) – transfering from one part of the speech
- 18. References 1. I.V. Arnold – “The English Word”. 2. G. B.
- 19. Скачать презентацию















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























