The mechanics in biomechanics презентация
Содержание
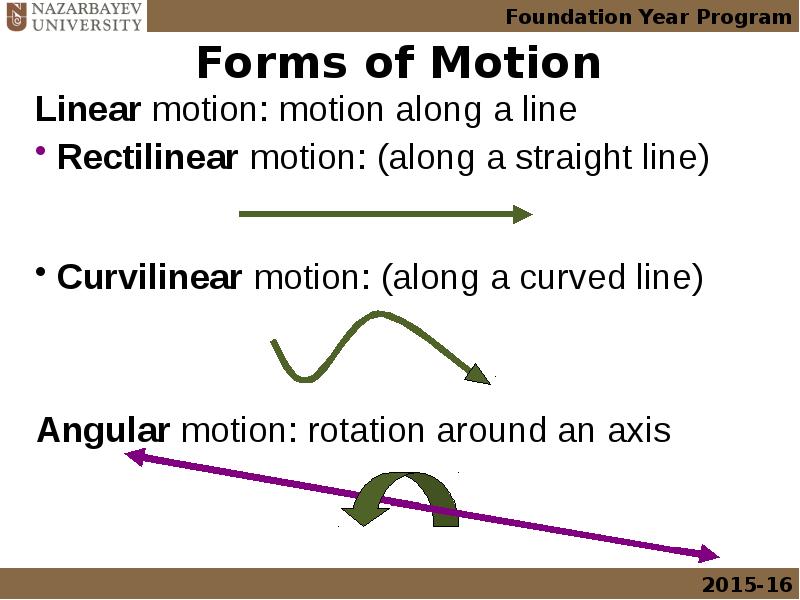
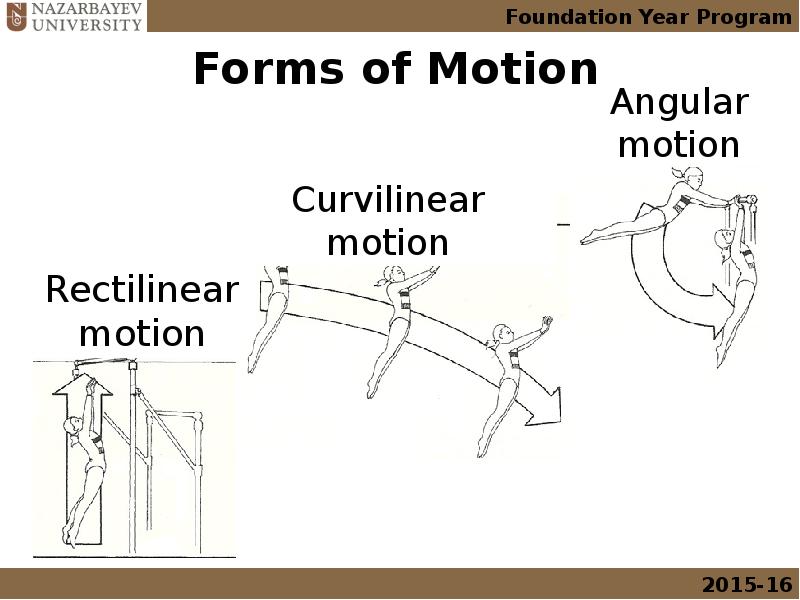
- 2. Outline Mechanics and its application to biological systems Forms of motion
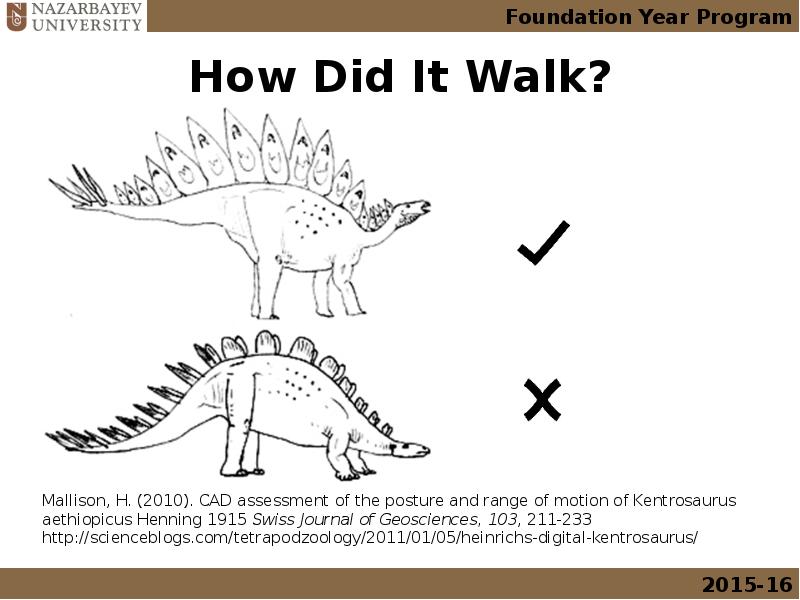
- 3. How Did It Walk?
- 4. How Did It Walk?
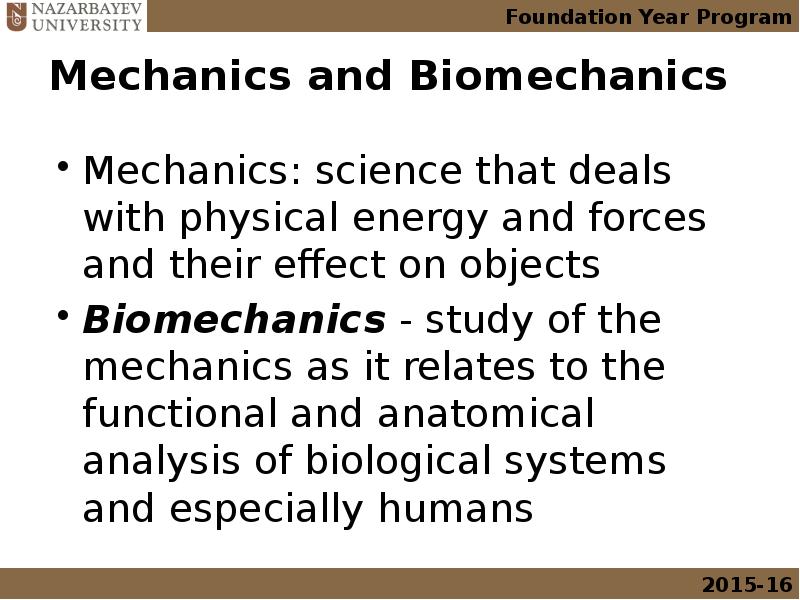
- 5. Mechanics and Biomechanics Mechanics: science that deals with physical energy and
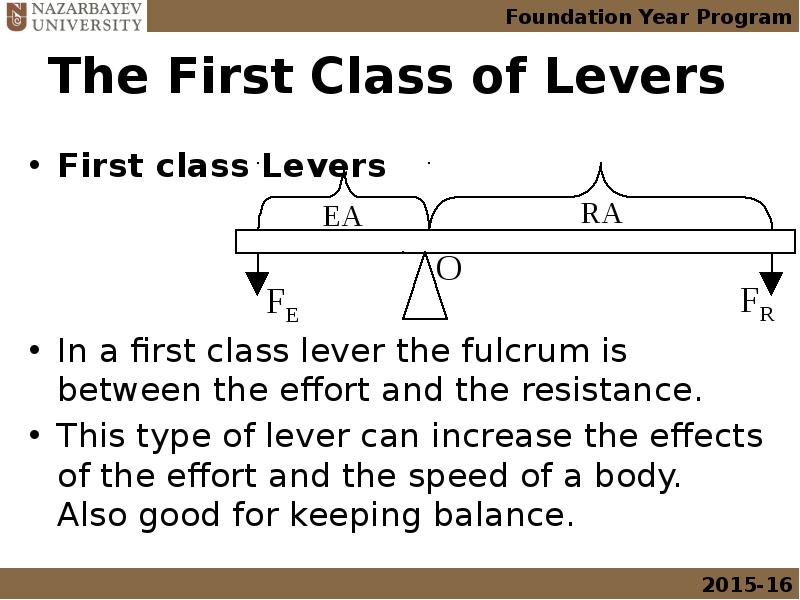
- 15. The First Class of Levers First class Levers In a first
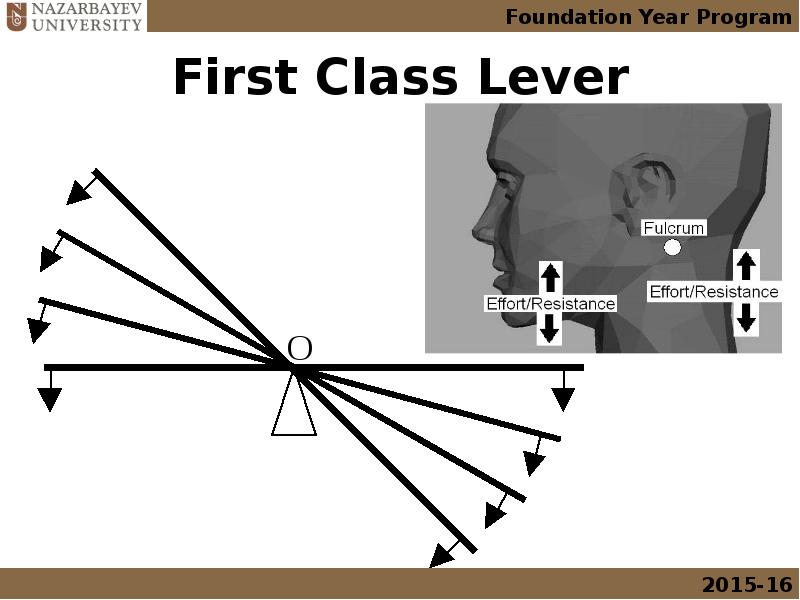
- 16. First Class Lever
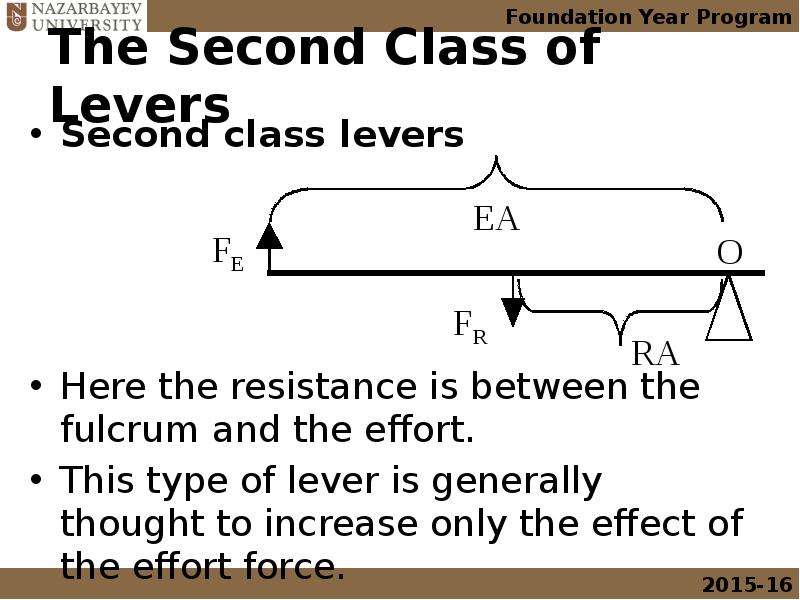
- 17. The Second Class of Levers Second class levers Here the resistance
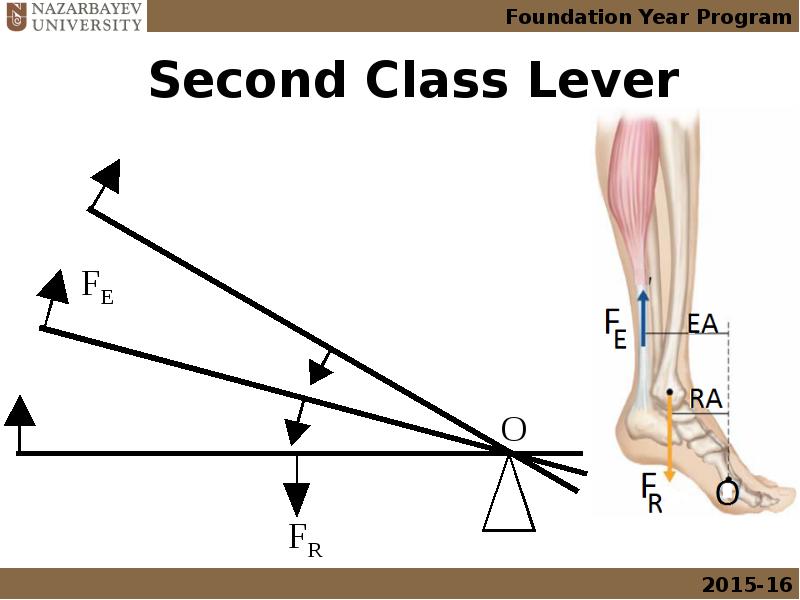
- 18. Second Class Lever
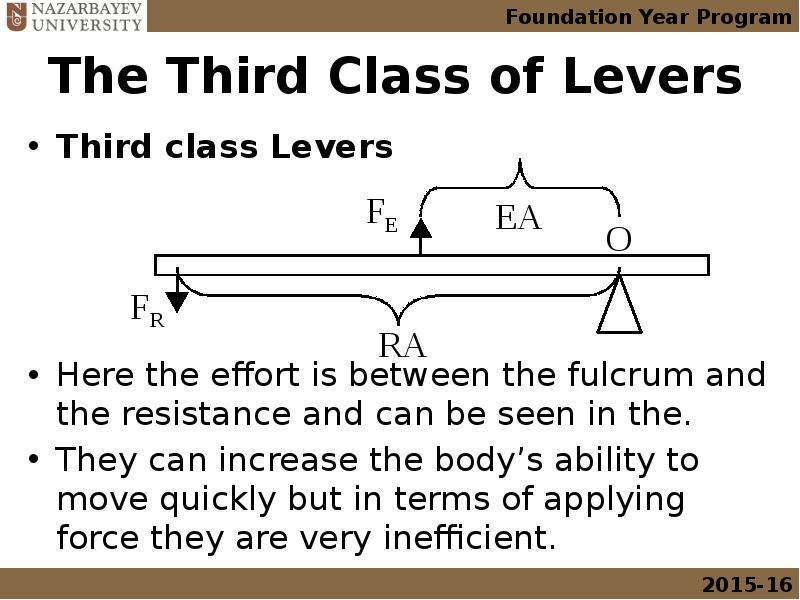
- 19. The Third Class of Levers Third class Levers Here the effort
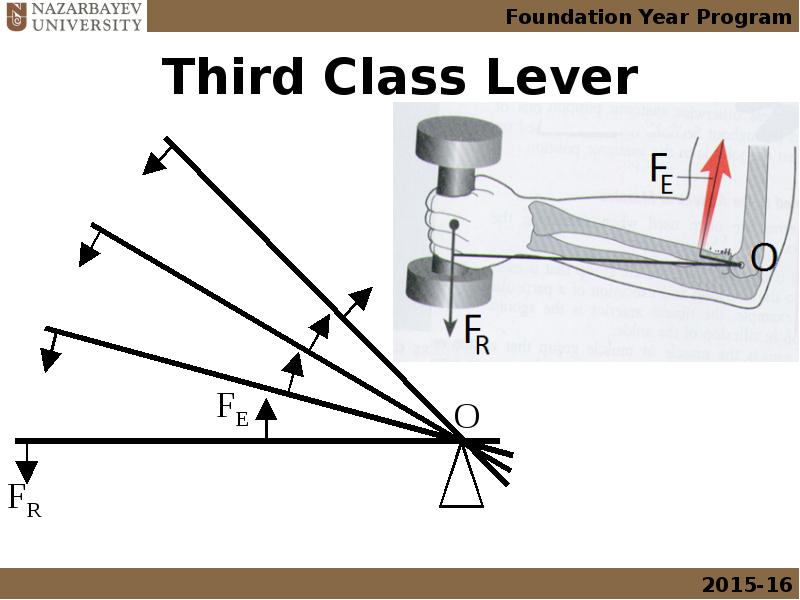
- 20. Third Class Lever
- 21. Human Body Levers Human’s levers are mostly built for speed and
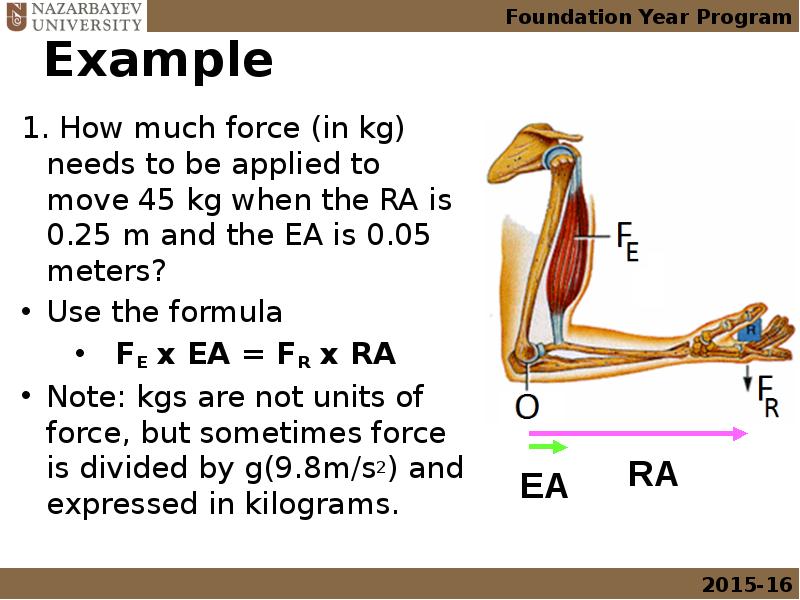
- 22. Example 1. How much force (in kg) needs to be applied
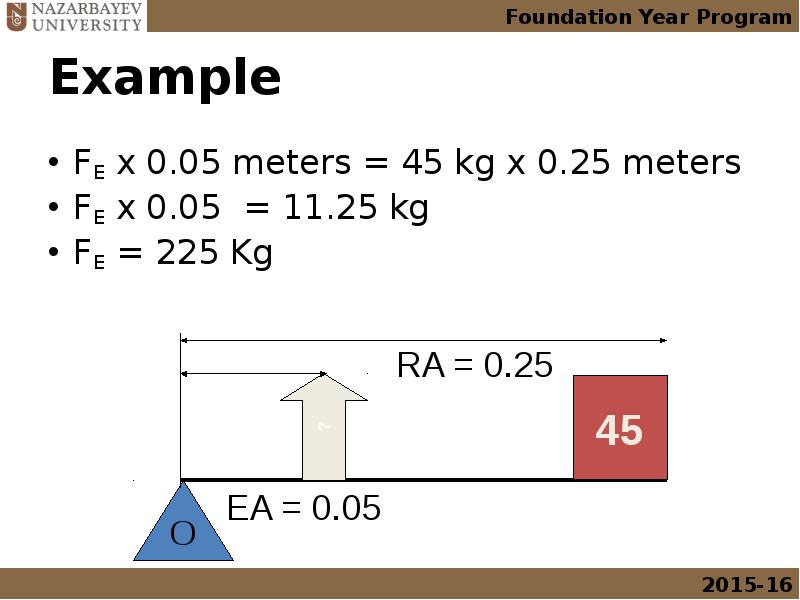
- 23. Example FE x 0.05 meters = 45 kg x 0.25 meters
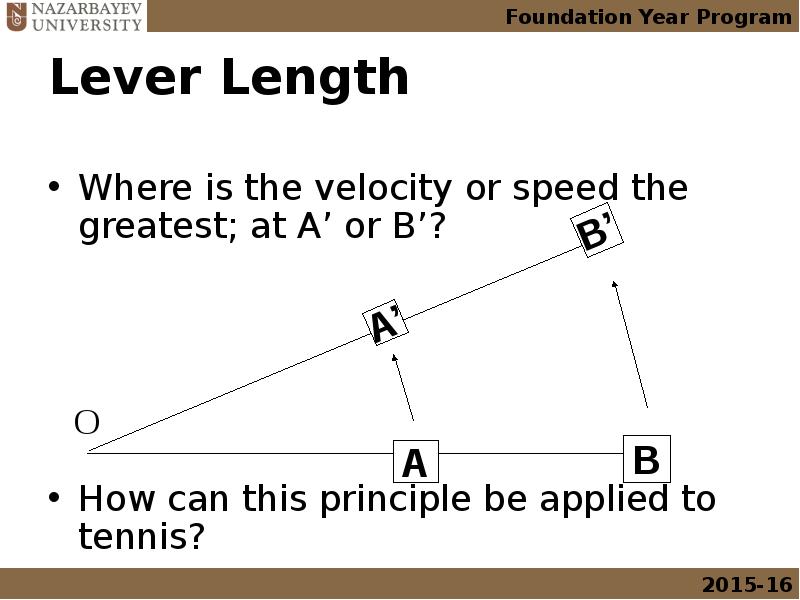
- 24. Lever Length Where is the velocity or speed the greatest; at
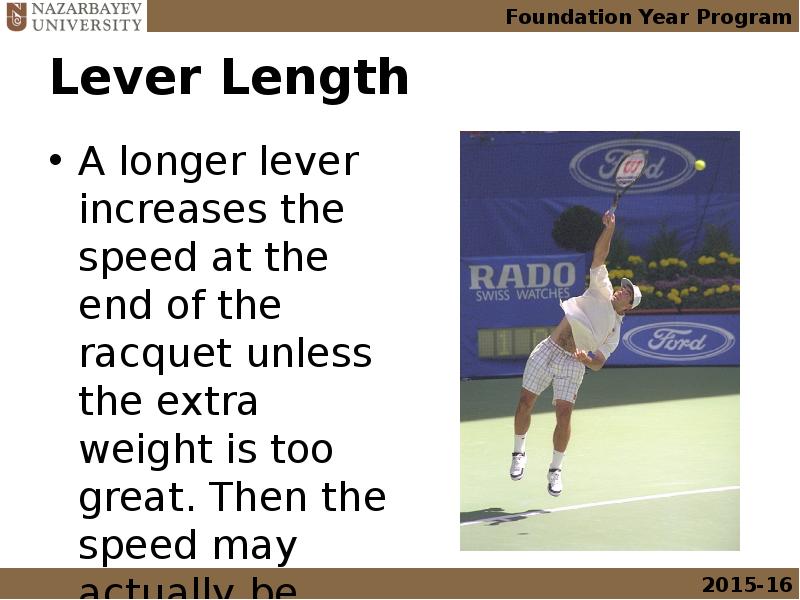
- 25. Lever Length A longer lever increases the speed at the end
- 26. Stability Center of gravity (CG): Point at which all parts
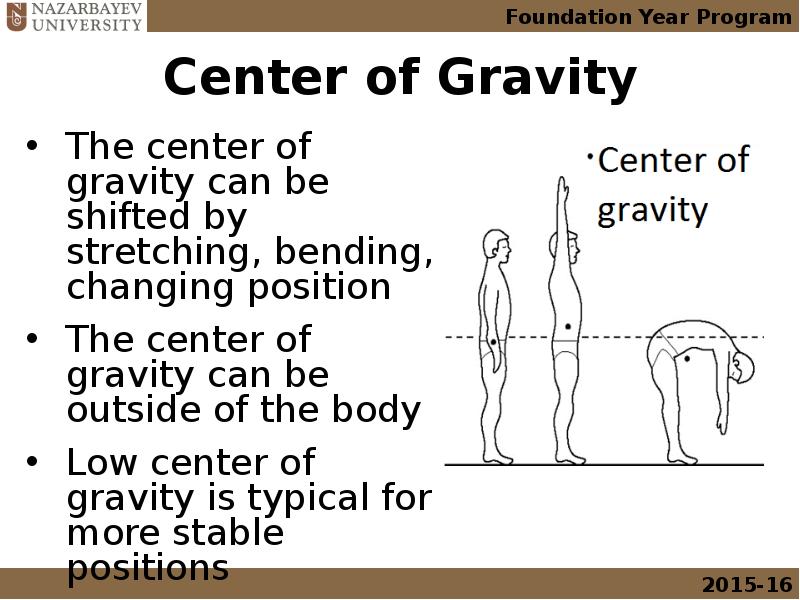
- 27. Center of Gravity
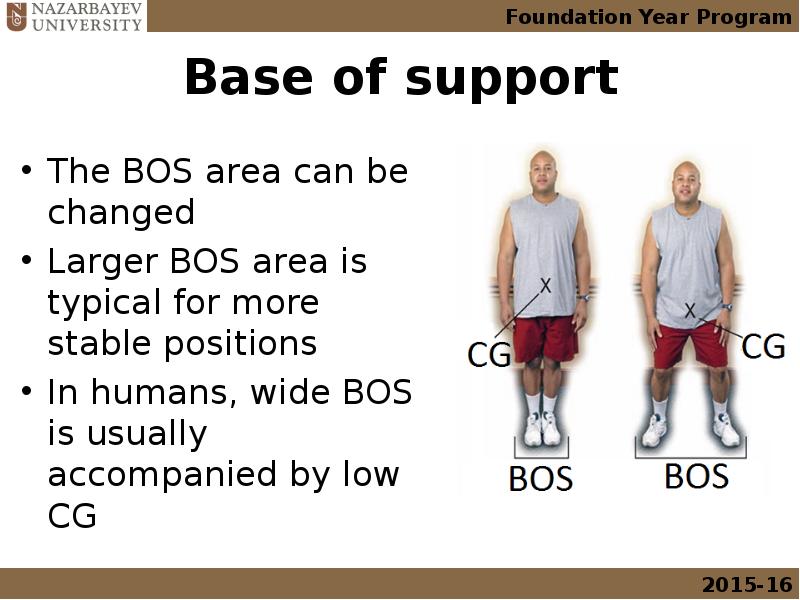
- 28. Base of support The BOS area can be changed Larger BOS
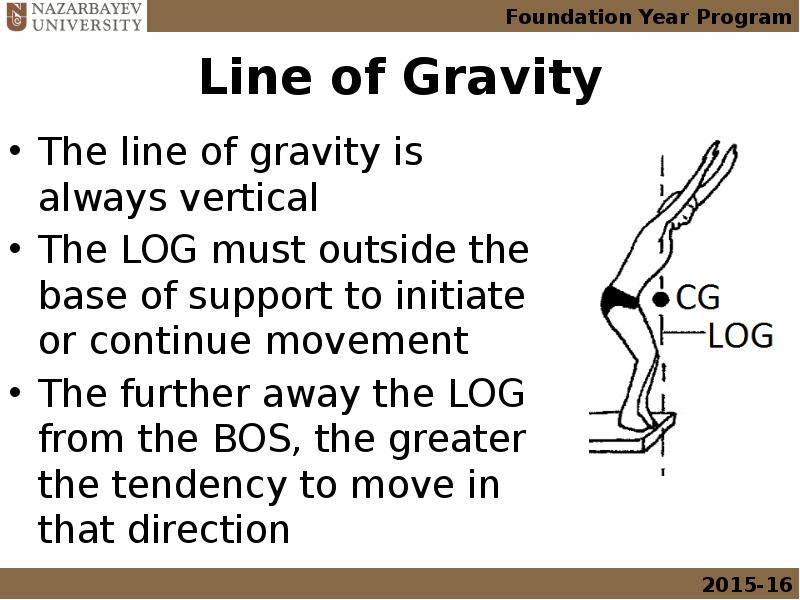
- 29. Line of Gravity The line of gravity is always vertical The
- 30. Stability Someone is more __________when they have a _______centre of _______,
- 31. Advantages/Disadvantages to Bipedal Locomotion Disadvantages Loss of speed Loss of agility
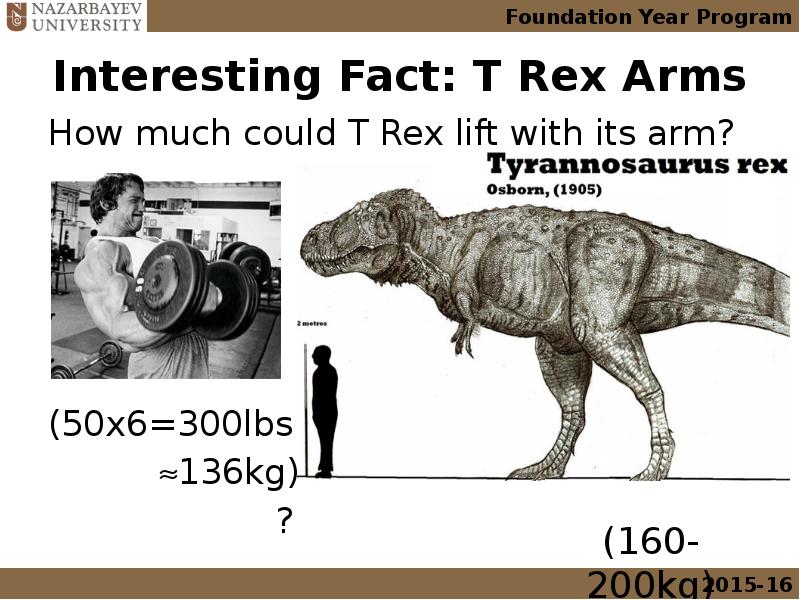
- 32. Interesting Fact: T Rex Arms How much could T Rex lift
- 36. Скачать презентацию














Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации