Semantic structure of the word and its changes. (Lecture 3) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Plan: Semantics / semasiology. Different approaches to word-meaning. Types of word-meaning.
- 3. List of Terms: semantics referent referential meaning grammatical meaning lexical meaning
- 4. It is meaning that makes language useful. George A. Miller,
- 5. 1. Semantics / semasiology. Different approaches to word-meaning
- 6. The function of the word as a unit of communication is
- 7. "The Meaning of Meaning" (1923) by C.K. Ogden and I.A. Richards
- 9. This linguistic study was pointed out in 1897 by M. Breal
- 10. Semasiology is a synonym for 'semantics' (from Gk. semasia
- 11. Different Approaches to Word Meaning: ideational (or conceptual) referential functional
- 12. The ideational theory can be considered the earliest theory of meaning.
- 13. A difficulty: not clear why communication and understanding are possible
- 14. Meaning: a concept with specific structure.
- 15. Do people speaking different languages have different conceptual systems? If
- 16. finger 'one of 10 movable parts of joints at the end
- 17. Referential theory is based on interdependence of things, their concepts and
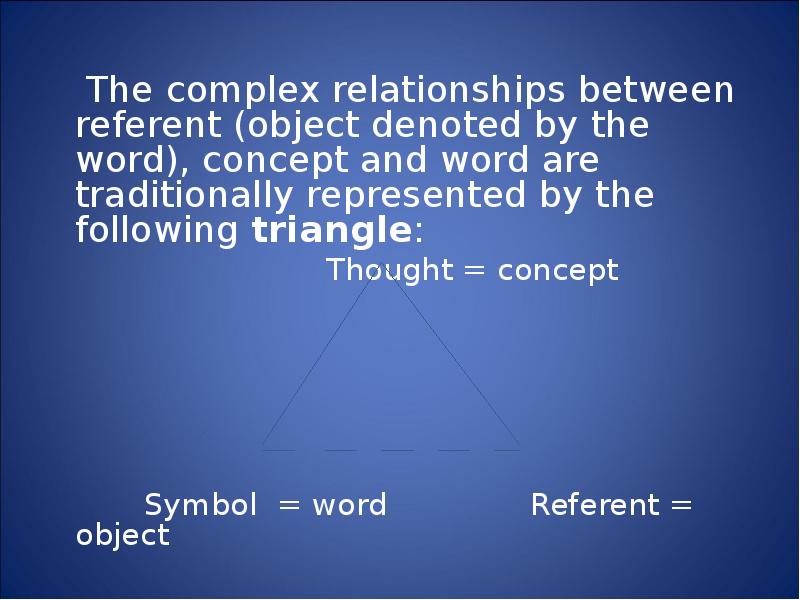
- 18. The complex relationships between referent (object denoted by the word), concept
- 19. an animal, with 4 legs and a tail, can bark and
- 20. Meaning concept different words having different meanings may be used
- 21. Concept of dying die pass away kick the bucket
- 22. Meaning symbol In different languages: a word with the same
- 23. Meaning referent to denote one and the same object we
- 24. A horse in various contexts: horse, animal, creature,
- 25. Word meaning: the interrelation of all three components of
- 26. Functionalists study word meaning by analysis of the way the word
- 27. The meaning of a word is its use in language.
- 28. cloud and cloudy have different meanings because in speech they
- 29. Meaning: a component of the word through which a concept
- 30. 2. Types of word-meaning
- 31. According to the conception of word meaning as a specific structure:
- 32. Lexical Meaning: denotational connotational
- 33. Denotational lexical meaning provides correct reference of a word to an
- 34. to glare – to look
- 35. Connotational lexical meaning is an emotional colouring of the word. Unlike
- 36. Connotations: Emotive charge may be inherent in word meaning (like in
- 37. 2. Stylistic reference refers the word to a certain style: neutral
- 38. 3. Evaluative connotations express approval or disapproval (charming, disgusting). 4.
- 39. Denotative component Lonely = alone, without company To glare = to
- 40. 3. Polysemy. Semantic structure of words. Meaning and context
- 41. A polysemantic word is a word having more than one meaning.
- 42. Most English words are polysemantic. A well-developed polysemy is
- 43. Monosemantic Words: terms (synonym, bronchitis, molecule), pronouns (this, my, both),
- 44. The main causes of polysemy: a large number of: 1) monosyllabic
- 45. The sources of polysemy: 1) the process of meaning change
- 46. blanket a woolen covering used on beds, a covering for keeping
- 47. Meanings of a polysemantic word are organized in a semantic structure
- 48. Lexical-semantic variant one of the meanings of a polysemantic word used
- 49. A Word's Semantic Structure Is Studied: Diachronically (in the process of
- 50. The meaning first registered in the language is called primary.
- 51. table a piece of furniture (primary meaning) the persons
- 52. The meaning that first occurs to our mind, or is understood
- 53. Fire
- 54. Processes of the Semantic Development of a Word: radiation (the primary
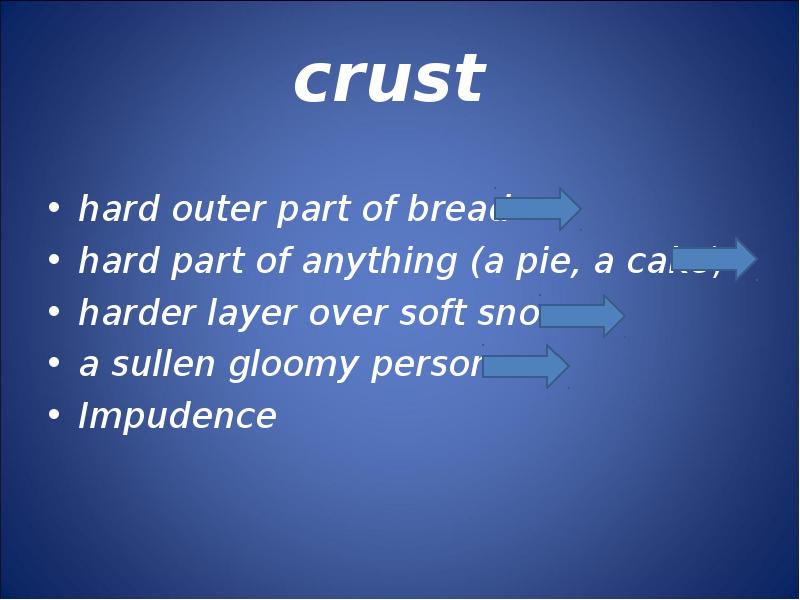
- 55. crust hard outer part of bread hard part of
- 56. Polysemy exists not in speech but in the language. It’s easy
- 57. Context: linguistic 1. lexical – a number of lexical
- 58. 4. Change of word-meaning: the causes, nature and results
- 59. The meaning of a word can change in a course of
- 60. Causes of Change of Word-meaning: 1. Extralinguistic (various changes in
- 61. Linguistic Causes: 1. ellipsis – in a phrase made up of
- 62. Linguistic Causes: 2. differentiation (discrimination) of synonyms – when a new
- 63. Linguistic Causes: 3. linguistic analogy – if one of the members
- 64. The nature of semantic changes is based on the secondary application
- 65. Association between Old Meaning and New: similarity of meanings or metaphor
- 66. Types of Metaphor: a) similarity of shape, e.g. head (of
- 67. Types of Metonymy: 'material — object of it' (She is wearing
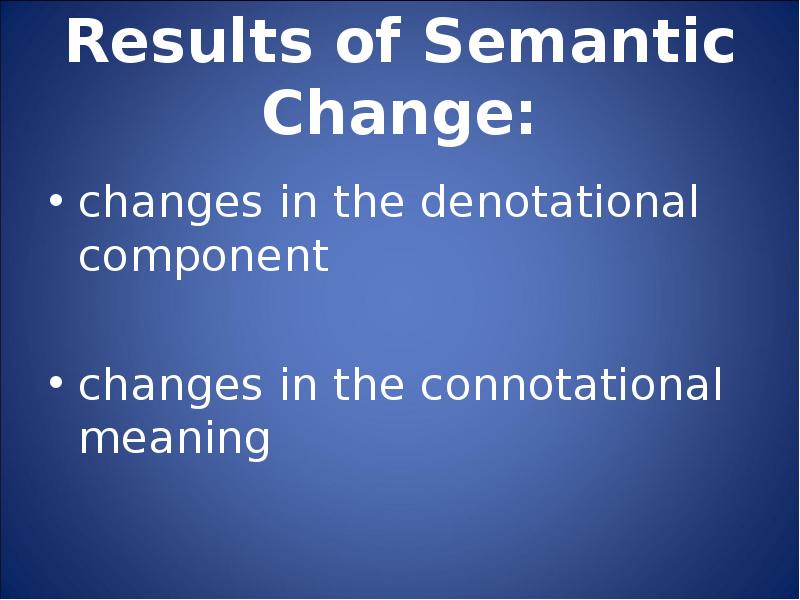
- 68. Results of Semantic Change: changes in the denotational component changes in
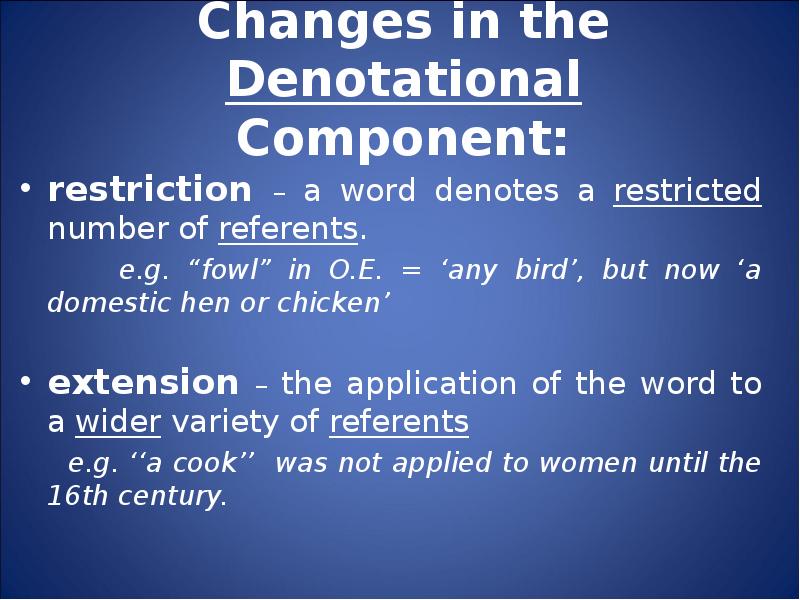
- 69. Changes in the Denotational Component: restriction – a word denotes
- 70. generalization – the word with the extended meaning passes from the
- 71. Changes in the Connotational Meaning: pejorative development (degradation) – the acquisition
- 72. List of Literature: Антрушина, Г. Б. Лексикология английского языка: учебник для
- 73. Скачать презентацию




































































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Semantic structure of the word and its changes. (Lecture 3) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























