University physics. Forces review of basic concepts презентация
Содержание
- 2. Vectors and Scalars All physical quantities (e.g. speed and force) are
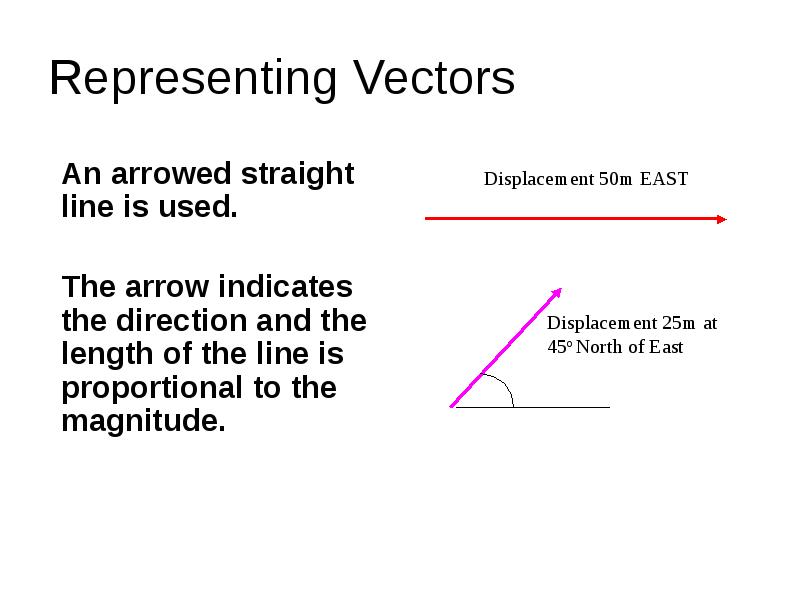
- 3. Representing Vectors An arrowed straight line is used. The arrow
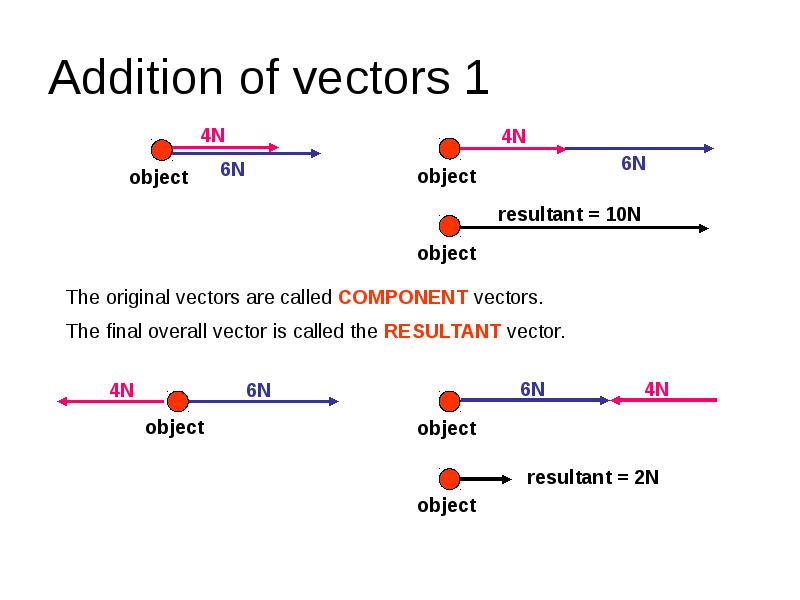
- 4. Addition of vectors 1
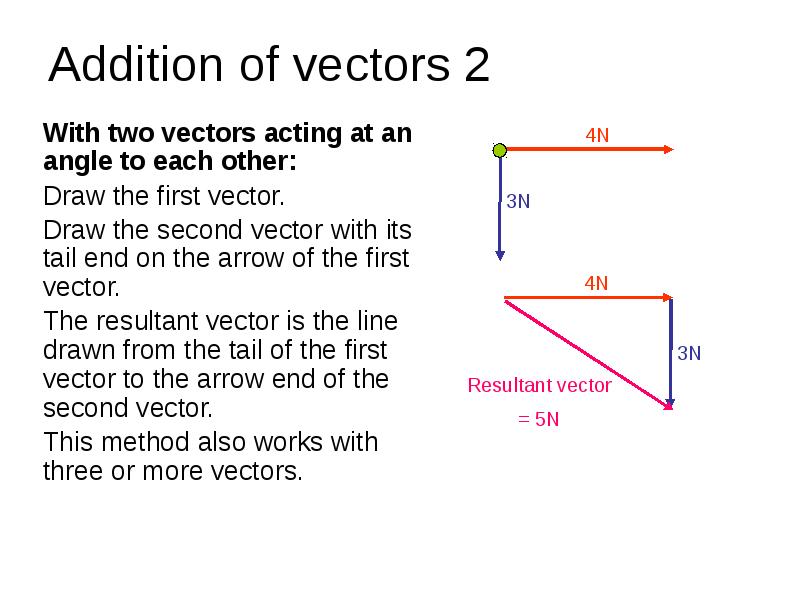
- 5. Addition of vectors 2 With two vectors acting at an angle
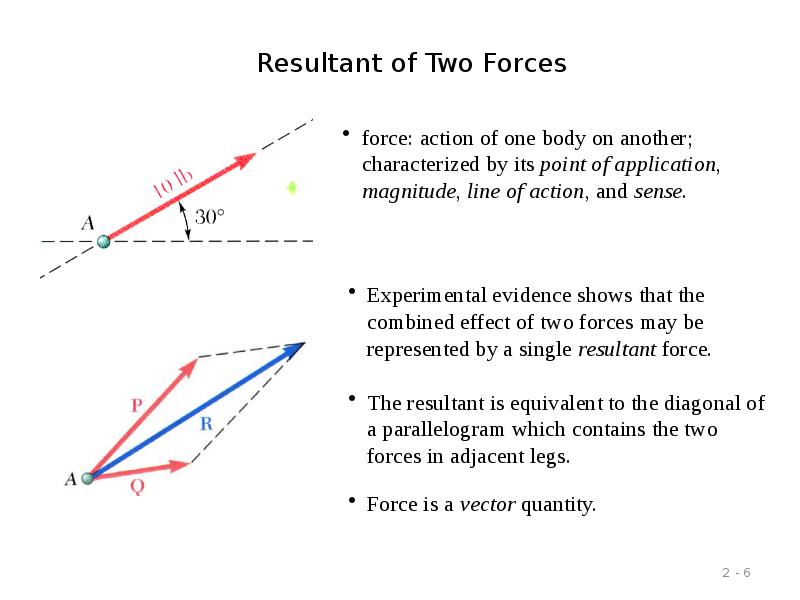
- 6. Resultant of Two Forces
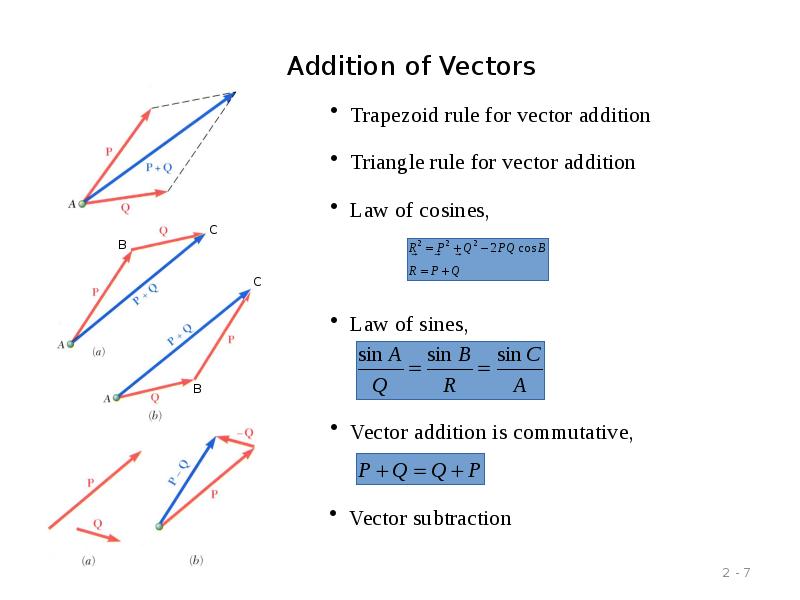
- 7. Addition of Vectors
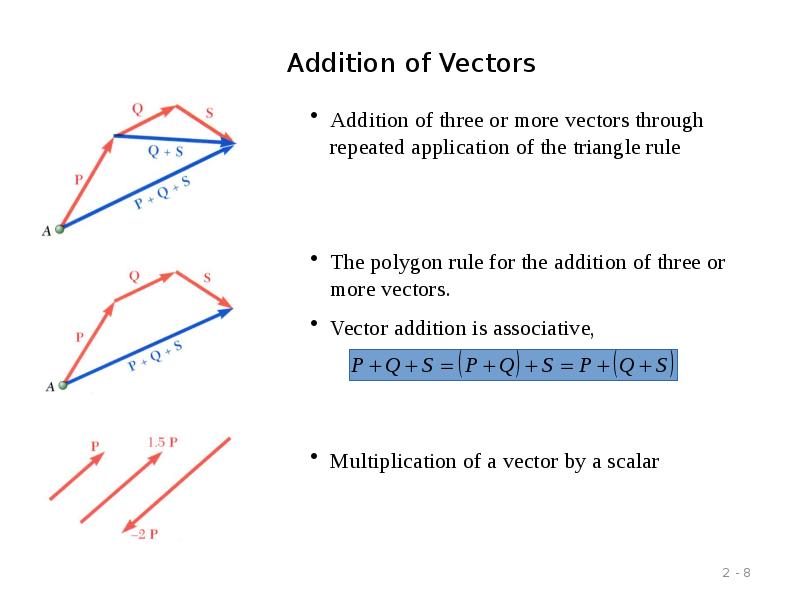
- 8. Addition of Vectors
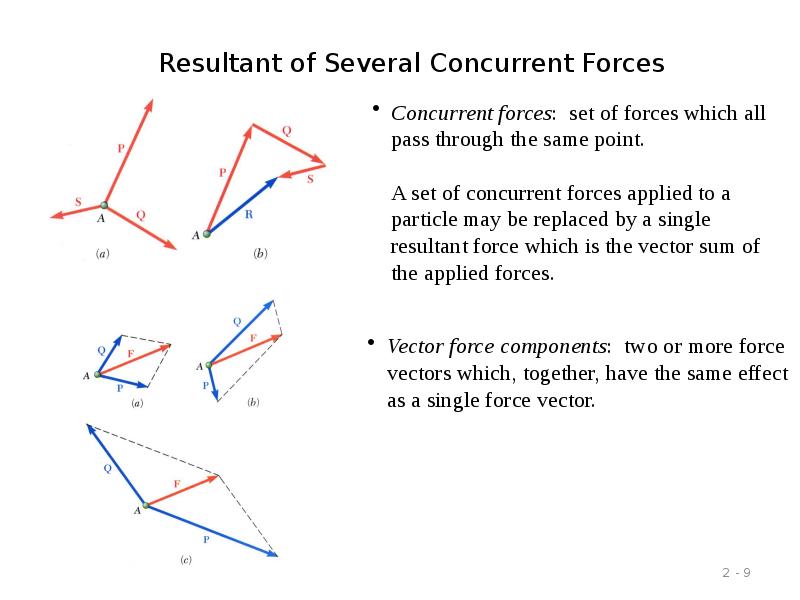
- 9. Resultant of Several Concurrent Forces
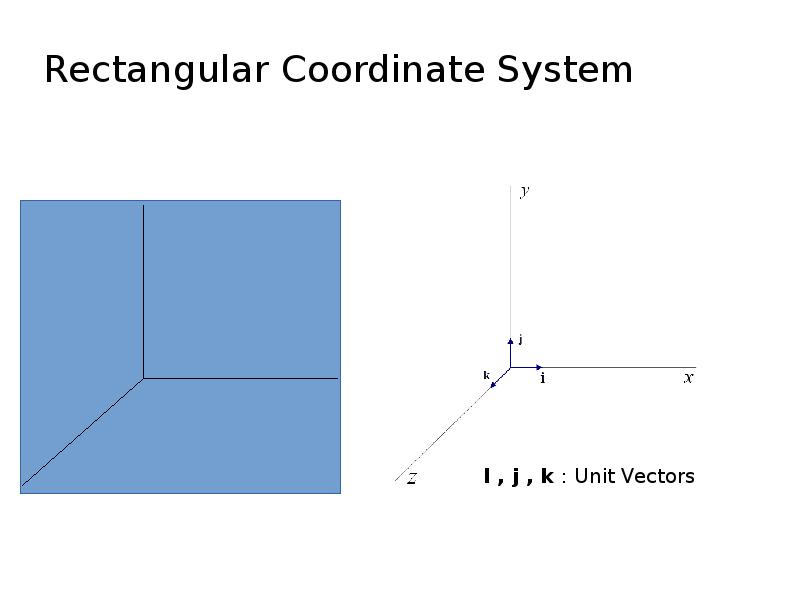
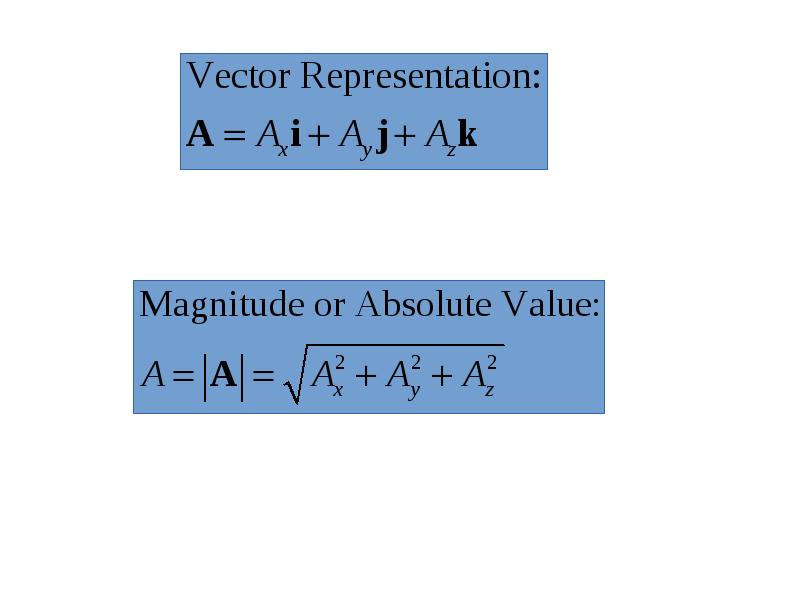
- 10. Rectangular Coordinate System
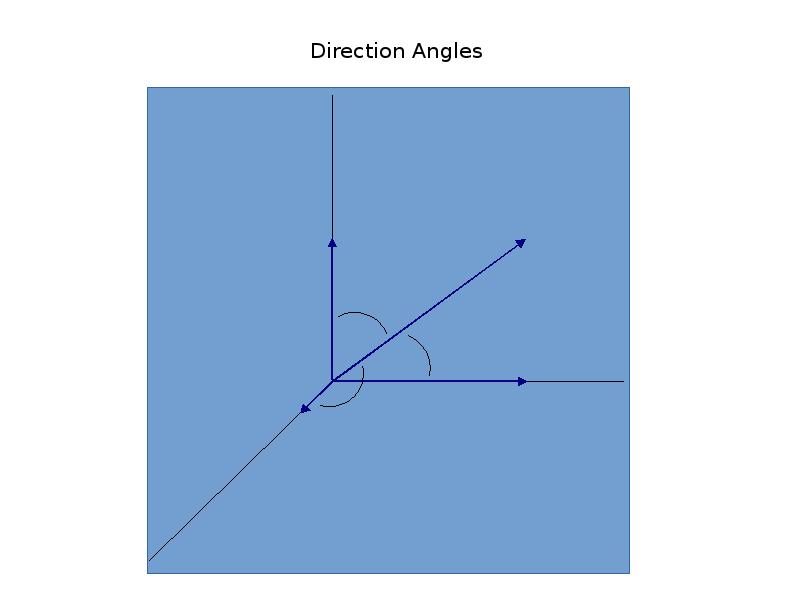
- 12. Direction Angles
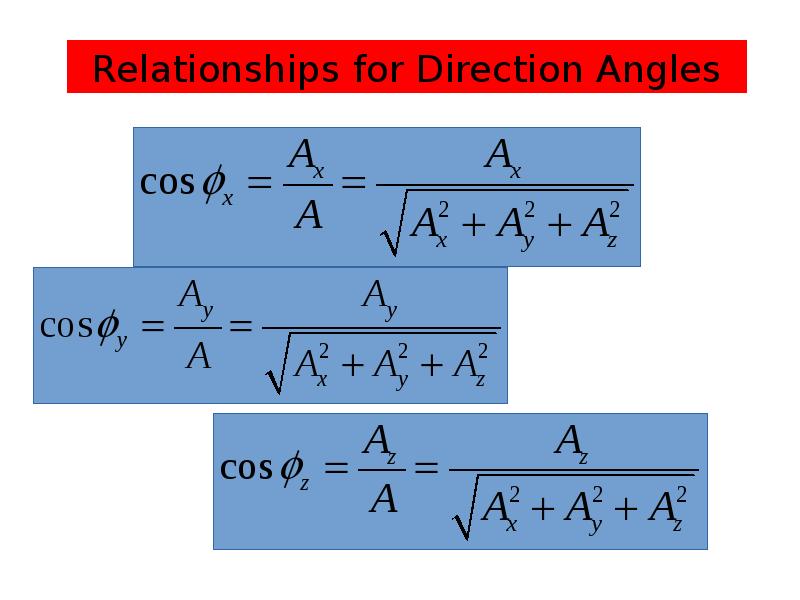
- 13. Relationships for Direction Angles
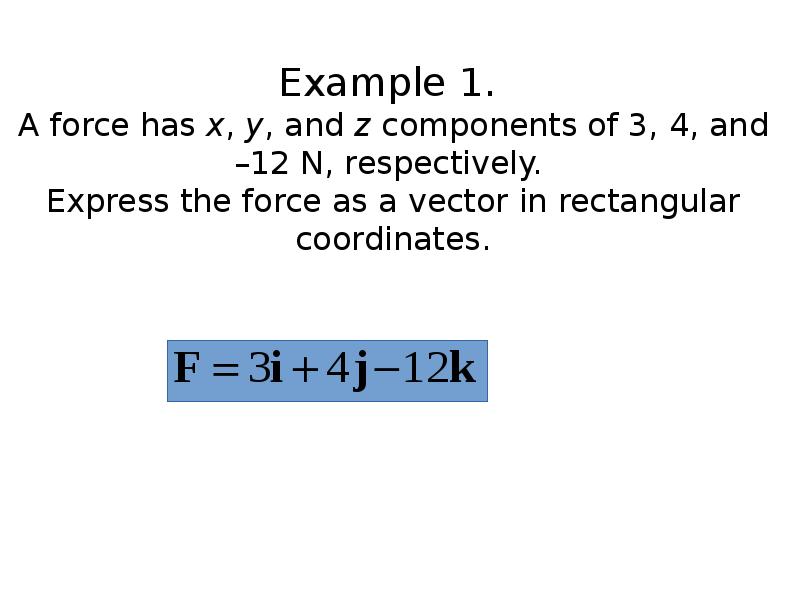
- 14. Example 1. A force has x, y, and z components of
- 15. Determine the magnitude of the force in previous example:
- 16. Determine the three direction angles for the force :
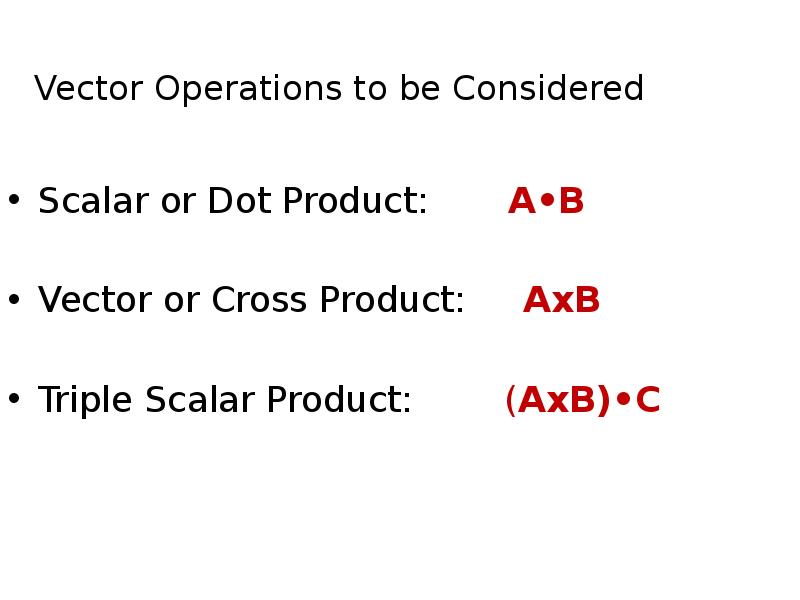
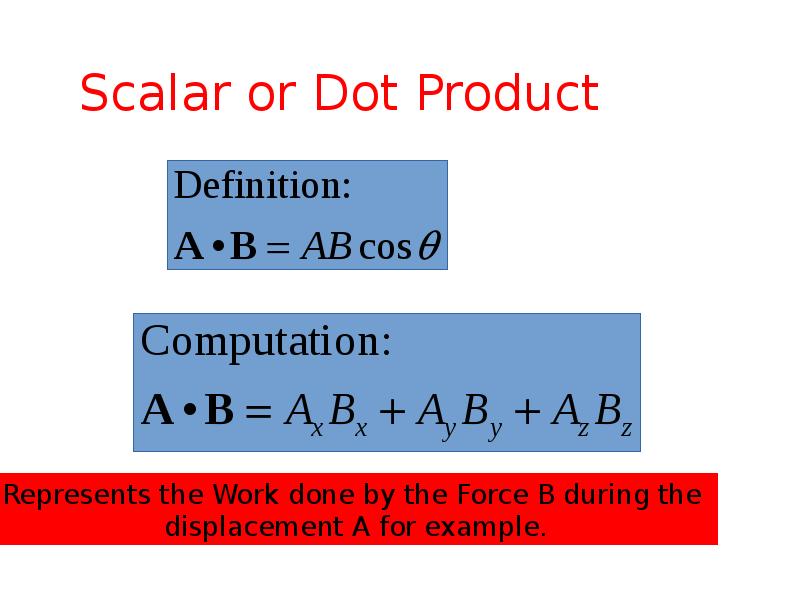
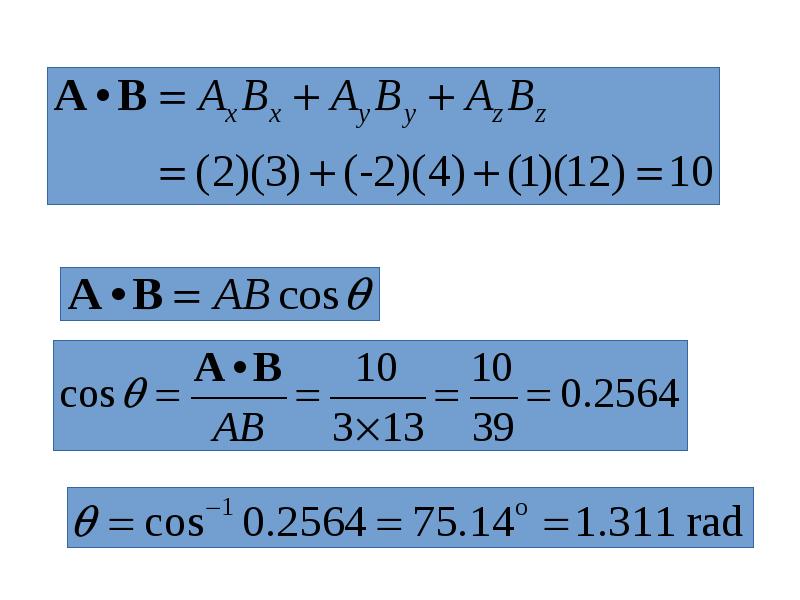
- 18. Vector Operations to be Considered Scalar or Dot Product: A•B
- 19. Consider two vectors A and B oriented in different directions.
- 20. Scalar or Dot Product
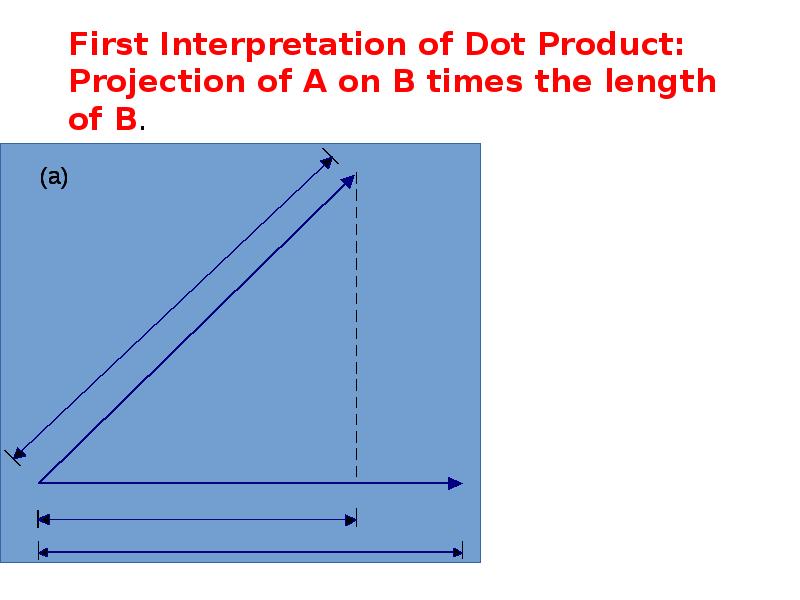
- 21. First Interpretation of Dot Product: Projection of A on B times
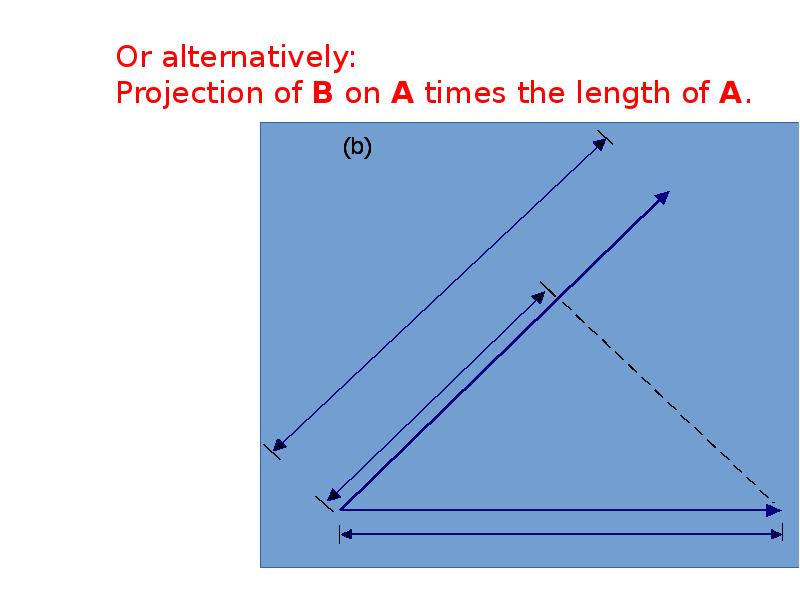
- 22. Or alternatively: Projection of B on A times the length of
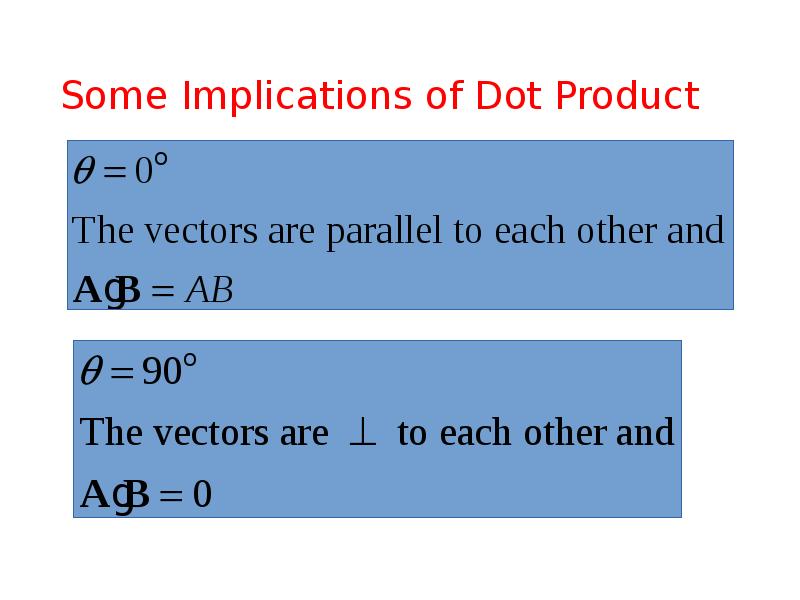
- 23. Some Implications of Dot Product
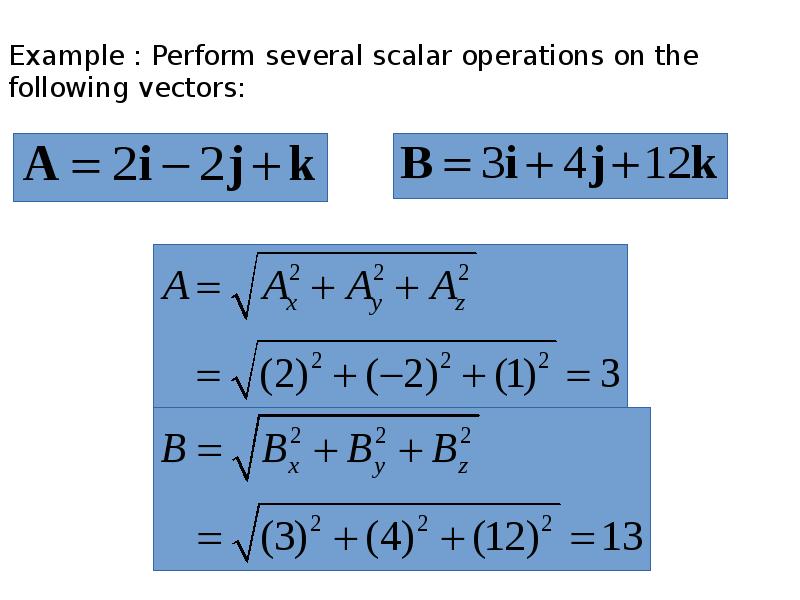
- 24. Example : Perform several scalar operations on the following vectors:
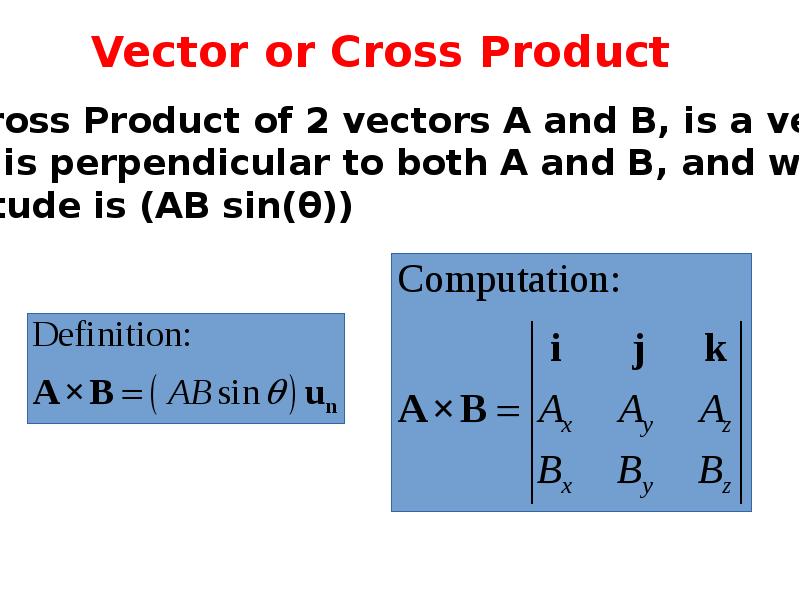
- 26. Vector or Cross Product
- 27. Скачать презентацию





Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему University physics. Forces review of basic concepts можно ниже:
Похожие презентации